Intel Core i5-9400F CPU Review: Cutting On-Die Graphics For A Slightly Lower Price
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Rendering, Encoding and Compression
Rendering
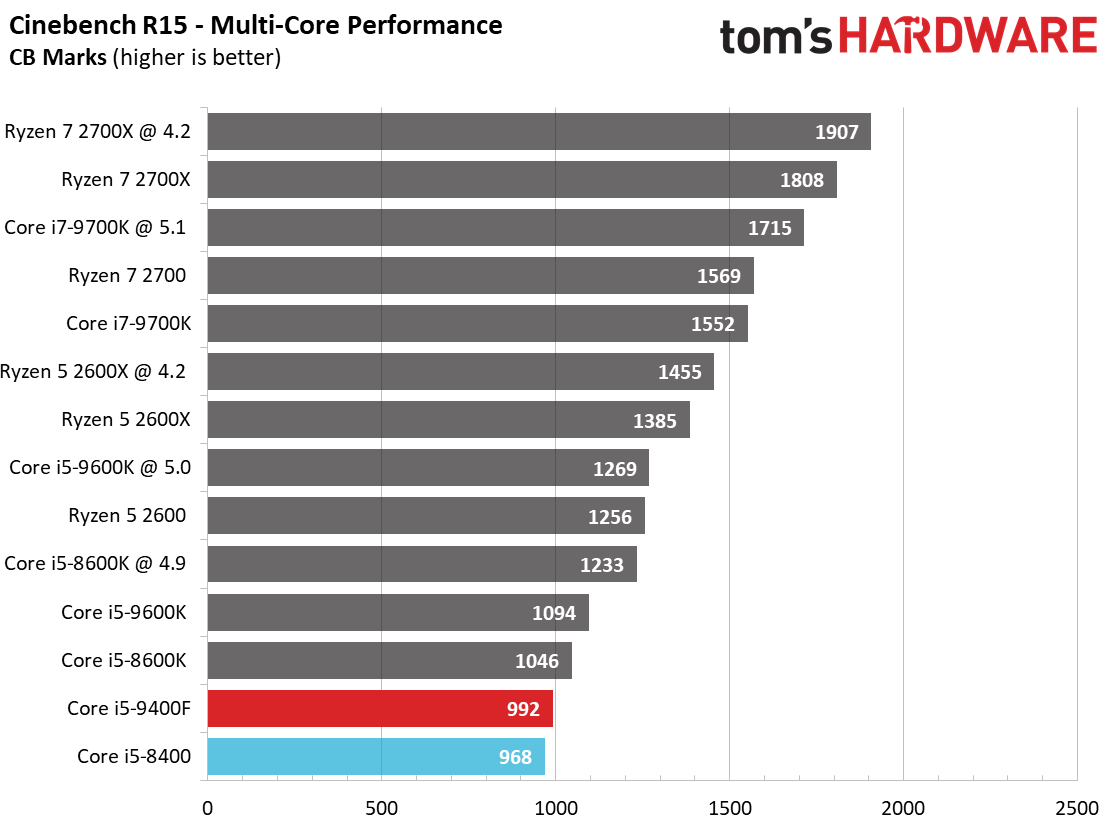
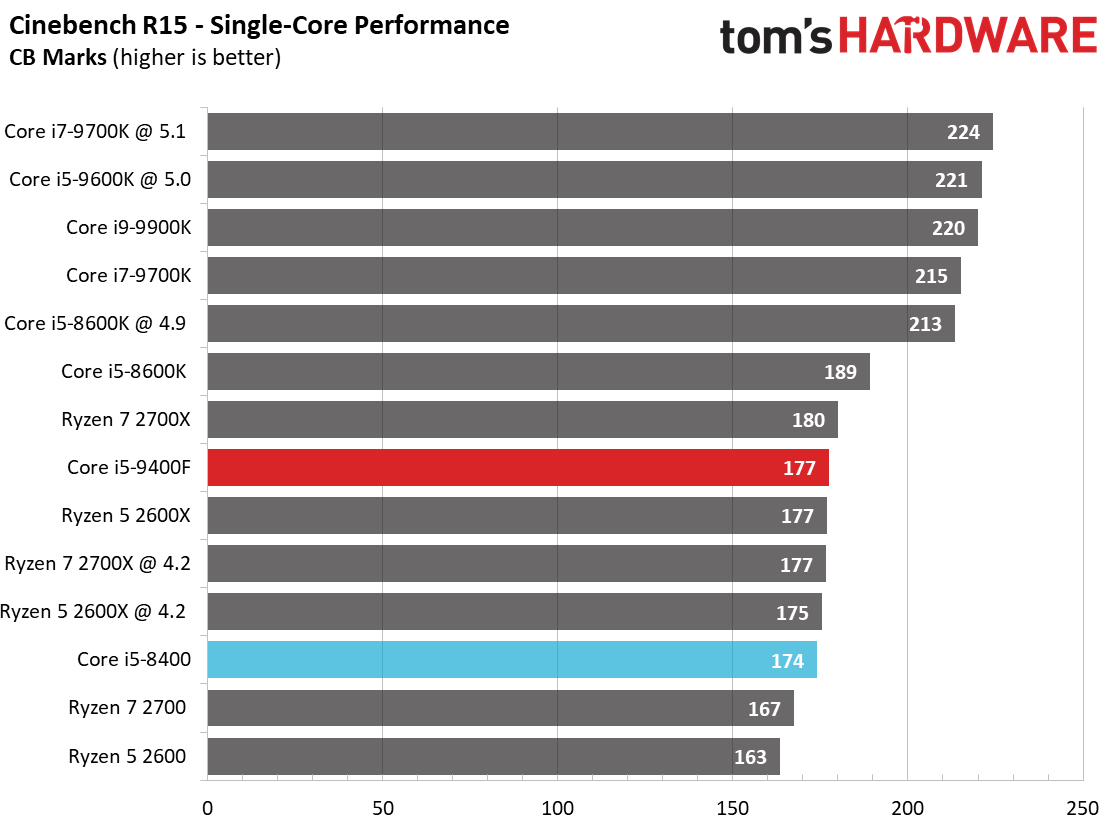
