Corsair CX450 PSU Review: Two Flavors, Tested and Compared
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Efficiency, Temperature & Noise
Efficiency
We detail our efficiency testing procedure here.
Using results from the previous page, we plotted a chart showing the CX450’s efficiency at low loads and loads from 10 to 110 percent of its maximum-rated capacity.
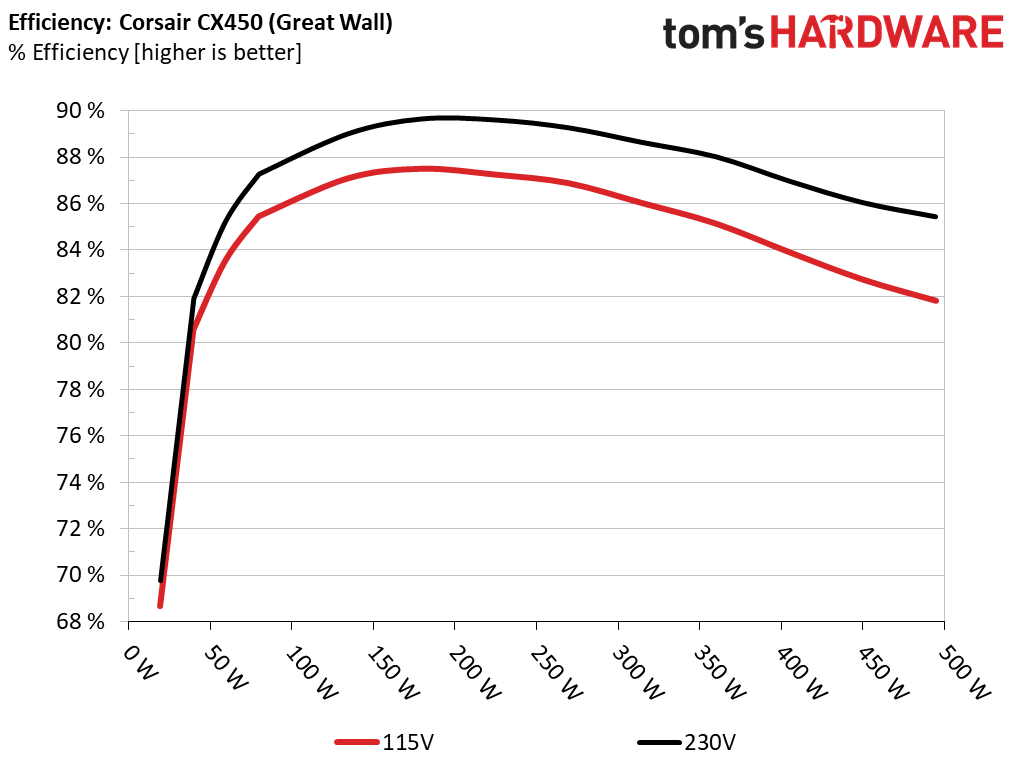
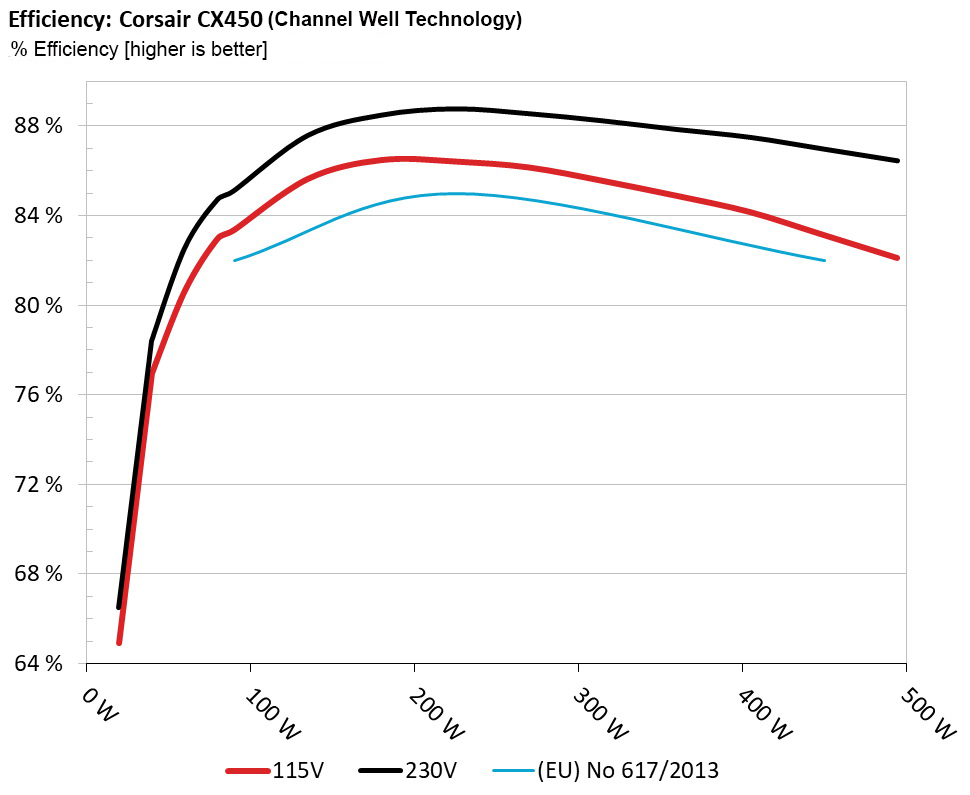
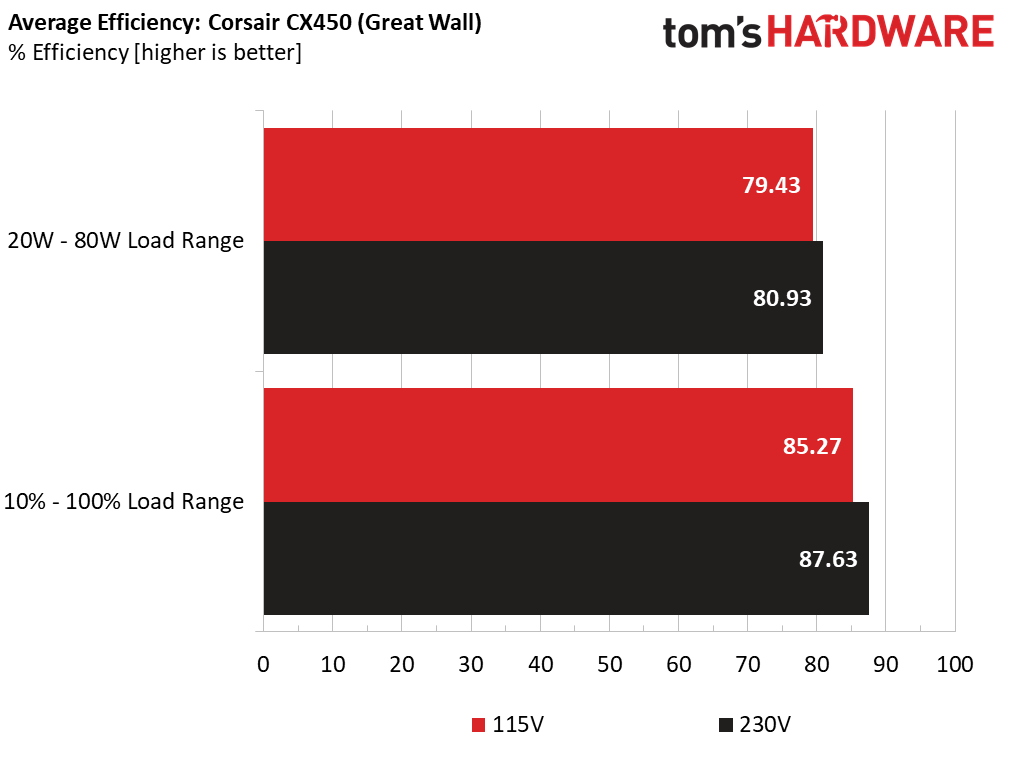
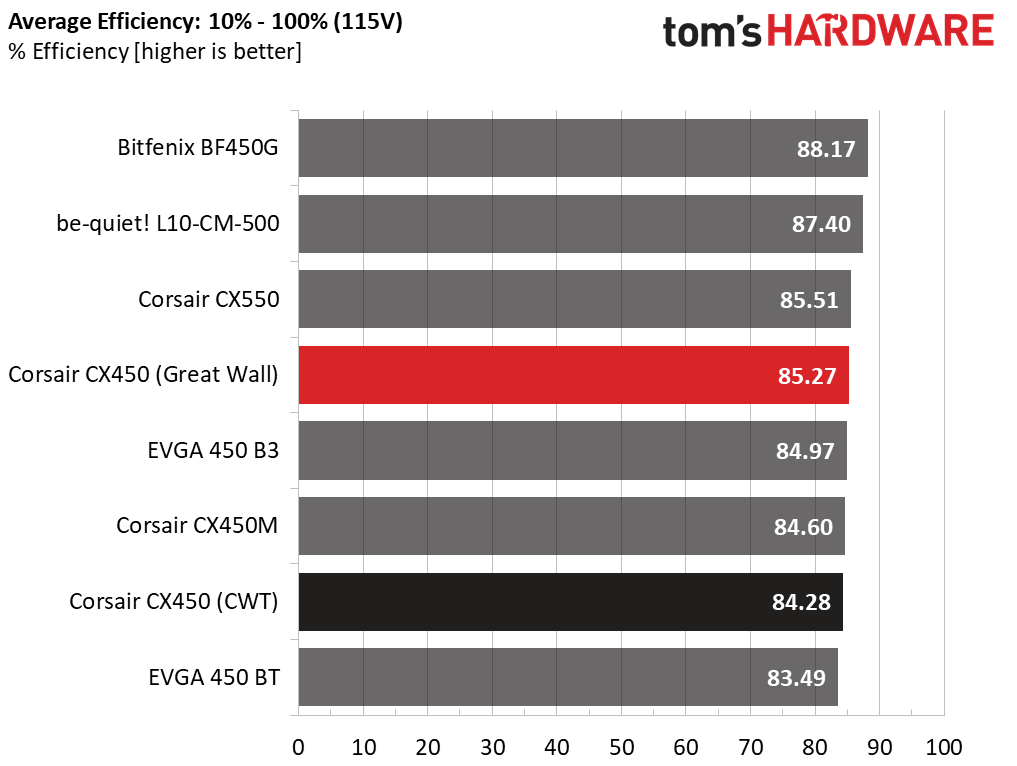
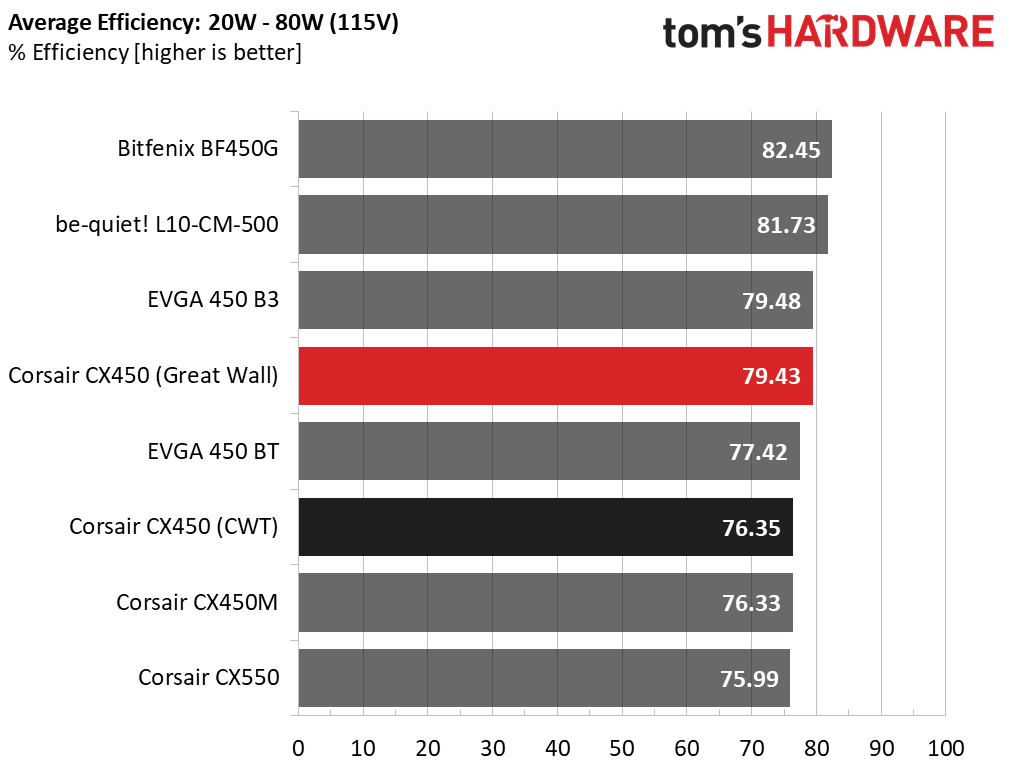
