Passive Cooling: XFX RX 460 Heatsink Edition Vs. Palit GTX 1050 Ti KalmX
After hacking together our own passively-cooled card, we now compare off-the-shelf solutions based on AMD and Nvidia GPUs. Was our attempt amateurish or could there be a more general problem with passively cooling current-gen graphics processors?
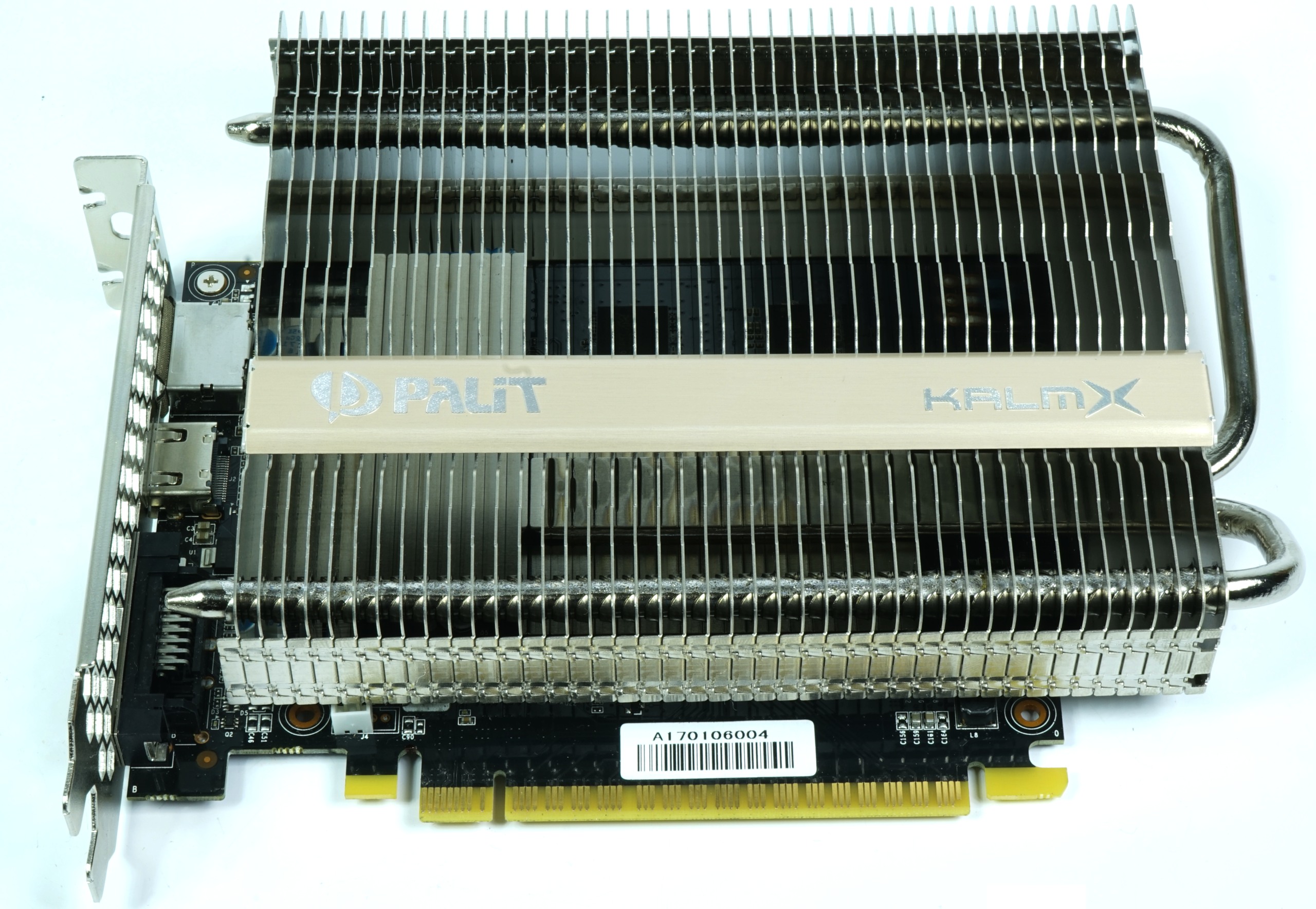
Palit GeForce GTX 1050 Ti KalmX
Palit introduced its first passively-cooled board in the GeForce GTX 750 Ti KalmX and followed up with the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti. Nothing much has changed visually, other than the new substructure. But how effective is Palit’s passive implementation and what are its limits? After all, the 750 Ti was a 60W board, while 1050 Ti is rated at 75W.
