Tom's Hardware Verdict
The Prusa MK3S+ continues to hold its own in a market saturated with low-cost competitors.
Pros
- +
+ PrusaSlicer provides best-in-class model slicing
- +
+ Flexible build platform sets the standard
- +
+ Automatic bed leveling
- +
+ Stealth Mode enables a nearly silent printing experience
Cons
- -
Assembled printer is pricey
- -
Monochrome interface feels outdated
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
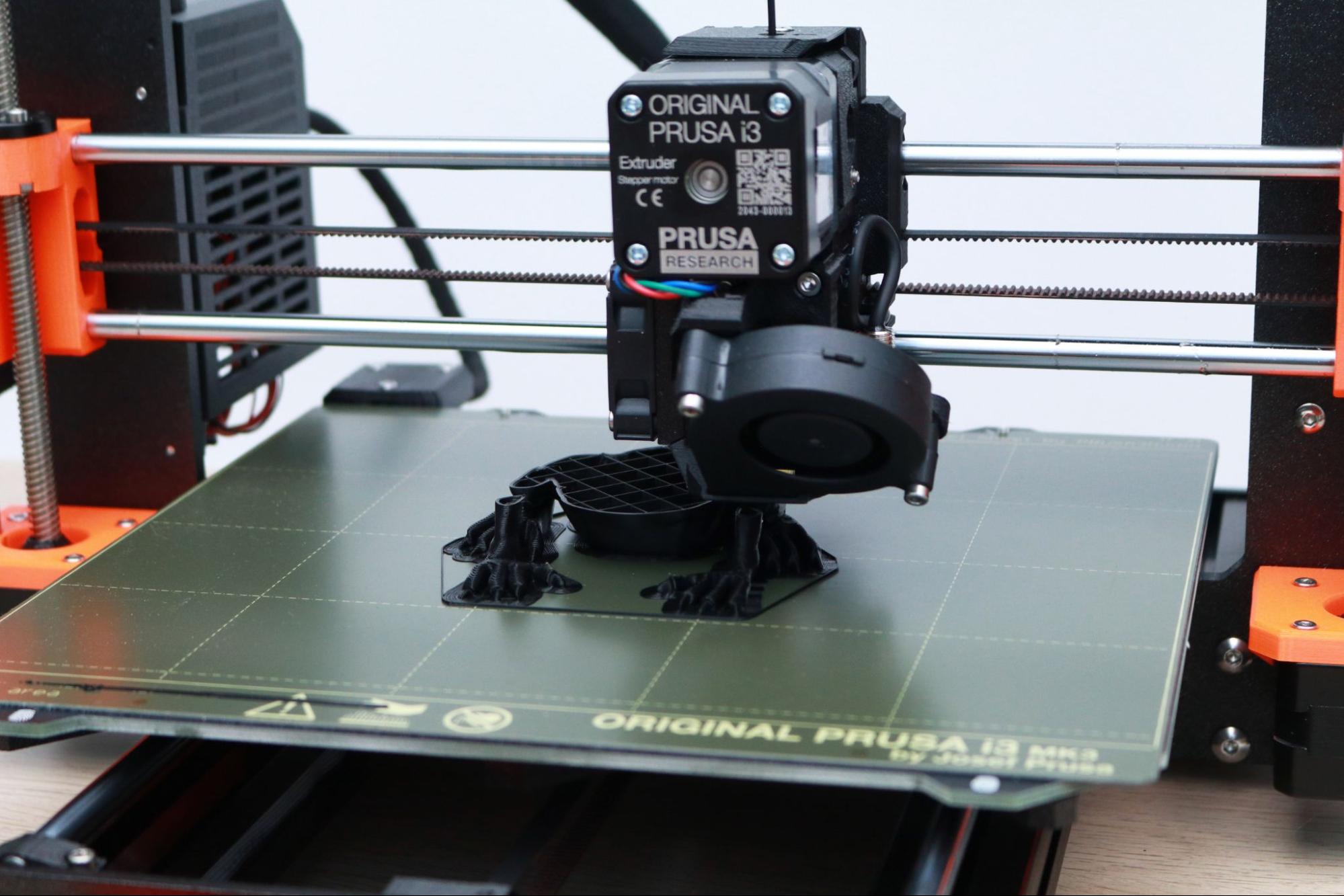
There are few 3D printers with as many industry accolades as the Prusa i3 MK3S+, and after spending some time with this printer, it’s easy to see why it’s one of the best 3D printers currently on the market. With a price tag of $999 for an assembled machine or $750 for a DIY kit, the price point of the MK3S+ is towards the high end for an open format consumer 3D printer, but the features of this machine and the ecosystem created by Prusa (they make their own hardware, software, filament, and more) have made the MK3S+ a formidable machine for anyone interested in taking their 3D printing game to the next level.
The features of the MK3S+ (silent stepper drivers, power-panic, etc.), noteworthy when originally launched, have largely become standard on lower-cost machines and may not seem particularly impressive on a spec sheet. However, clever software implementation and well-written documentation have created a machine that provides a best-in-class printing experience. For instance, the auto-leveling SuperPINDA probe of the MK3S+ maps the build platform for surface distortions, but the printer firmware is capable of storing multiple Z-offsets so you can switch build platforms without having to recalibrate every time.
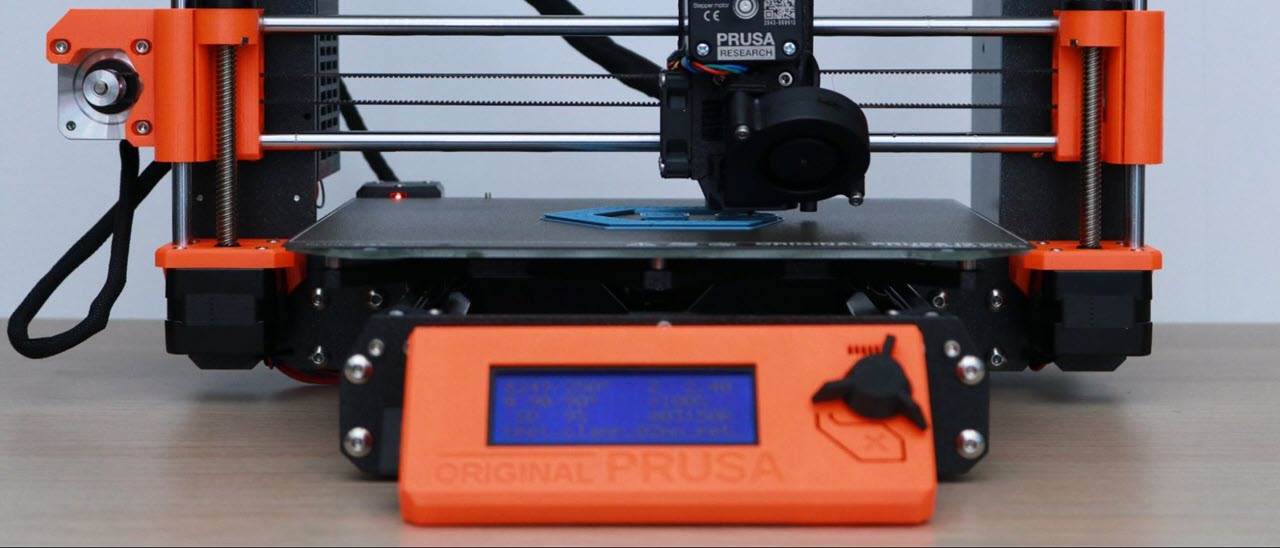
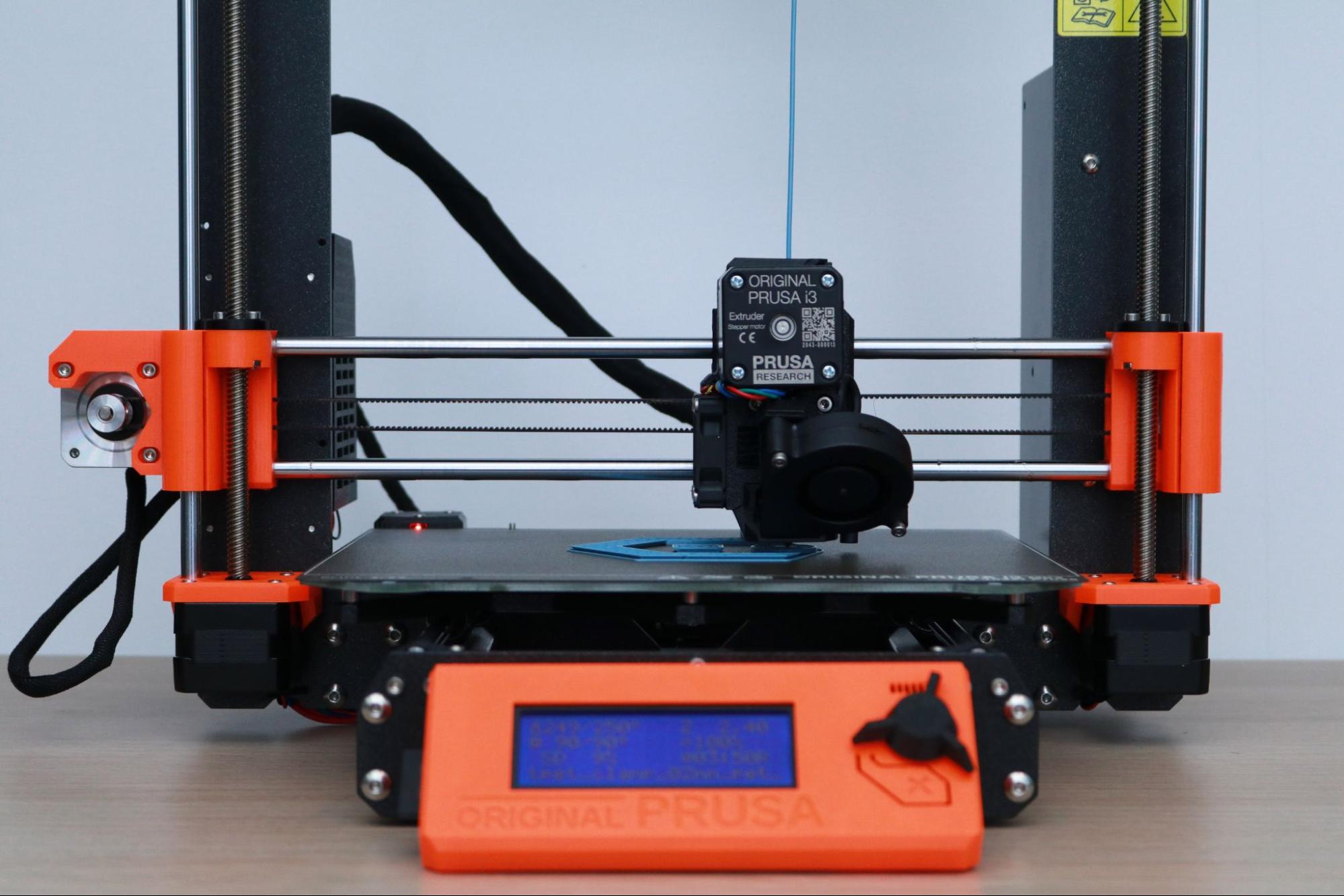
The MK3S+ is a visually distinct machine; and the Prusa team has kept their black and orange color scheme for their smaller printer, the Prusa Mini+. The bright orange printed parts on the MK3S+ have created instant brand-recognition for the Prusa line of printers, and Prusa has doubled down on this by reinforcing their branding across their machine. In fact, you can find the word ‘Prusa’ printed, engraved, or etched into the MK3S+ in 25 places, 29 if you’re using a spool of their Prusa Polymers Prusament PLA material.
Specifications
| Machine Footprint | 16.5 x 16.5 x 15 inches (42.0cm x 42.0cm x 38.0cm) |
| Build Volume | 9.84 x 8.3 x 8.3 inches (250mm x 210mm x 210mm) |
| Material | 1.75mm PLA, ABS, ASA, PETG |
| Extruder Type | Direct Drive |
| Nozzle | .4mm |
| Build Platform | Magnetic Heatbed with removable PEI spring steel sheets |
| Power Supply | 240 Watts |
| Connectivity | USB, SD Card |
| Interface | 3.4-inch Mono LCD and click wheel |
| Filament Run-Out Sensor | Yes |
Included with Prusa MK3S+
The fully assembled Prusa MK3S+ ships with all of the accessories required to make your first print, and also includes enough spare parts to replace almost every fastener on the machine. The fully assembled MK3S+ also includes a bag of Haribo Goldbears, a signature addition from the Prusa team.
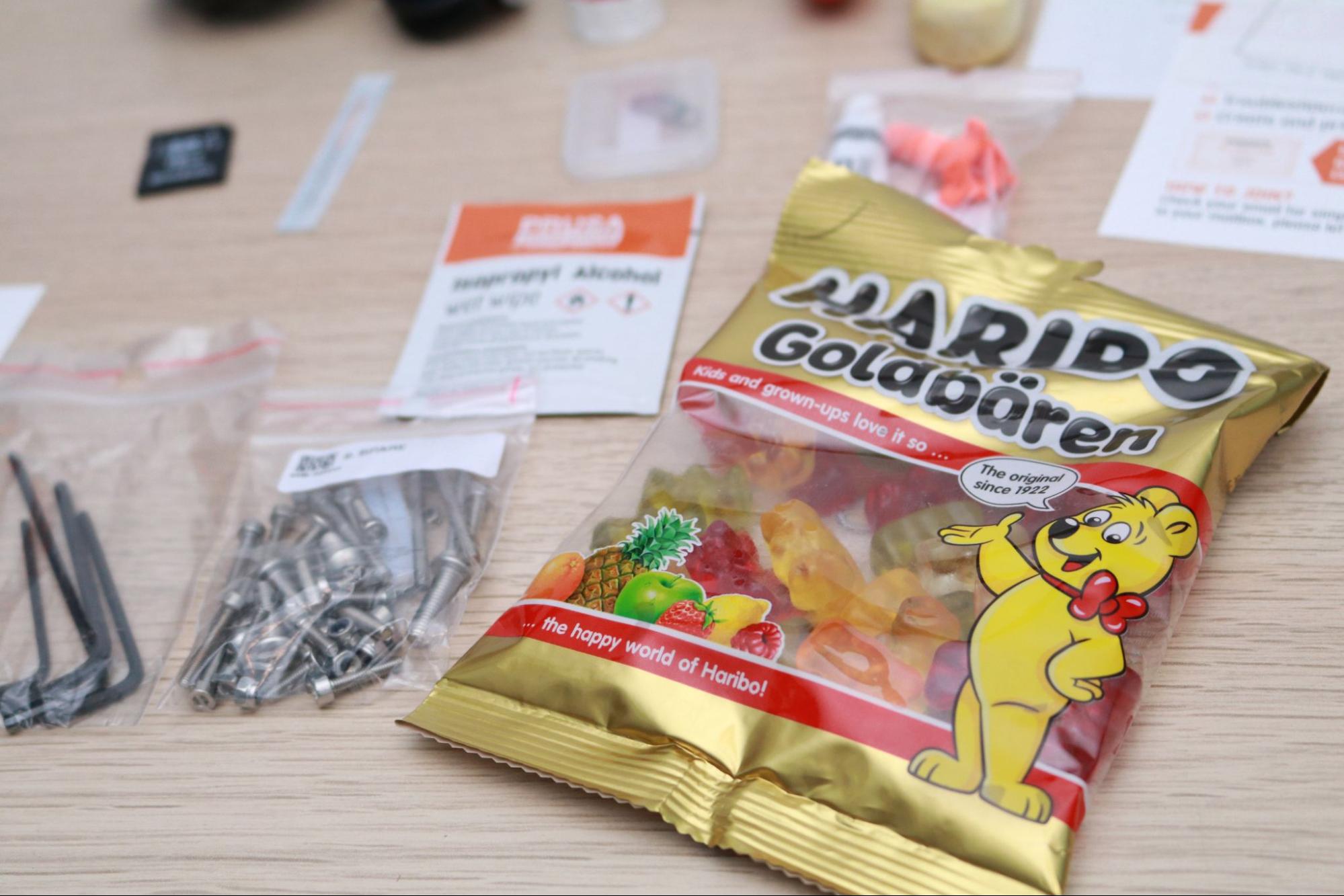


The Prusa MK3S+ includes a full spool of silver PLA material, screwdriver, a metal part scraper, a glue stick (for adhesion), an isopropyl alcohol wipe, lubricant for the linear rails, power and USB cables, a sheet of stickers, a printed handbook, and a diagnostic printout that confirms the functionality of the mechanical and electrical systems.

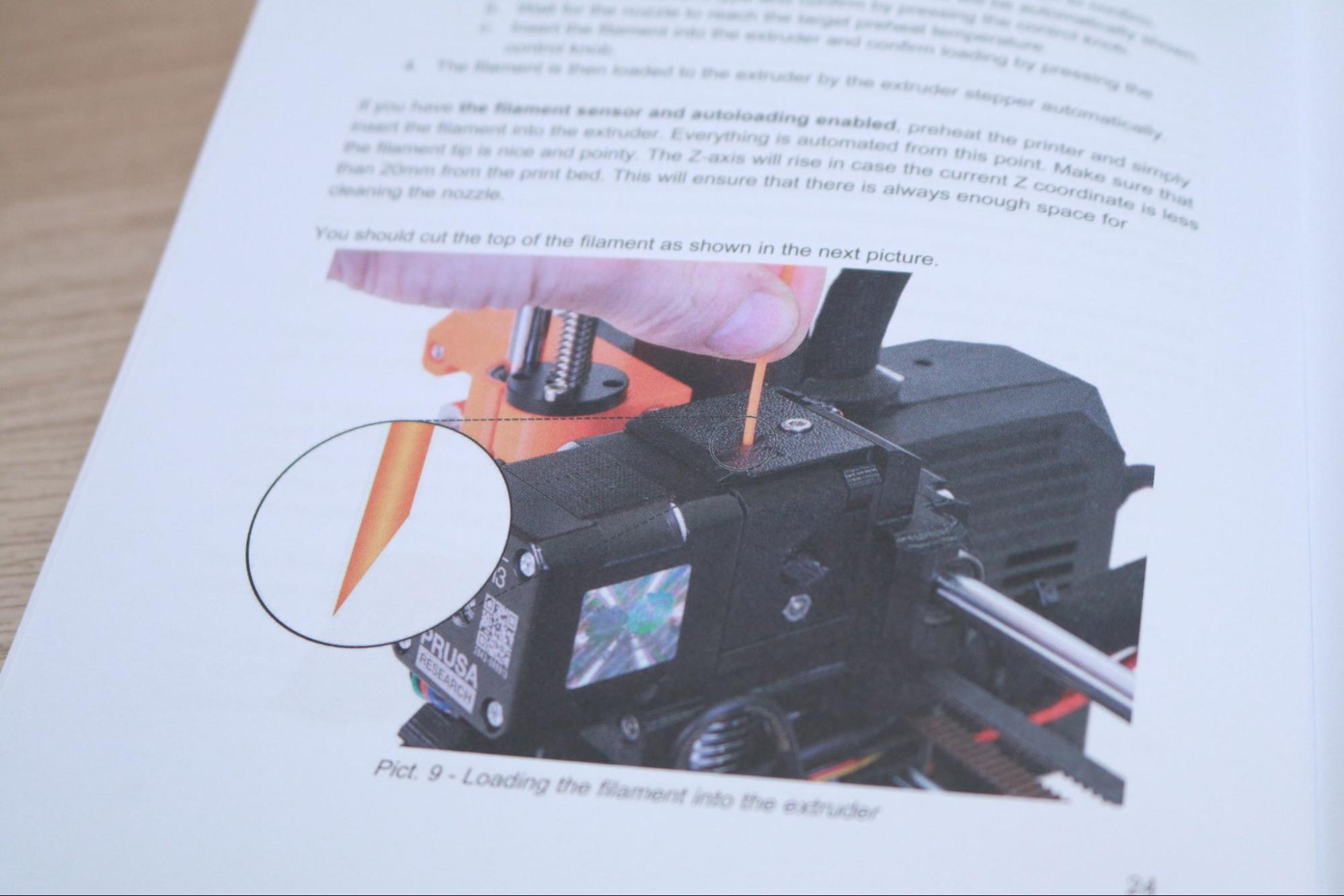
The usefulness of the handbook is hard to overstate. When you’re starting out with your first 3D printer, it can be difficult to pinpoint the cause of problems such as loss-of-extrusion, poor layer adhesion, or a clogged extruder. The included handbook is full of detailed photographs, troubleshooting workflows, and solutions to common problems. This is an invaluable resource for beginners, amateurs, and experts alike, and it’s clear to me that Prusa has set the standard for technical documentation.
