Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Intel Alder Lake Core i9-12900K and i5-12600K Power Consumption, Efficiency, and Thermals
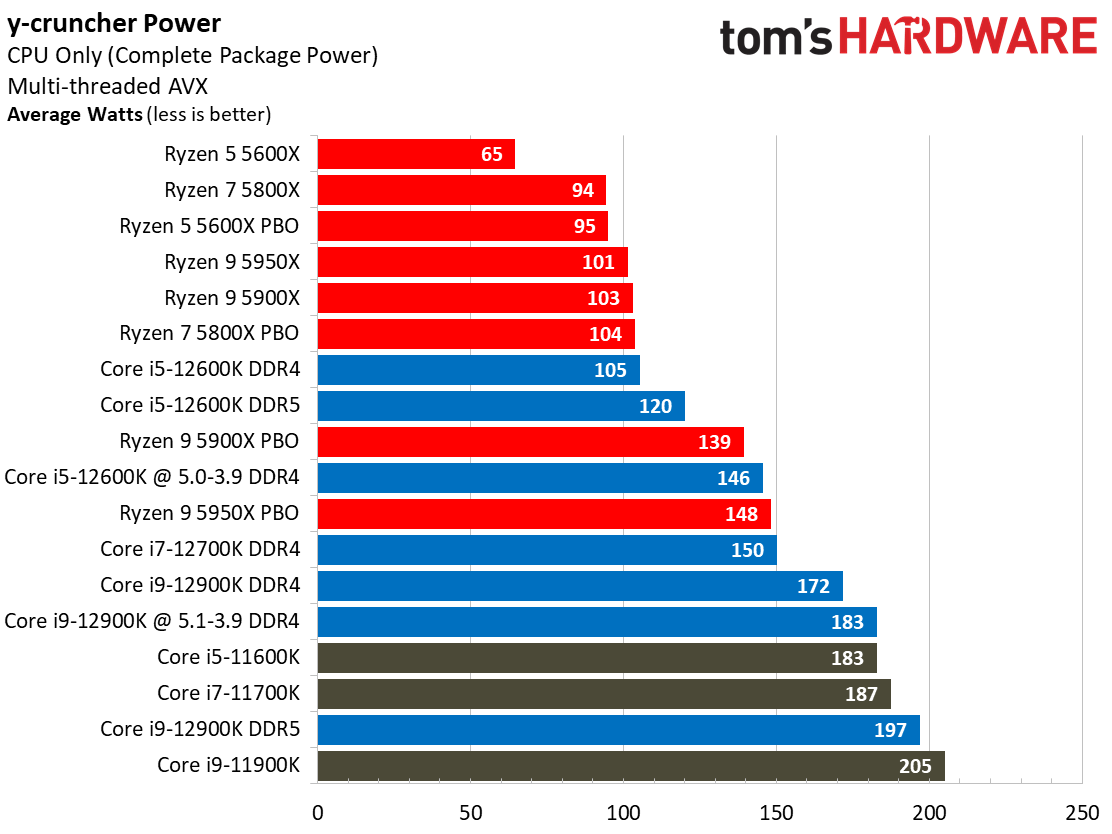
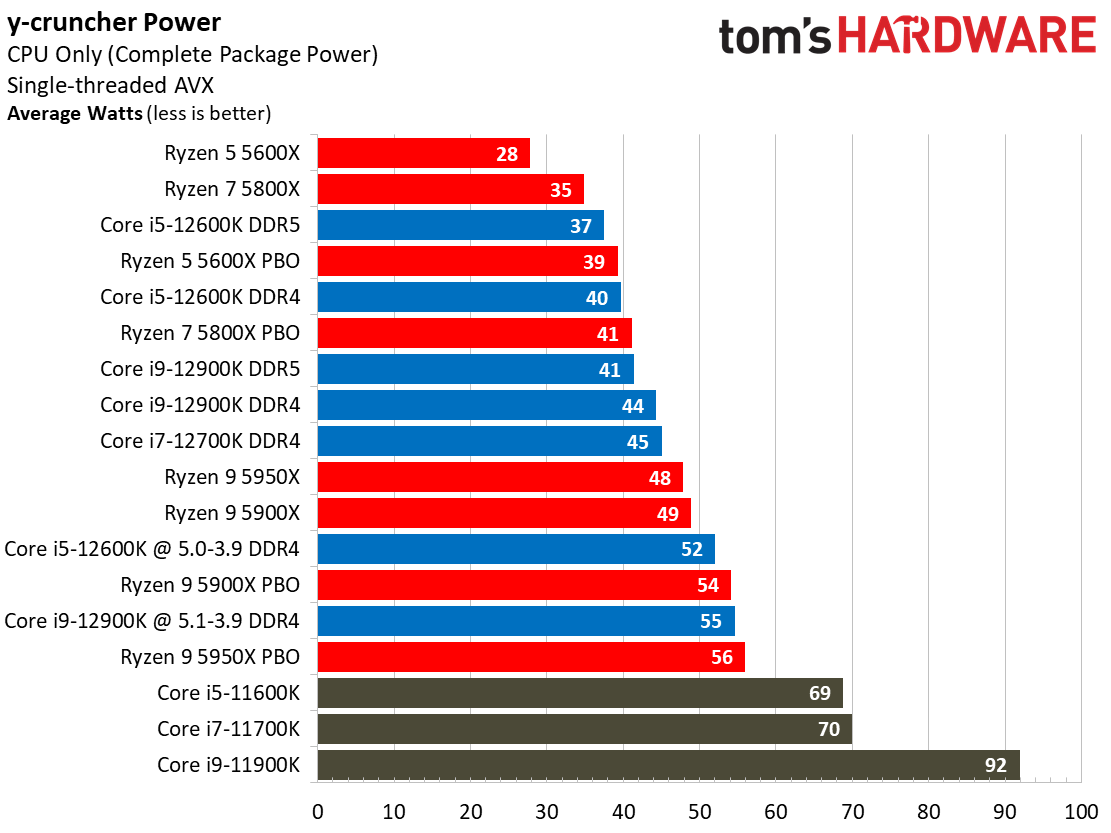
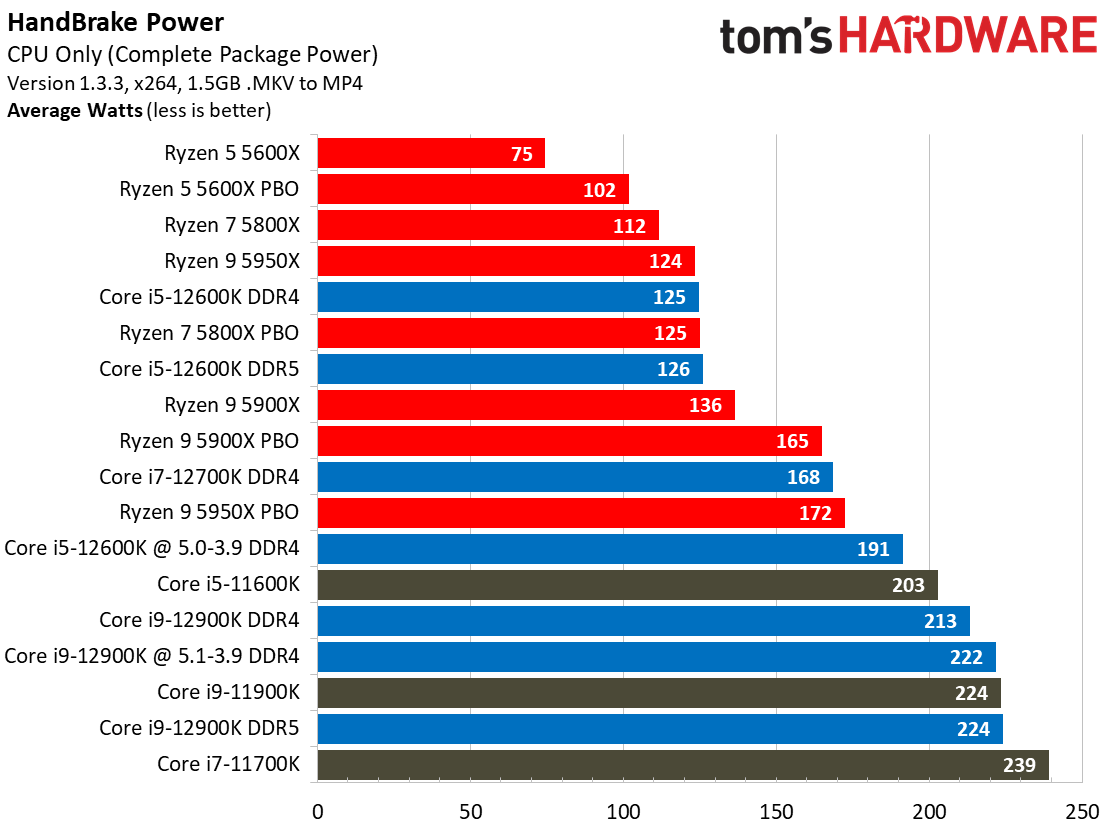