Great Wall's platform was more efficient under normal and light loads.
Efficiency at Low Loads
In the following tests, we measured the CX450's efficiency at loads significantly lower than 10 percent of its maximum capacity (the lowest load the 80 PLUS standard measures). The loads we dialed were 20W, 40W, 60W and 80W. This is important for symbolizing when a PC is idle with power saving features turned on.
Corsair CX450 - Great Wall
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed | PSU Noise | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.197A | 0.499A | 0.478A | 0.198A | 19.535 | 68.672% | 1105 RPM | 24.0 dB(A) | 0.880 |
| 12.067V | 5.009V | 3.329V | 5.045V | 28.447 | 115.35V | ||||
| 2 | 2.455A | 0.999A | 0.990A | 0.397A | 39.928 | 80.127% | 1100 RPM | 24.0 dB(A) | 0.948 |
| 12.069V | 5.008V | 3.328V | 5.039V | 49.831 | 115.32V | ||||
| 3 | 3.649A | 1.495A | 1.472A | 5.032A | 59.420 | 83.556% | 1170 RPM | 26.1 dB(A) | 0.969 |
| 12.068V | 5.008V | 3.327V | 5.032V | 71.114 | 115.30V | ||||
| 4 | 4.910A | 1.997A | 1.982A | 0.796A | 79.834 | 85.380% | 1235 RPM | 27.7 dB(A) | 0.979 |
| 12.066V | 5.006V | 3.326V | 5.026V | 93.504 | 115.26V |
Efficiency under light loads was very high, especially for a mainstream 450W unit.