A known limitation of this card is its relatively constrained clock, which starts at 1291 MHz and is rated for a GPU Boost frequency of 1392 MHz.
MORE: Best Deals
MORE: Best PC Builds
Exterior
The card weighs 466g, only a bit more than XFX's board. Its 18.3cm length, 13.7cm height, and 3.6cm width are all manageable in a dual-slot form factor.


Palit dispenses with a backplate and overhanging rear fins, in contrast to its older passive coolers, preventing possible conflicts with CPU coolers in mini-ITX enclosures.
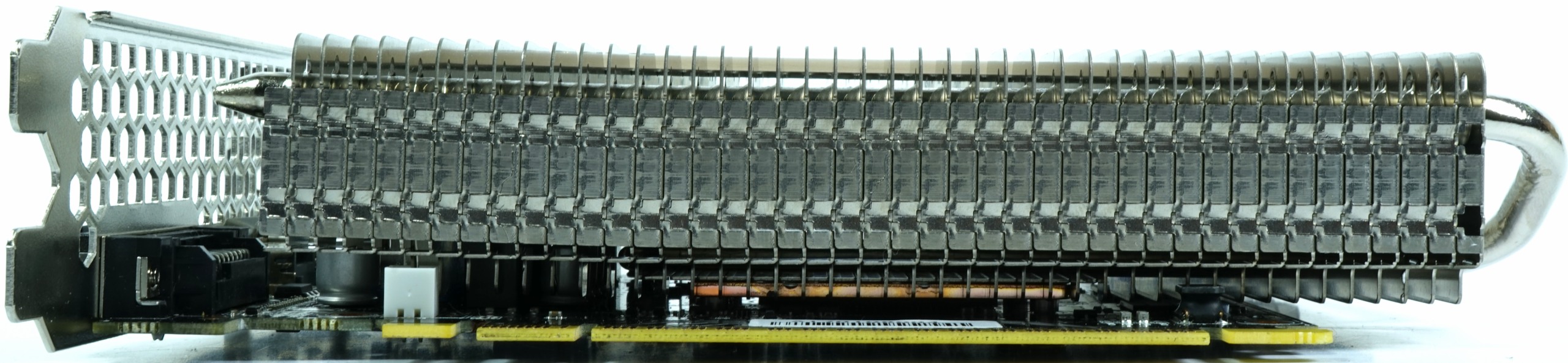
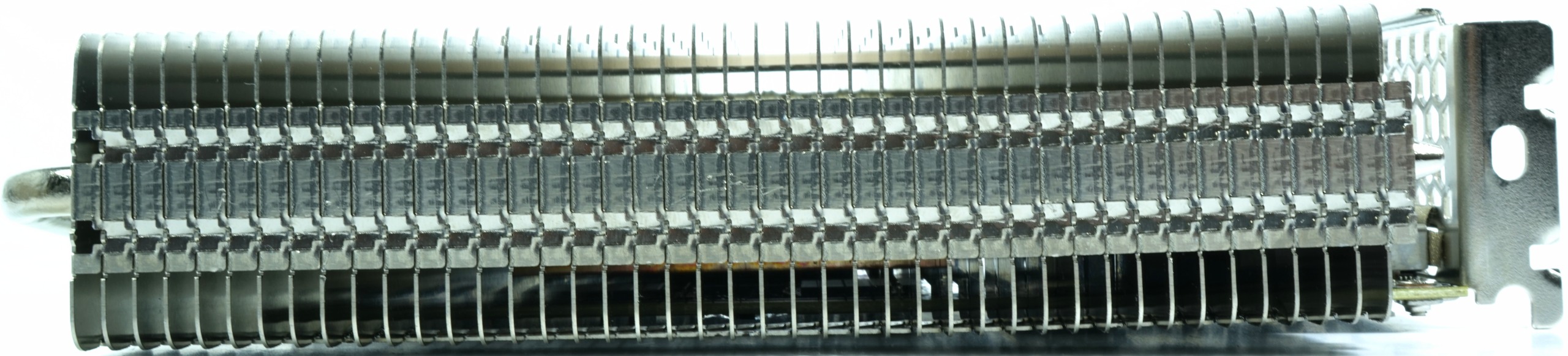
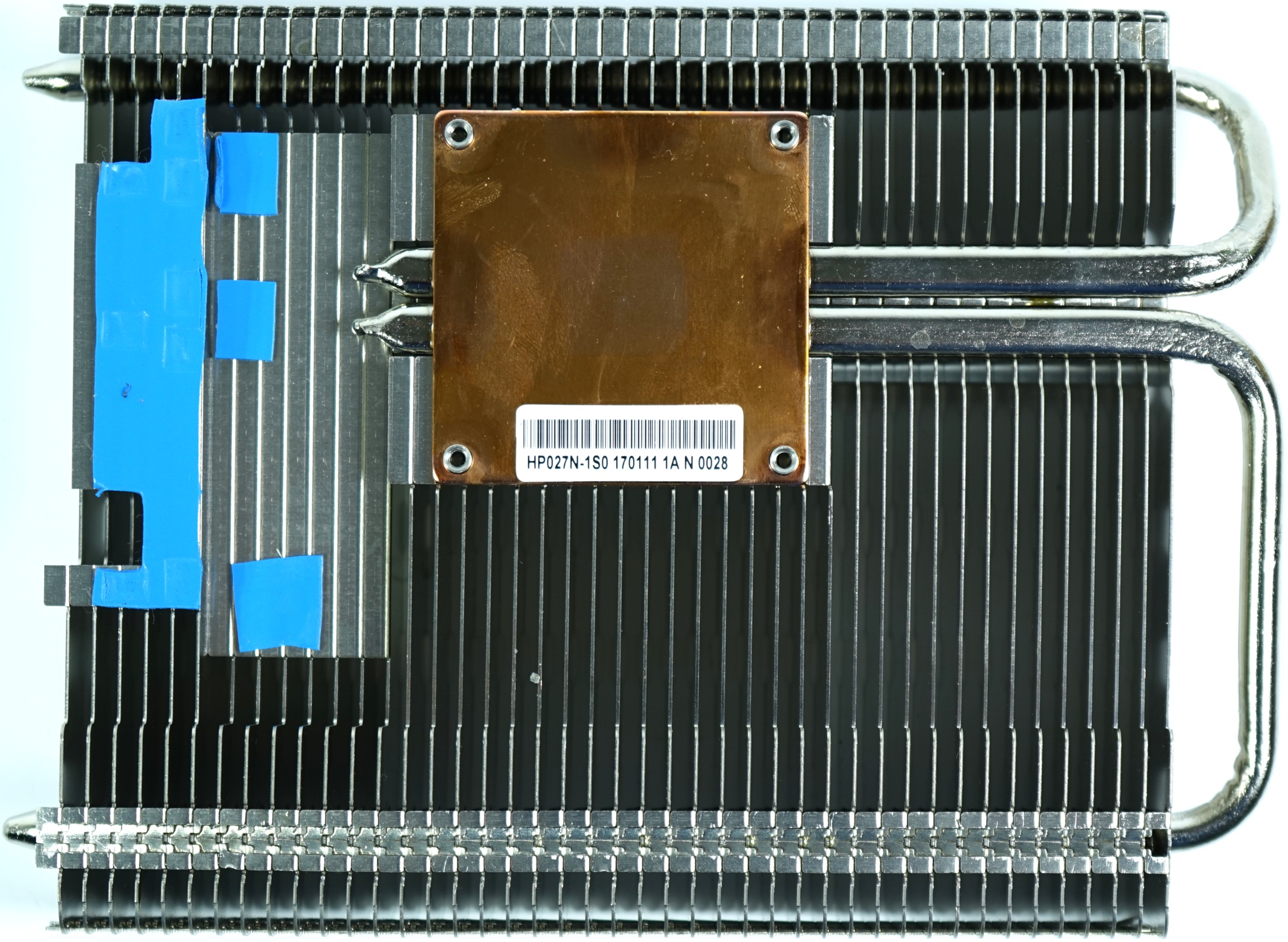