Setting up the Prusa MK3S+
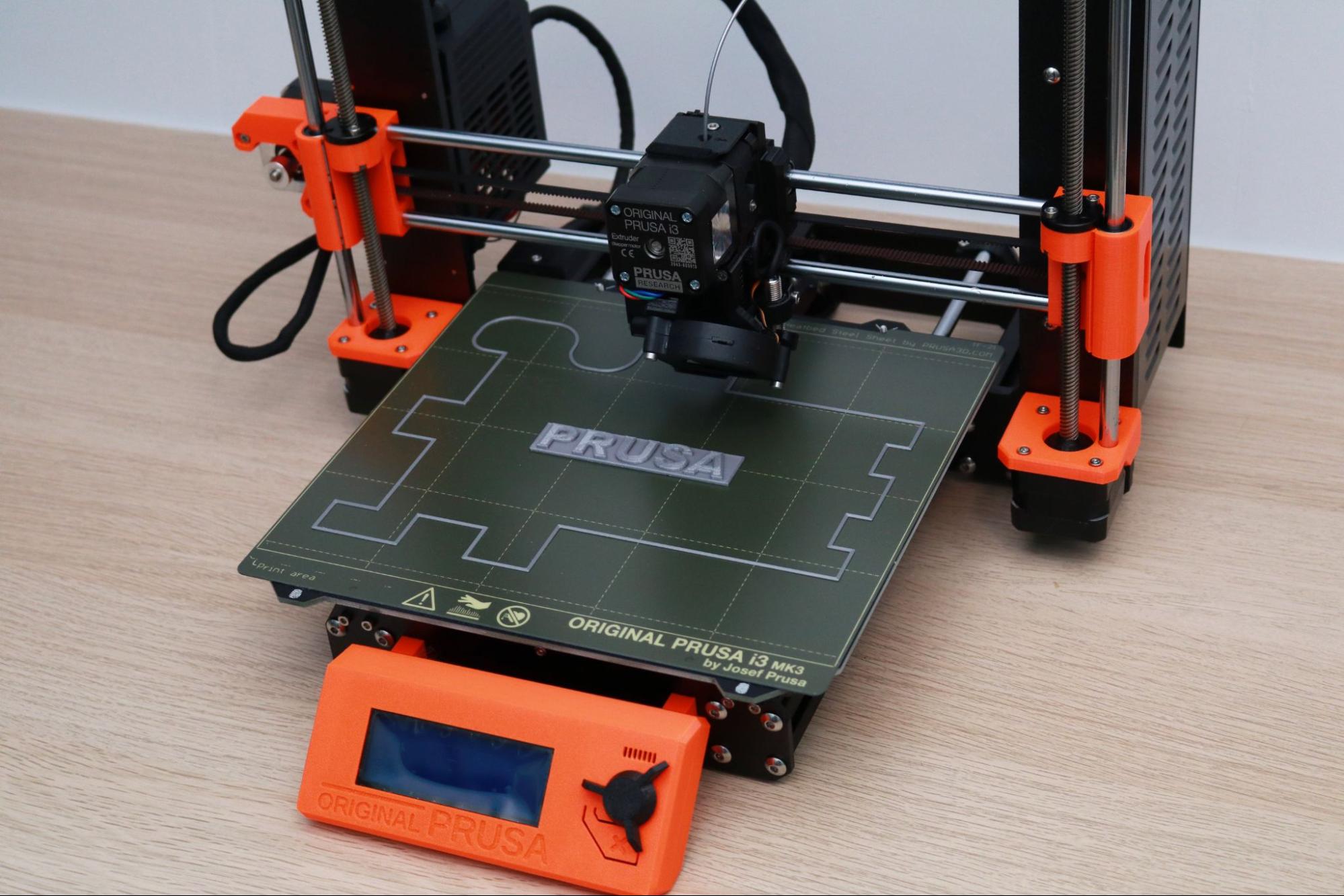
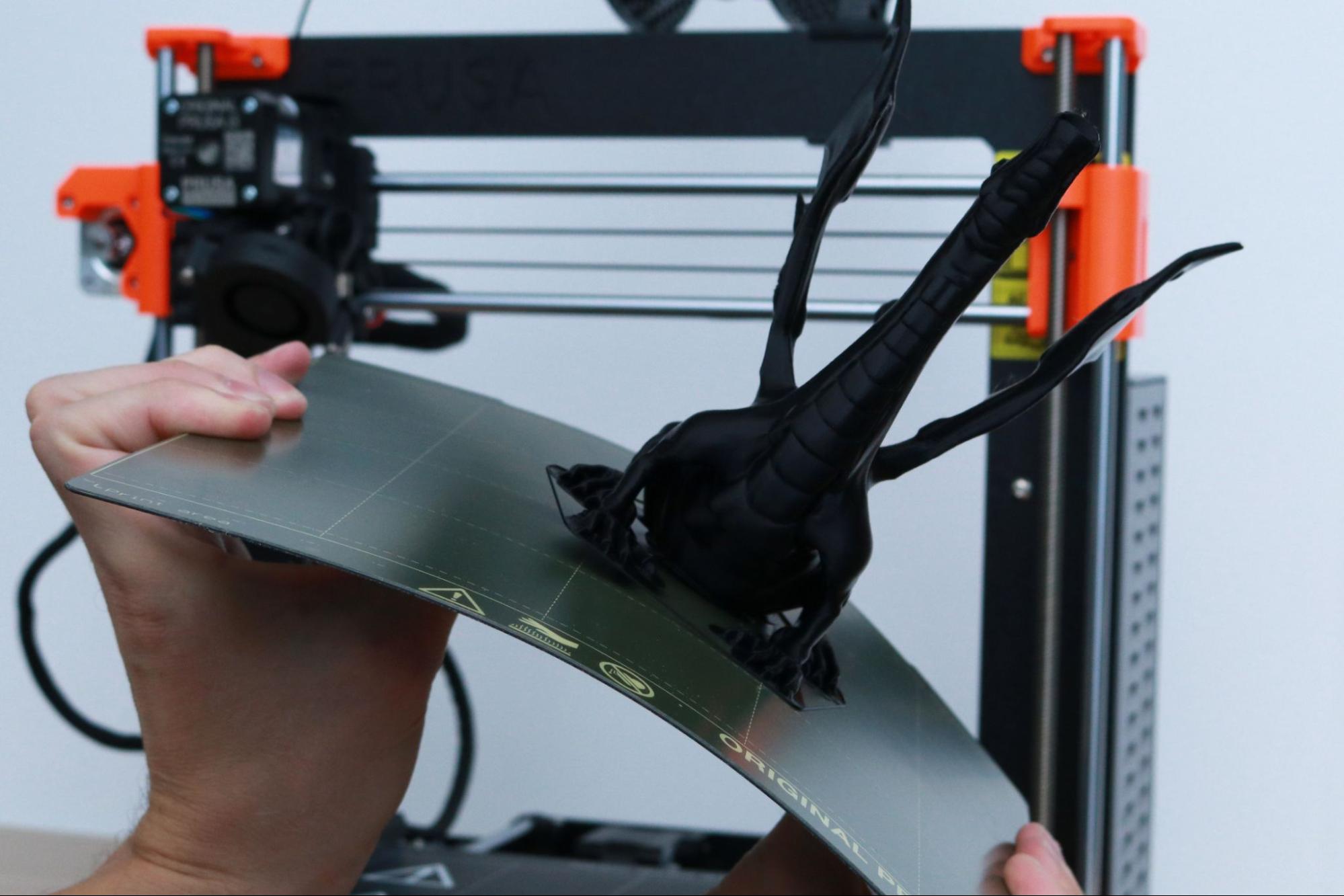
The Prusa MK3S+ ships with a completed print attached to the build platform. This print features a serpentine line with 90 degree angles, curves, and a solid block in the center with the Prusa logo facing upwards. This print serves to confirm that the printer is functional and has been properly assembled and calibrated. I was able to easily remove the print from the build platform by bending the steel sheet and carefully removing it.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
After powering on, the printer automatically runs through an initial setup process. This process involves calibrating the Z axis by running it all the way to the top of the printer, running the mesh bed leveling process to set the Z offsets, and loading the filament. This entire process only took me a few minutes, and the high level of automation involved means that the only thing I needed to do was insert the filament into the extruder after it had heated up.
Design of Prusa MK3S+
You might be surprised to find that the Prusa MK3S+ is based on the RepRap i3 (third iteration) frame, originally released in September of 2012. Despite this nearly decade-old release date, the MK3S+ is full of modern advancements and enough innovative features to still be a top contender in the prosumer 3D printer market.
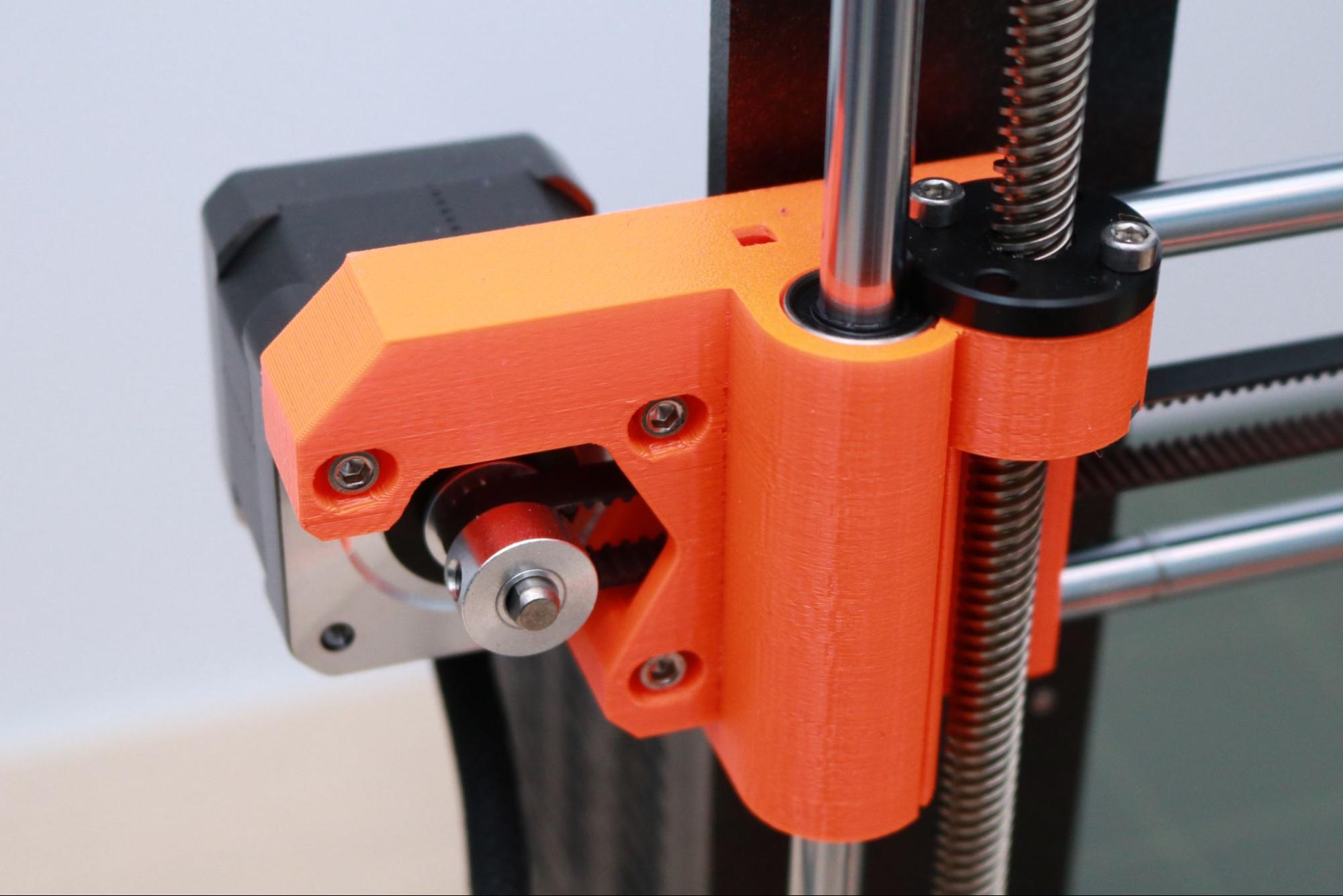
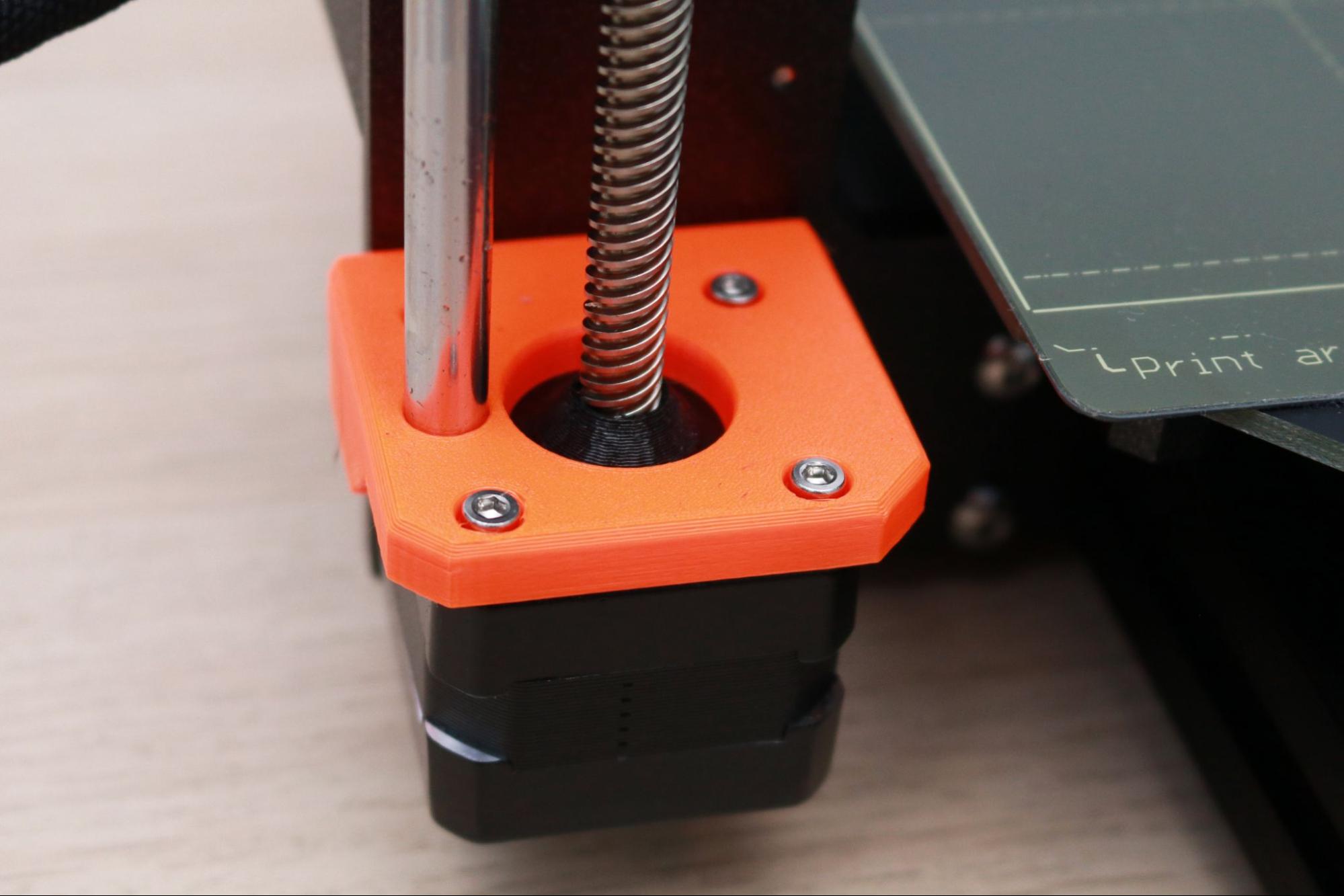


The bright orange color makes the 3D printed parts on the MK3S+ easy to spot. The brackets mounted to the printer are printed in-house by Prusa using their own Prusament PETG filament. These brackets are robust and sturdy, and the uniform appearance between the printed parts give the printer a professional appearance. This version of the MK3S+ shipped with orange printed brackets, but the printer is also available in an all-black variant. A large selling point of the MK3S+ is the open-source nature of the machine, which means the printed parts are all available to download if you want to download, modify, or print them out yourself.
The monochrome LCD interface and click-wheel on the MK3S+ is one of the few less-than-impressive features on this machine; it feels dated and the UI navigation can be a little clunky. This stands in contrast with printers like the Anycubic Vyper, a sub-$400 machine that features a bright and responsive color touchscreen that shows detailed print statistics during printing. This monochrome display was industry standard when the original 8-bit i3-style of printers was introduced, but it feels outdated when compared to recent printers with color touchscreens.
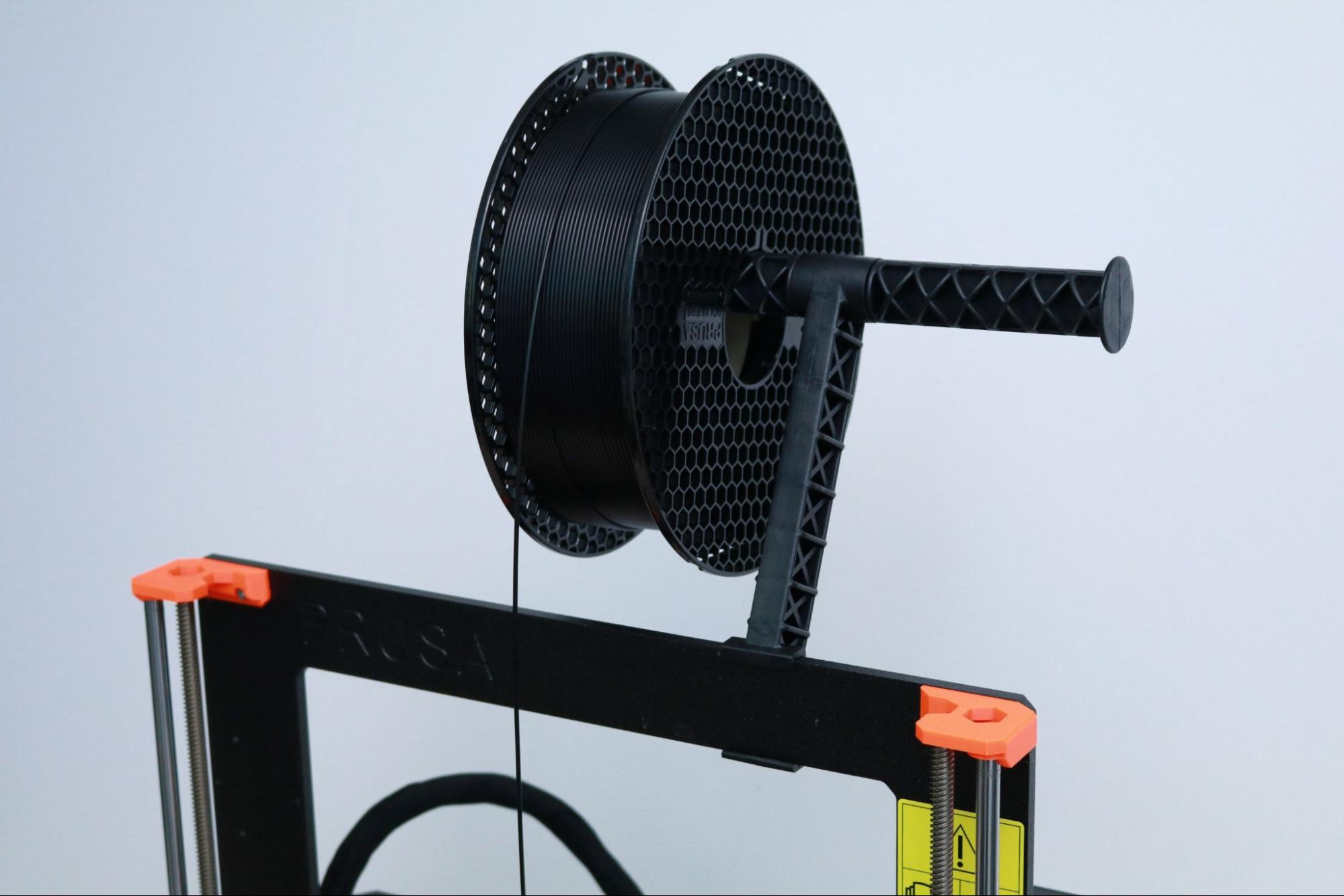
The MK3S+ uses a filament spool holder that mounts directly to the frame of the printer. The T-shaped holder is able to hold two spools simultaneously, which is ideal if you plan on swapping between multiple colors to produce a multicolor 3D print. The direct-drive extruder on the MK3S+ feeds filament straight down into the hot end, so mounting the filament directly above the extruder gives the filament a straight path between the spool and the extruder.