Corsair CX450 - CWT
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed | PSU Noise | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.211A | 0.493A | 0.483A | 0.196A | 19.686 | 64.915% | 818 RPM | 13.8 dB(A) | 0.930 |
| 12.060V | 5.057V | 3.299V | 5.075V | 30.326 | 115.14V | ||||
| 2 | 2.448A | 0.980A | 0.999A | 0.391A | 39.744 | 76.855% | 818 RPM | 13.8 dB(A) | 0.976 |
| 12.056V | 5.055V | 3.298V | 5.070V | 51.713 | 115.13V | ||||
| 3 | 3.685A | 1.478A | 1.514A | 5.064A | 59.863 | 80.657% | 818 RPM | 13.8 dB(A) | 0.983 |
| 12.052V | 5.053V | 3.296V | 5.064V | 74.219 | 115.13V | ||||
| 4 | 4.915A | 1.974A | 1.998A | 0.791A | 79.780 | 82.976% | 818 RPM | 13.8 dB(A) | 0.988 |
| 12.049V | 5.053V | 3.295V | 5.058V | 96.148 | 115.12V |
CWT's fan spun at a lower RPM (revolutions per minute), but the PSU's efficiency levels weren't as high as Great Wall's implementation.
5VSB Efficiency
The ATX specification (revision 1.4), along with CEC, ErP Lot 3 2014 and ErP Lot 6 2010/2013, states that 5VSB standby supply efficiency should be as high as possible, recommending 75 percent or higher with 550mA, 1A and 1.5A of load. The PSU should also achieve higher than 75 percent efficiency at 5VSB under full load, or with 3A if its max current output on this rail is higher than 3A.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
We took six measurements: one each at 100mA, 250mA, 550mA, 1,000mA and 1,500mA and one with the full load the 5VSB rail can handle.
| Test # | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.100A | 0.505 | 75.826% | 0.056 |
| 5.049V | 0.666 | 115.37V | ||
| 2 | 0.250A | 1.262 | 79.924% | 0.125 |
| 5.046V | 1.579 | 115.37V | ||
| 3 | 0.550A | 2.772 | 81.290% | 0.230 |
| 5.039V | 3.410 | 115.37V | ||
| 4 | 1.000A | 5.029 | 81.205% | 0.322 |
| 5.028V | 6.193 | 115.38V | ||
| 5 | 1.500A | 7.526 | 81.884% | 0.375 |
| 5.016V | 9.191 | 115.36V | ||