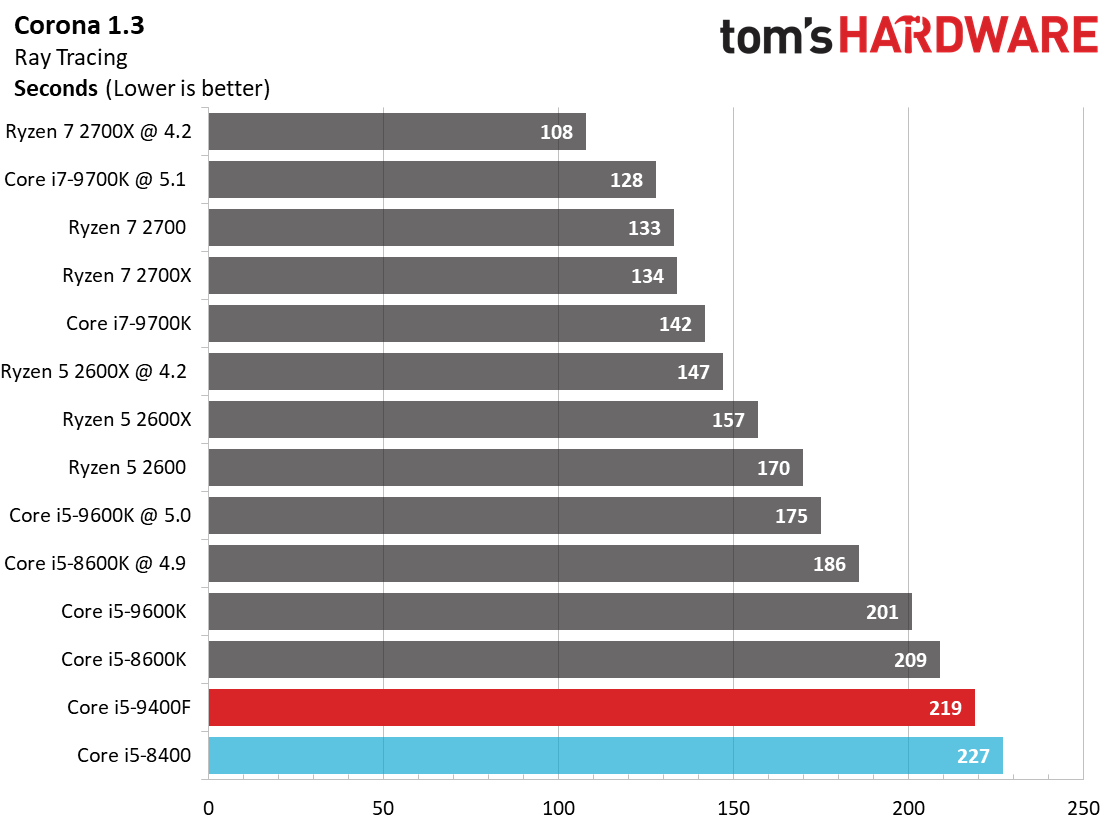
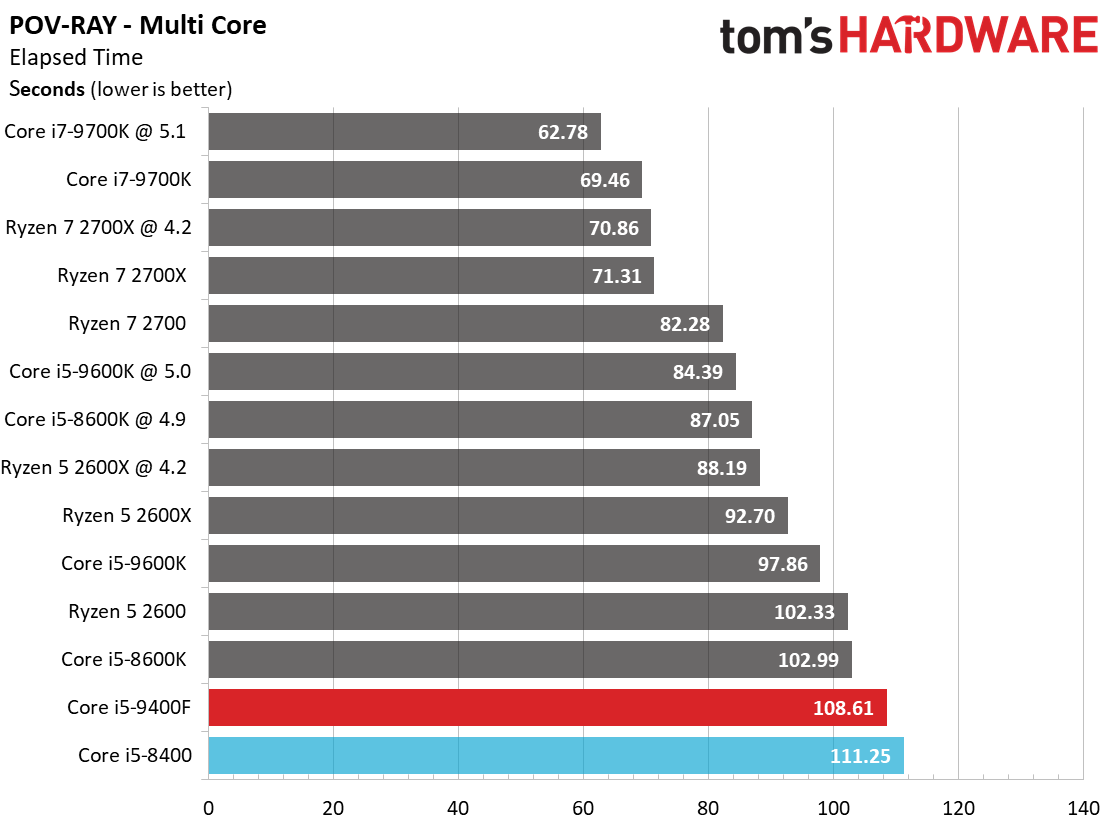
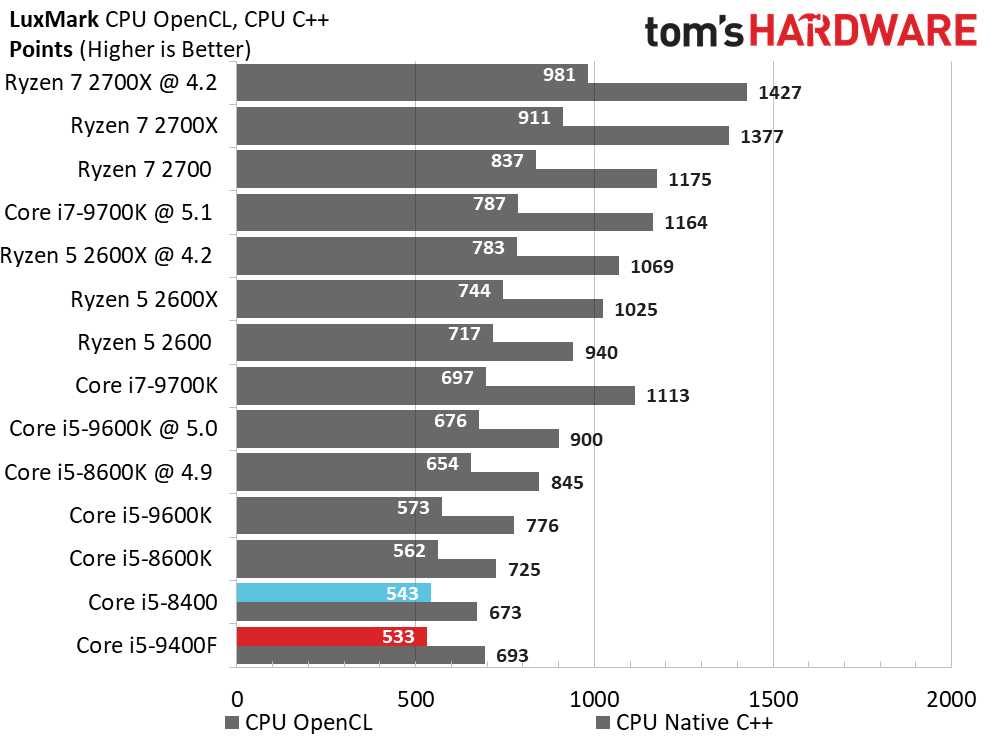
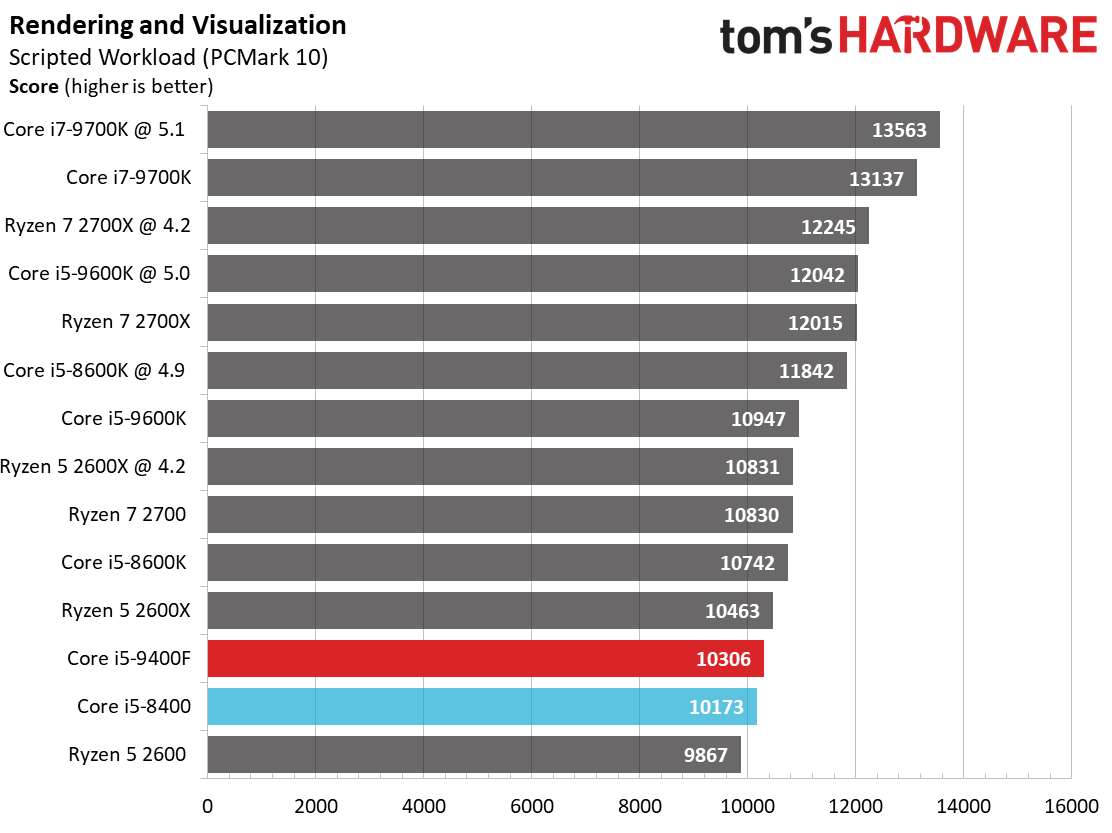
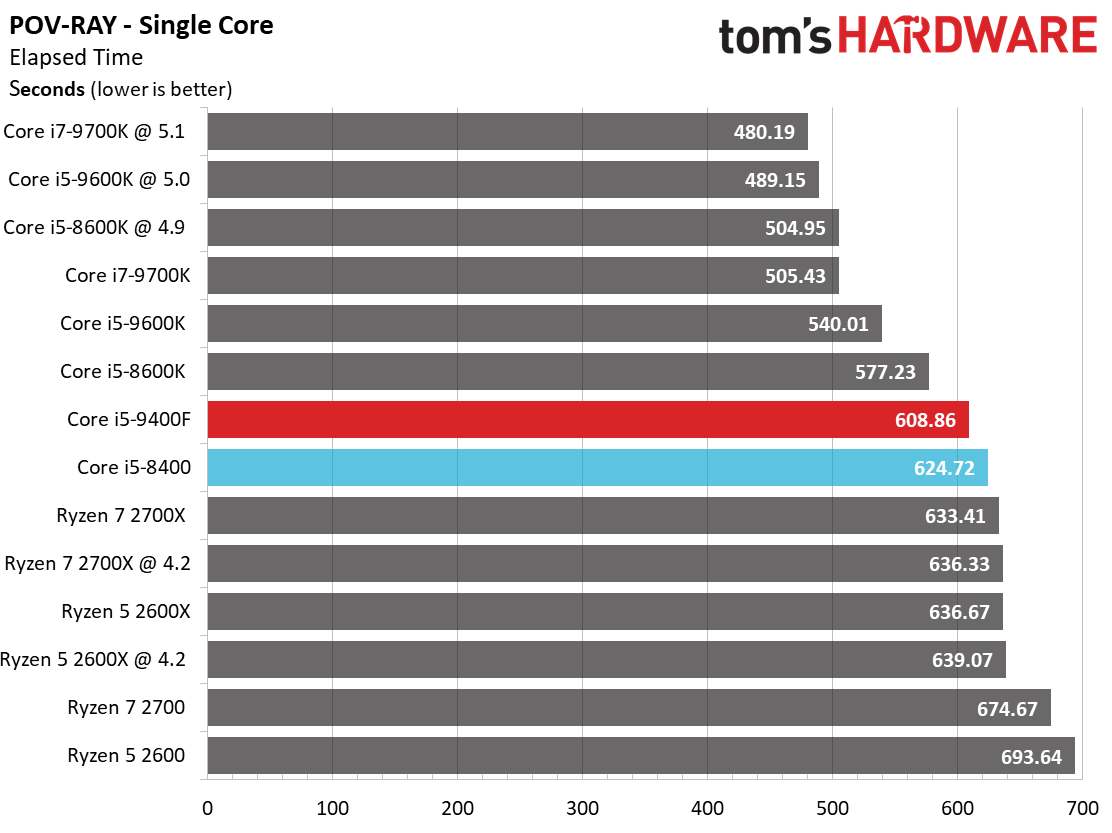
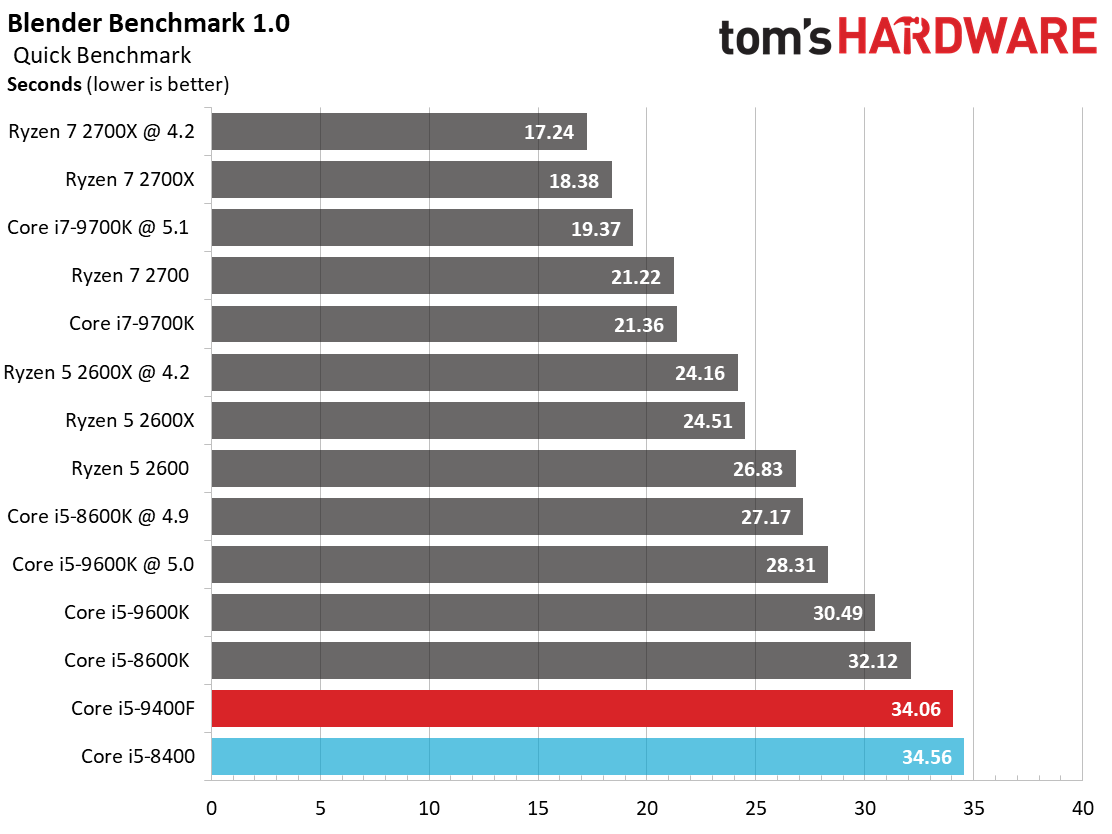