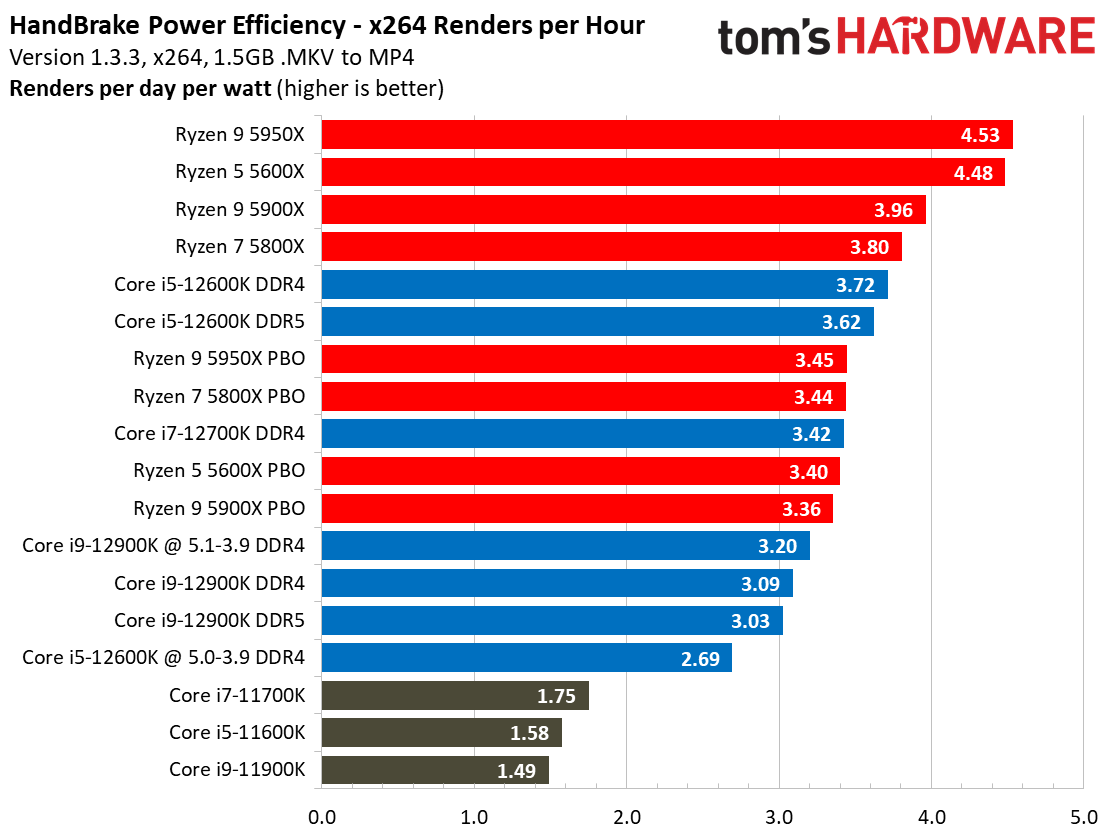
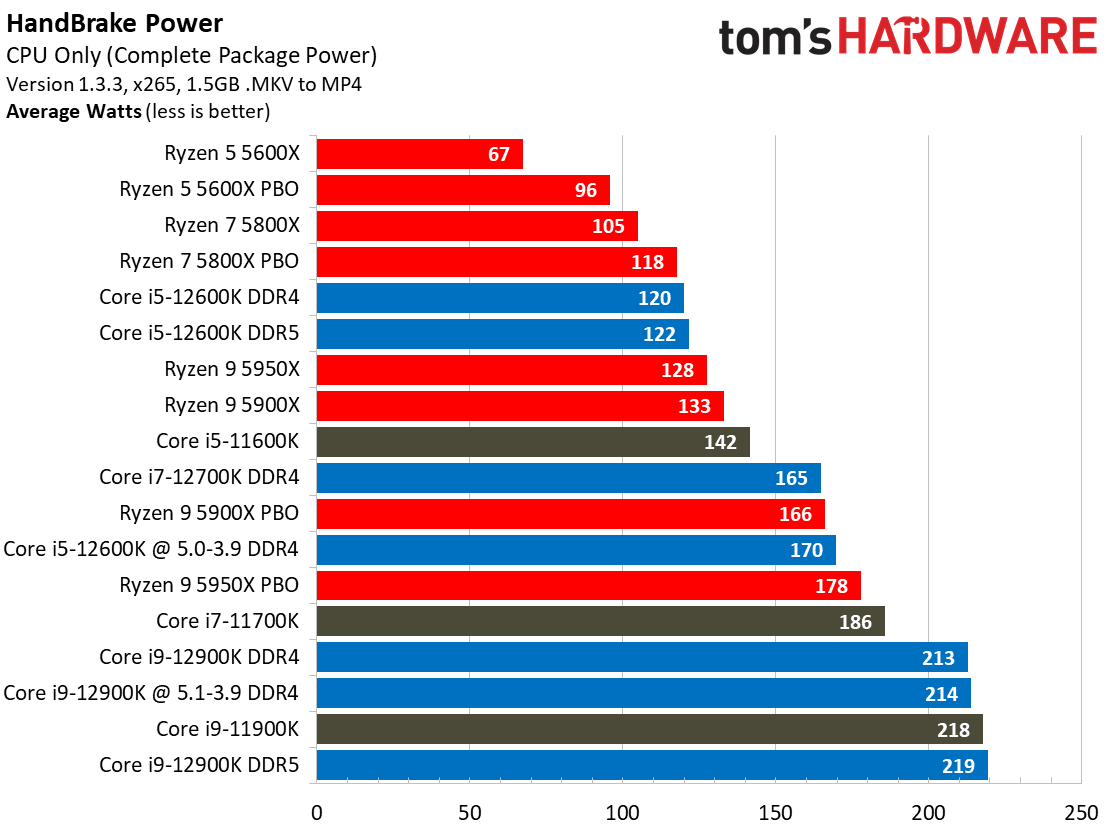
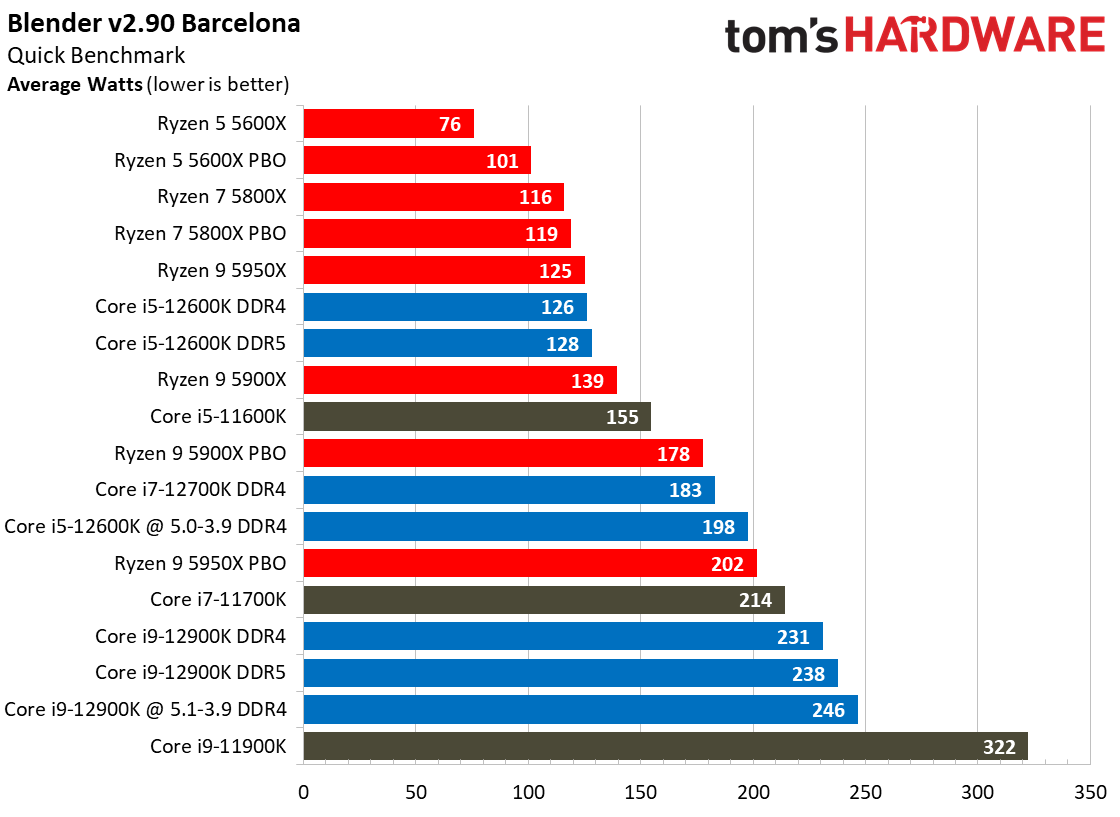
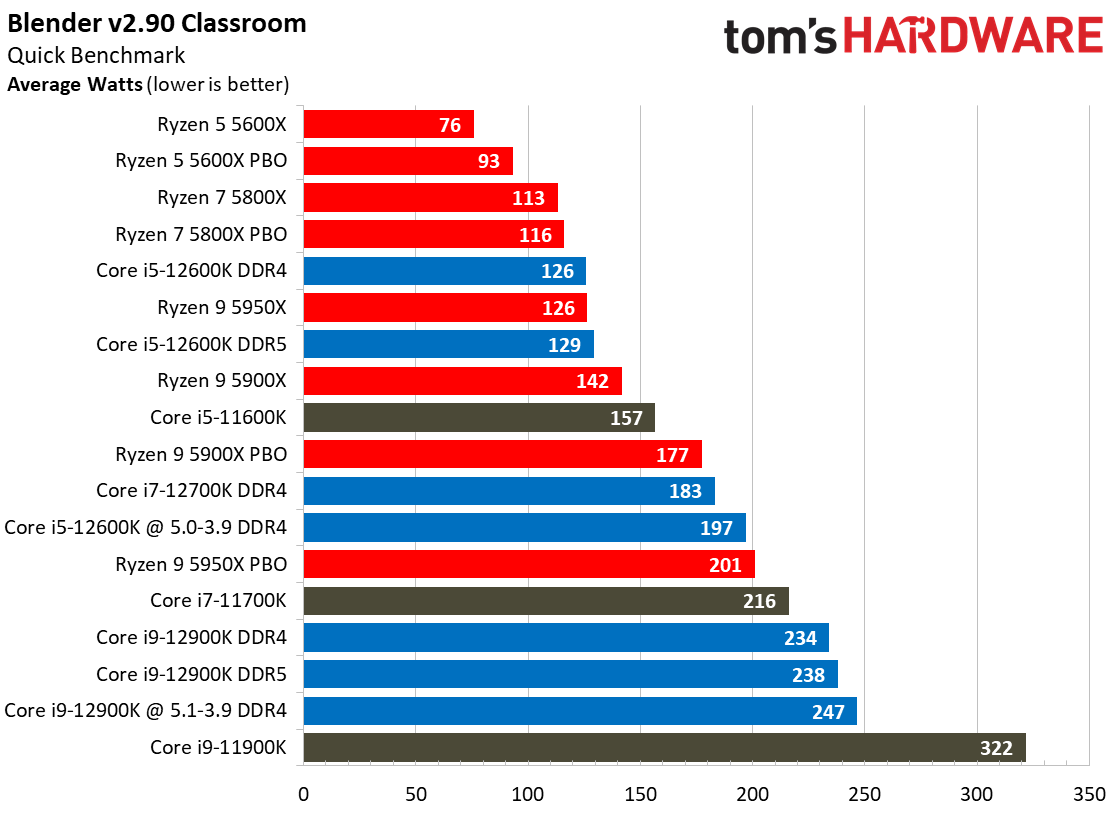
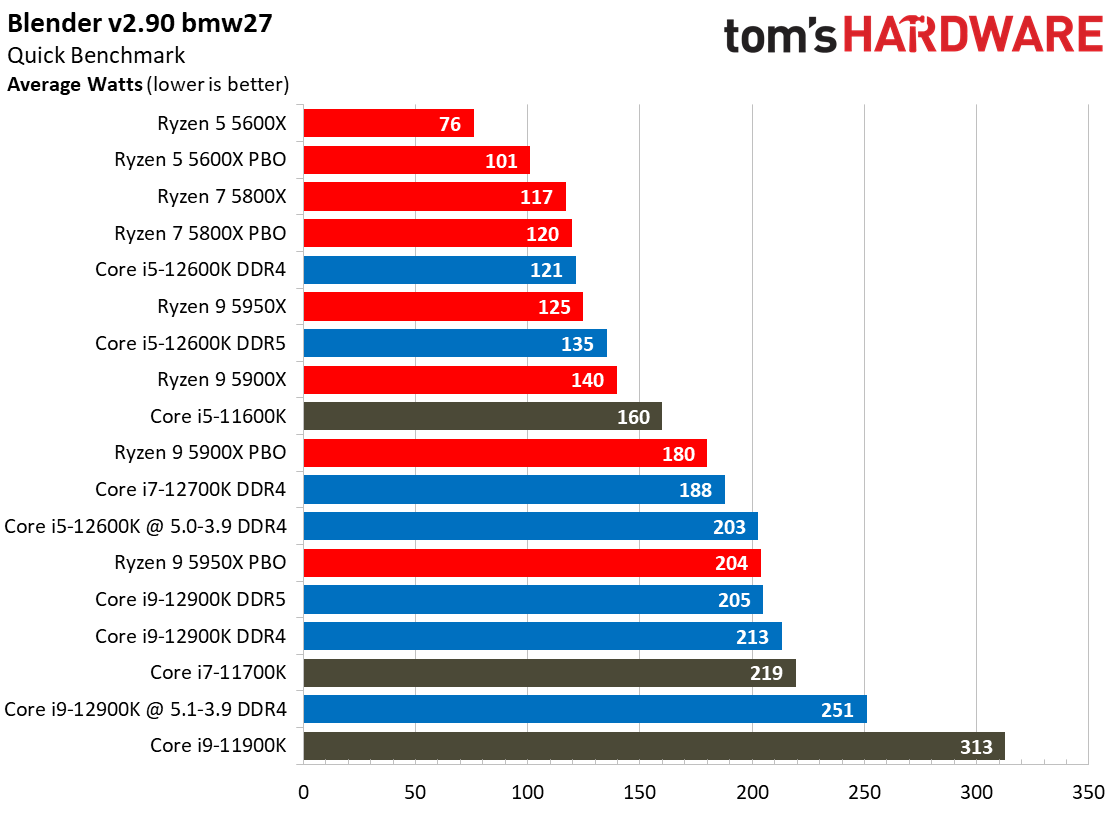
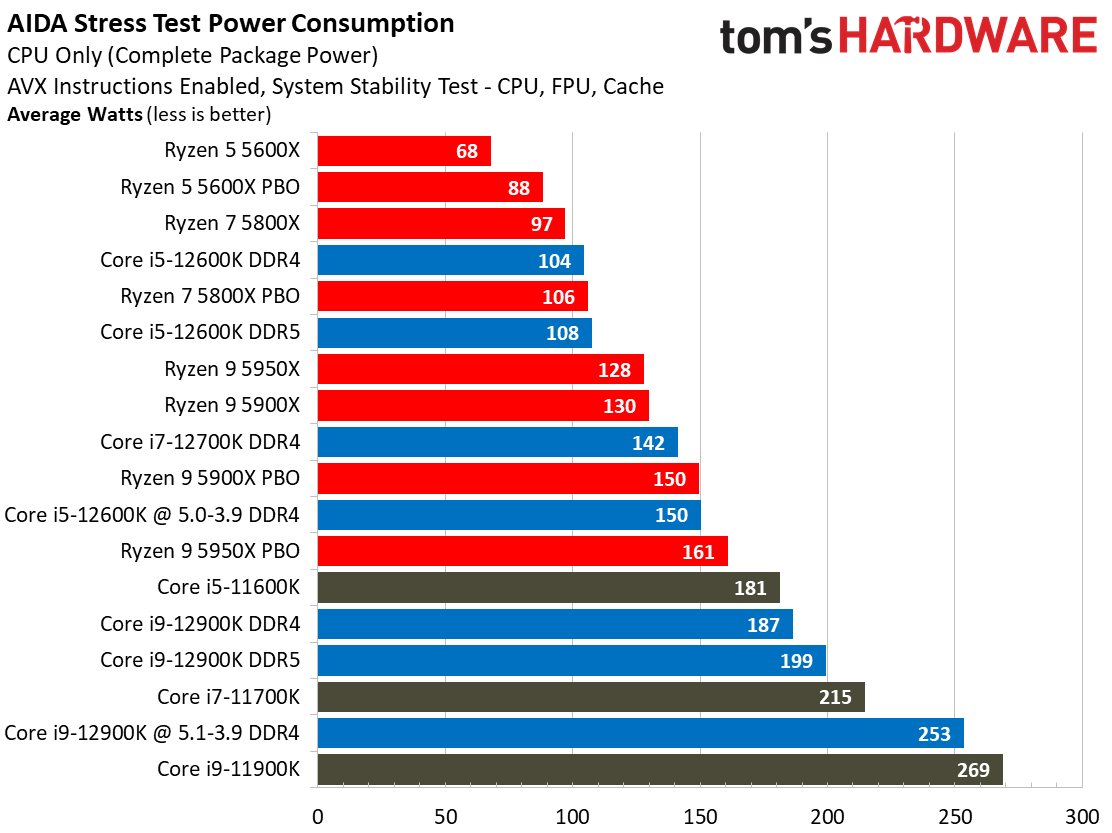
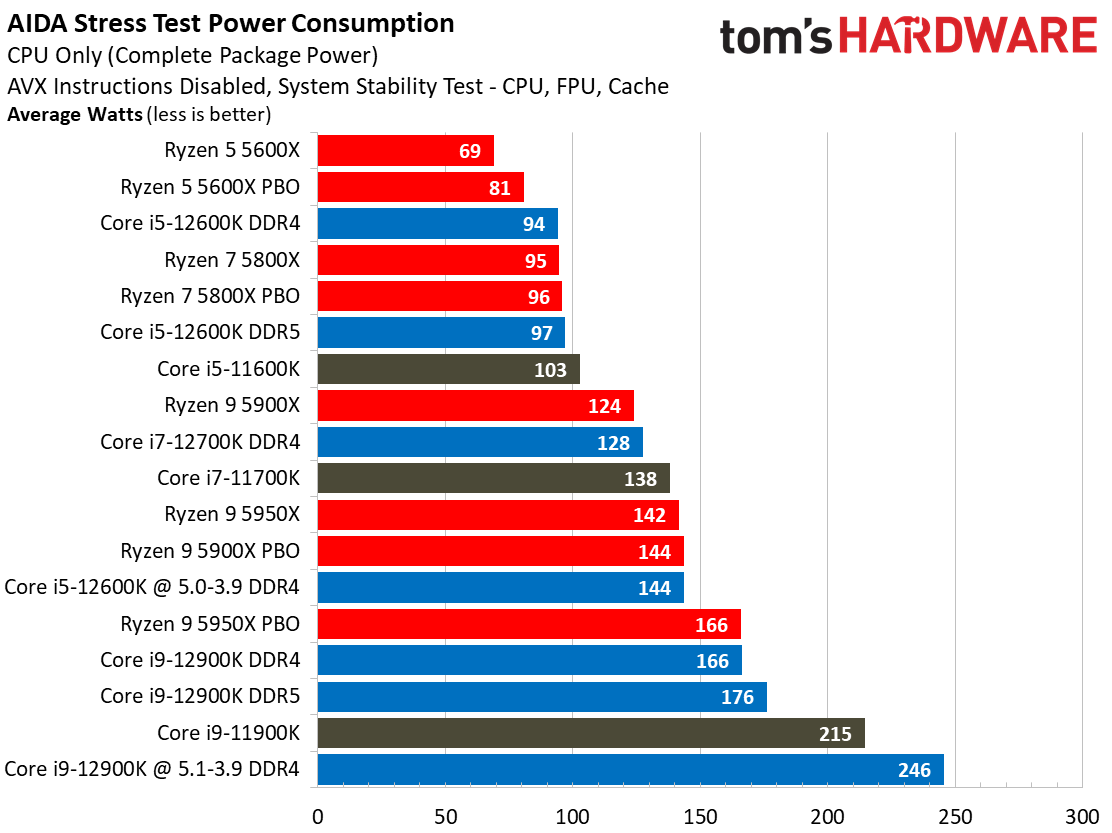