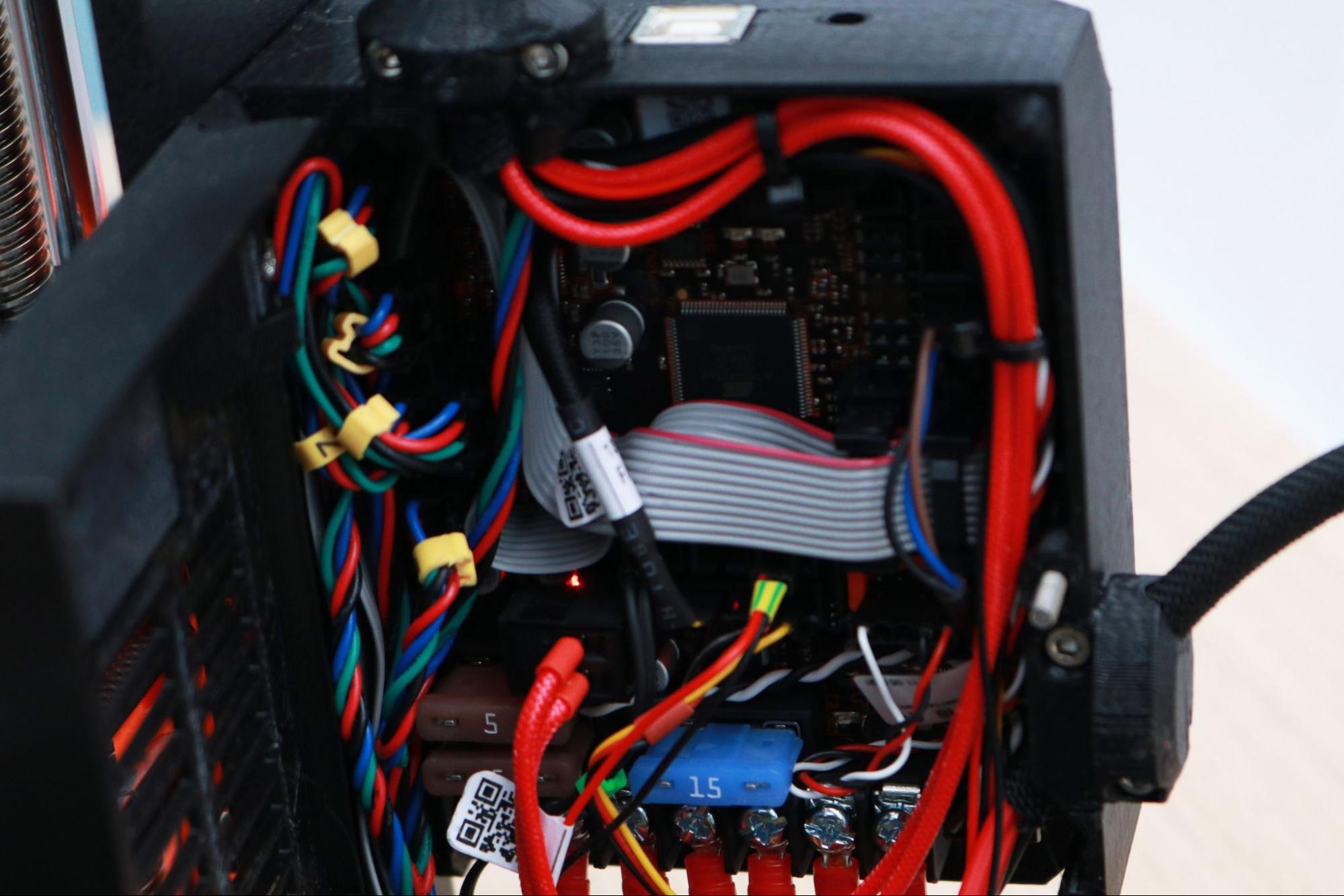
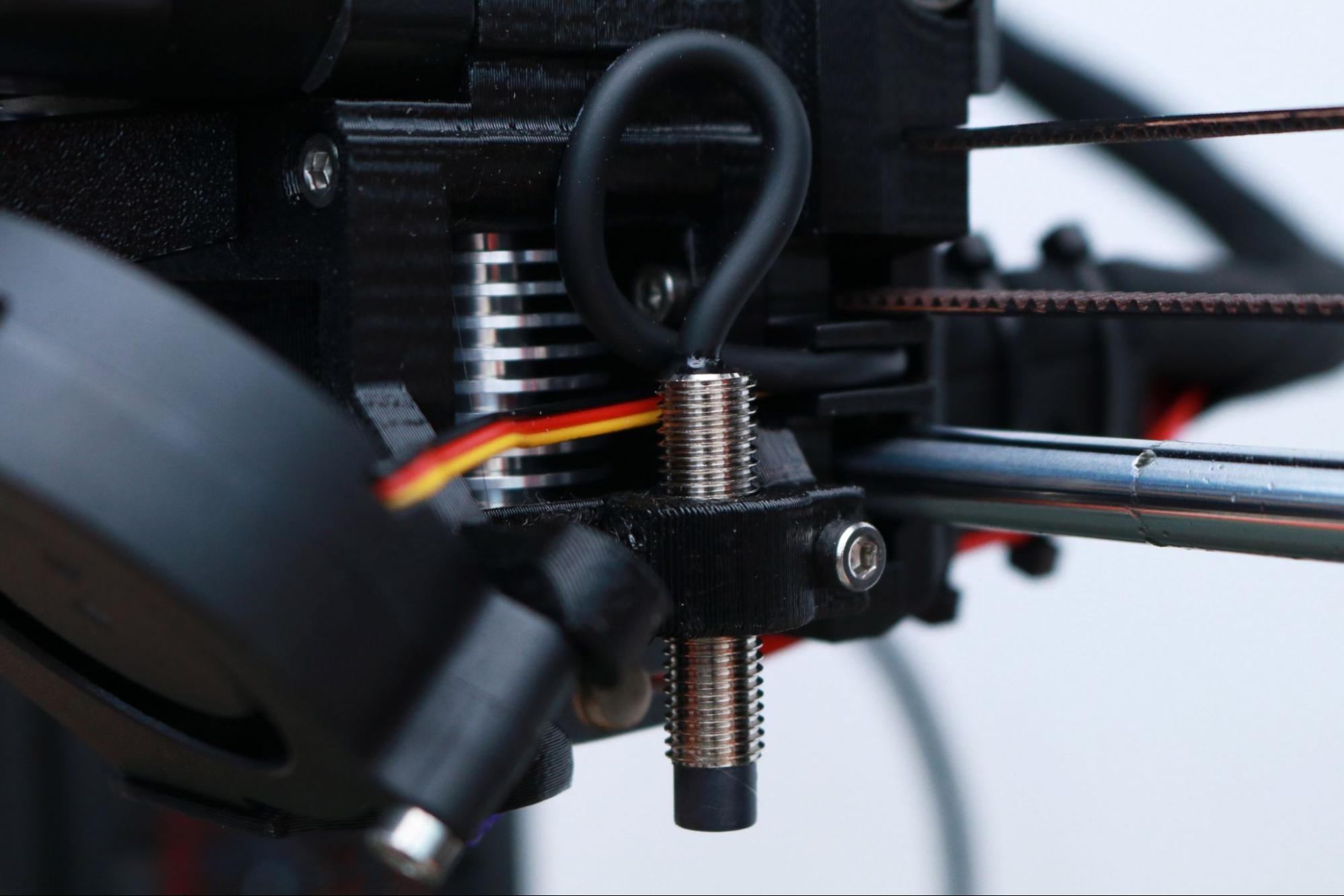
At the heart of the MK3S+ is the 8-bit Einsy RAMBo board, housed in a 3D printed enclosure mounted to the frame of the machine. This board is equipped with Trinamic 2130 silent stepper drivers, user-replaceable fuses, and the cable management is clean and professional.
The features made possible by this board (power-panic, live-Z adjust, silent steppers) were all major leaps when originally introduced, but many of these features have made their way down to less expensive FDM 3D printers like the Elegoo Neptune 2. The interface feels sorely in need of an update, and the addition of a color touchscreen and a 32-bit board (such as the one equipped on the Prusa Mini+) would refresh this platform.
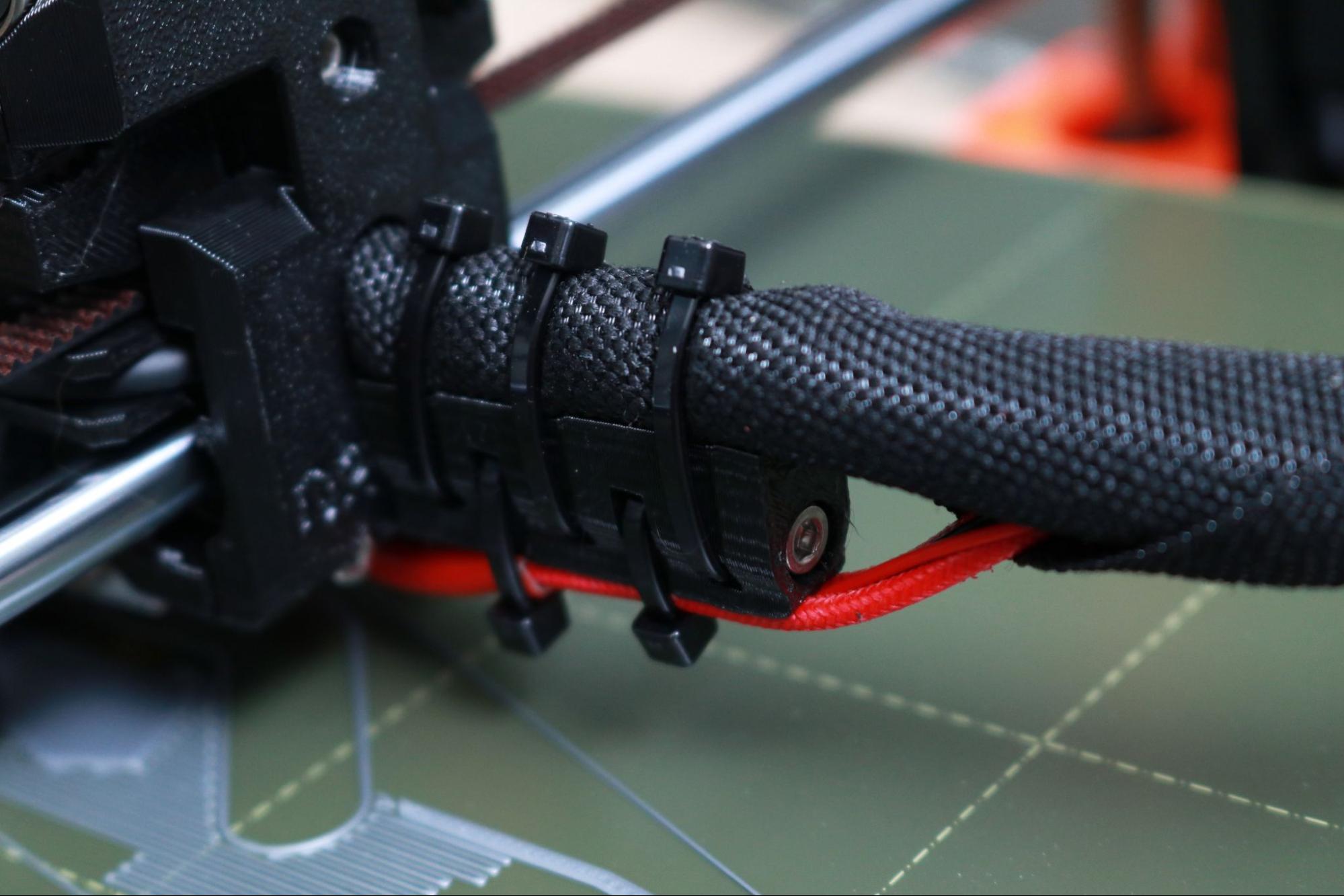
The attention to detail on the Prusa MK3S+ is clear, and a perfect example of this is the wire management across the machine. Current-carrying wires are attached to the extruder module with zip ties that act as a strain-relief to prevent the wires from fatiguing and separating. The wires from the power supply are tucked neatly under the frame of the machine, out of sight and reach from users to prevent accidentally unplugging them during printing.
What Makes the Prusa MK3S+ Different?
It can be hard to understand why the Prusa MK3S+ costs so much more than a printer like the Creality Ender 3 Pro, which seems to have similar specs on paper. To understand why this machine is so much more expensive, we need to take a closer look at the individual components of the MK3S+.
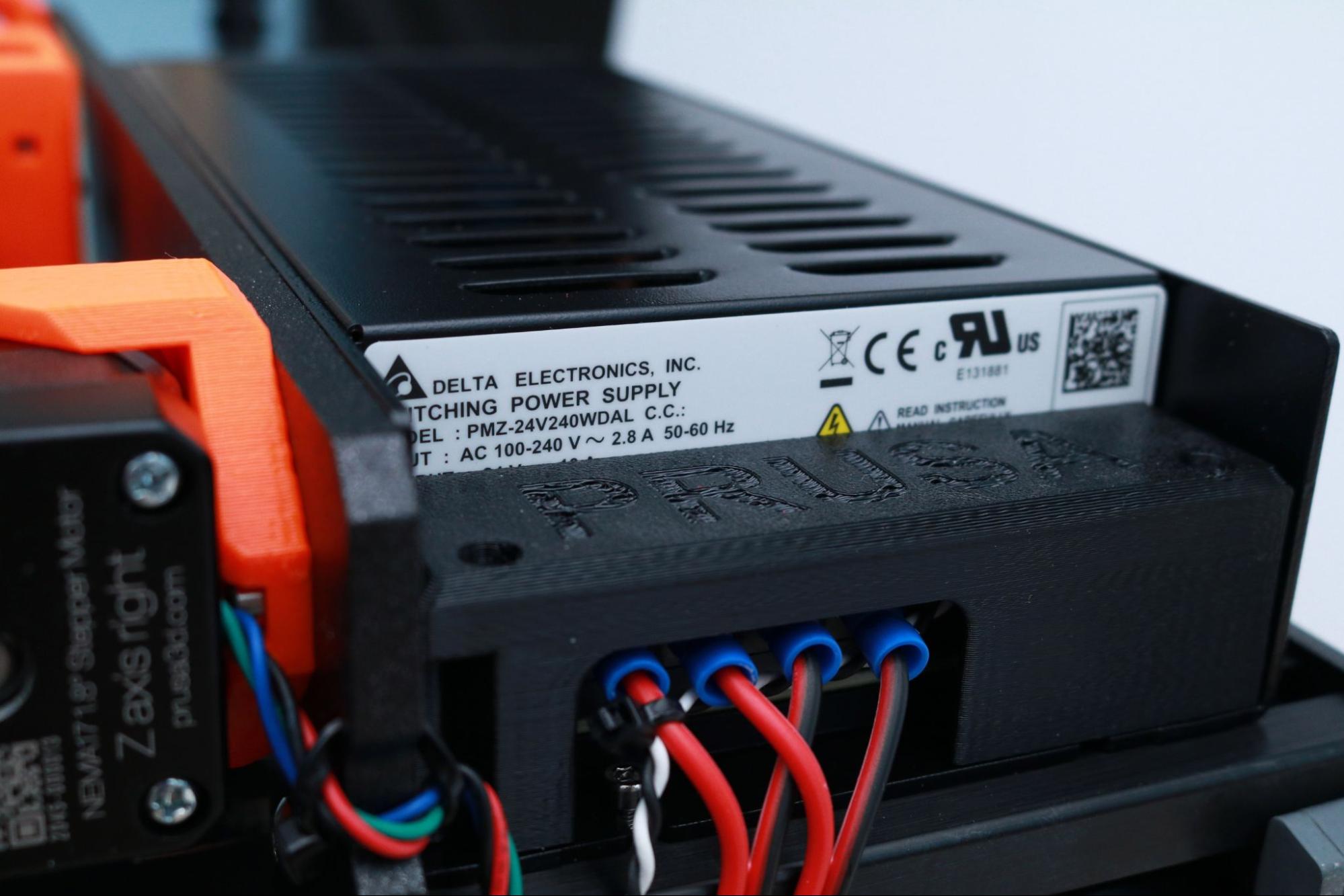
Critical to the success of the MK3S+ is its custom-made Delta 240 Watt power supply, mounted to the frame of the machine. This unit supplies 24V power to the bed with a max current of 10 Amps, which provides fast and reliable heating for printing high temperature materials like PETG and ASA. Less expensive machines typically use lower wattage power supplies, such as the 150W power supply used by the Flashforge Adventurer 3 Lite, which take longer to heat and can have difficulty maintaining a higher temperature.
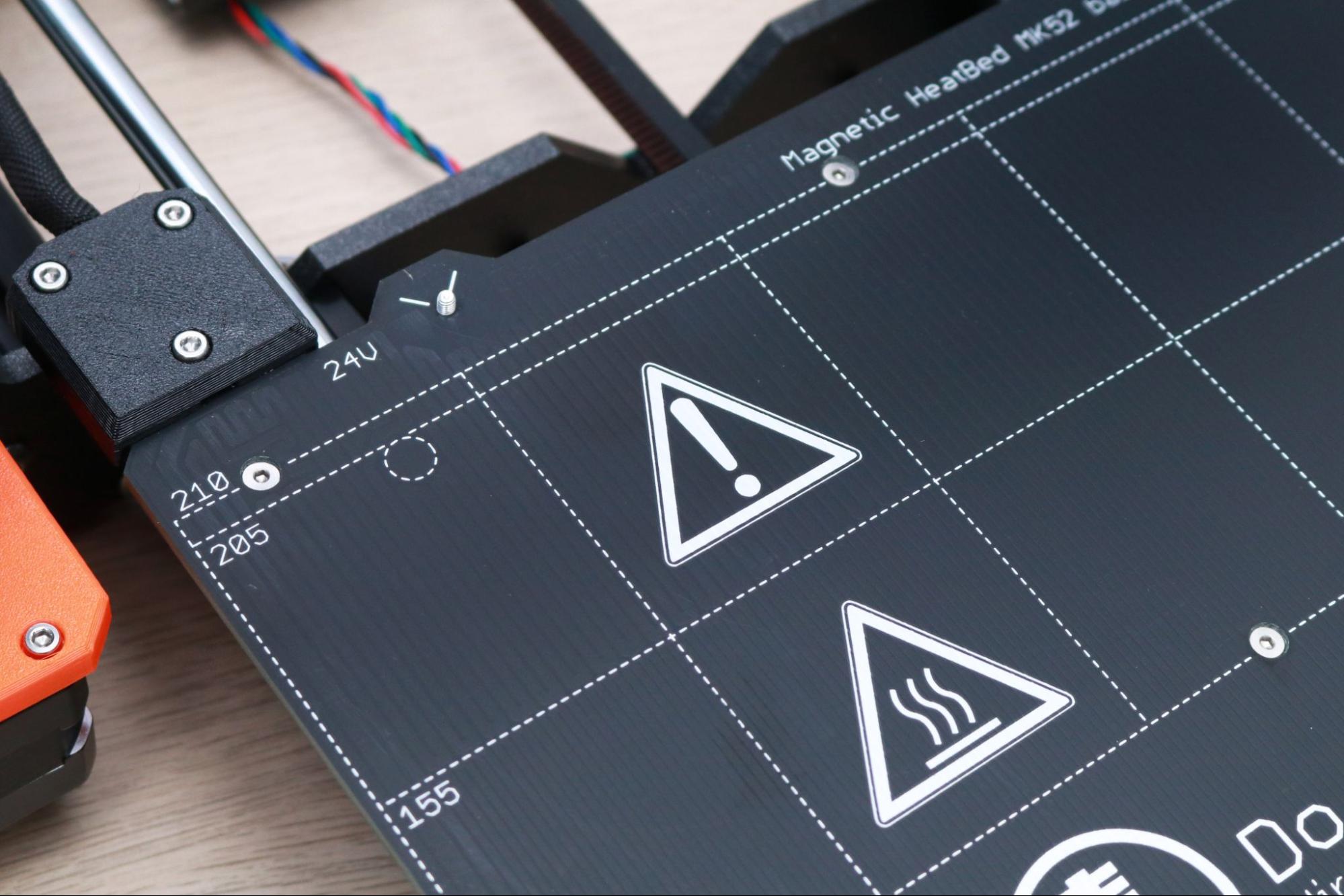
The 24V heated bed is able to reliably hit 100C, which is more than enough to allow high temperature materials like PETG and ASA to adhere to the build platform without delaminating. The magnetic build platform is firmly held in place without any clips or latches and can easily be removed once it cools to room temperature. PETG in particular is easy to remove from the textured surface of the textured spring steel sheet, and the MK3S+ build platform is best-in-class for high-temperature adhesion.