Palit again employs two nickel-plated heat pipes within a copper slug to dissipate thermal energy as effectively as possible. The sink, with its embedded aluminum fins, juts out the end and top edge of the PCB to capture circulating air. The fins are oriented vertically, similar to Palit's previous-gen design. Although this is better for natural convection, it benefits less from air flowing from the front of the case.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Vertically-oriented fins also benefit when the card is installed standing up, as you'd find in a cube-style case.


The display output bracket is limited to one DVI-D port, one HDMI 2.0 interface, and DisplayPort 1.4-capable connector. This leaves a lot of room for the many honeycomb-shaped air openings (though they seem fairly useless, given Palit's fin orientation).
Circuit Board Layout And Power Supply
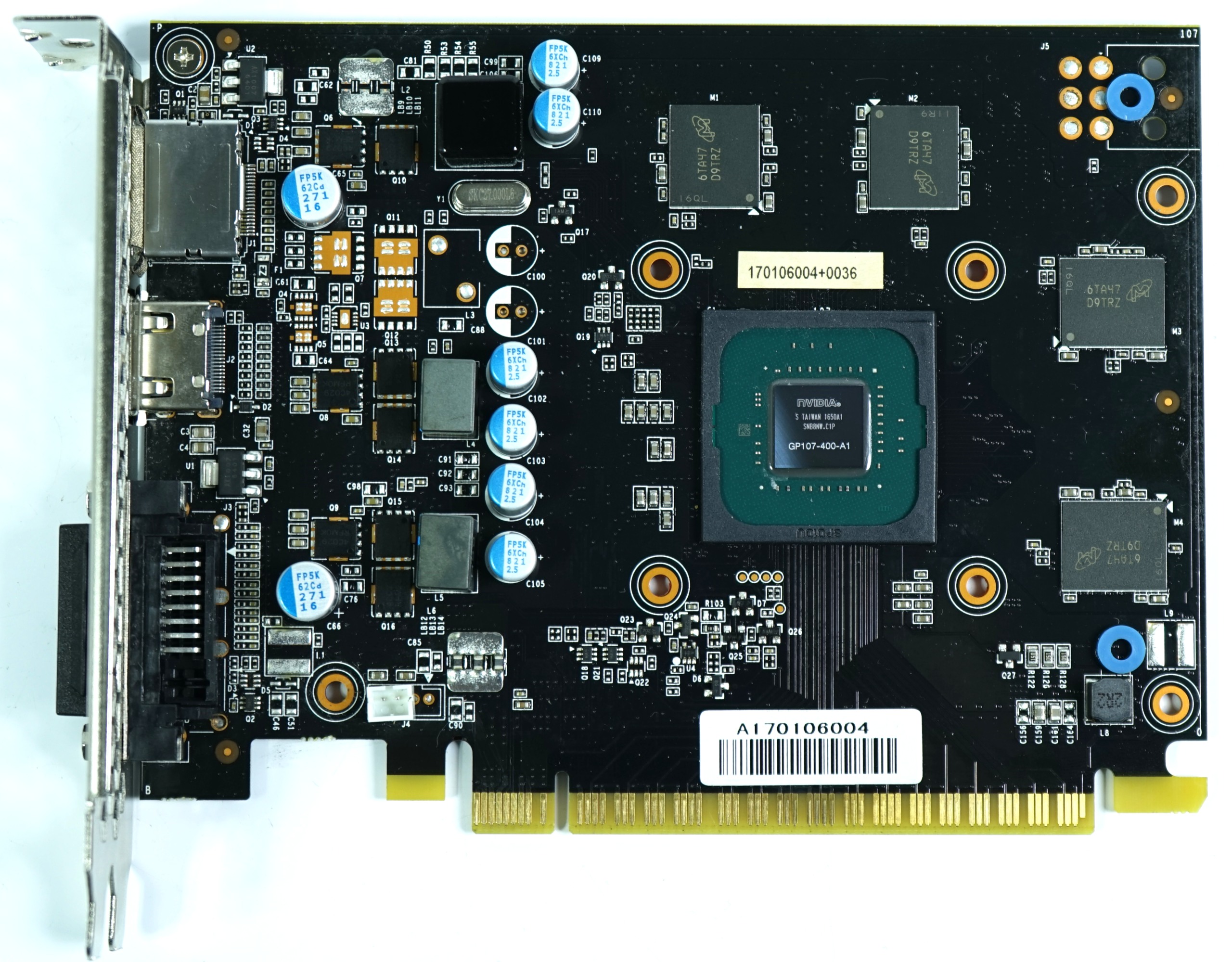
Palit’s power target for this card is modest, as you might guess from the missing six-pin auxiliary connector. Similar to XFX, Palit also situates its voltage regulation circuitry near the output bracket, closer to the PCIe slot's relevant pins.
Although the PCB can accommodate three power phases for the GPU, only two are implemented.
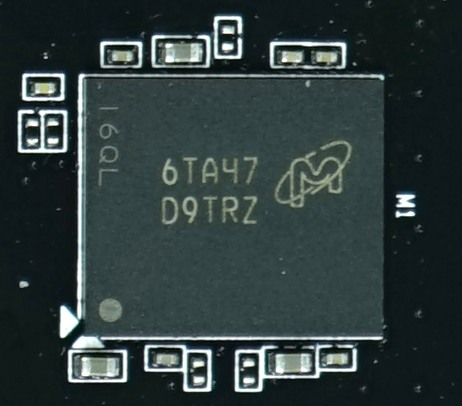
In contrast to XFX, Palit uses memory modules from Micron, each with a capacity of 8Gb (32x256Mb). These operate at 1752 MHz and are not actively cooled, which creates a bit of an issue since Micron's memory runs somewhat hotter than Samsung's. Fortunately, we have the right tools to quantify the difference.
Back to the GPU's voltage regulation, which is controlled by a uPI Semiconductor uP9509. Each of the high-side GPU phases employs a 4C019 N-channel MOSFET, while the low side has two 4C024 N-channel MOSFETs. Standard ferrite coils, poured into cups, are manually fastened to the board.

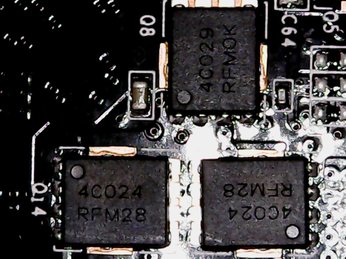
The memory's power comes from a Richtek RT8128 synchronous buck PWM controller, as well as an On Semiconductor NTMFS4C024N single N-channel MOSFET for the high and low side.