| 6 | 3.000A | 14.942 | 78.605% | 0.447 |
| 4.980V | 19.009 | 115.35V |
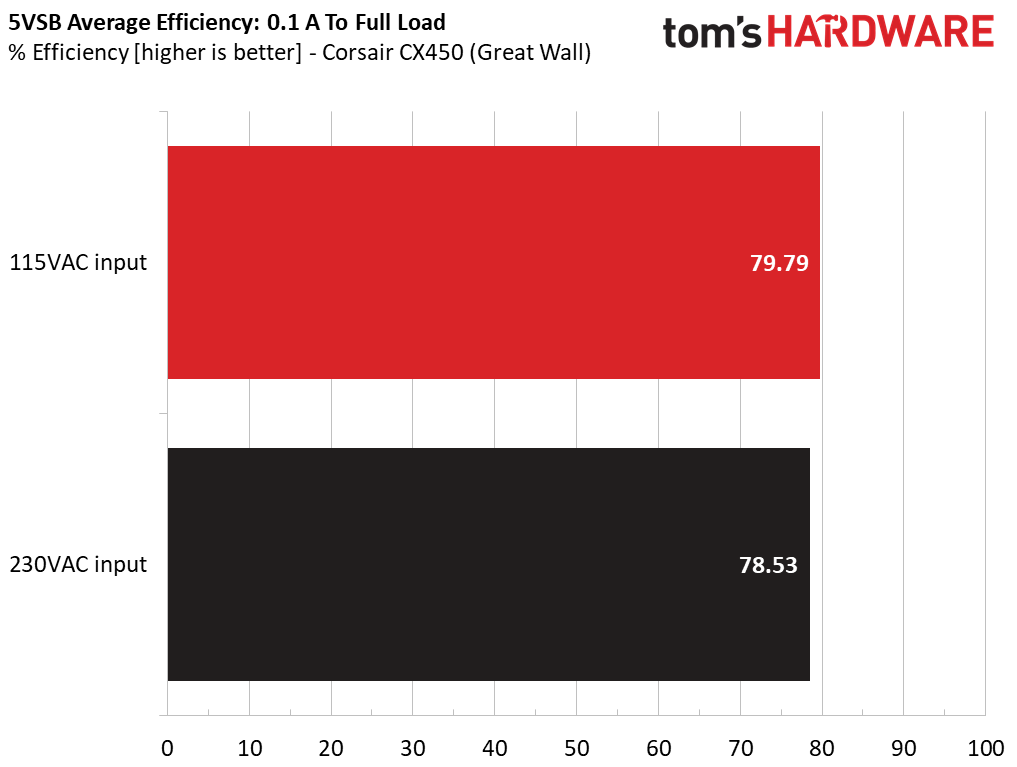
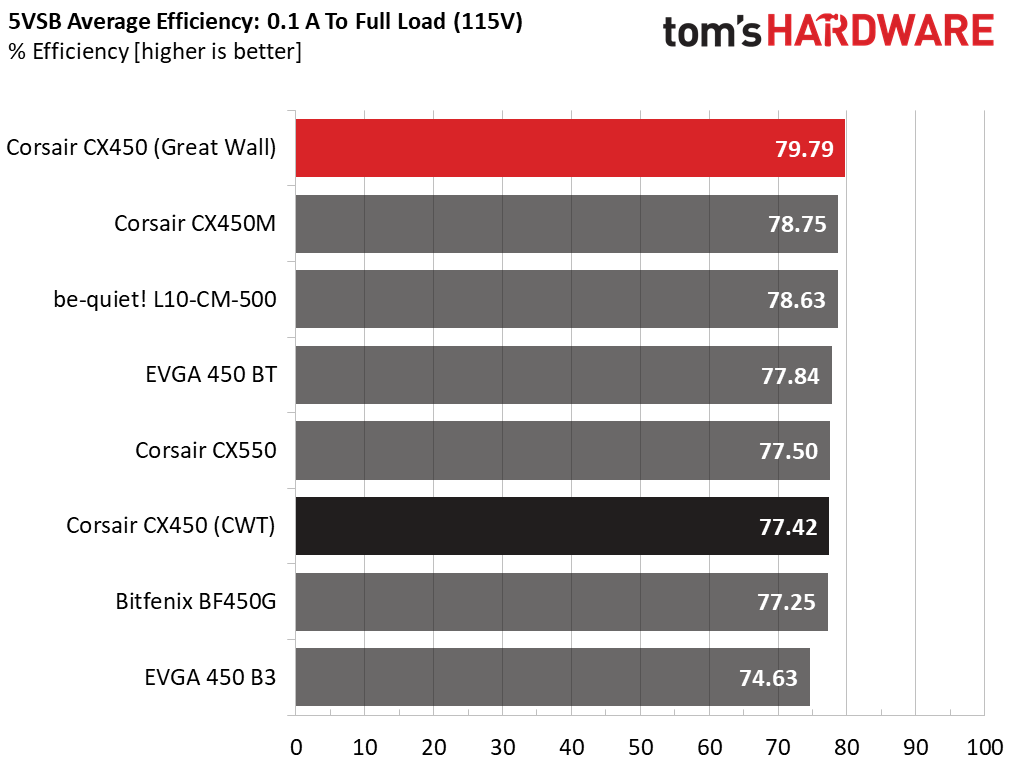
Great Wall's CX450 had a highly efficient 5VSB rail.
Power Consumption in Idle and Standby
The table below shows the power consumption and voltage values of all rails (except -12V) when the PSU was idle (powered on, but without any load on its rails) and the power consumption when the PSU was in standby mode (without any load, at 5VSB).
| Mode | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Watts | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idle | 12.094V | 5.007V | 3.329V | 5.050V | 13.314 | 0.682 |
| 115.4V | ||||||
| Standby | 0.067 | 0.006 | ||||
| 115.4V |
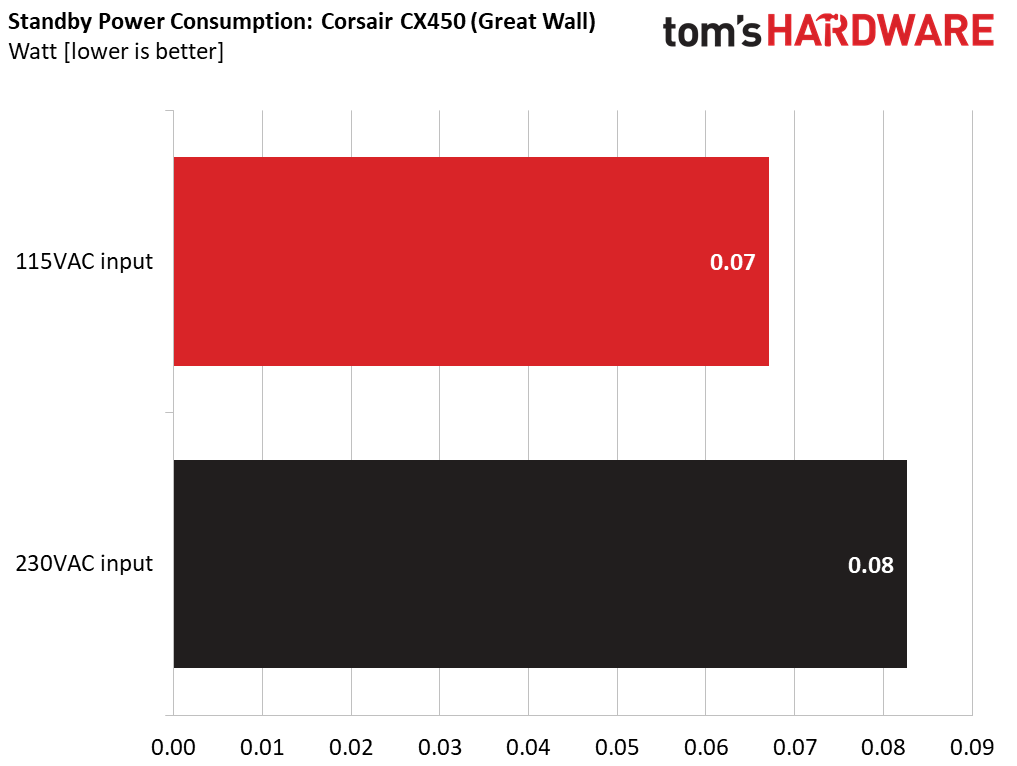
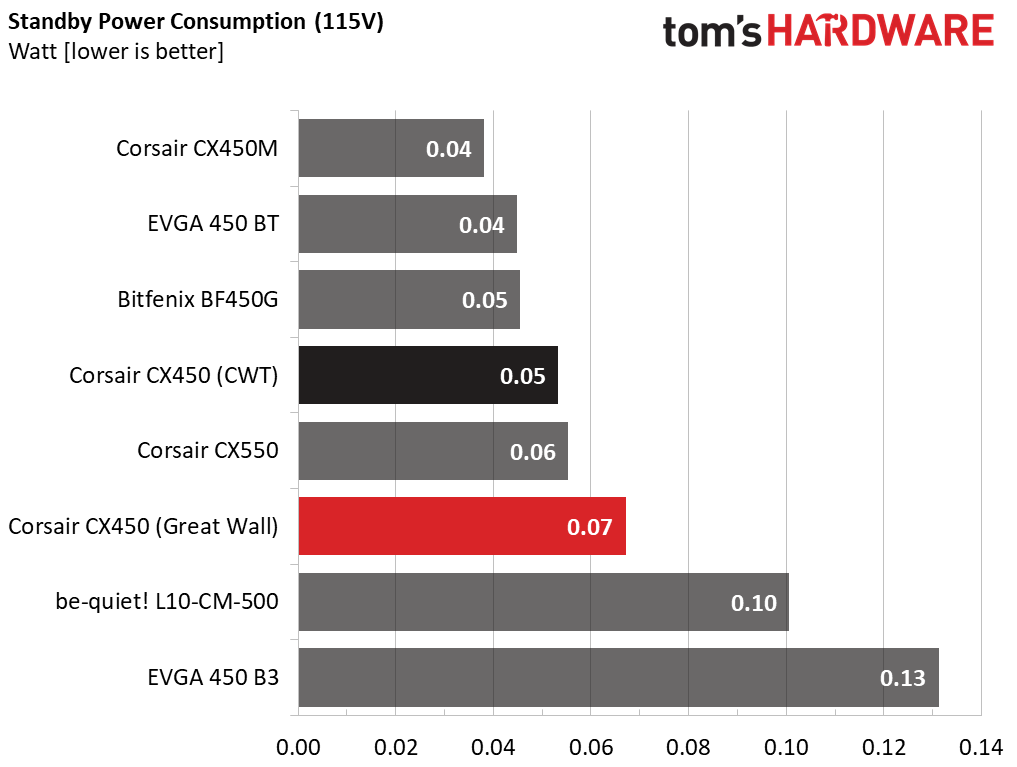
The power consumption of both CX450s was very low at idle.
Fan RPM, Delta Temperature & Output Noise
We describe our mixed noise testing in detail here.