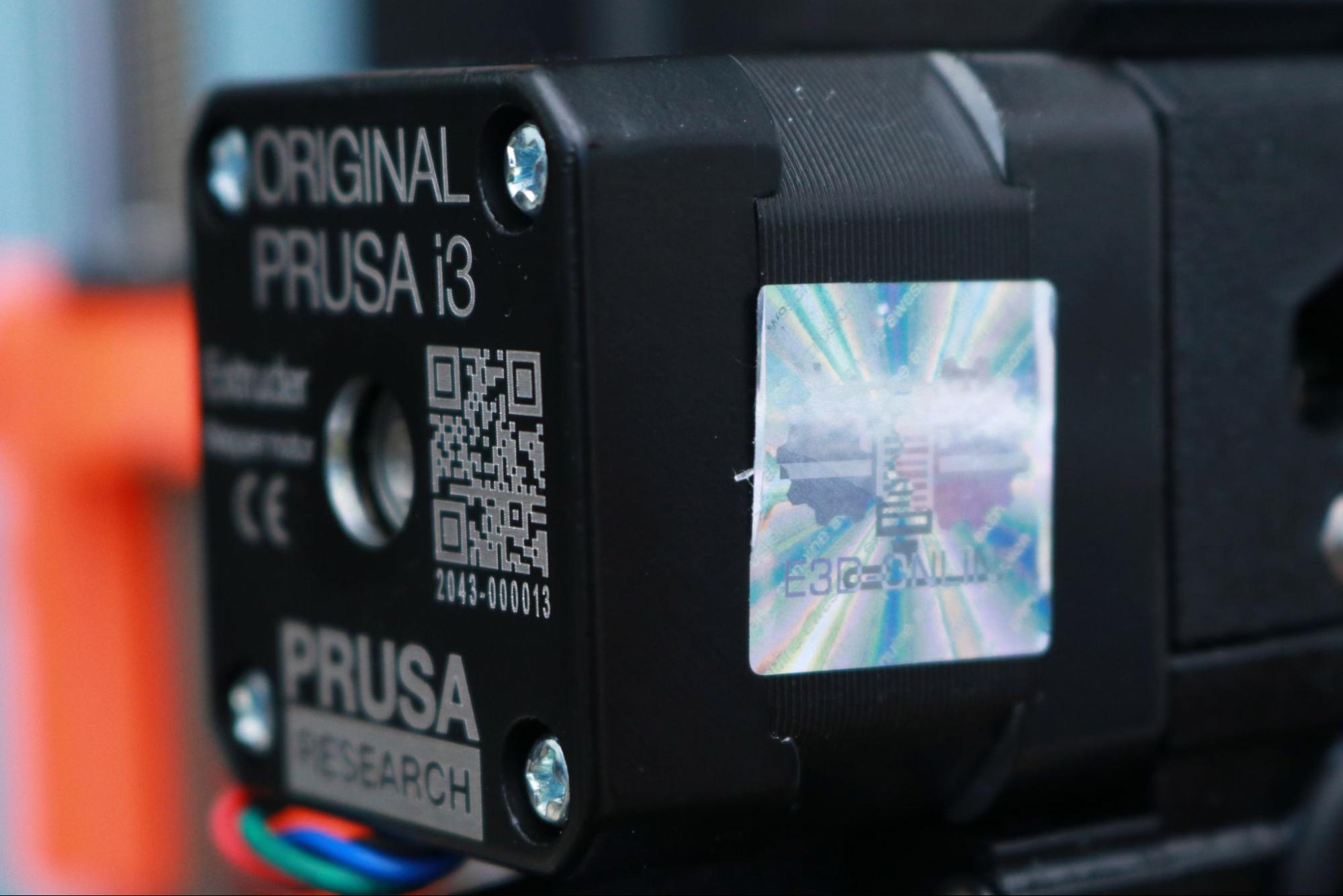
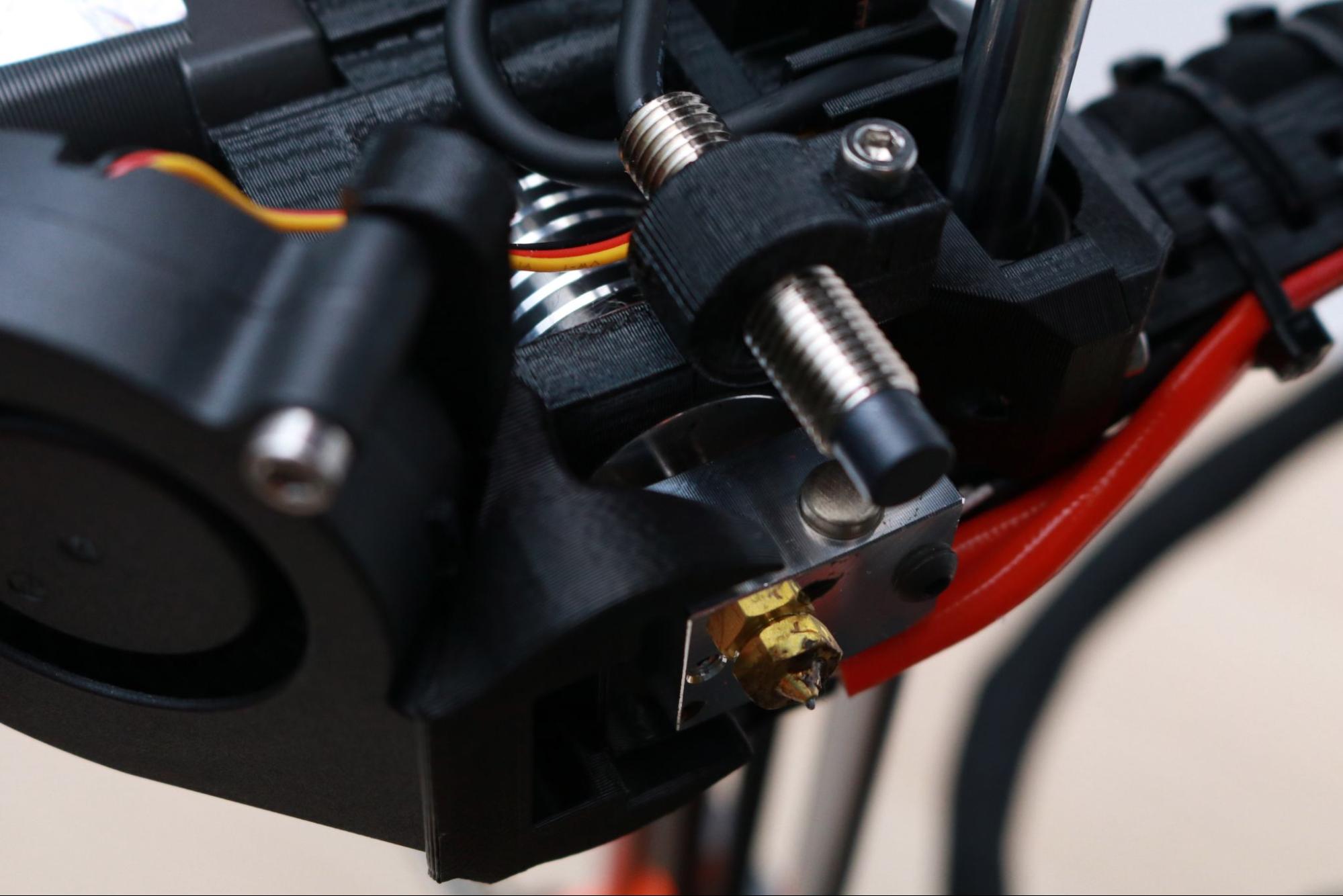

The MK3S+ is equipped with a genuine E3D hot end, and it has the holographic sticker to prove it (seriously). E3D manufactures every component in the hot end from the nozzle to the heatbreak which means you are very unlikely to run into the type of manufacturing defects that occasionally pop up on less expensive printers (incorrectly drilled nozzles, degraded PTFE tube liner, etc.) In addition, this nozzle is rated for a max temperature of 300C (572F), which is easily hot enough to extrude most common thermoplastics and even some higher-temperature engineering-grade materials like Nylon and Polycarbonate.
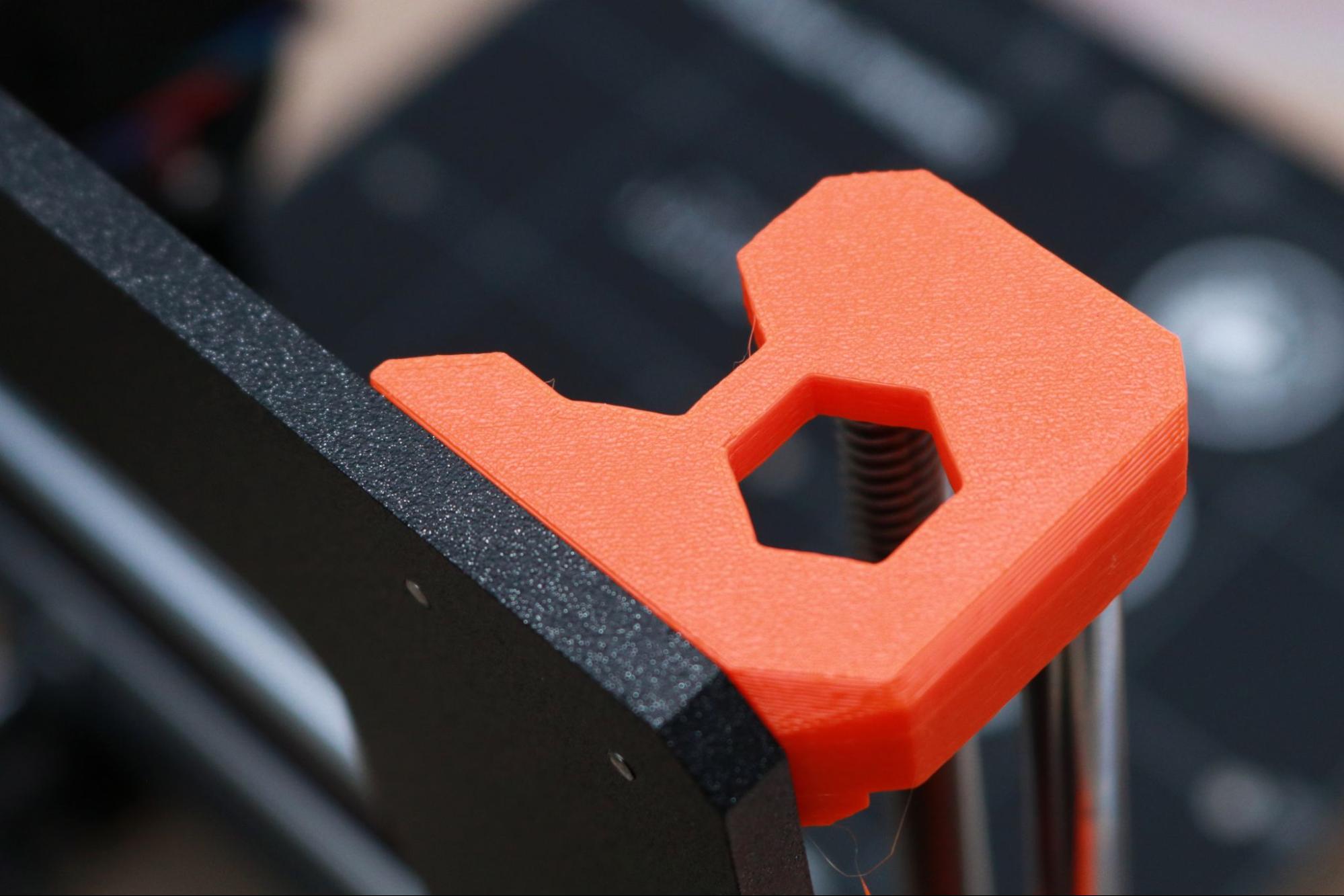
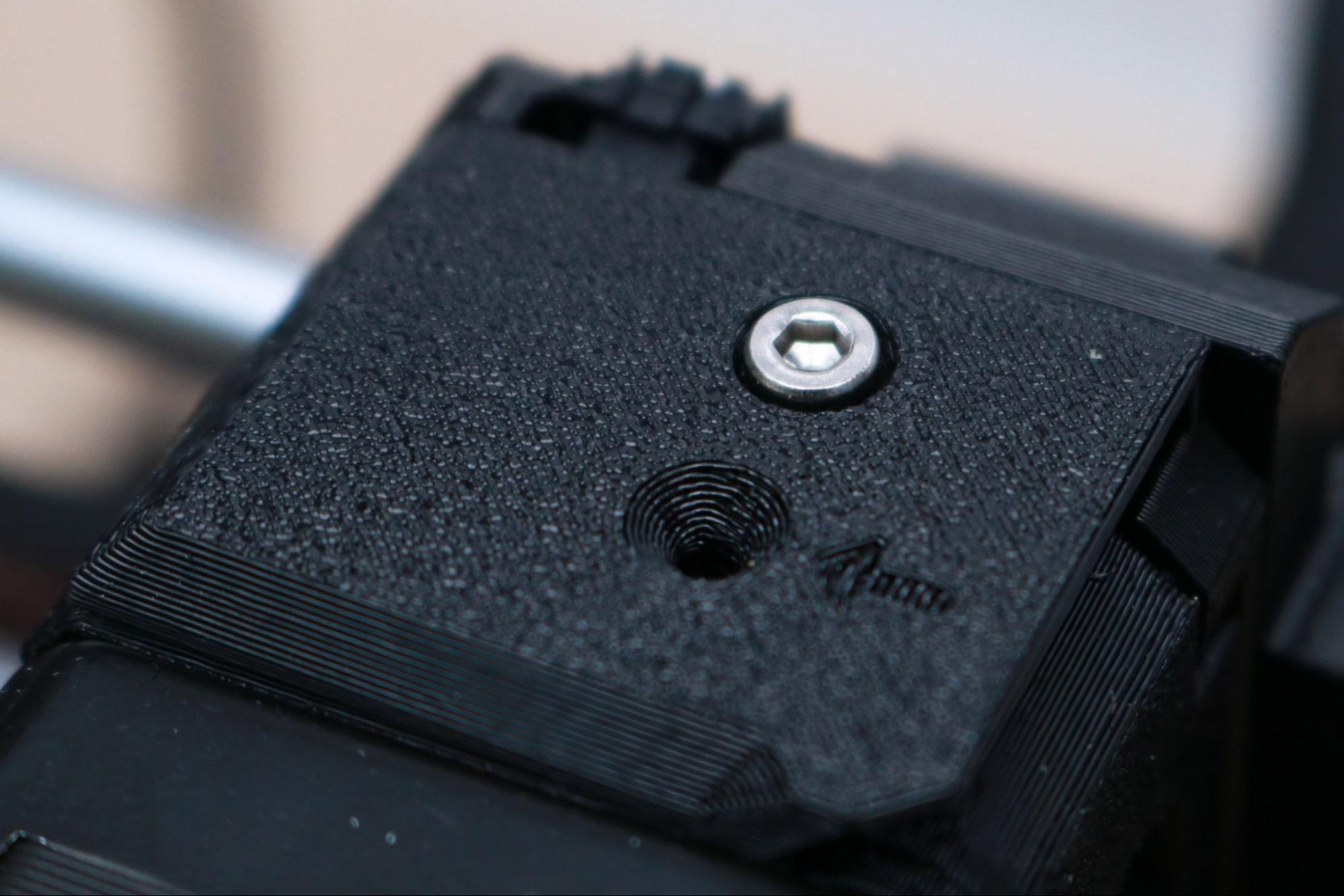


The printed parts on the MK3S+ are a perfect example of a company applying its in-depth knowledge of a subject to its product. The printed brackets found on the MK3S+ have been printed in PETG, and the outward-facing textured surface shows the level of quality you can expect from using a textured sheet.
In addition, I appreciate that Prusa has applied DFAM (Design for Additive Manufacturing) principles to these parts. These DFAM principles include concepts like printing hexagons instead of circles for relief holes, which print without requiring support material, and printing brackets perpendicular to their intended load to create mechanically tough parts.
The Prusa MK3S+ comes equipped with a SuperPINDA probe which is used for hands-free leveling of the build platform. The SuperPINDA (which stands for Super Prusa INDuction Autoleveling sensor) operates by detecting the proximity of the probe to the build platform and storing that information in firmware. The MK3S+ isn’t the first printer to use a probe for bed leveling, but the software implementation in PrusaSlicer means that after the printer has been set up, you can print without spending much time thinking about calibration.
Compared to the manual bed leveling process of a printer like the Creality Ender 3 Pro, the MK3S+ is faster, easier to use, and requires less trial and error. PrusaSlicer includes a “G80” command in the start G-code (the instructions the printer reads when making a part), and this command performs a ‘Mesh Bed Leveling’ which probes the bed in a 3x3 grid to create a mesh surface that is used for calibration. This mesh surface causes the Z-axis motors to undulate over uneven areas while the print head remains perpendicular in the X/Y axis. During my testing, I didn’t need to run a single non-print calibration on the printer after the initial mesh bed leveling.
Build Platforms on Prusa MK3S+
Removing a printed part from the build platform of a 3D printer can be a challenging experience if the printer isn’t calibrated correctly. The Prusa MK3S+ attempts to solve this problem by using a removable build platform that is held in place magnetically and can be flexed to remove parts after the platform has cooled. I’ve tried many different types of build surfaces, and the smooth PEI sheet used by Prusa is by far one of the easiest to print on, remove parts from, and clean.
Prusa also offers a textured steel build platform for the MK3S+ that has a gritty surface which can give printed parts a more uniform appearance. In fact, the signature textured look of the printed parts on the MK3S+ come from this build platform.
Parts printed on a smooth build platform will have a smooth bottom surface, which looks visually distinct from the striations on the sides of the part. By using a textured sheet, I was able to make prints that have a textured appearance on the bottom as well as the sides. This sheet is ideal for printing with PETG; the high print temperature of the material requires a textured surface to stick to, but also needs a surface that it can easily detach from.