Yes, Alder Lake still sucks more power than AMD's Ryzen 5000 series chips, but the arrival of the Intel 7 process does mark a big improvement. As we can see, the Alder Lake chips consume far less power than the Rocket Lake chips — we measured a peak of 238W with the 12900K, while the previous-gen 11900K drew nearly 100W more during the same Blender workload.
Overall, Intel has reduced its power consumption from meme-worthy to an acceptable level. Besides, Alder Lake is much faster than its predecessor, earning it some leeway.
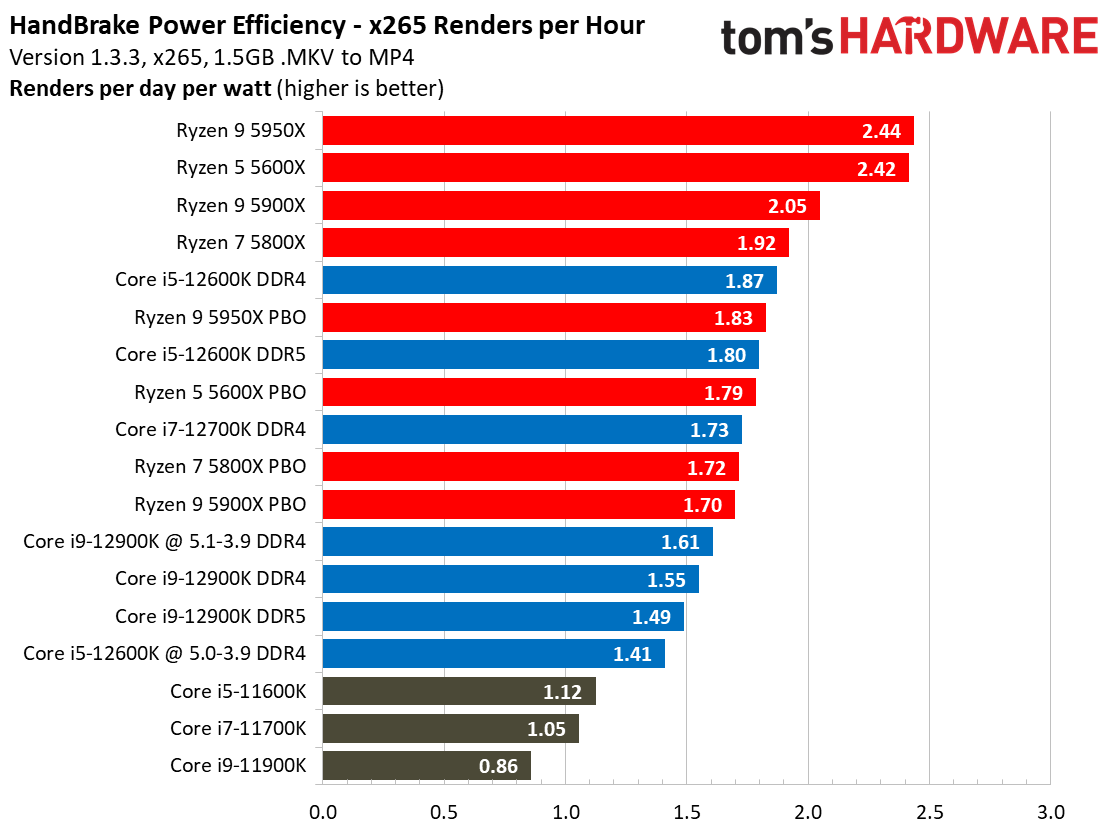
For instance, as you can see in our renders-per-day measurements, the Core i9-12900K and 12600K are both twice as efficient as their predecessors, which is commendable. This lower power consumption results in lower cooling requirements, too.
