Acer Iconia Tab A500: A Tablet With Honeycomb 3.1
GPU Performance: Tegra 2
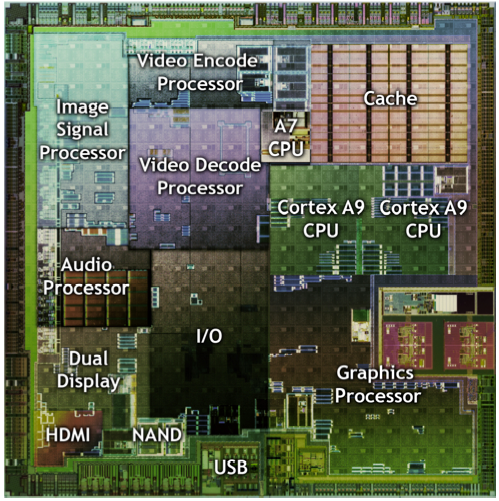
As we’ve mentioned in the past, mobile devices like smartphones and tablets use what’s known as a system-on-chip (SoC). This integrates the processor, GPU, RAM, and several other subsystems onto single device. Since all of those components sit next to each other on the same chip, there is greater efficiency in data transfers, while reducing the amount of space consumed on the PCB.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Apple A4 (iPad) | Apple A5 (iPad 2) | Tegra 2 (Xoom/Iconia A500) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | 1 GHz ARM Cortex-A8 (single-core) | 1 GHz ARM Cortex-A9 (dual-core) | 1 GHz ARM Cortex-A9 (dual-core) |
| Memory | 256 MB 333 MHz LP-DDR (single-channel) | 512 MB 1066 MHz LP-DDR2 (dual-channel) | 1 GB 667 MHz LP-DDR2 (single-channel) |
| Graphics | PowerVR SGX535 (single-core) | PowerVR SGX545MP2 (dual-core) | ULP GeForce (single-core) |
| L1 Cache(Instruction/Data) | 32 KB / 32 KB | 32 KB / 32 KB | 32 KB / 32 KB |
| L2 Cache | 640 KB | 1 MB | 1 MB |
Tegra is Nvidia’s SoC brand, and it symbolizes the company’s effort to tap into the mobile market beyond its desktop-derived GeForce graphics processors. A lot of engineering is tied up in this initiative, and what we see today in tablets like the Xoom represents the company's second incarnation of Tegra.
You may be asking "What happened to the first Tegra?" Flatly, it was far less impressive, even when it hit the market in 2009. Compared to Apple’s A4, it was a much more conservative design. Nvidia choose the older ARM11 processor, which probably explains the lack of design wins. Microsoft’s Zune HD was the only major product that employed the original Tegra.
Tegra 2 is an entirely different beast. It’s based on the Cortex-A9, which is a generation ahead of the older ARM11. This is the same CPU seen in Apple’s A5 (iPad 2). Read Apple's iPad 2 Review: Tom's Goes Down The Tablet Rabbit Hole for a full discussion of Cortex-A9 performance.
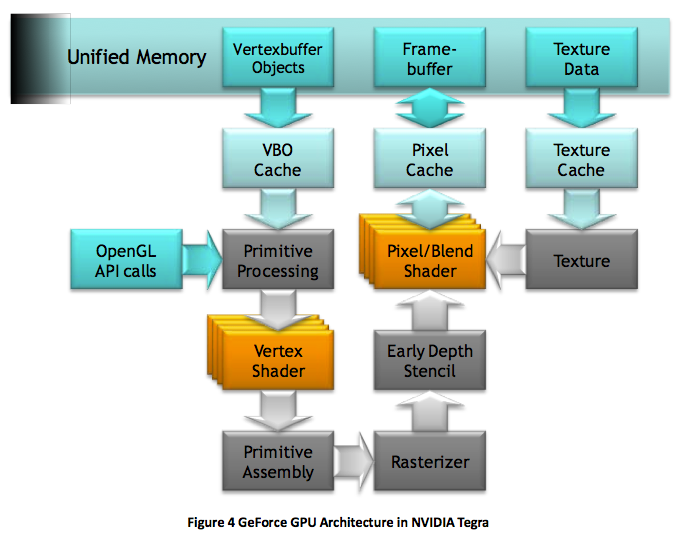
The ultra-low power GeForce isn't just a physically smaller GPU than the A5’s SGX 543MP2. Unlike Nvidia's desktop GPUs, Tegra 2 is based on an architecture that pre-dates its unified design. So, you’re looking at four pixel shader cores and four vertex shader cores. This means Tegra 2 operates most efficiently when it's presented with an even mix of vertex and shader code. We expect Nvidia to address that constraint in Tegra 3 (code named Kal-El).
| GPU (System-on-Chip) | PowerVR SGX 535(Apple A4) | PowerVR SGX 543(Apple A5) | ULP GeForce (Tegra 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIMD | USSE | USSE2 | Core |
| Pipelines | 2 (unified) | 4 (unified) | 8 (4 pixel / 4 vertex) |
| TMUs | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Bus Width (bit) | 64 | 64 | 32 |
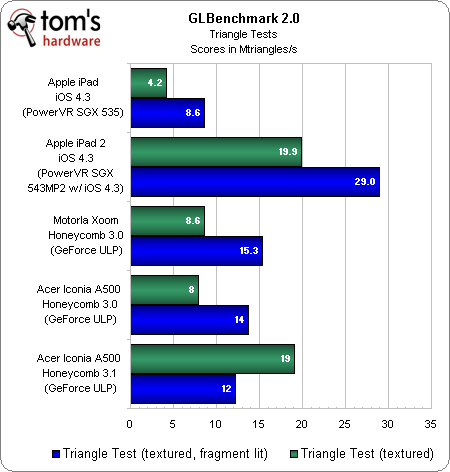
| Triangle rate @ 200 MHz | 14 MTriangles/s | 35 MTriangles/s | ? |
The ULP GeForce has a maximum operating frequency of 300 MHz, but device vendors can tweak this setting to save on power. Nvidia provides less information on the Tegra 2 than it does for its desktop GPUs, so it’s best to move on to benchmarks. As in our iPad 2 review, we're turning to GLBenchmark 2.0.
