Processor and Chipset Tables: How to Configure a CPU Correctly
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Introduction
For all of you do-it-yourself experts and tuning fans who want to build or upgrade your own PC system we introduce these tables as quick reference. They provide an overview of all relevant processor and chipset features. The most important things to watch out for when installing a new processor or exchanging the CPU are the core voltage and the multipliers. Apart from this, you'll find important information about the size of the L2 cache, its ratio to the actual processor clock speed and additional items such as the system bus, architecture and micron manufacturing process here. An extensive chipset overview follows the processor overview. This tells you which CPU is supported by which chipset and gives you the most essential details. Every abbreviation is explained for each table and some are explained using figures.
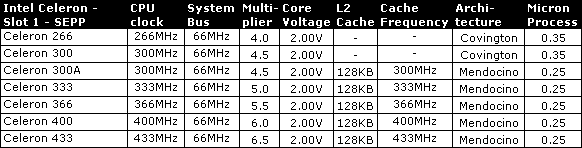
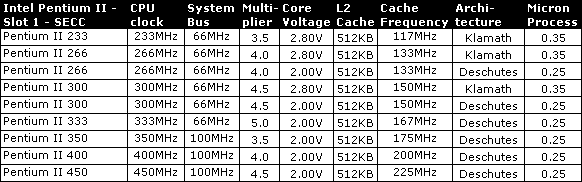
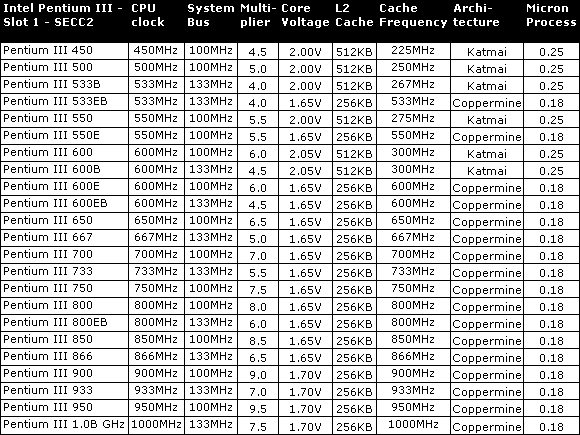
Slot 1 - SEPP/SECC/SECC2 - Celeron, Pentium II, Pentium III
| CPU Tags | |
|---|---|
| A | Regarding Celeron 300A: Mendocino core instead of the older Convington core |
| B | Those Pentium-III processors operate at 133 MHz Front Side Bus |
| E | stands for 0.18 micron process and full speed cache |
| MMX | Instruction set extension for Celeron, Pentium II and III which can be used for multimedia applications, but rarely applied. |
| SSE | Streaming SIMD Extension |
| Package | |
| SEPP | Single Edge Processor Package |
| SECC | Single Edge Contact Cartridge |
| SECC2 | Single Edge Contact Cartridge 2 |
| Connectors | |
| Slot 1 (SC242) | Connector for Pentium II/IIIs as well as old Celeron processors with 242 pins |
| Note | Slot 1 and Slot A (Athlon) are mechanically identical (SC242). However, signals and protocols are different. |
| Architecture/Cache | |
| Mendocino/Coppermine | L2 cache is incorporated on die und runs at full speed. On all other Slot-1 CPUs the L2 cache runs at half speed. |
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.