Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Protection Features
Check out our PSUs 101 article to learn more about PSU protection features.
|
Protection Features | |
|
OCP | 12V: 84.8A (119.72%), 12.023V 5V: 30.1A (150.5%), 5.037V 3.3V: 31.5A (157.5%), 3.324V 5VSB: 5.3A (176.67%), 4.914V |
|
OPP |
1090.01W (128.24%) |
|
OTP | ✗ (>200°C & +12V Heat Sink) |
|
SCP |
12V: ✓ |
|
PWR_OK |
Proper operation |
|
NLO |
✓ |
|
SIP | Surge: MOV Inrush: NTC Thermistor & Bypass Relay |
The OCP triggering point at +12V is at a reasonable level, but this is not the case for the minor rails where the respective thresholds are set too high. There is no reason for such high OCPs on the minor rails, from the moment today's systems only lightly use them. Finally, the OPP is adequately configured, within 130% of the PSU's max-rated-capacity.
Unfortunately, we were unable to make the PSU shut down during our over-temperature test, so it is safe to assume that either there is no OTP or it is just set too high, so practically it is useless.
DC Power Sequencing
According to Intel’s most recent Power Supply Design Guide (revision 1.4), the +12V and 5V outputs must be equal to or greater than the 3.3V rail at all times. Unfortunately, Intel doesn't mention why it is so important to always keep the 3.3V rail's voltage lower than the levels of the other two outputs.
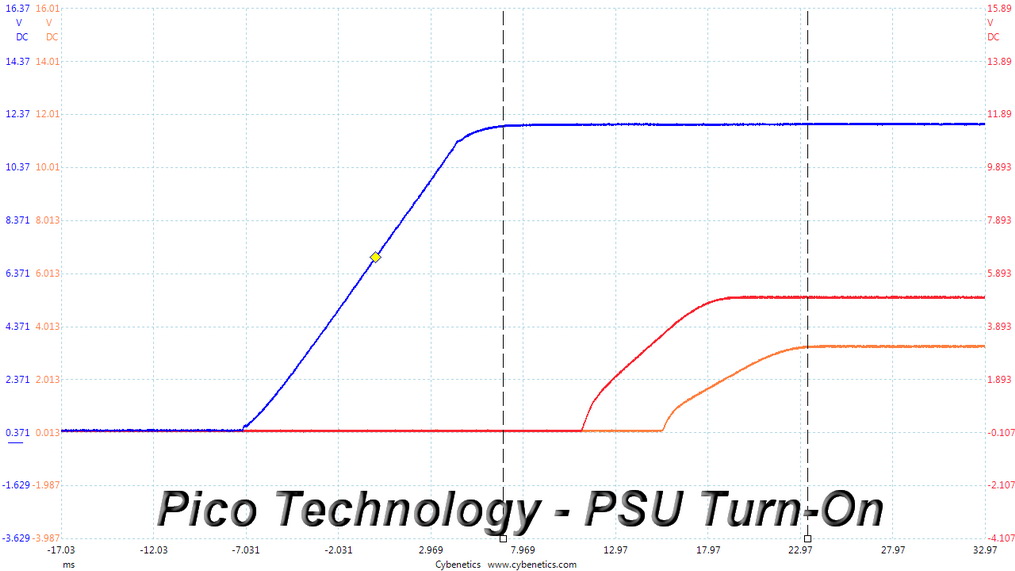
DC Power Sequencing Scope Shots
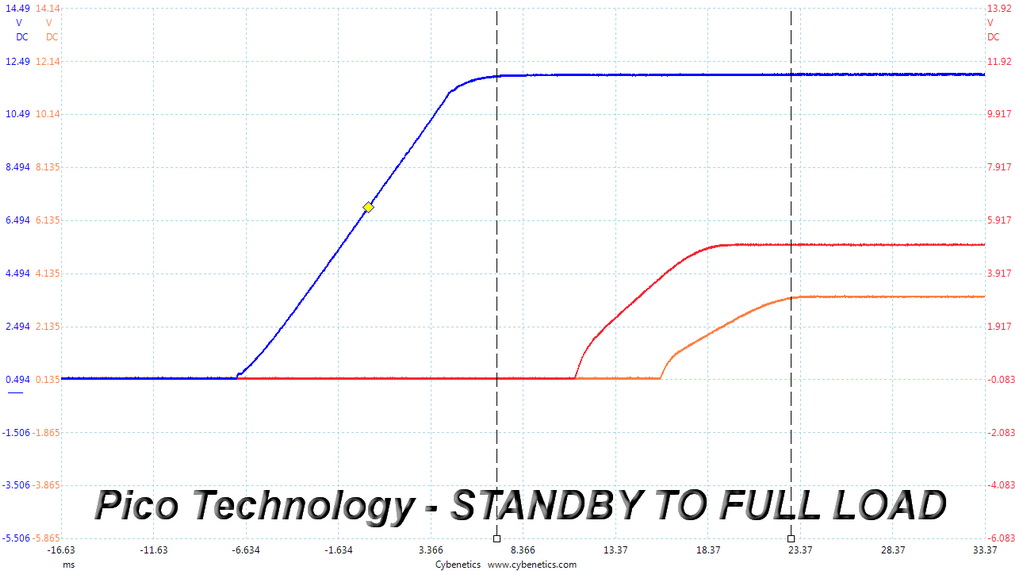
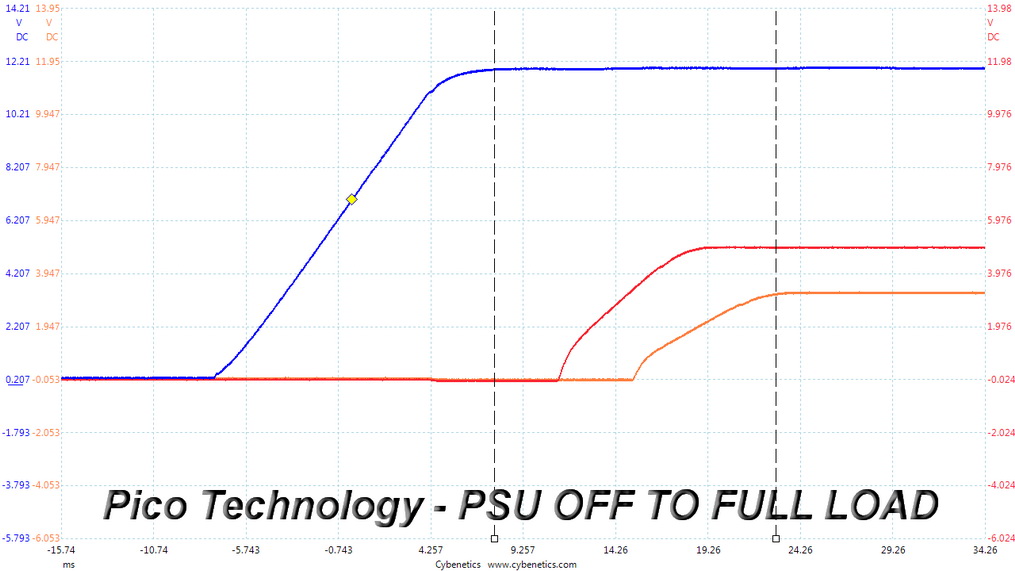
The 3.3V rail is always lower than the other two.
