Overclocking Core i7: Power Versus Performance
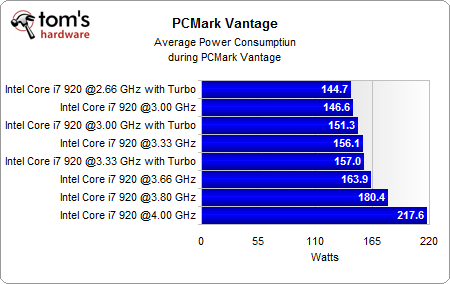
Average And Total Power During PCMark
We looked at the average power requirements during PCMark Vantage, to see the power consumption numbers at a given workload.
| Core i7 920 (2.66 GHz/ 213 W Peak Power) | Performance Increase | Average Power Increase |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 GHz | 8.8% | 4.6% |
| 3.33 GHz | 14.7% | 8.5% |
| 3.66 GHz | 24.6% | 13.3% |
| 3.8 GHz | 31.1% | 24.7% |
| 4.0 GHz | 23.3% | 50.4% |
*Core i7 Overspeed Protection led to throttling
While the average power consumption increases by a maximum of 24.7% at 3.8 GHz, going one step farther to 4.0 GHz results in a jump to 50%. Compared to the 36% increase in idle power paired with a performance increase of 23.3%, the 4.0 GHz setting does not make sense from a practical standpoint.
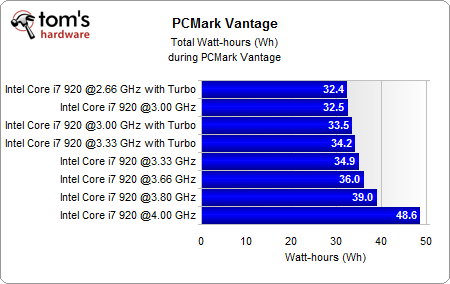
Finally, we also looked at the total power used to complete a PCMark Vantage run:
| Core i7 920 (2.66 GHz / 213 W Peak Power) | Performance Increase | Total Power Increase |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 GHz | 8.8% | 3.4% |
| 3.33 GHz | 14.7% | 5.6% |
| 3.66 GHz | 24.6% | 11.1% |
| 3.8 GHz | 31.1% | 20.4% |
| 4.0 GHz | 23.3% | 50% |
Keep in mind that the total power used does not increase that much, as the faster system typically terminates its computations more quickly, allowing the system to switch into a power efficient mode.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Average And Total Power During PCMark
Prev Page Idle/Peak Power Consumption Analysis Next Page Efficiency Results