By and large, the Ryzen processors are better-suited for heavy rendering workloads due to their higher core counts and simultaneous multi-threading capabilities. They dominate our threaded tests, as a result.
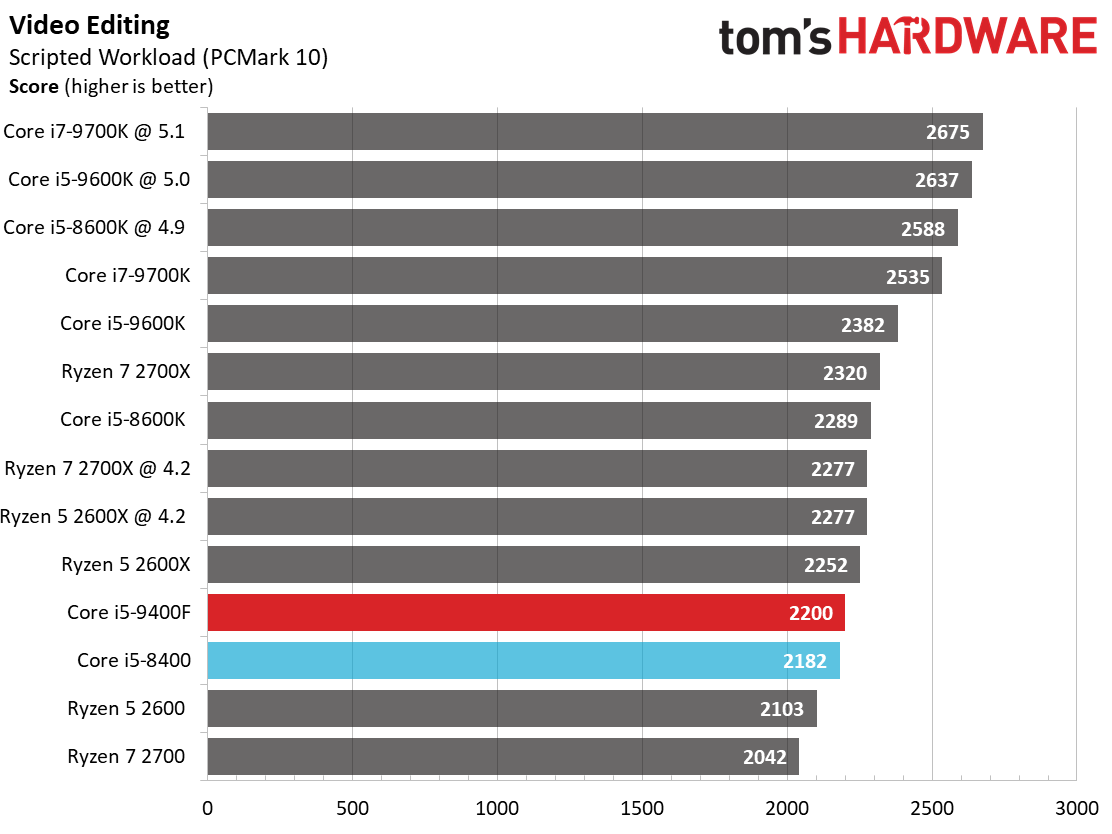
Single-threaded workloads, regardless of their genre, are still best addressed with Intel CPUs. The Core i5-9400F demonstrates small improvements over its predecessor, but basically offers the bare minimum to count as an upgrade. We certainly wouldn't recommend this chip as an upgrade.