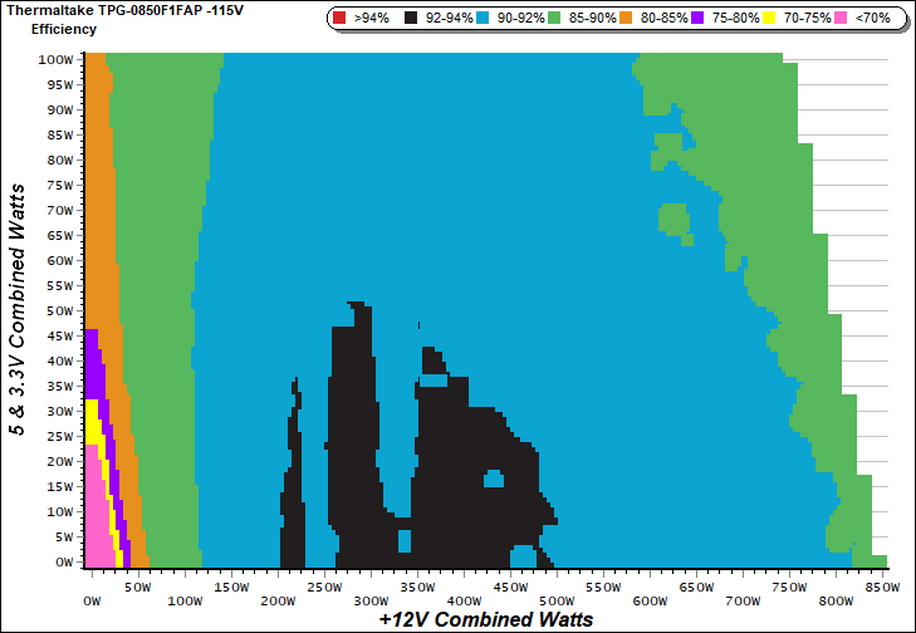
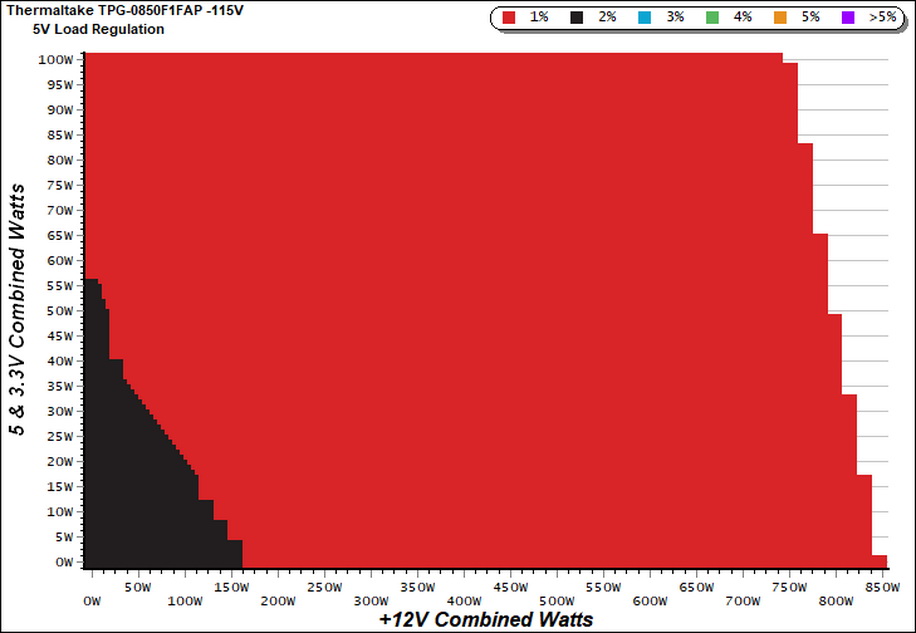
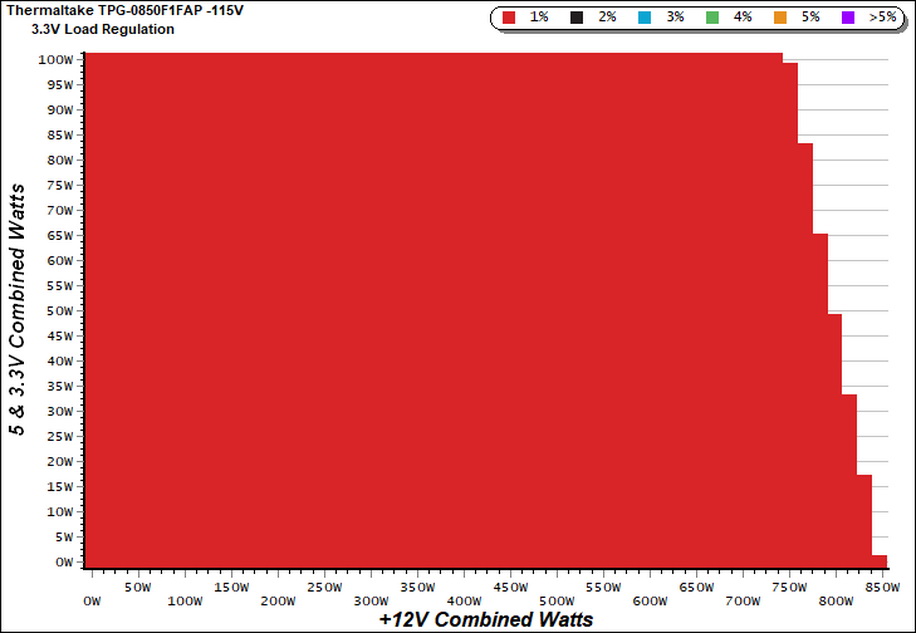
Cross Load Tests
To generate the following charts, we set our loaders to auto mode through custom-made software before trying more than 25,000 possible load combinations with the +12V, 5V, and 3.3V rails. The deviations