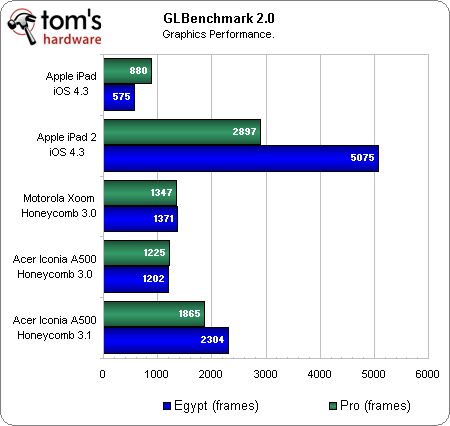
In terms of frames rendered in a set period of time, the Xoom and Iconia A500 offer more performance than the original iPad but both still falls short of the iPad 2. Interestingly, the Iconia A500 falls ever so slightly behind the Xoom. We don't have performance numbers for the Xoom after the 3.1 update, which makes this a difficult comparison. Google added a performance-oriented optimizations in 3.1 that explain the large delta.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
| GPU (System-on-Chip) | PowerVR SGX 535(Apple A4) | PowerVR SGX 543(Apple A5) | ULP GeForce (Tegra 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIMD | USSE | USSE2 | Core |
| Channels | Single | Dual | Single |
| Memory Bandwidth | 2.6 GB/s | 17.0 GB/s | 2.6 GB/s |
You can't use fill or triangle rates to draw a direct comparison of how well Tegra 2 utilizes its memory bandwidth, even though it's a quick-and-dirty way of sizing up other mobile GPUs.
| GLBenchmark 2.0 | Apple iPad(iOS 4.3) | Apple iPad 2(iOS 4.3) | Motorola Xoom(3.0) | Acer Iconia A500(3.0) | Acer Iconia A500 (3.1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egypt frames (frames) | 575 | 5075 | 1371 | 1202 | 2304 |
| Egypt with FSAA (frames) | 436 | 5057 | - | - | - |
| Pro (frames) | 880 | 2897 | 1347 | 1225 | 1865 |
| Pro with FSAA (frames) | 672 | 2851 | - | - | - |
| Egypt with FSAA Fixed Time (sec) | 825.6 | 65.0 | - | - | - |
| Pro with FSAA Fixed Time (sec) | 123.3 | 22.6 | - | - | - |
| Swap Buffer Test (frames) | 600 | 599 | 603 | 526 | 614 |
| Fill Test (texture fetch) ktexel/s | 170980 | 918551 | 129897 | 122164 | 16766 |
| Trigonometric Test (vertex weighted) kvertex/s | 1039 | 3326 | 2632 | 2292 | 3159 |
| Trigonometric Test (fragment weighted) kfragment/s | 1191 | 3512 | 4452 | 4577 | 563 |
| Trigonometric test (balanced) kshader/s | 1259 | 3158 | 2543 | 2600 | 311 |
| Exponential Test (vertex weighted) kvertex/s | 3130 | 3535 | 2628 | 2291 | 2781 |
| Exponential Test (fragment weighted) kfragment/s | 3774 | 11165 | 3003 | 2965 | 4961 |
| Exponential Test (balanced) kshader/s | 2043 | 11735 | 1656 | 1658 | 2575 |
| Common Test (vertex weighted) kvertex/s | 1524 | 3727 | 1973 | 2270 | 2477 |
| Common Test (fragment weighted) kfragment/s | 1634 | 3699 | 4451 | 4584 | 7964 |
| Common Test (balanced) kshader/s | 1065 | 4114 | 2530 | 2722 | 4513 |
| Geometric Test (Vertex Weighted) kvertex/s | 1949 | 3776 | 1316 | 1375 | 1465 |
| Geometric Test (Fragment Weighted) kfragment/s | 2081 | 6388 | 2888 | 2870 | 5639 |
| Geometric Test (Balanced) kshader/s | 1281 | 6181 | 1628 | 1638 | 3129 |
| For Loop Test (Vertex Weighted) kvertex/s | 1671 | 3860 | 1315 | 1373 | 1468 |
| For Loop Test (Fragment Weighted) kfragment/s | 1842 | 6237 | 7271 | 7202 | 11856 |
| For Loop Test (balanced) kshader/s | 1275 | 3718 | 3583 | 3604 | 5320 |
| Branching Test (vertex weighted) kvertex/s | 3906 | 3778 | 2633 | 2501 | 3443 |
| Branching Test (fragment weighted) kfragment/s | 6045 | 22557 | 3211 | 3153 | 3995 |
| Branching Test (balanced) kshader/s | 2106 | 11193 | 1493 | 1496 | 1858 |
| Array Test (uniform array access) kvertex/s | 2918 | 3658 | 3946 | 3438 | 5487 |
| Triangle Test (white) ktriangle/s | 9548 | 29957 | 12595 | 9708 | 14613 |
| Triangle Test (textured, vertex lit) ktriangle/s | 7058 | 21129 | 10520 | 9171 | 12517 |
Current page: GPU Performance: Tegra 2
Prev Page USB Support: The Hidden Gem Next Page Display Quality: Color Gamut