Power Consumption
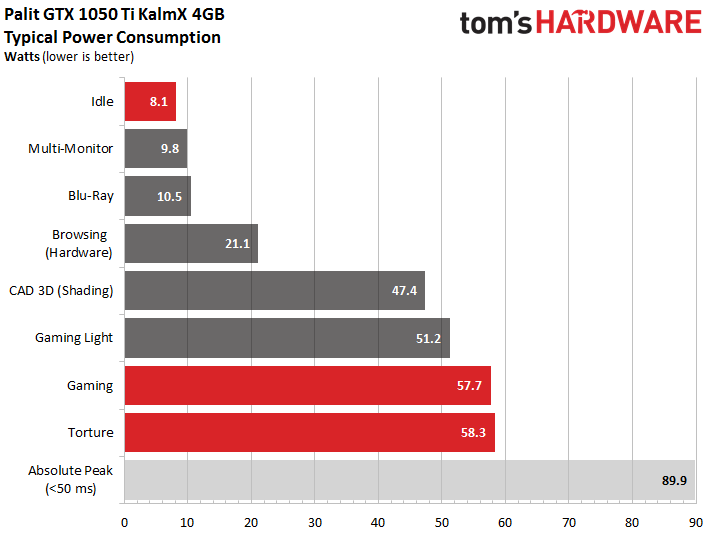
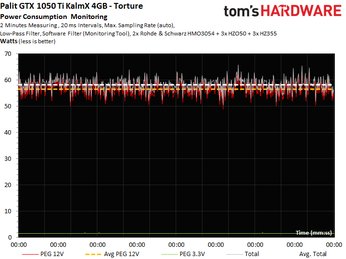
This card's power consumption is manageable, as it was for XFX's passively-cooled RX 460. The GeForce GTX 1050 Ti KalmX barely reaches 58W in our gaming loop, and slightly exceeds that figure during the stress test. Given a power target of 60W, this card simply can’t deliver much more.
Our peak measurement represents a brief moment in time; it can't be used to characterize the board's power consumption over longer periods.
So, both of the cards we're testing consume roughly the same amount of power, even though the GeForce's performance is expected to be appreciably higher.
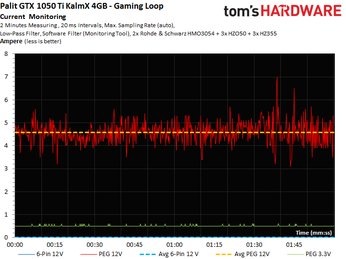
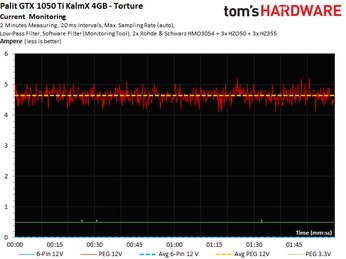
The following graphs show two-minute runs in our gaming loop and stress test; they provide the basis for calculating average power consumption.
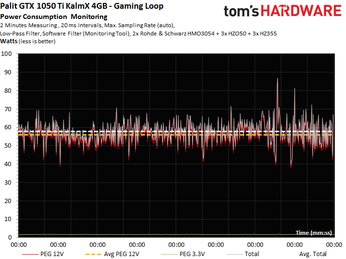
Now we get to look at our current measurements, which fall below the PCI-SIG's 5.5A limit for the 12V motherboard slot.
Cooler Assembly
Two 6mm nickel-plated copper alloy heat pipes are sandwiched between a small, yet beefy, copper sink and an aluminum block above it. The aluminum block supports the actual cooler assembly, while the pipes dissipate waste heat through the fin array.
Both vendors’ coolers differ in their fin orientations and resulting heat pipe structures. Palit at least also tries to establish thermal contact between the voltage regulation circuitry and cooler using thicker thermal pads. Do they help? Again, we have the tools to answer that.