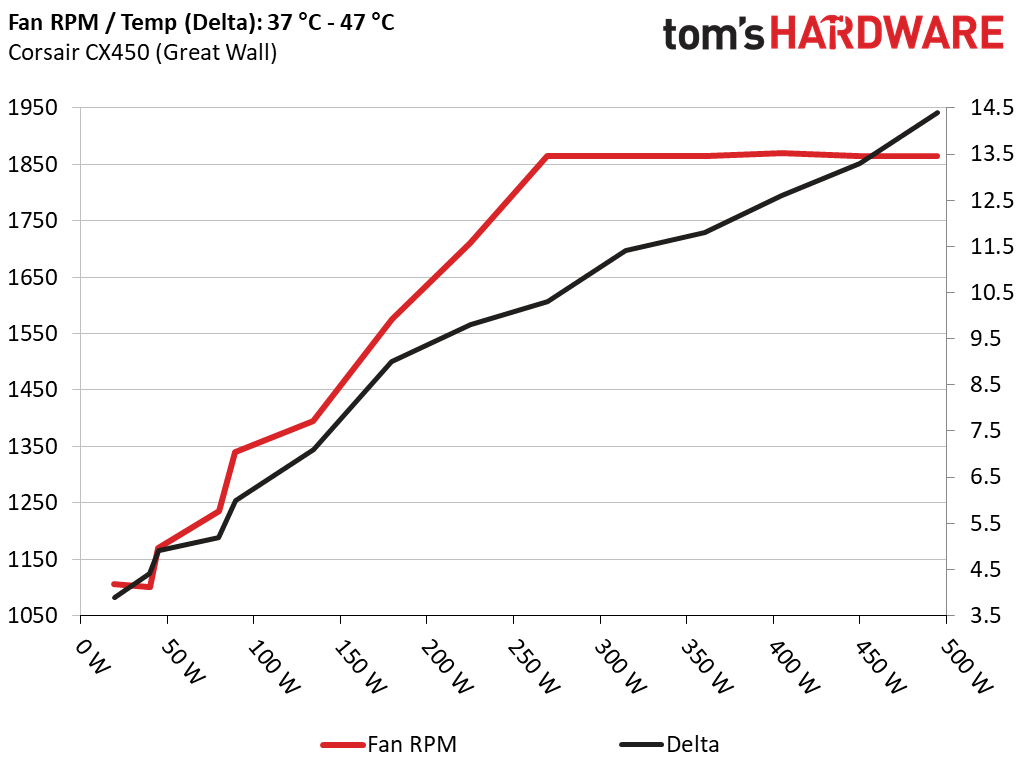
The first chart below illustrates the cooling fan's speed in RPM, and the delta between input and output temperature. We obtained the results at 37°C (98.6°F) to 47°C (116.6°F) ambient temperature.
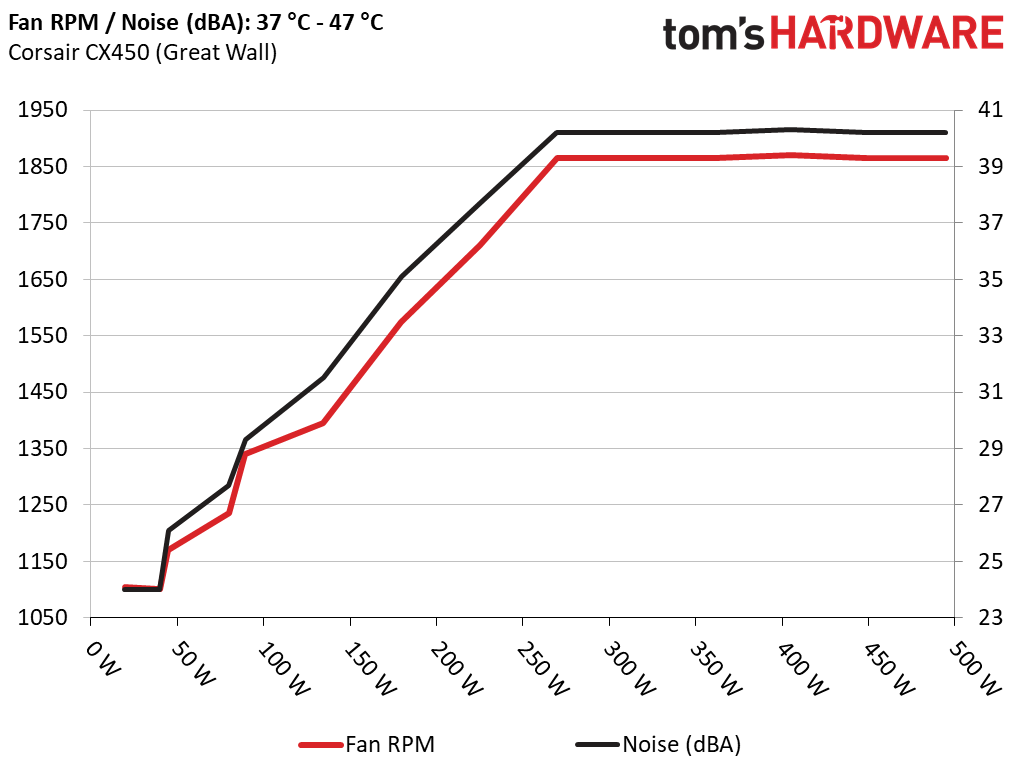
The next chart shows the cooling fan's speed in RPM and output noise. We measured acoustics from one meter away inside a hemi-anechoic (anechoic means non-echoing) chamber. Background noise inside the chamber was below 6 dB(A) during testing (it's actually much lower, but our sound meter’s microphone his its floor). We obtained the results with the PSU operating at 37°C (98.6°F) to 47°C (116.6°F) ambient temperature.