Printing on the Prusa MK3S+
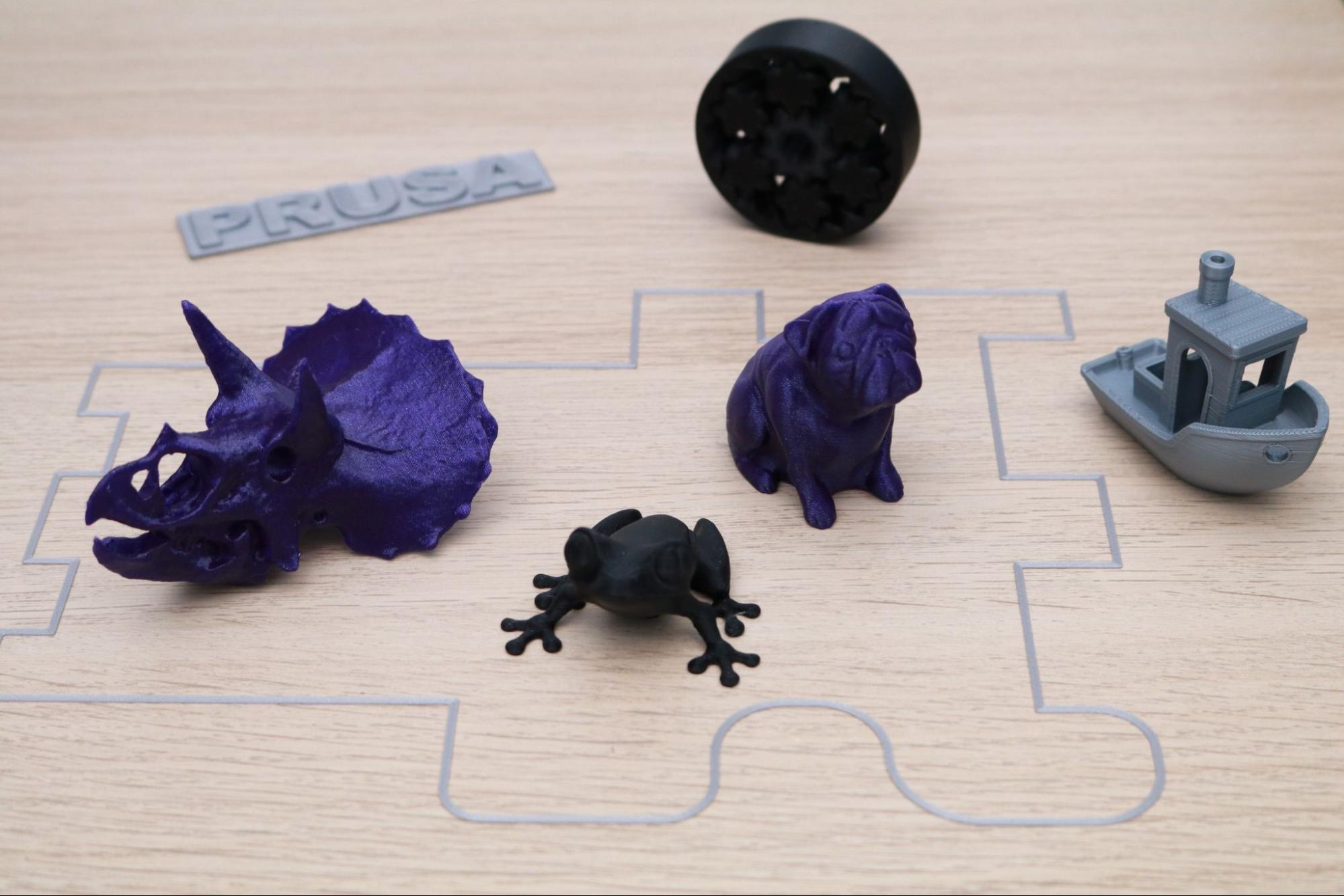
The sample prints on the included SD card with the Prusa MK3S+ are a refreshing change from the sample parts that are typically included with low-cost 3D printers. The MK3S+ includes 16 pre-sliced parts that have been prepared for PLA with the total print time included in the file name. The sample prints vary in time from 23 minutes (a simple block with the word PRUSA on it) to almost 14 hours (a castle printed at .1mm layer height), and have all been prepared using sensible settings for the machine and highlight various features (variable layer height, multicolor printing, and fine .1mm layer resolution).
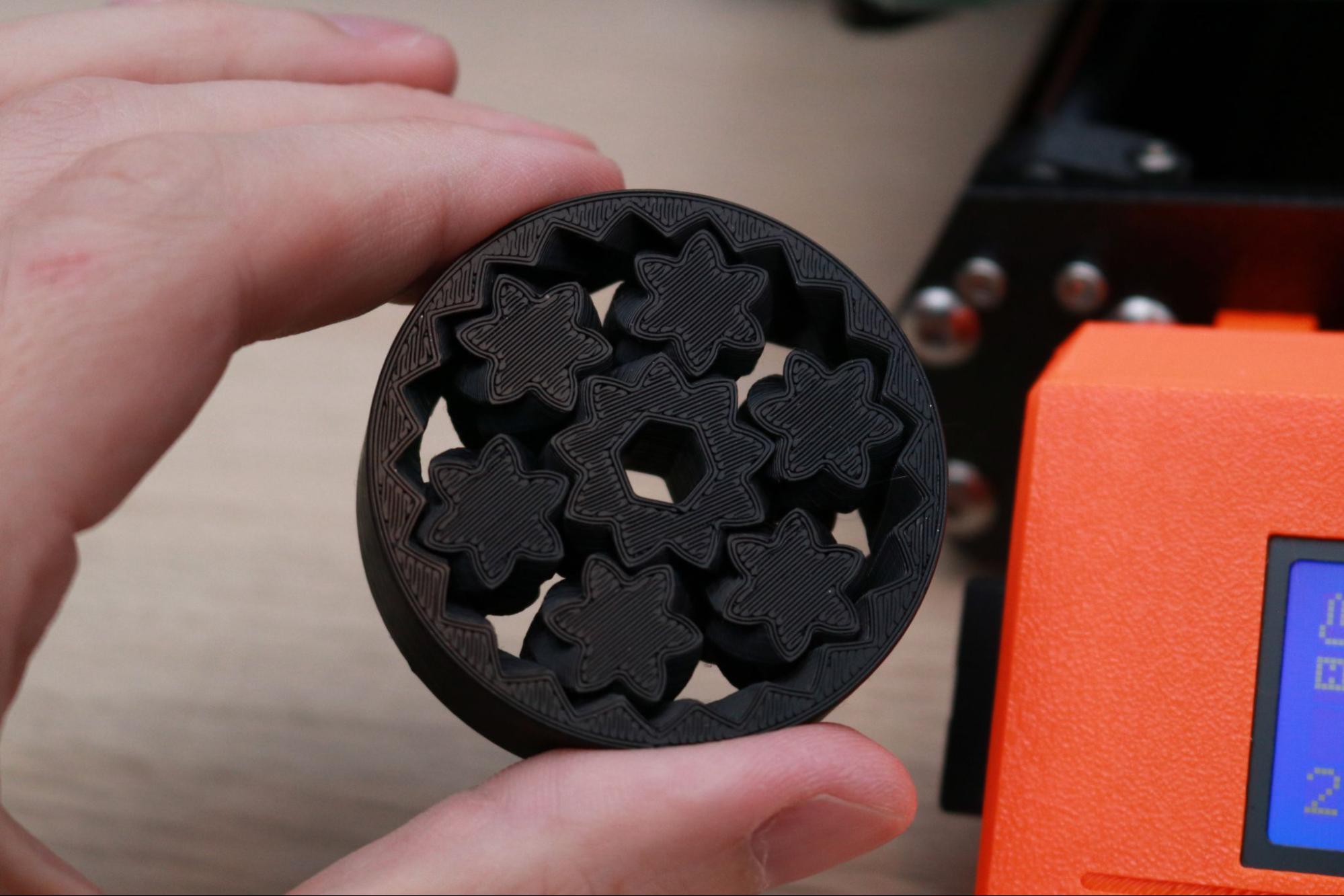
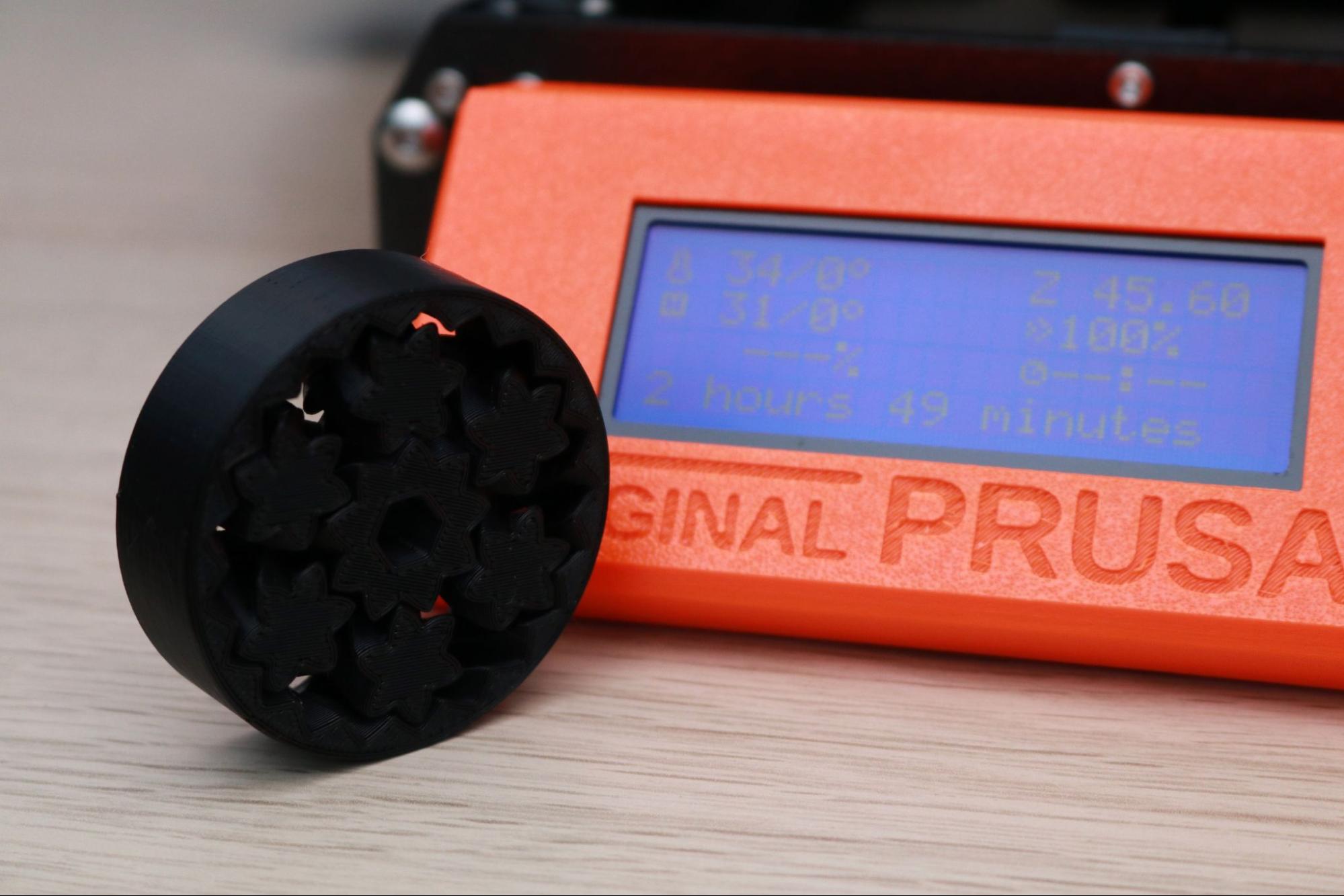


One of my favorite sample parts is the planetary gear bearing that prints in a single print. I printed this model using the Prusament Jet Black PLA material, and after removing it from the build platform I was able to easily spin the gear freely. This part really highlights the ability of the MK3S+ to produce parts with functional strength and purpose in addition to parts designed with aesthetics in mind.
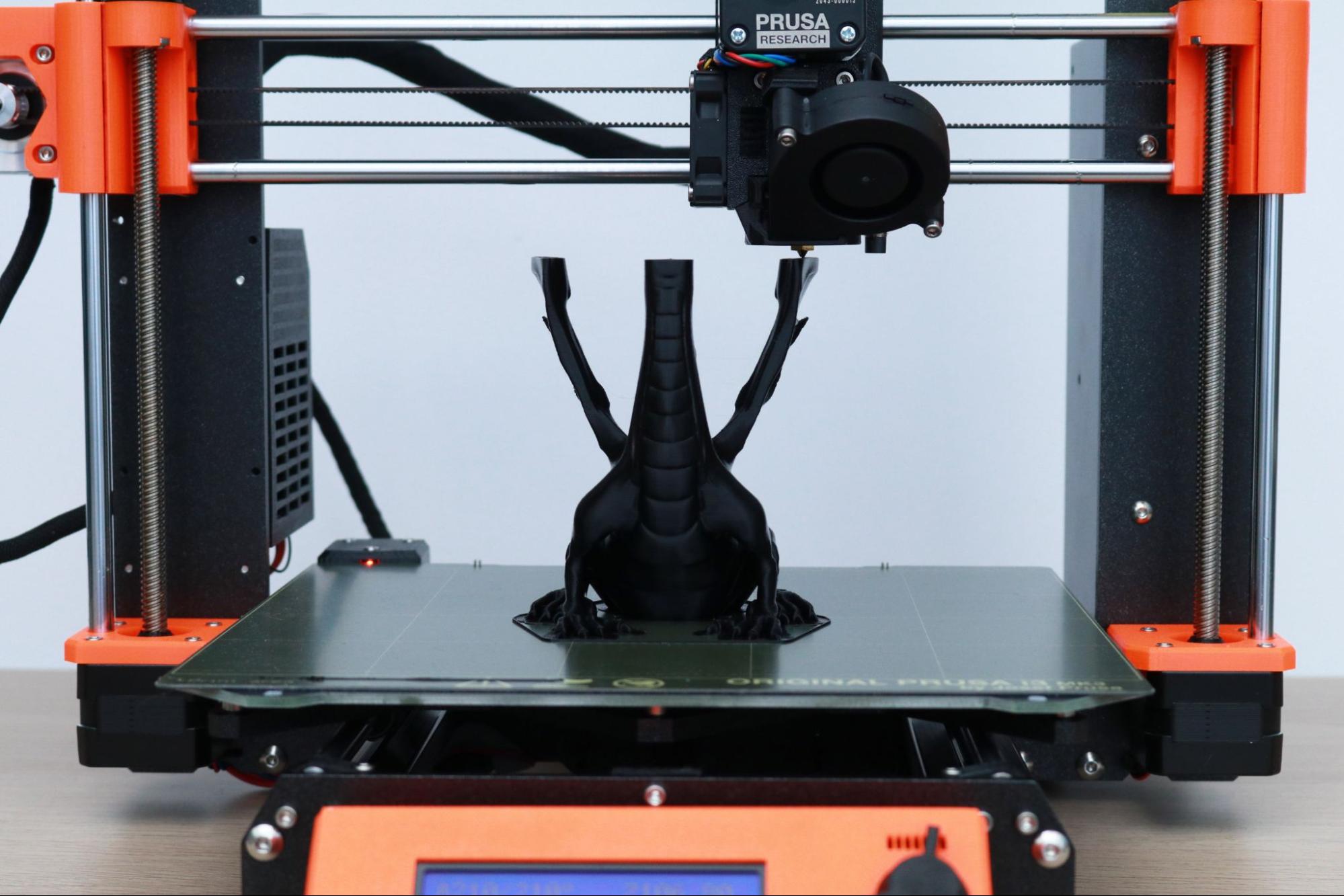
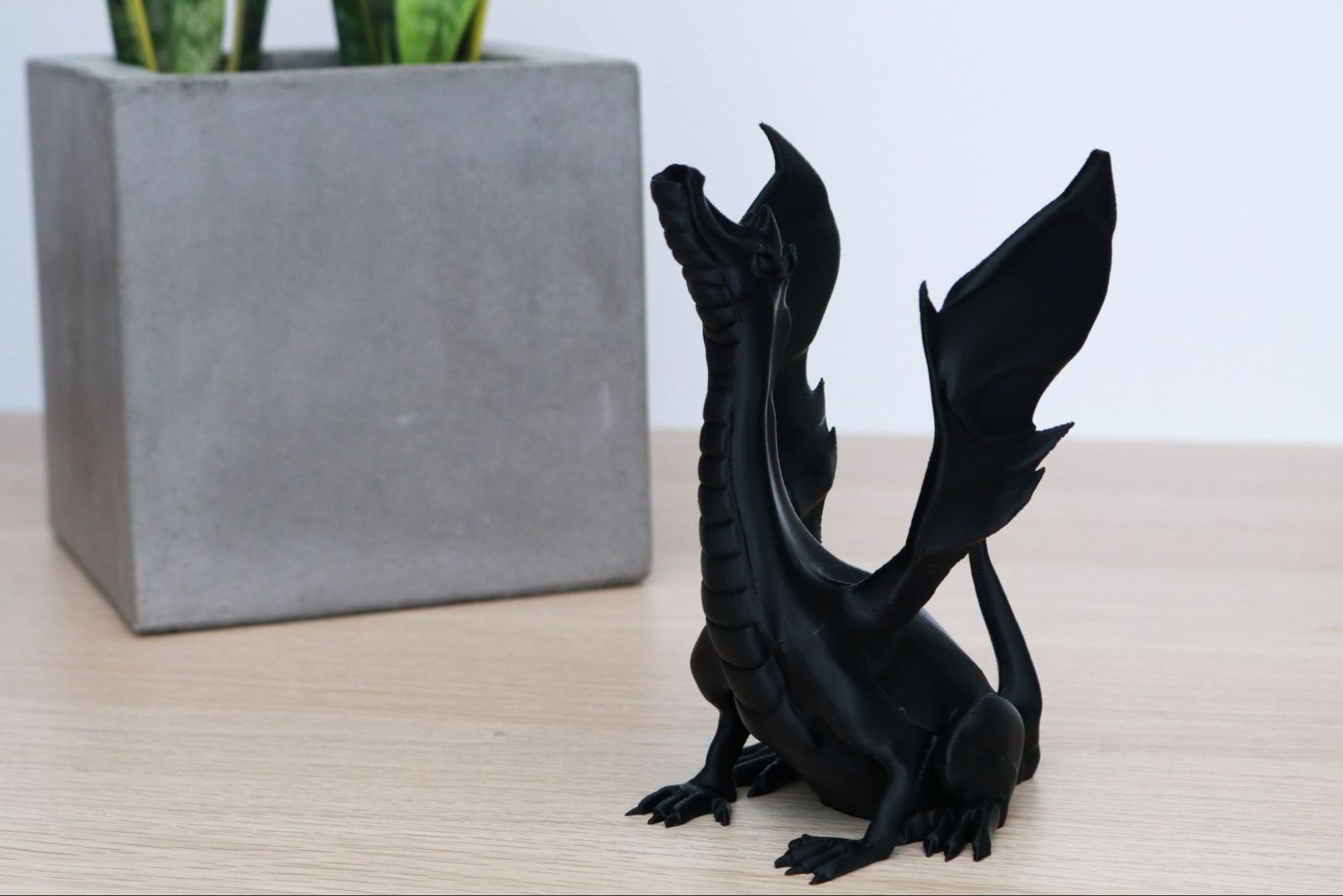
Another stand-out sample print included with the MK3S+ is the dragon model titled Adalinda the Singing Serpent by Loubie3D. This model takes a little longer to print (about 8 hours), but the final print is another favorite of mine. Because this model was sliced by Prusa for the MK3S+ printer, the sample print comes out with a high level of detail and no unexpected settings that can cause problems (too many exterior shells, no retraction, etc.) like the sample prints included with other FDM 3D printers.
Printing with PrusaSlicer on the Prusa MK3S+
Prusa has developed its own in-house slicer for the Prusa MK3S+, called PrusaSlicer. PrusaSlicer is a fork of the confusing-to-pronounce Slic3r app, which is also a free and open-source app. Prusa has invested a considerable amount of time and effort in PrusaSlicer, and this has translated into one of the most powerful 3D printing slicer apps available for desktop 3D printers on the market.
The current version of PrusaSlicer (2.3.3) includes profiles for printers by Prusa, Creality, Lulzbot, and more, and also includes a library of material profiles. In addition to these profiles, PrusaSlicer also includes multiple print setting profiles, which range from ultra-high detail at 0.05mm layer height to a draft mode which offers .3mm layers fast print speed at the expense of reduced quality.