MORE: Best Graphics Cards
MORE: Desktop GPU Performance Hierarchy Table
MORE: All Graphics Content
Current page: Palit GeForce GTX 1050 Ti KalmX
Prev Page XFX Radeon RX 460 Heatsink Edition Next Page Temperatures, Clock Rates, And Performance
Igor Wallossek wrote a wide variety of hardware articles for Tom's Hardware, with a strong focus on technical analysis and in-depth reviews. His contributions have spanned a broad spectrum of PC components, including GPUs, CPUs, workstations, and PC builds. His insightful articles provide readers with detailed knowledge to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape
-
derekullo Watch Dogs 2Reply
1920 x 1080 Pixels
"High Settings"
FPS (Lower is better)
Made me Laugh. -
Rookie_MIB Wow. You know, they could fit a small incredibly slow fan in there somewhere that would generate zero noise and improve their results dramatically. I guess you could use the XFX in a server as the airflow scenario would allow cooling from the fans, but why would you use a GPU in a server anyhow?Reply -
Math Geek i can't think of a single scenario where this is needed. fanless gpu but you need multiple case fans to keep it cool and barely at that. why not just have the fans right on the card? double slot so you don't save any space that way, so those few cases that truly need a single slot card can't even be claimed as a market for this card.Reply
now that single slot slim fan design His showed off a while ago would be an awesome thing if it worked and was actually released.
but i just don't see this filling any need at all in a gaming pc. in a non-gaming pc a regular gpu would likely stay cool enough for the passive mode to keep the fans totally off or barely moving. yet still be able to kick it up when needed for a bit of funtime distraction. -
Pompompaihn Dumb products. If have to run system fans for them to work than what's the point of a completely fanless product? It's like saying my car gets infinite gas mileage as long as it's hooked to a tow truck...Reply -
RomeoReject Only situation where I can see them being worthwhile is in a mineral oil setup. The fan on the GPU I have in mine baaaaarely moves as is. More oil moves as a result of convection. So in that situation, it could be worth having the extra metal on there and relying on the convection effect rather than wasting that space on a fan.Reply
But that is so incredibly niche, I agree with you all: These are products searching for a purpose. -
80-watt Hamster Reply19487062 said:now that single slot slim fan design His showed off a while ago would be an awesome thing if it worked and was actually released.
Are you talking about something like this?
-
Math Geek Reply19488039 said:19487062 said:now that single slot slim fan design His showed off a while ago would be an awesome thing if it worked and was actually released.
Are you talking about something like this?
not the exact one but that's the idea. i did not know XFX had finally released it, must have missed that announcement. This article also pointed out that XFX bought HiS which i did not know. so i expect that this is the design HiS teased a while ago with XFX colors on it. this was the one they teased a while ago that seems to also have been relased http://www.hisdigital.com/gb/product2-940.shtml -
FormatC XFX bought nobody. XFX is a brand from the mother company Pine and Pine bought HIS as brand, not as single company. So are both vendors at the end only a brand from Pine and must share a lot of ressources and production lines. I saw, that they are using similar PCB layouts, only the cooling and design is a little bit different.Reply
XFX seems a real poor company. I got the card a few days for the review but I had to send it back on my own costs (because they had no more samples to rotate and no money for carriers). So it is impossible to answer on questions that requires a re-test or second look at the product. -
RomeoReject Reply
Surprised XFX has fallen so far.19491648 said:XFX bought nobody. XFX is a brand from the mother company Pine and Pine bought HIS as brand, not as single company. So are both vendors at the end only a brand from Pine and must share a lot of ressources and production lines. I saw, that they are using similar PCB layouts, only the cooling and design is a little bit different.
XFX seems a real poor company. I got the card a few days for the review but I had to send it back on my own costs (because they had no more samples to rotate and no money for carriers). So it is impossible to answer on questions that requires a re-test or second look at the product.
I know with both of my XFX R9 280X cards I had from them, they're both in great condition, and currently overclocked a wee bit (It's cold where I live). XFX also says that they'll maintain warranty despite overclocks (Below a certain power threshold) which is why I picked them in the first place.
Sad that they seem to be more dirt-baggish these days.