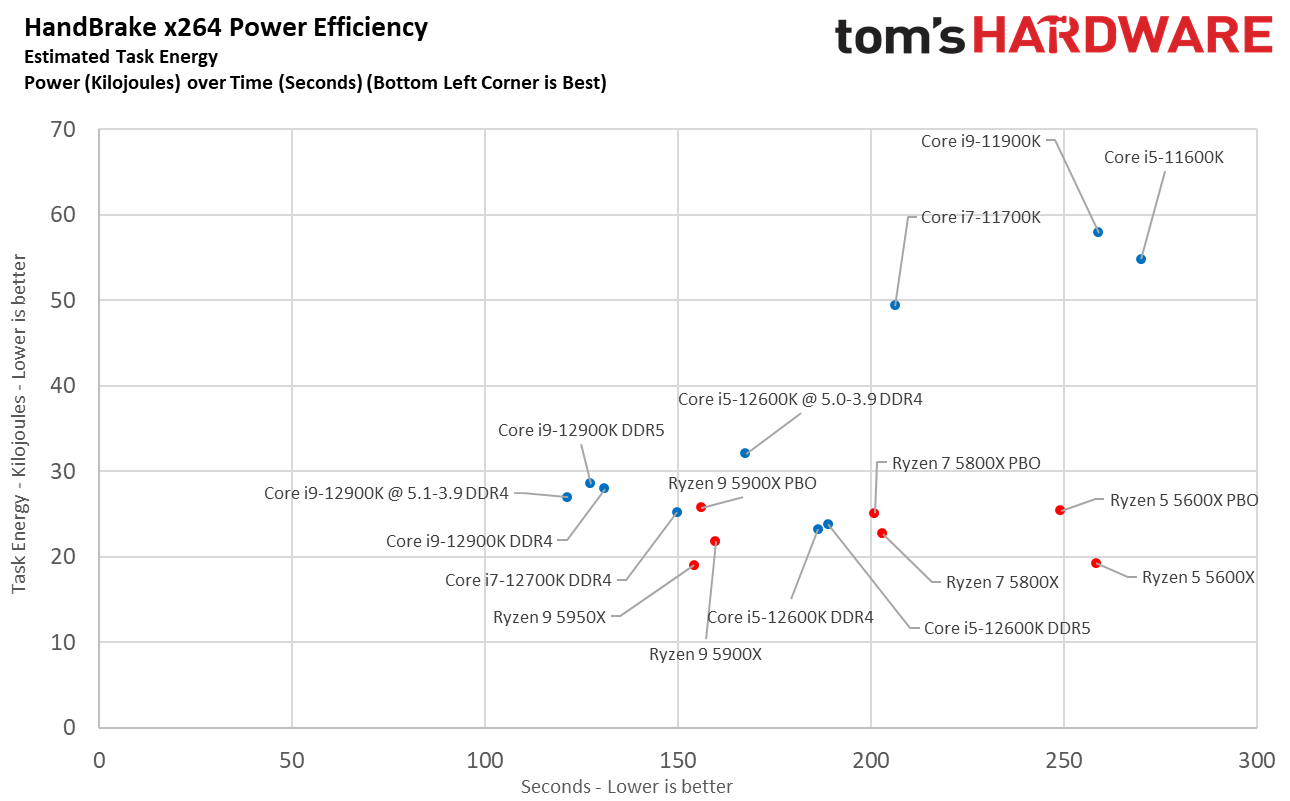
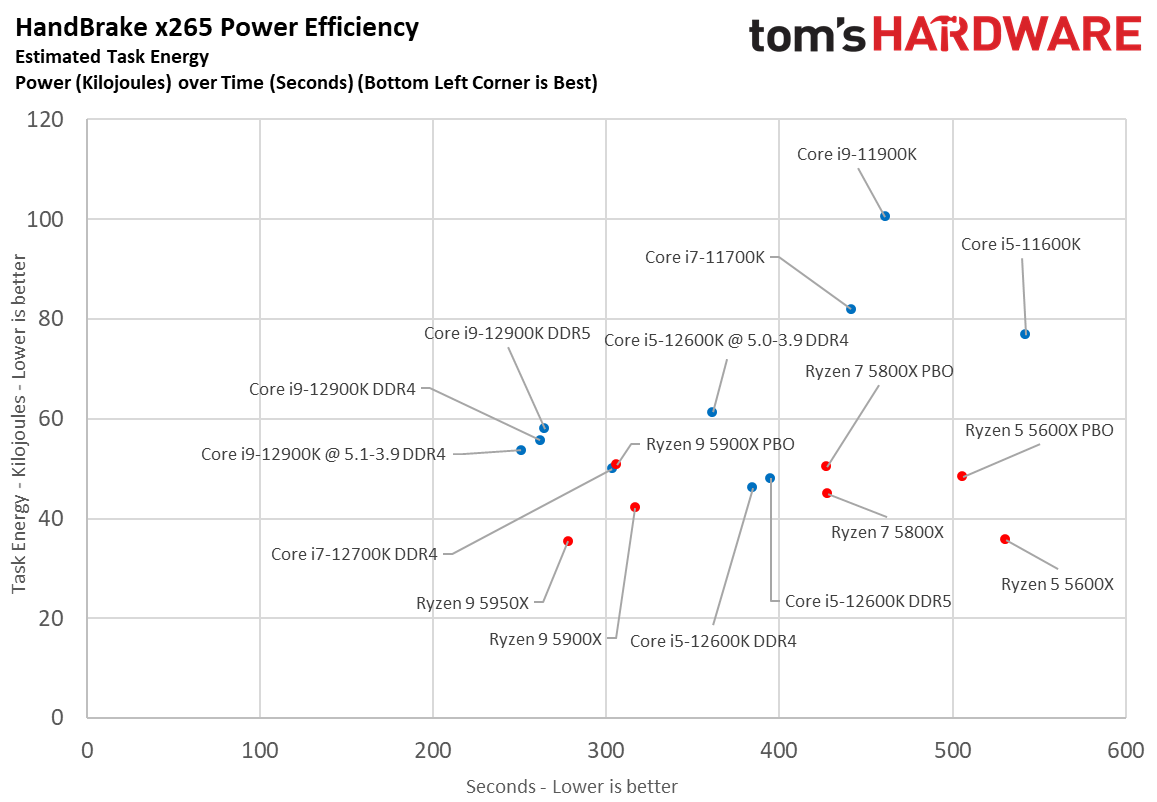
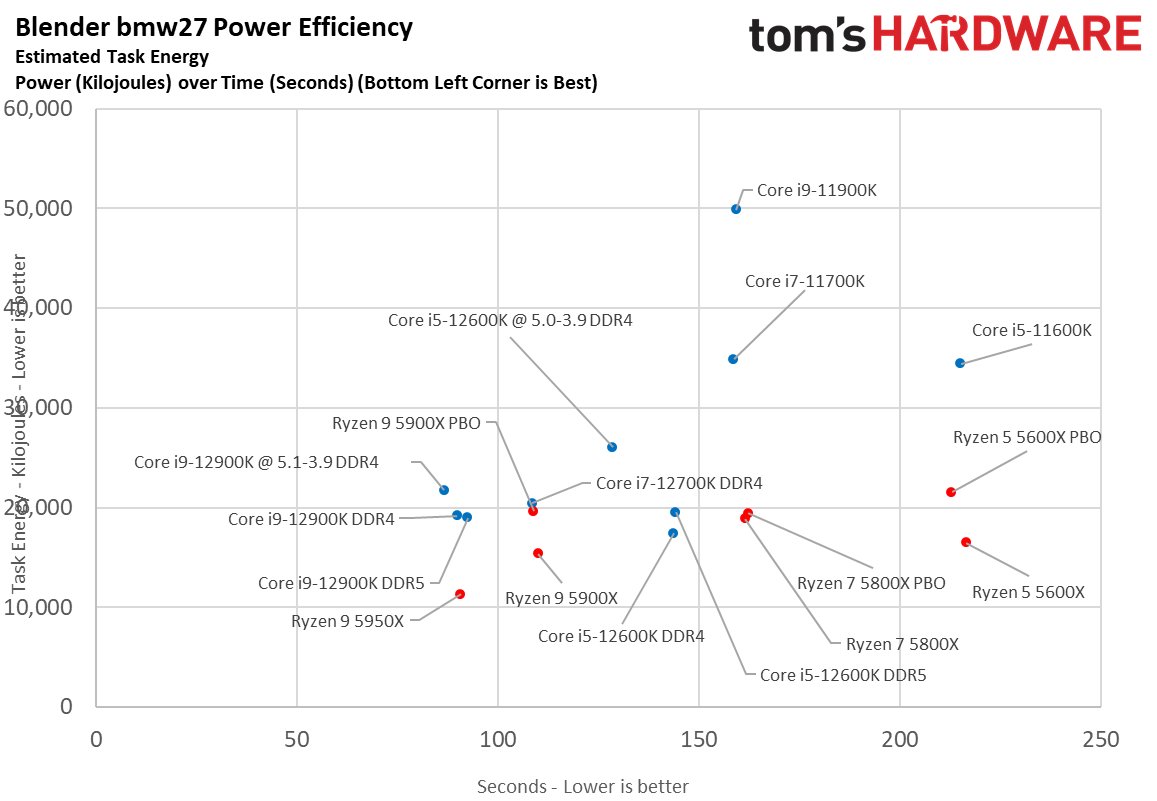
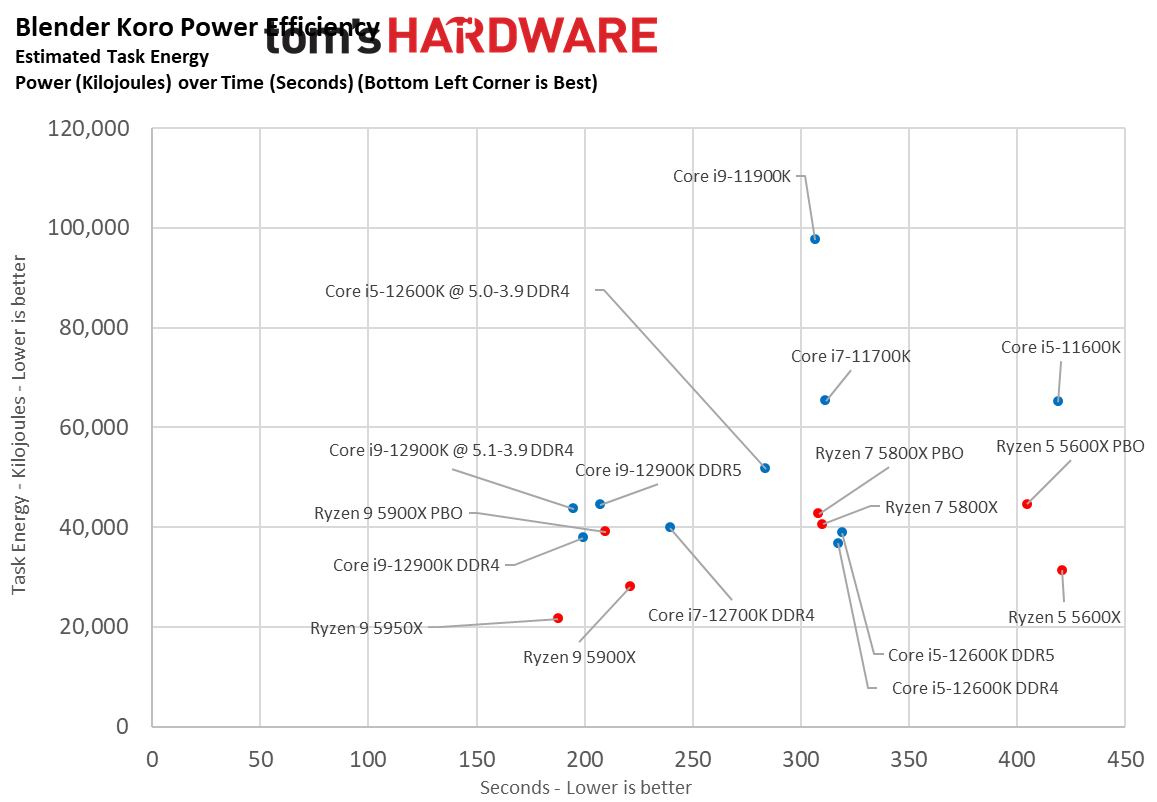
Here we take a slightly different look at power consumption by calculating the cumulative amount of energy required to perform Blender and x264 and x265 HandBrake workloads, respectively. We plot this 'task energy' value in Kilojoules on the left side of the chart.
These workloads are comprised of a fixed amount of work, so we can plot the task energy against the time required to finish the job (bottom axis), thus generating a really useful power chart.
Bear in mind that faster compute times, and lower task energy requirements, are ideal. That means processors that fall the closest to the bottom left corner of the chart are best.