Slicing Models in PrusaSlicer for the Prusa MK3S+
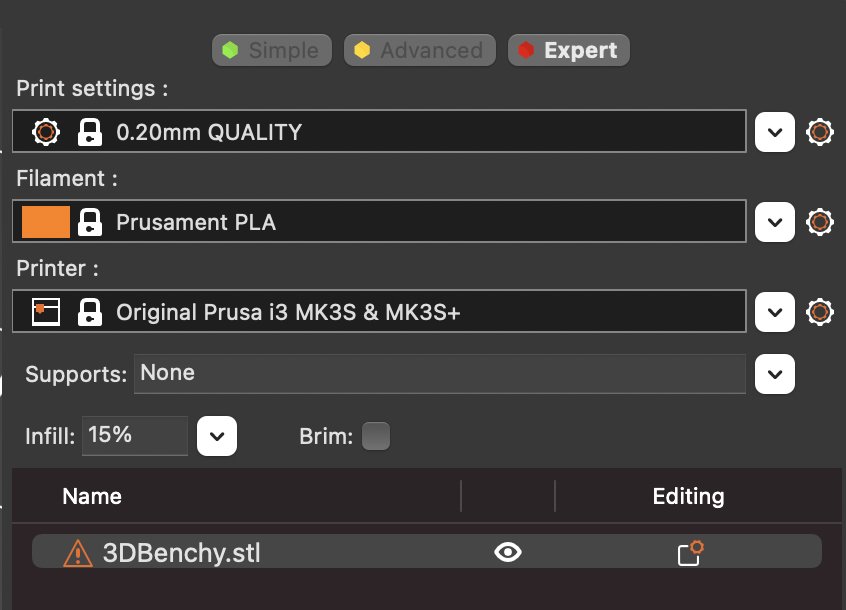
PrusaSlicer is a feature-rich program with a simplified interface that is accessible to beginners, experts, and everyone in between. I’ve spent a lot of time in the PrusaSlicer settings, and I appreciate how much work Prusa has put into making almost every parameter of the printing process addressable without creating an overwhelming interface.
The settings are broken down into three primary categories: Print Settings, Filament Settings, and Printer Settings. Print Settings generally focuses on the speed / quality of the print, Filament Settings is used to determine temperature and extrusion parameters, and Printer Settings is used for global parameters and determining start / stop instructions.
The primary interface offers three settings: Simple, Advanced, and Expert. Simple offers a stripped-down experience with only a few parameters able to be adjusted, while Advanced and Expert allow you to adjust the print on a more granular level.
PrusaSlicer Quality Settings for the Prusa MK3S+ / PLA
| Material | Prusa Basic PLA, Silver |
| Layer Height | 0.20 mm |
| Infill Percentage | 15%, Gyroid |
| Print Speed | 45mm/second |
| Extruder Temperature | 215 degrees Celsius (419 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Heated Bed Temp | 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) |
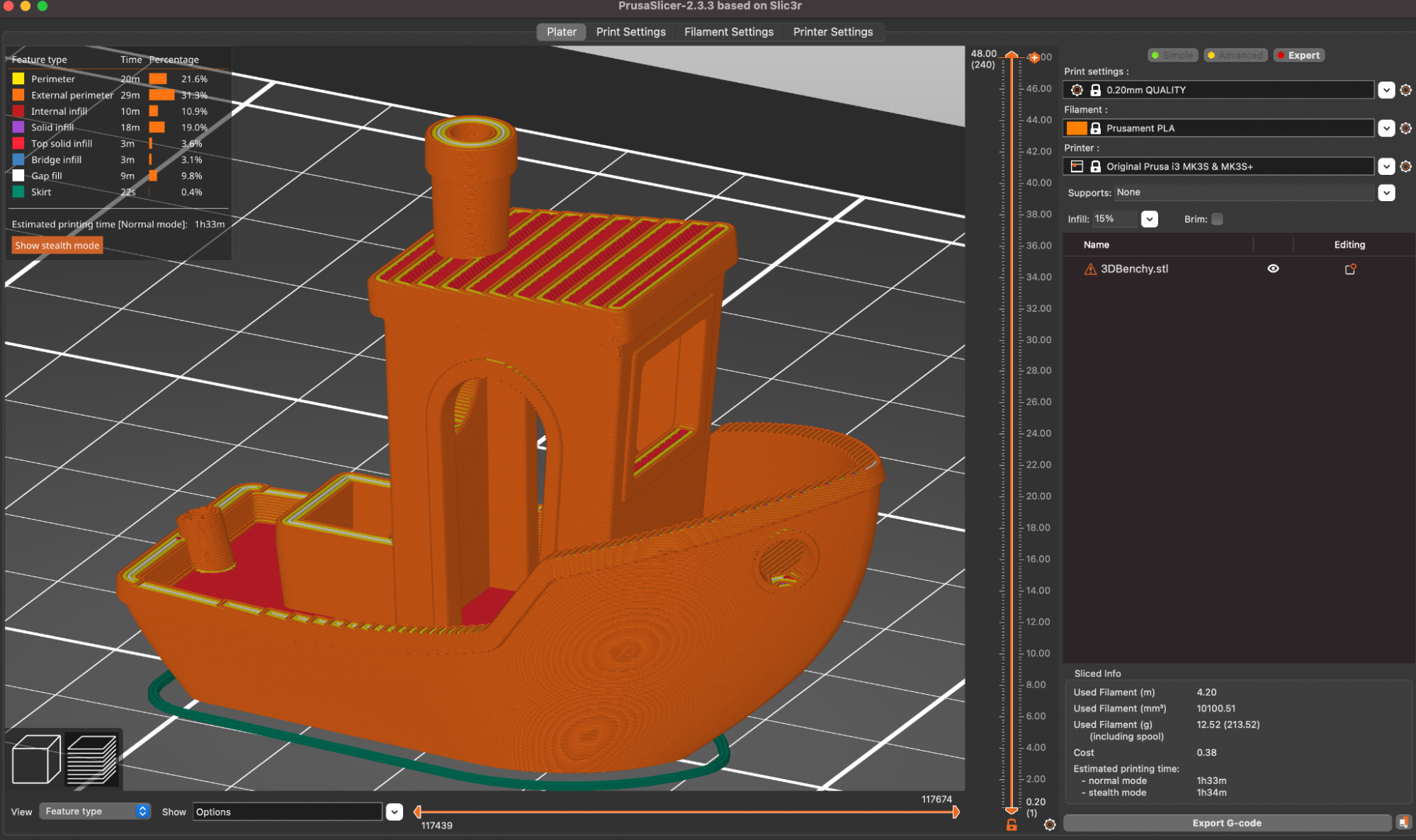
| Print Time | 1 Hour, 34 Minutes |
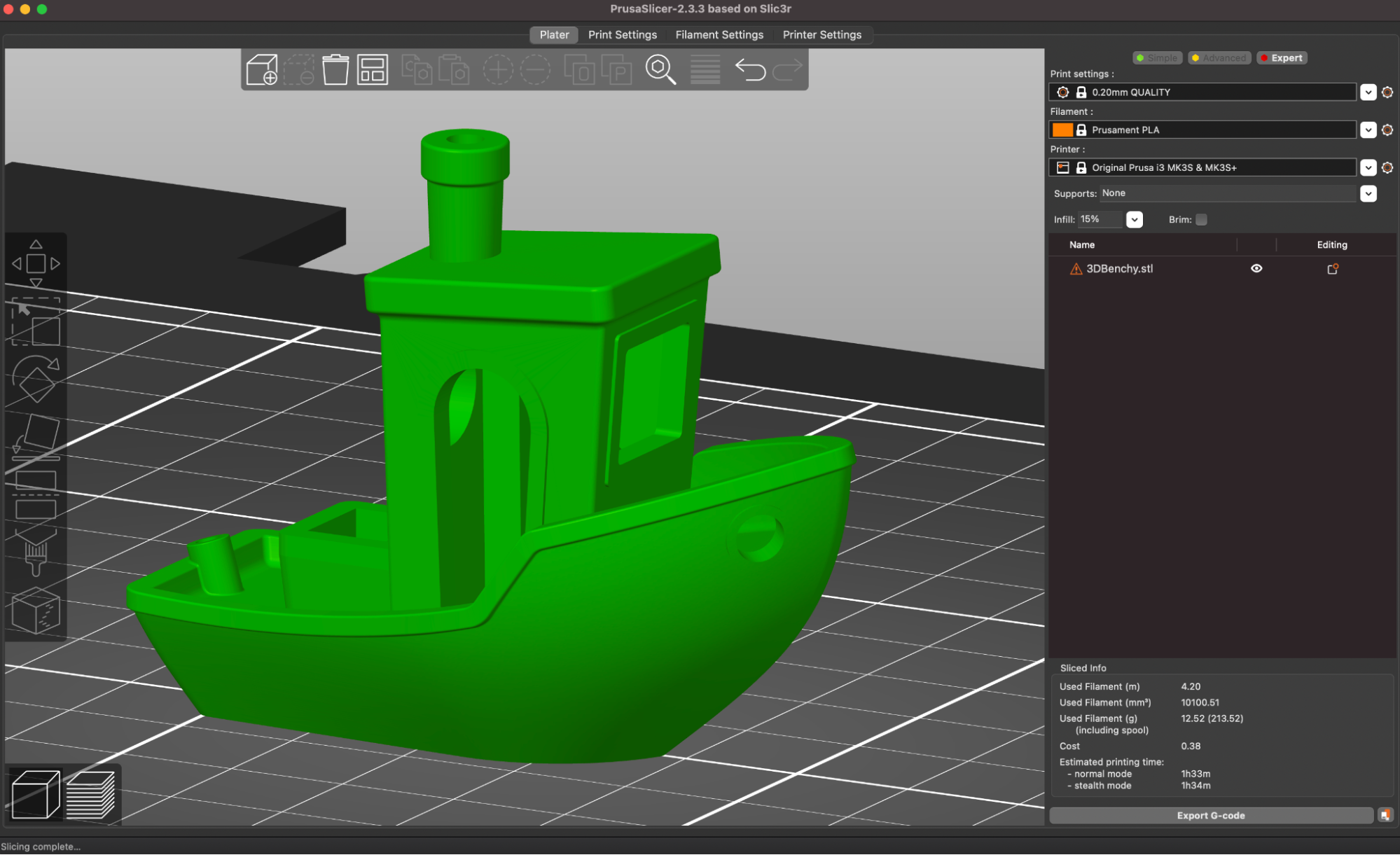
There are few prints that are better at testing out a printer than the 3DBenchy, so I used the included spool of silver Prusa PLA to print this model out using the default .2mm Quality PrusaSlicer settings. I was impressed with the overall quality of the Benchy, and even with a highly-reflective material like a silver PLA which can highlight defects from uneven layers, the layers looked even and consistent throughout.
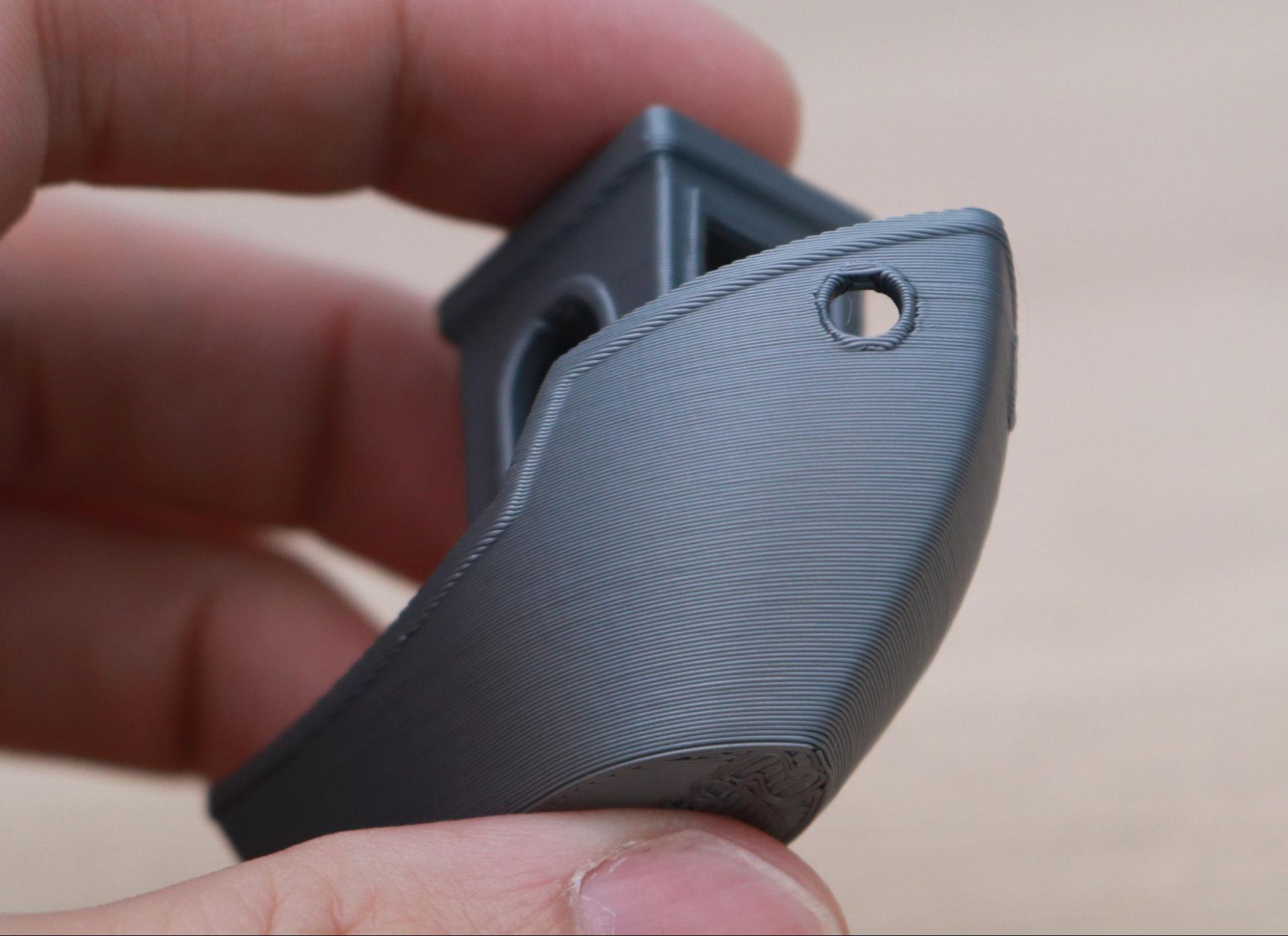
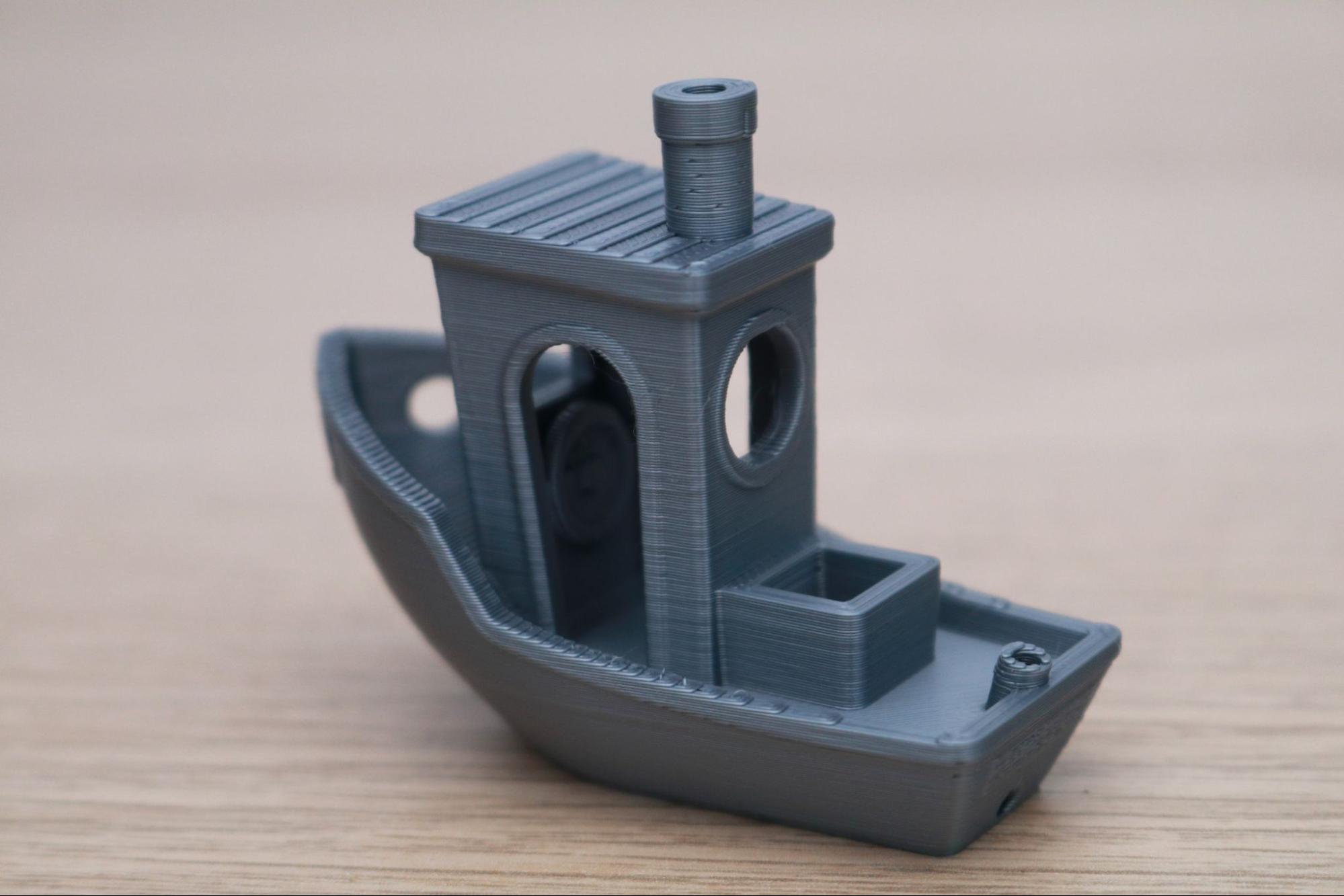


The Benchy boat model is designed to highlight various features of a printer (such as the ability to print steep overhangs, small features, etc.), and a quick examination of the model shows that the MK3S+ performed very well and didn’t have any of the common defects typically seen on this model.