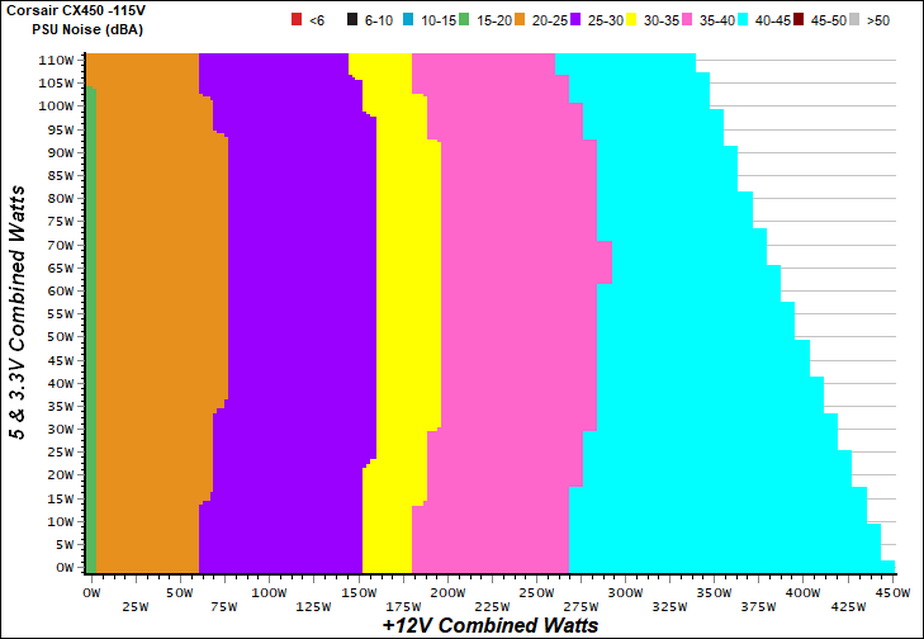
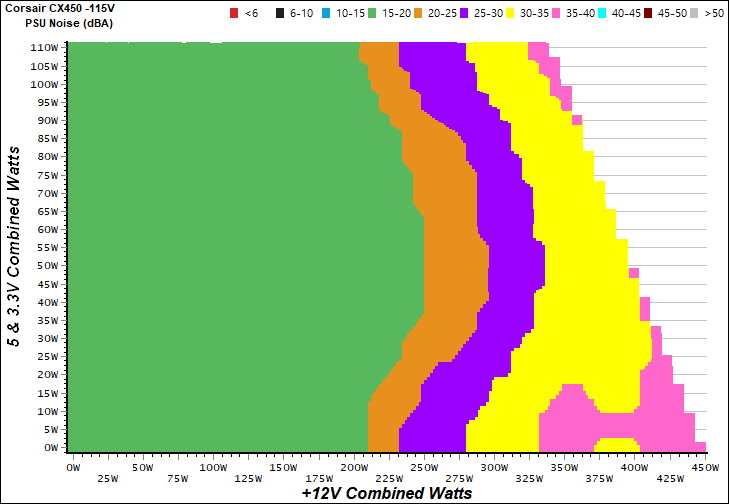
The following graph illustrates the fan's output noise over the PSU's operating range. The same conditions of the above graph apply to our measurements, though the ambient temperature was between 30°C (86°F) to 32°C (89.6°F).
Great Wall's CX450 wasn't particularly quiet, as you can see in the graph above. With 150W of load, the noise output was greater than 30 dB(A). Above 270W, it exceeded 40 dB(A).
CWT's CX450 had a much more relaxed fan profile. Up until 200W, its fan spun at low RPM. Even in a worst-case scenario, the noise output remained below 40 dB(A).
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Efficiency, Temperature & Noise
Prev Page Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time & Inrush Current Next Page Protection Features & DC Power Sequencing
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
jpe1701 Oh thank you Aris, I've been waiting for a review of this. It's always low in price and tempting to recommend but there weren't any reviews.Reply -
Darkbreeze Why do both of the review summary boxes list the Great Wall version? Both the one on the front page and the last page are the same. Seems like you ought to include a summary box for both versions since there seems to be some major differences between them. And even more so since you seem to indicate the CWT version is the better unit, but only include a summary box for the Great Wall unit.Reply -
Darkbreeze I totally understand. No worries mate. Editorial has a bad habit of effectively pooping all over the independent contributors writing as well. Not surprising that they are doing so with your work, but I sure wish somebody in editorial would make a few changes to policy that keeps the finished product a bit more in line with what the contributor intended, which often they don't. In this case, it totally makes zero sense that they didn't leave it as you had it.Reply -
Rexper ReplyWe preferred CWT's version of Corsair's CX450, but that doesn't mean you should avoid Great Wall's
Not that we have a choice.
Great article, once again, Aris!
There is some controversy appearing relating to the fan bearings used in the CX450. JonnyGURU, who works at Corsair, claims both CX450 versions use a rifle bearing.
Unfortunately, we can't know for certain until someone dismantles the fan.
http://www.jonnyguru.com/forums/showthread.php?t=15943&page=2 -
Darkbreeze I don't think it even makes a tremendous amount of difference. Fan failure on power supplies due to bearing fatigue is the least of the issues I've usually seen in the past on older units. Plus, it's not terribly difficult to replace a PSU fan if you have at least of a modicum of common sense and don't possess four thumbs.Reply
If fan noise is the biggest worry, or bearing failure over the long term, then I'd say these are winners for the price point. Most would never hear them over the sound of the rest of the system in any case.