Encoding and Compression
Our threaded compression and decompression metrics work directly from system memory, removing storage throughput from the equation.
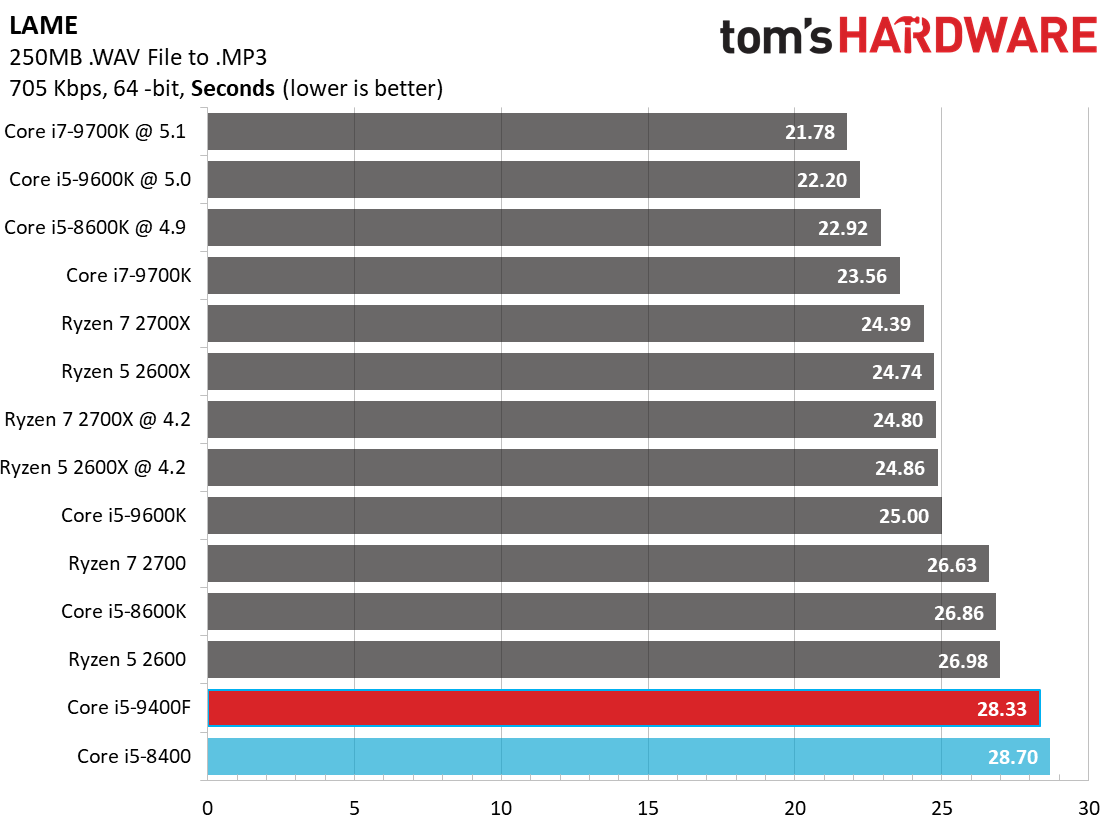
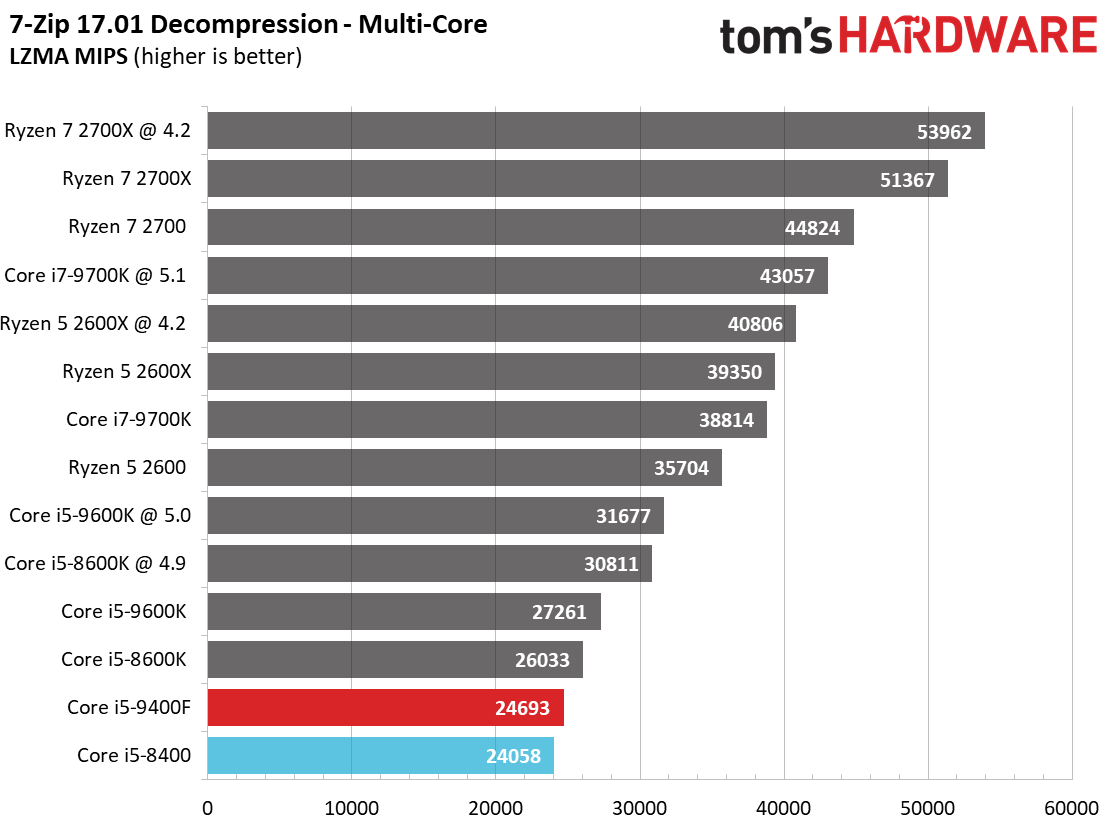
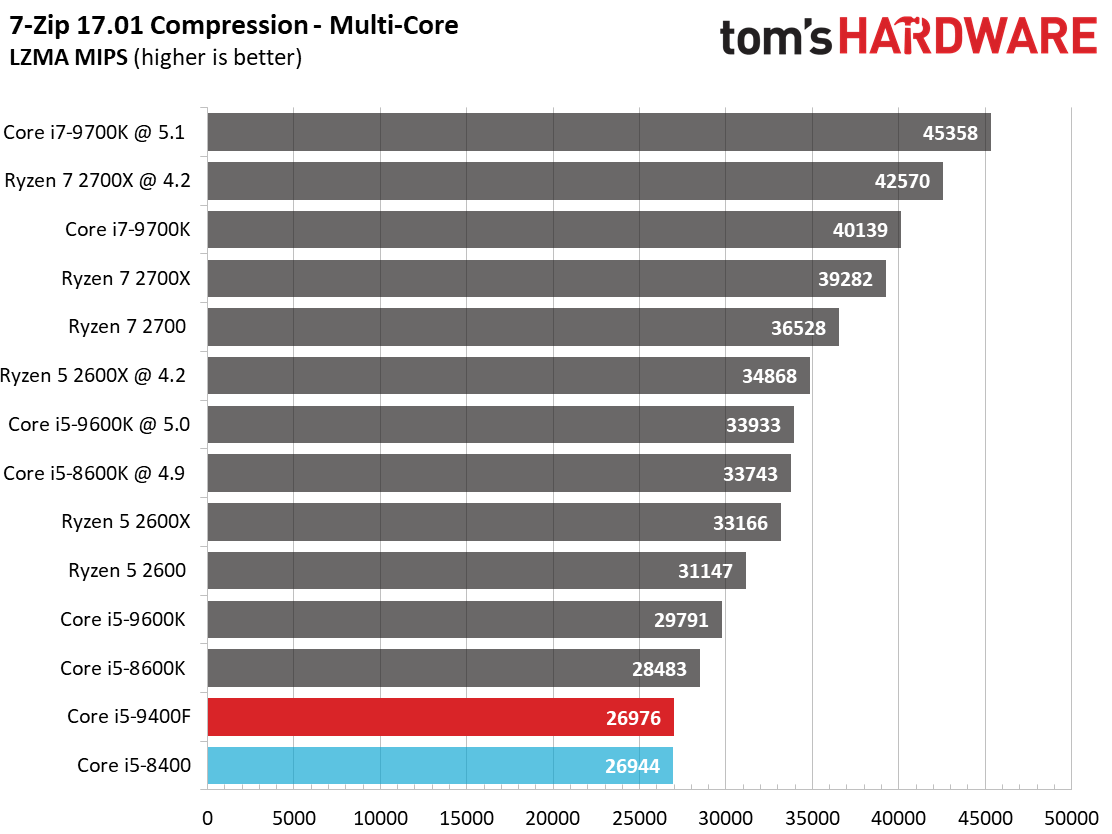
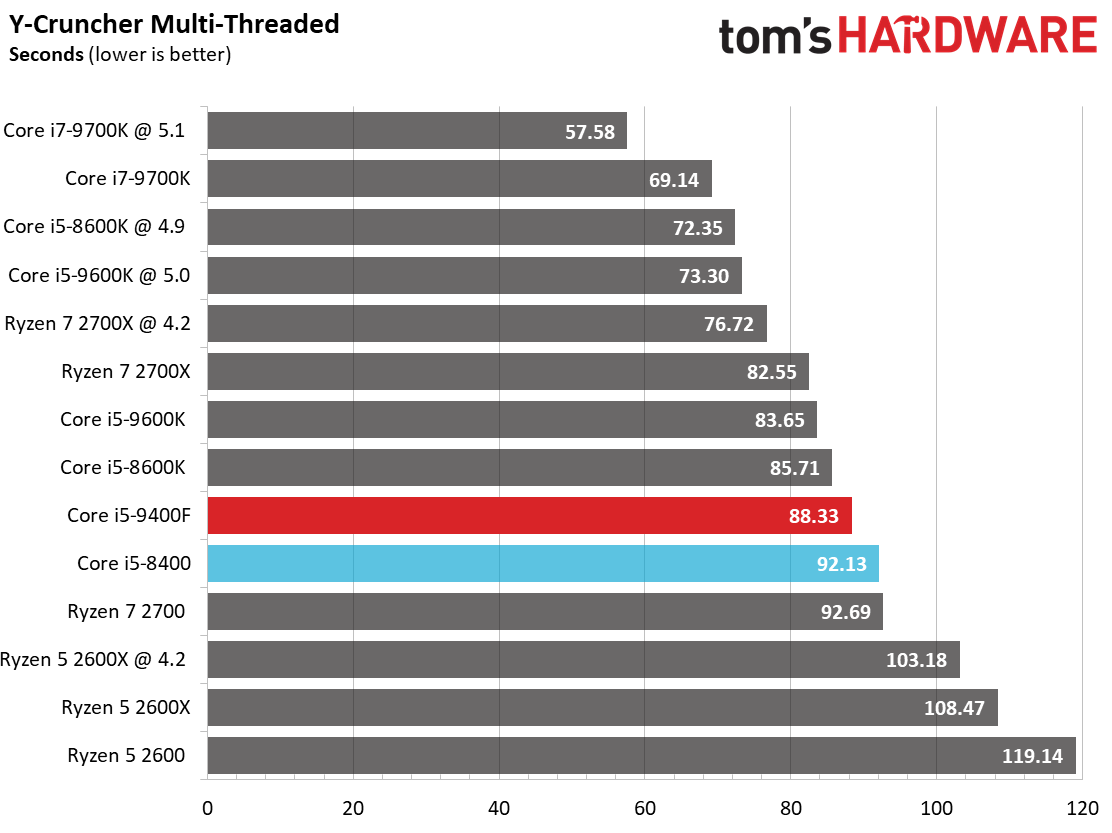
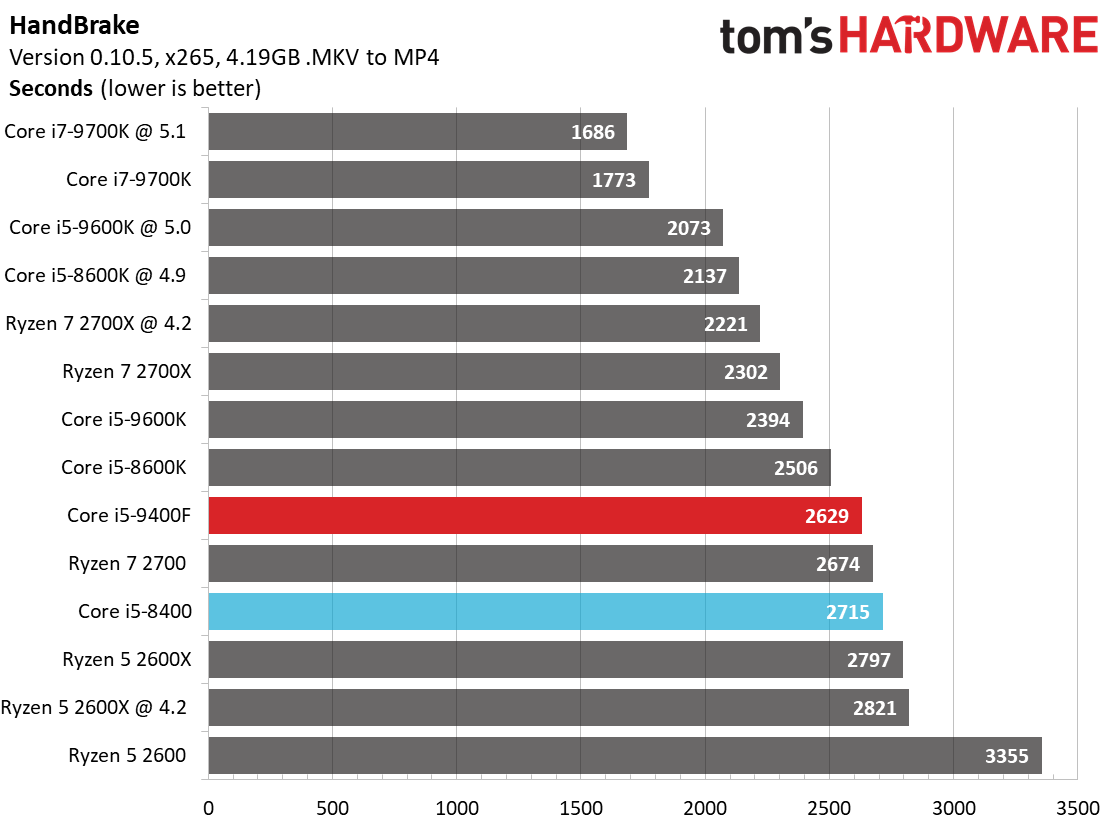
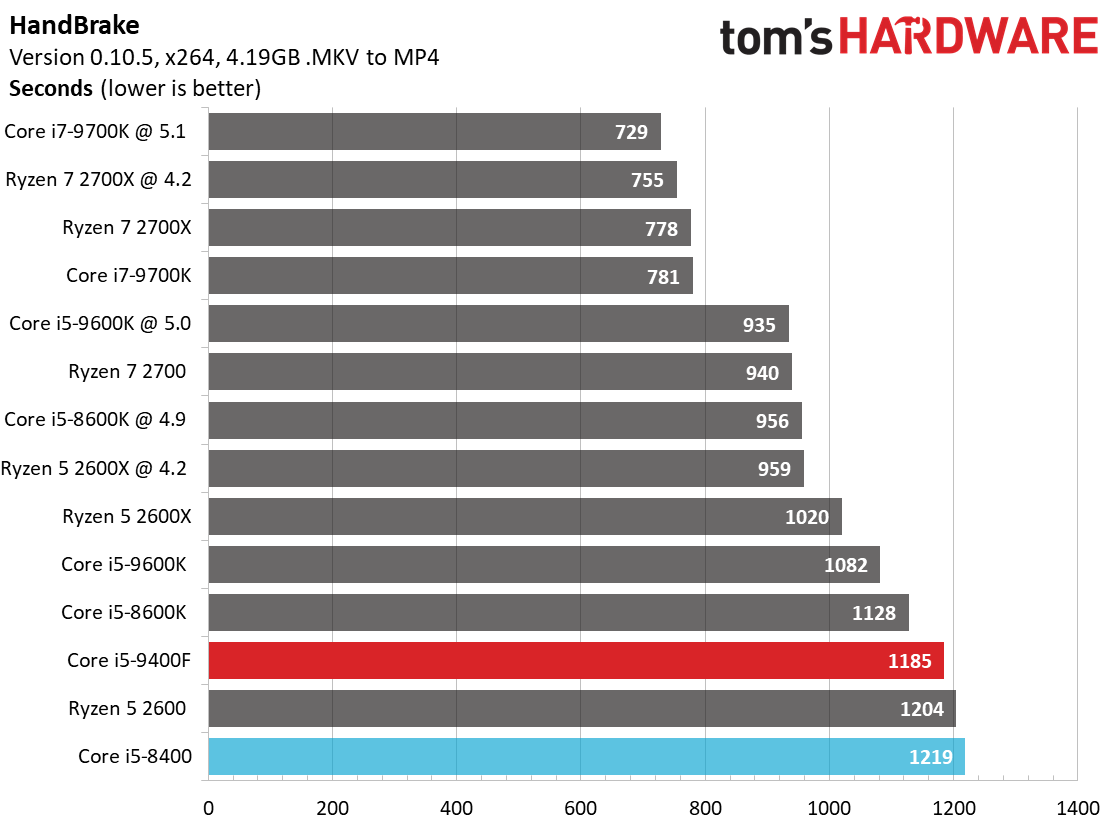
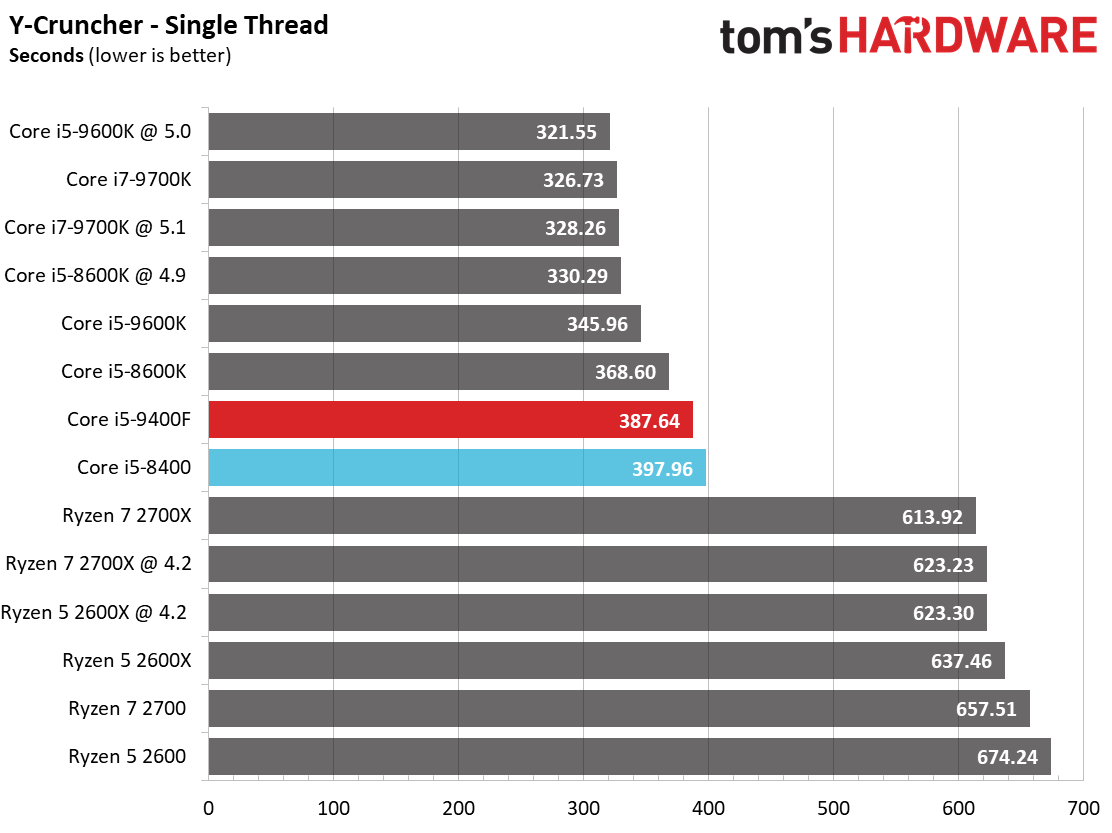
Like its predecessor, the Core i5-9400F falls to the bottom of our chart. This is due to a combination of relatively tame frequencies and six physical cores. In comparison, the Ryzen 5 2600X offers a tremendous amount of performance at its price point.
y-cruncher, a single- and multi-threaded program that computes pi, is a great benchmark for measuring the effect of AVX instructions. As per usual, Intel's architectures chew through these taxing workloads with ease. The Core i5 models even beat AMD's 8C/16T Ryzen 7 2700 in a testament to the effectiveness of Intel's AVX implementation.