PrusaSlicer Spiral Vase Settings for the Prusa MK3S+ / PLA
| Material | Prusament PLA, Galaxy Purple |
| Layer Height | 0.20mm |
| Infill Percentage | 0% |
| Print Speed | 60mm/second |
| Extruder Temperature | 215 degrees Celsius (419 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Heated Bed Temp | 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) |
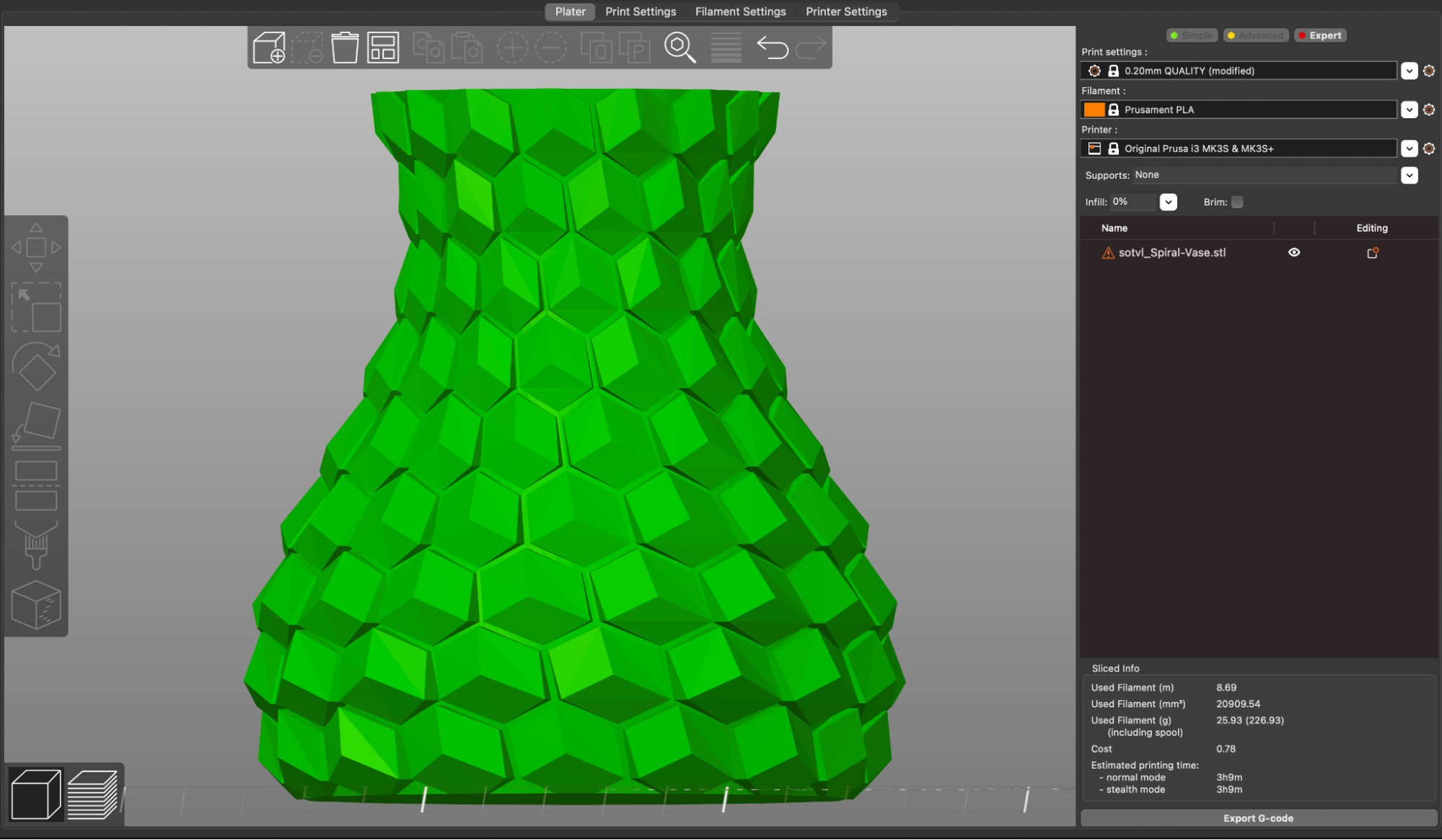
| Print Time | 3 Hours, 9 Minutes |
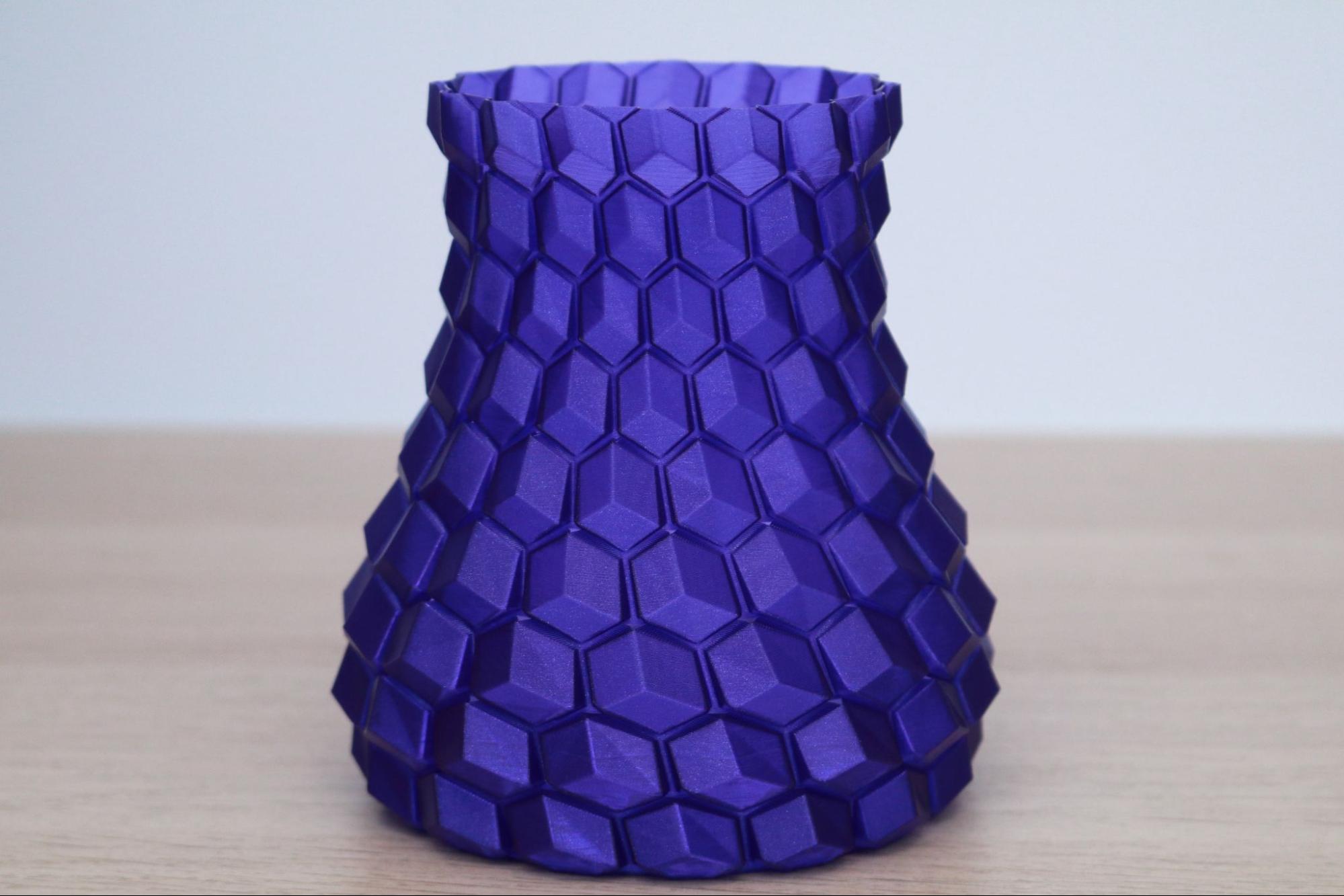
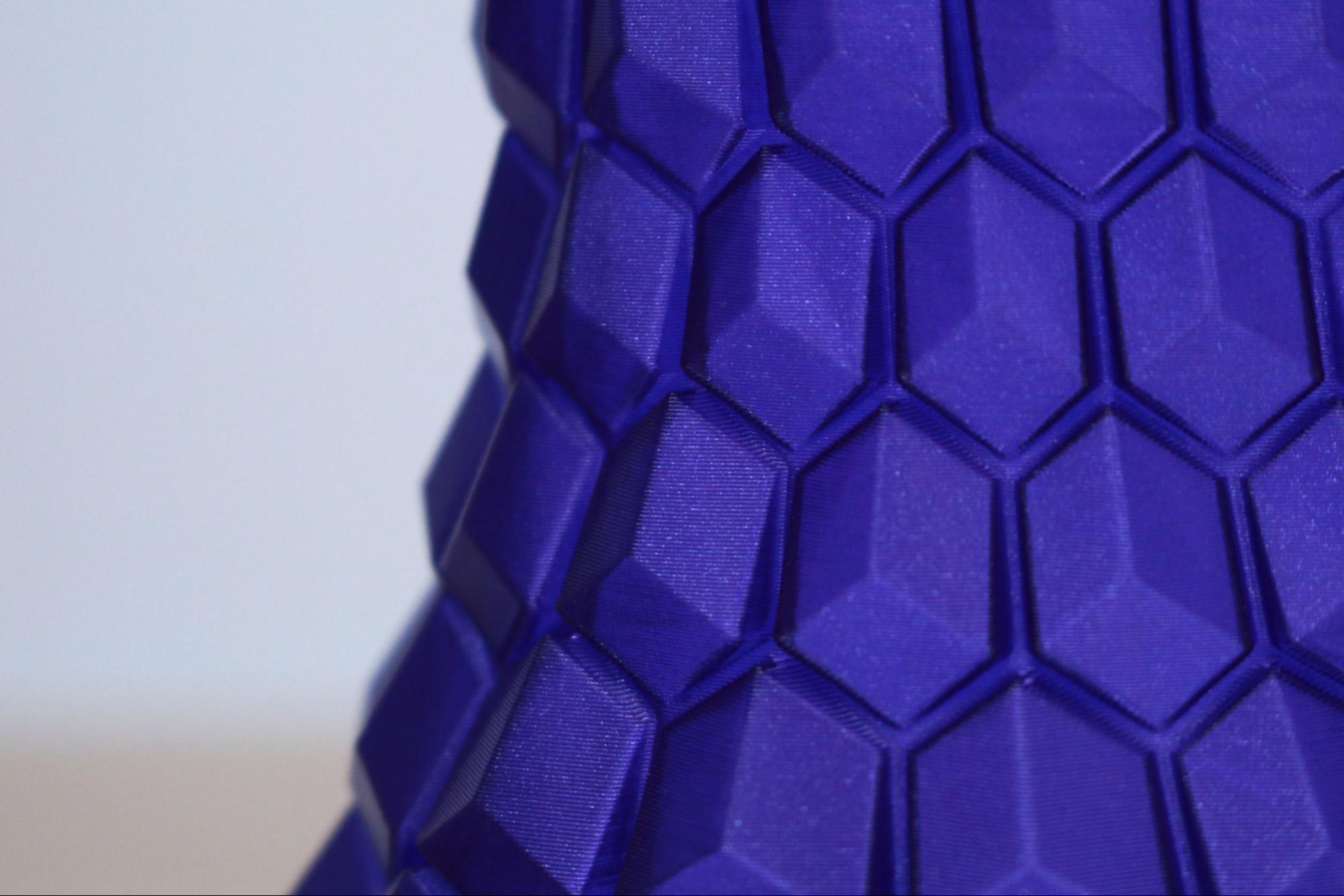
Slicing a model using the ‘Spiral Vase’ mode in PrusaSlicer will automatically create a model that is composed of a single continuously rising helical contour, which allows models to be printed a fraction of the time it would normally take to print using multiple layers. This mode is ideal for printing objects like vases or enclosures that only require a single contour as opposed to multiple contours and an infill structure. I printed the Curved Honeycomb Vase by eggnot to highlight this printing mode.
The Prusament Galaxy Purple is a favorite color of mine due to the glitter additive in the filament. This additive creates layer lines that are evenly blended and have a textured appearance. Combining this material with the Spiral Vase mode produces parts that look almost conventionally manufactured, with layer lines that are difficult to see. This model printed in just over 3 hours in Spiral Vase mode, as opposed to over 13 hours if it had been printed using conventional settings.
PrusaSlicer Speed Settings for the Prusa MK3S+ / PETG
| Material | Prusament PETG, Chalky Blue |
| Layer Height | 0.2mm |
| Infill Percentage | 15%, Grid |
| Print Speed | 60mm/second |
| Extruder Temperature | 250 degrees Celsius (482 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Heated Bed Temp | 90 degrees Celsius (194 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Print Time | 4 Hours, 5 Minutes |
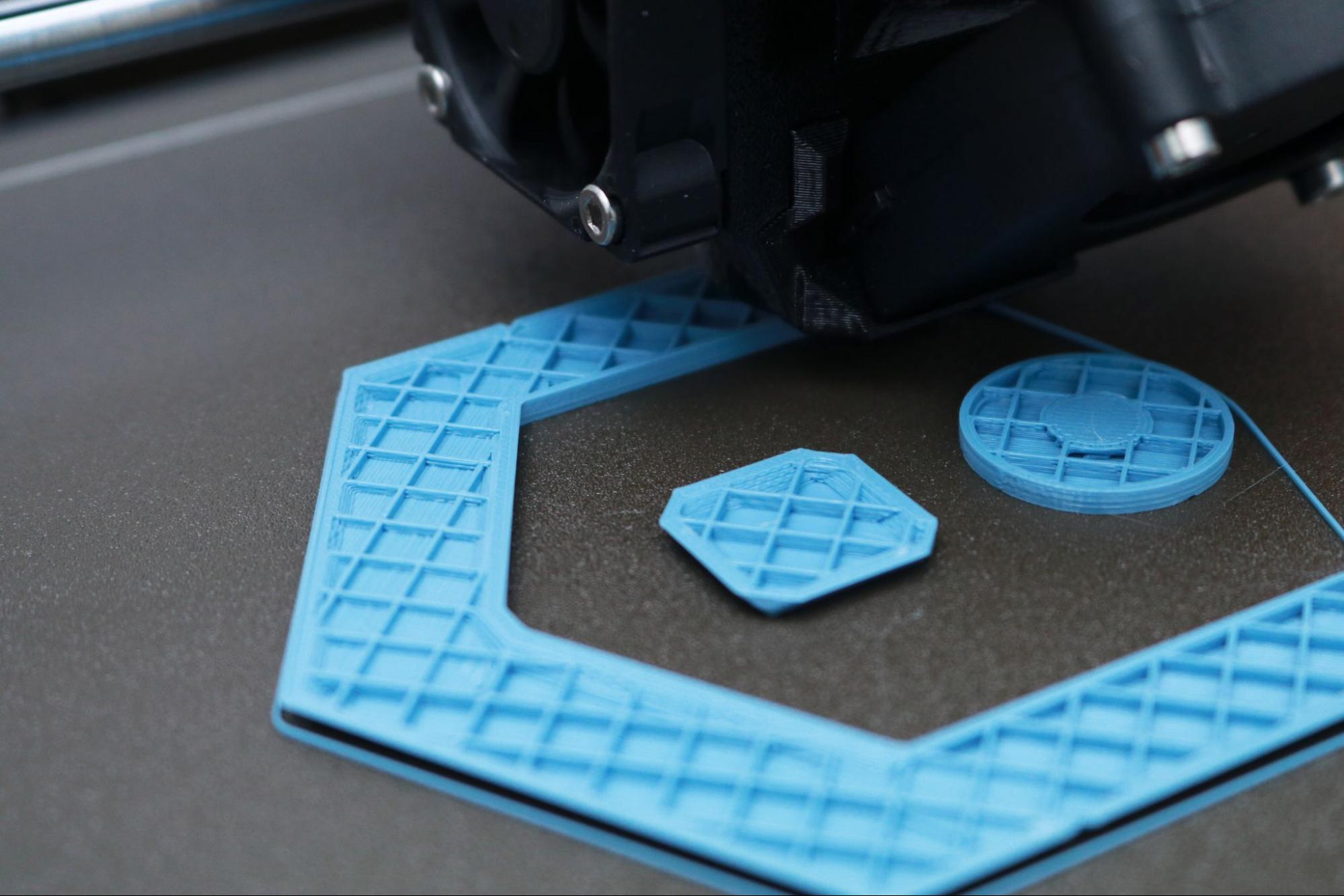
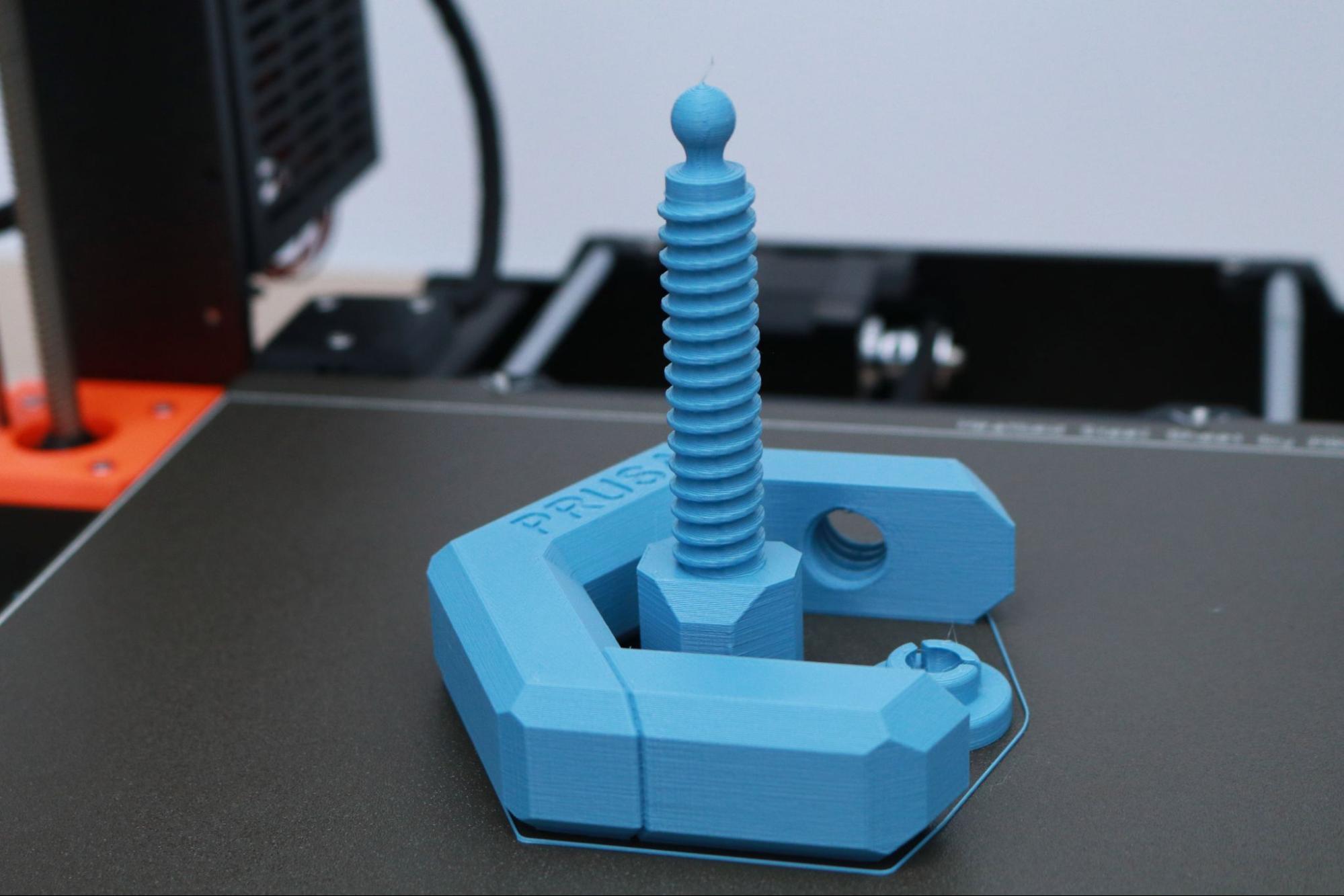
PETG is a material that offers increased mechanical toughness, heat resistance, and flexibility when compared with parts printed with PLA. Prusa has taken advantage of these material properties by printing many of the components on the MK3S+ with PETG, which creates a rigid part that is able to withstand mechanical stress. PETG is also notoriously difficult to print with due to the high level of stringing that can occur when printing multiple parts simultaneously, but I didn’t have any issues when printing with the Prusament PETG material on the MK3S+.