As you can see, Intel's chips have descended from the undesirable upper right of the chart down to the lower left hand, nearly matching AMD's chips in power consumption while actually being faster. That's an outstanding improvement after six years of power-guzzling 14nm chips.
- MORE: Best CPUs for Gaming
- MORE: CPU Benchmark Hierarchy
- MORE: AMD vs Intel
- MORE: All CPUs Content
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Intel Core i9-12900K and Core i5-12600K Power Consumption and Efficiency
Prev Page Core i9-12900K and Core i5-12600K Overclocking, Thermals, and Test Setup Next Page Intel Core i9-12900K and Core i5-12600K Windows 11 Gaming Benchmarks
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
Alvar "Miles" Udell I'm not so sure it will be a short crown retaking. AMD hasn't shown any indication yet they are officially reducing prices to compete, and with Zen 3+ likely to be more expensive than Zen 3, it may be quite the role reversal with Intel the best value. When Zen 4 becomes widely available in 2023 who knows, but as it stands I'd have a tough time recommending AMD over Intel at this point.Reply -
VforV LMAO, 29 days ago this same guy had this article:Reply
Intel Core i9-12900K vs Ryzen 9 5900X and 5950X: Alder Lake and Ryzen 5000 Face Off
Now he has a "review" of them. Pffft.
Why don't you do another "review" again in 1 month, since intel does not have enough promo pieces already...
P.S. Even with the exaggerated positive press Alder Lake had and has, still is not selling great... Still I see their CPUs in stock at better prices than Ryzen and not moving that stock. I find it hilarious. -
m3city I just don't get it. Maybe I just can't find the right numbers. Maybe I'm cherry picking but when I see:Reply
5900 vs 12900, CPU price somewhat similar.
Cruncher multi 100W@37sec, 170W@107s. Single thread shows better Intel.
Handbrake x264 4 renders vs 3 renders, 130W vs 213W, 151s vs 262s.
Noted, Intel has iGPU - thats BIG, at least for me.
Better CPU overall? As I said, I just don't see it. Intel is bigger, stronger. Not a better athlete at all. -
helper800 I do not know what the others are on about. The new Alder lake CPU's are objectively better at more things than AMDs offerings are vs Alder lake. @VforV Anyone could argue the same about positive press for the zen 1 and 2 products. Personally I am just happy some semblance of competition is back. If you are looking at this with anything other than it being a win for consumers, than you've got brand loyalties that may make you buy into objectively worse hardware. Intel also comes in cheaper at most all price points (with exception to some whole platform considerations).Reply -
VforV Reply
I'm glad for competition, but no Alder Lake is not an outstanding success beating Zen3 from A to Z and at everything and anything. Far from that...helper800 said:I do not know what the others are on about. The new Alder lake CPU's are objectively better at more things than AMDs offerings are vs Alder lake. @VforV Anyone could argue the same about positive press for the zen 1 and 2 products. Personally I am just happy some semblance of competition is back. If you are looking at this with anything other than it being a win for consumers, than you've got brand loyalties that may make you buy into objectively worse hardware. Intel also comes in cheaper at most all price points (with exception to some whole platform considerations).
Like nvidia, intel too has to win back a lot of good will before I even care about them, after all the **** they done in the last 7 or so years.
I rather buy an inferior product than step over my principles and dignity and s*** up to those 2 companies and give them my money for a minority performance advantage (at a point in time). Nvidia is actually worse than intel, but intel is bad enough still.
Coming Zen3D, interest in Alder Lake will drop even more (it already has worse sales than predicted/wanted).
Yes, competition is good, but only because it pushes AMD to be even better than if they did not have at all. That's the only part I care about. -
helper800 Reply
I can respect your opinion, but I disagree. In my opinion companies all do what they can to stay as profitable as they can. Consumer "goodwill" is just another currency these large multinational companies spend and receive for various conduct. AMD currently has a decent amount of goodwill, however, they spent a major chunk of it by not releasing a 5600, 5300, 5700 / 5800 while also increasing prices by 50 dollars across the board. They did this for money and they knew they could get away with it because they had garnered enough consumer goodwill.VforV said:I'm glad for competition, but no Alder Lake is not an outstanding success beating Zen3 from A to Z and at everything and anything. Far from that...
Like nvidia, intel too has to win back a lot of good will before I even care about them, after all the **** they done in the last 7 or so years.
I rather buy an inferior product than step over my principles and dignity and s*** up to those 2 companies and give them my money for a minority performance advantage (at a point in time). Nvidia is actually worse than intel, but intel is bad enough still.
Coming Zen3D, interest in Alder Lake will drop even more (it already has worse sales than predicted/wanted).
Yes, competition is good, but only because it pushes AMD to be even better than if they did not have at all. That's the only part I care about. -
VforV Reply
There is no innocent company, AMD included. I also don't like those same things you stated about AMD that they did recently, but compared to nvidia and intel (on topic), the amount of scummy or s* things AMD did is almost meaningless.helper800 said:I can respect your opinion, but I disagree. In my opinion companies all do what they can to stay as profitable as then can. Consumer "goodwill" is just another currency these large multinational companies spend and receive for various conduct. AMD currently has a decent amount of goodwill, however, they spent a major chunk of it by not releasing a 5600, 5300, 5700 / 5800 while also increasing prices by 50 dollars across the board. They did this for money and they knew they could get away with it because they had garnered enough consumer goodwill.
... so far. And that is what matters to me. It's not like I'm losing so much performance if I use AMD, like it was the case 5-7 years ago, they are either on top or very close to the top, depending on the generation. -
DSzymborski If you want a site that writes articles that only conform to your personal philosophical ideals, you'll need to start up VsHardware.com. It's not the job of a reviewer to review CPUs based on who "deserves" anything, but what the performances are.Reply -
VforV Reply
Sure, I'd love to see that professional impartiality from all the tech sites and YT channels, but the reality is so much different than these utopian journalism rules... which almost no one cares about or abides by them anymore. The trend is actually in the opposite direction.DSzymborski said:If you want a site that writes articles that only conform to your personal philosophical ideals, you'll need to start up VsHardware.com. It's not the job of a reviewer to review CPUs based on who "deserves" anything, but what the performances are.
So in that regard, in a perfect world you would be right.
Then I am also right when I say, everyone that buys a product does it based on it's own preference and subjective feeling and beliefs towards that product.
Thus, we all give or money to those that we think they deserve out money. And we don't give to those that don't.
Which means I don't give my money to those companies that do NOT: in this case, intel and nvidia. At least not until they prove they are atoning for all the s* they did up until now and start to do better. But if they never change and keep doing s*, then it's a no from me. It's as simple as that and I don't see a problem with this whatsoever. I may be in a minority thinking like this, but I know I'm not the only one.