The Core i5-9400F beats AMD's Ryzen 5 processors during the HandBrake x265 test, which is heavily optimized for AVX instructions. The x264 benchmark, which has a lighter distribution of AVX instructions, finds the Ryzen 5 2600X better able to leverage the advantage of its extra threads (not to mention its overclocking headroom).
MORE: Best CPUs
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Rendering, Encoding and Compression
Prev Page Office and Productivity Next Page Conclusion
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
tennis2 Would like to see some testing done to determine how core count affects games these days with the "core count race" going on. It still seems like 4-6 cores is where the cutoff is before frequency is the determining factor of frame rates.Reply
Also show if/how online multiplayer changes that conclusion. -
R_1 in the comparison chart you have the 9400f having graphics and the 9400 as not having graphics.Reply -
NightHawkRMX 9400f would be a good deal if it had a higher turbo or overclocking support. Z390 boards suitable for overclocking are expensive as well.Reply
Otherwise, Ryzen 5 2600x has 6 more threads, higher turbo, overclocking support, and cheap overclocking boards than negate the slightly higher chip price.
Still waiting on Computex. -
Karadjgne I'm still wondering why there's even testing of single core performance. In the rendering test, multi-core, the Ryzens dominated Intel. Very next test was a single core performance test where as usual, Intel was stronger. Why? I can't think of any single core rendering, or games for that matter. It's kind of archaic to my mind. A multi-core test on software that that uses multiple cores makes perfect sense. It shows how well the software responds to the amount of threads. Saying an intel beats a Ryzen in single core rendering is.....Reply
(I'm not gonna use those words in polite company) -
pete_101 I see the CPU has a base frequency of 2.9 and a turbo of 4.1 GHz, but this will be a single core maximum speed. Although it's locked, it should be possible in the mobo BIOS to set all 6 cores to run at this frequency.....if you have a good enough cooler.Reply -
NightHawkRMX There should be an 8 thread Cinebench test to compare CPUs. Most games only use around 8 threads or a little more (battlefield comes to mind). An 8 thread test would be the most accurate way to test gaming CPUs.Reply -
Anubis666 It's funny how prices are different in different countries.. In one thread ,a guy says 15-20$ less than Ryzen 2600 so just go with the i5 9400f..Reply
Here in India i5 9400f is 60$ cheaper than Ryzen 2600 and 95$ cheaper than 2600X..
I'm still confused to go with i5 9400f over 2600 just for the multi thread.. As I wanted it for playing , recording Games,Edit and upload to YouTube and, probably streaming Dota 2 in near future.
The price of i5 9400f is tempting but I'm not sure it can able to do stuff I mentioned above with close to ease..
I'm sure coming Ryzen 3000 is even high price due to high demand in here.