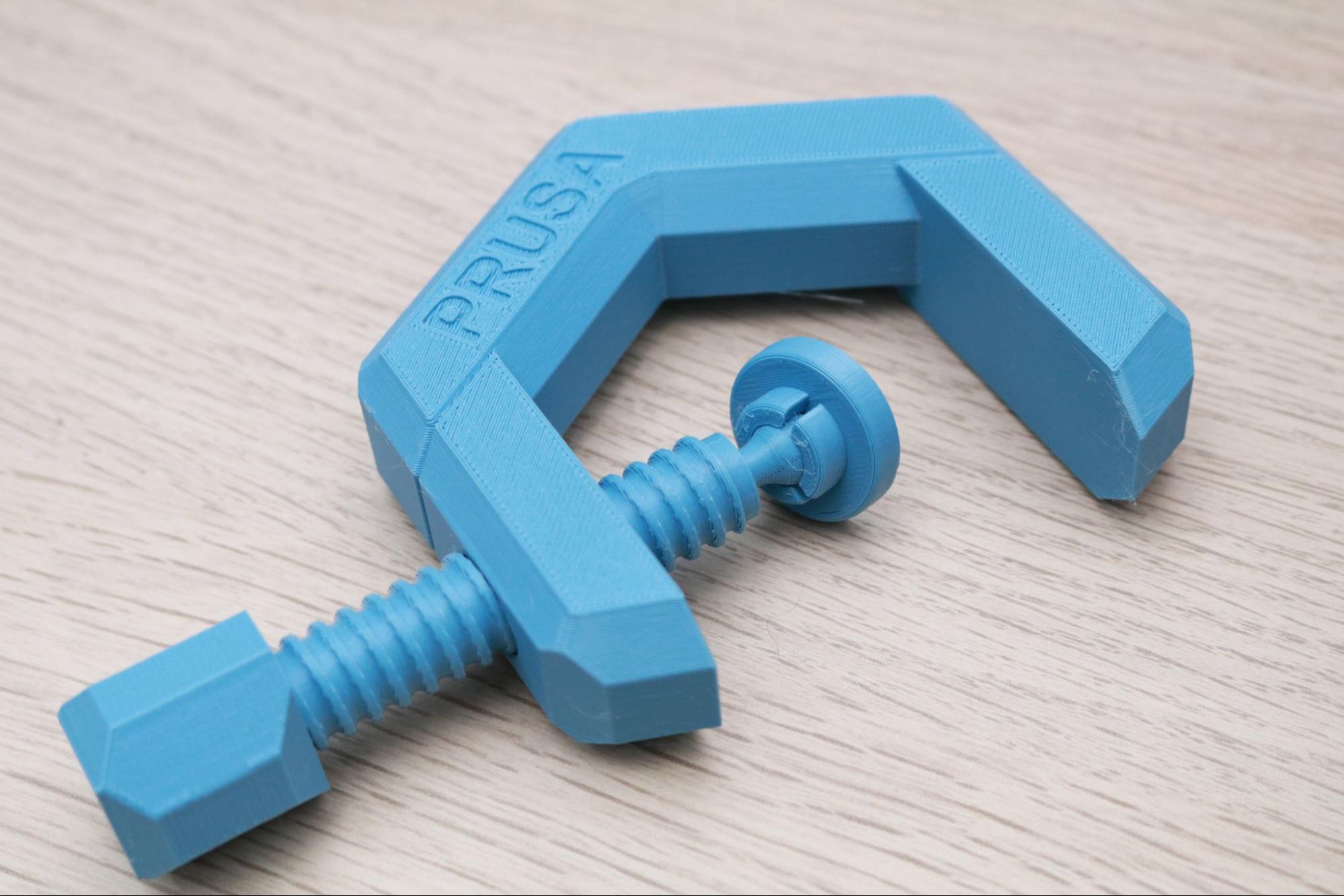

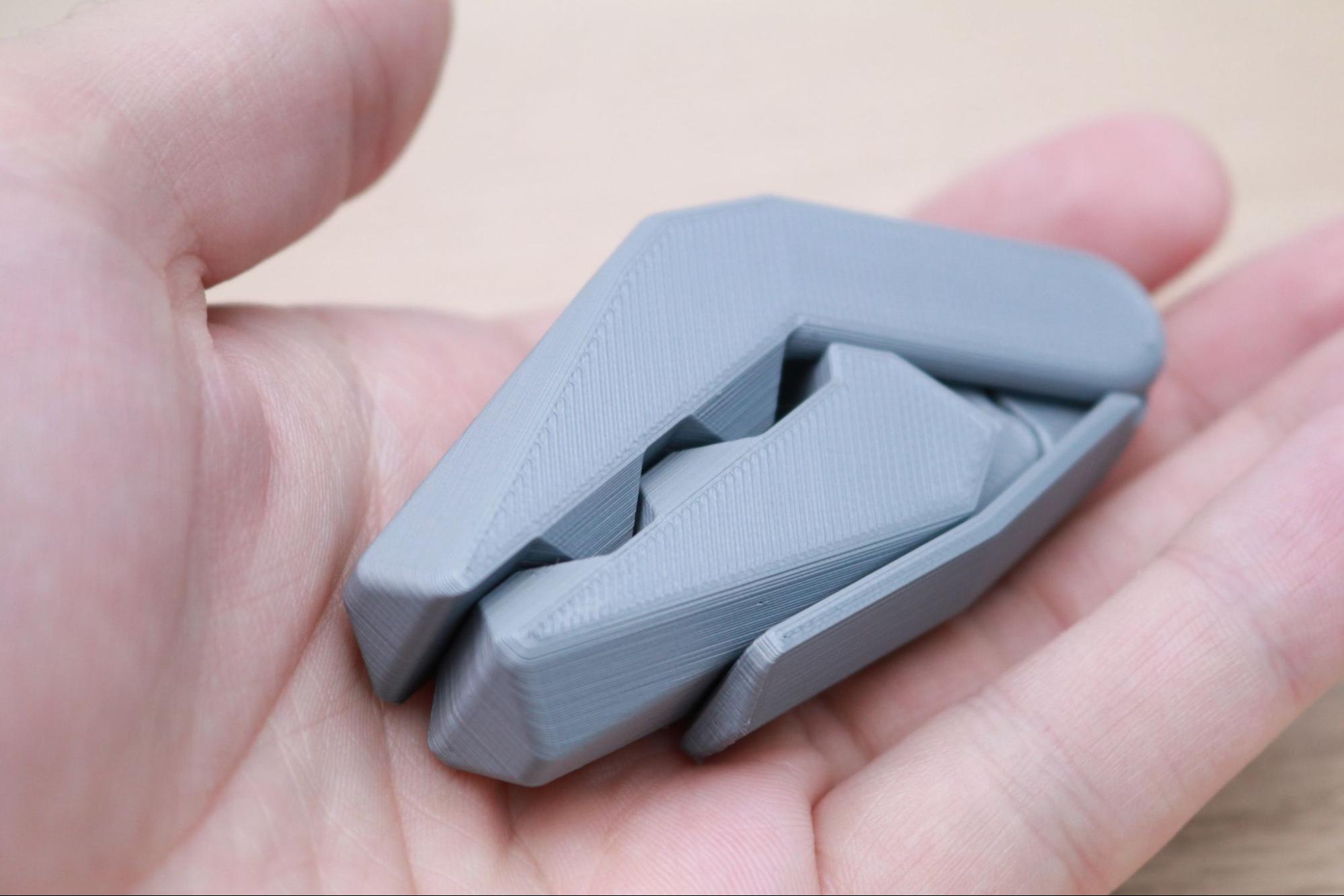
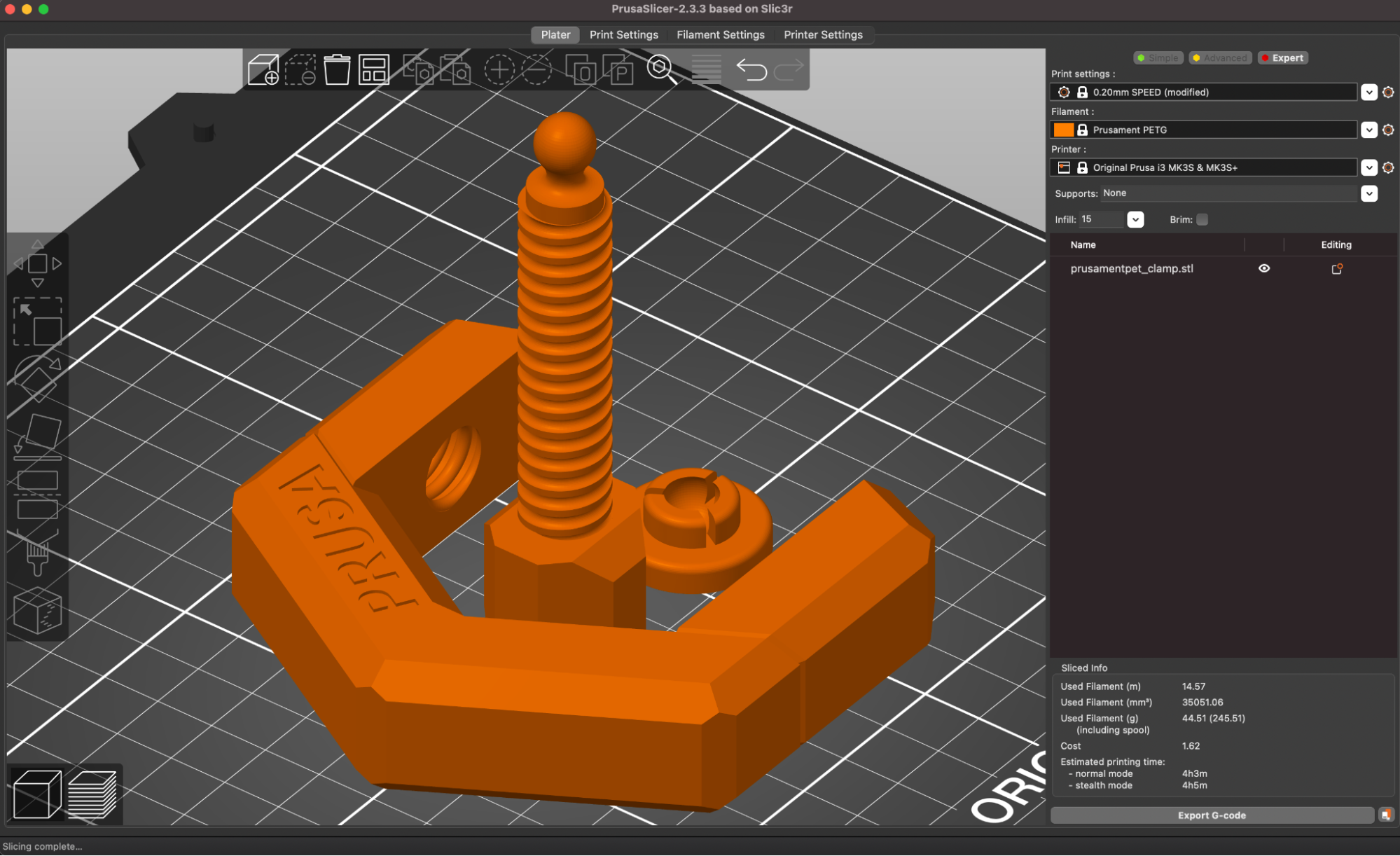
I used the default settings in PrusaSlicer to print the clamp model provided by Prusa that was designed specifically for PETG. This model features a functional thread, a flexible ball-and-socket joint, and can be tensioned without snapping the body of the clamp. The part printed in multiple pieces without stringing, and I was able to easily assemble it and verify functionality without damaging the clamp. If printed in a more brittle material (like PLA), I would expect the clamp to crack at a transition point on the body, but the PETG was able to hold tension without deforming or breaking.
PrusaSlicer 3MF Import for the Prusa MK3S+ / PLA
| Material | Prusa Basic PLA, Silver |
| Layer Height | 0.20mm |
| Infill Percentage | 15%, Grid |
| Print Speed | 60mm/second |
| Extruder Temperature | 215 degrees Celsius (419 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Heated Bed Temp | 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Print Time | 2 Hours, 17 Minutes |
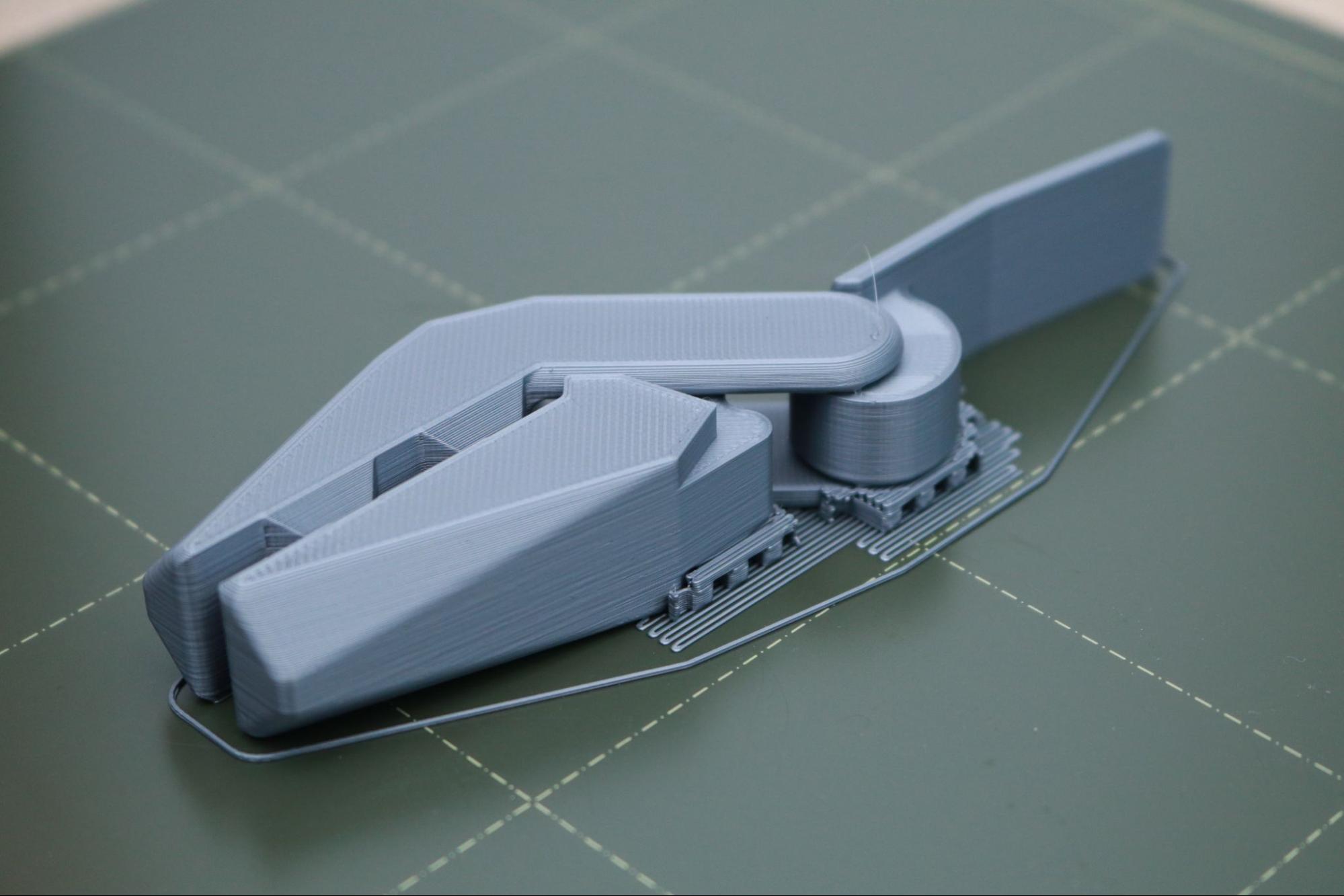
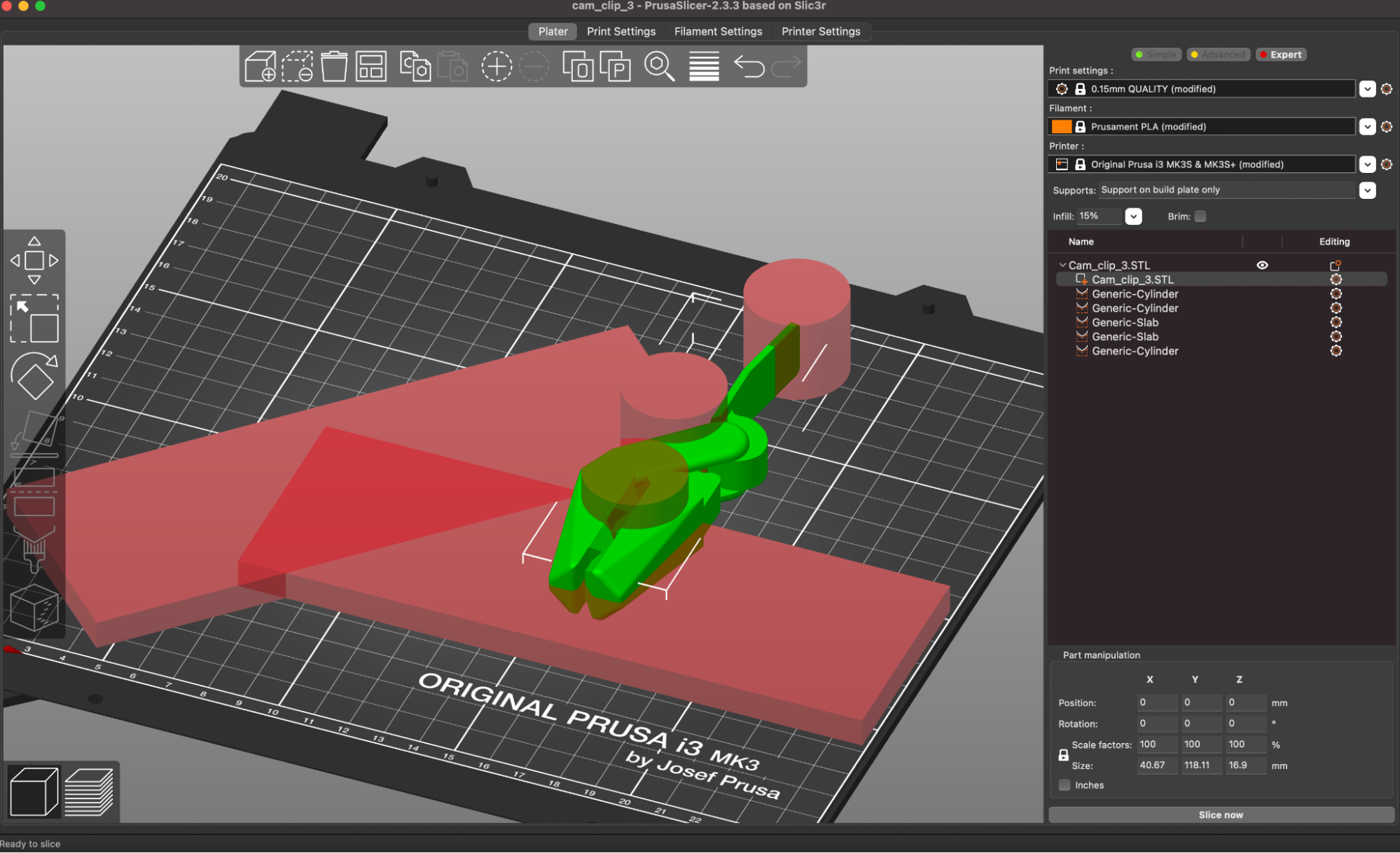
PrusaPrinters (the online file repository created and maintained by Prusa) offers the unique ability to share 3D printable files that have been pre-sliced and prepared for the MK3S+ with detailed print statistics available from the site. A perfect example of this is the Bag Clip by Andrei; a cam-driven bag clip that highlights the type of design freedom offered by a 3D printer.
This model has been uploaded as a .3MF file that contains all of the information required to print, such as slicer settings, nozzle and bed temperature, and custom support structures (visibile in the screenshot above.) 3MF is an increasingly popular alternative to the STL file, which doesn’t contain much information aside from the raw geometry of a model.
This part printed flawlessly on the first try, and the provided .3MF (or .gcode) allows a user to send this file to anyone else with the same printer and material and feel confident that the part will be indistinguishable in appearance and performance. I’ve always thought of a 3D printer as the replicator from the Michael Crichton novel Timeline, which is able to produce identical objects at various locations by converting them into digital information. However, the success of a part is frequently beholden to the settings selected by a user for fabrication, so the ability to share the fabrication plans is one step closer to being able to send a physical product as a form of digital data.
Bottom Line
At a price-point of $999 for an assembled printer (or $749 for a kit), the Prusa MK3S+ is a machine that doesn’t compromise on user experience and is absolutely one of the best 3D printers currently on the market. The MK3S+ has a professional and neat appearance, but the 8-bit monochrome LCD user interface might be a challenge for some users to get past, given the steep price. Interface aside, the prosumer features of the MK3S+ make it a stand-out machine for anyone who is looking for a reliable machine to produce functional parts without worrying about spending a lot of time tinkering.
If you are looking for a less expensive machine outside of the Prusa ecosystem, the Elegoo Neptune 2 (currently on Amazon for $180) offers similar printing size and features (with the notable exception of automatic bed leveling) at a fraction of the price but without the same level of robust support and documentation provided by the MK3S+ or any of the name-brand components like the E3D hotend. If you want the Prusa experience but are looking to spend a little less money, the Prusa Mini+ (available from Prusa for $399 assembled, $349 for a kit) is an excellent place to start.

Andrew Sink first used a 3D printer in 2012, and has been enthusiastically involved in the 3D printing industry ever since. Having printed everything from a scan of his own brain to a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, he continues to dive ever more deeply into the endless applications of additive technology. He is always working on new experiments, designs, and reviews and sharing his results on Tom's Hardware, YouTube, and more.