in each of the charts below are calculated by taking the nominal values of the rails (12V, 5V, and 3.3V) as point zero. The ambient temperature during testing was between 30 to 32 degrees Celsius (86 to 89.6 degrees Fahrenheit).
Load Regulation Charts
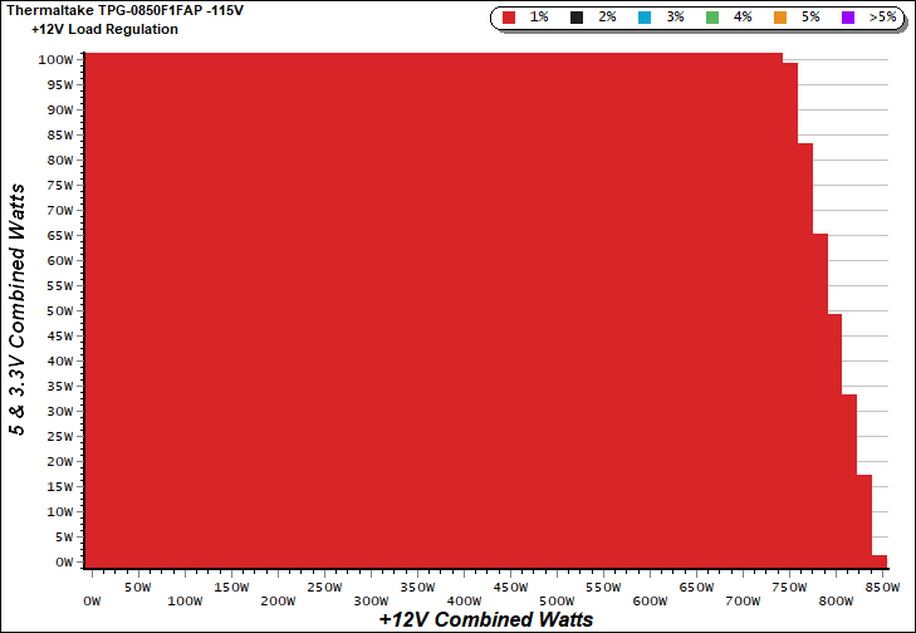
Load Regulation Charts
Efficiency Chart
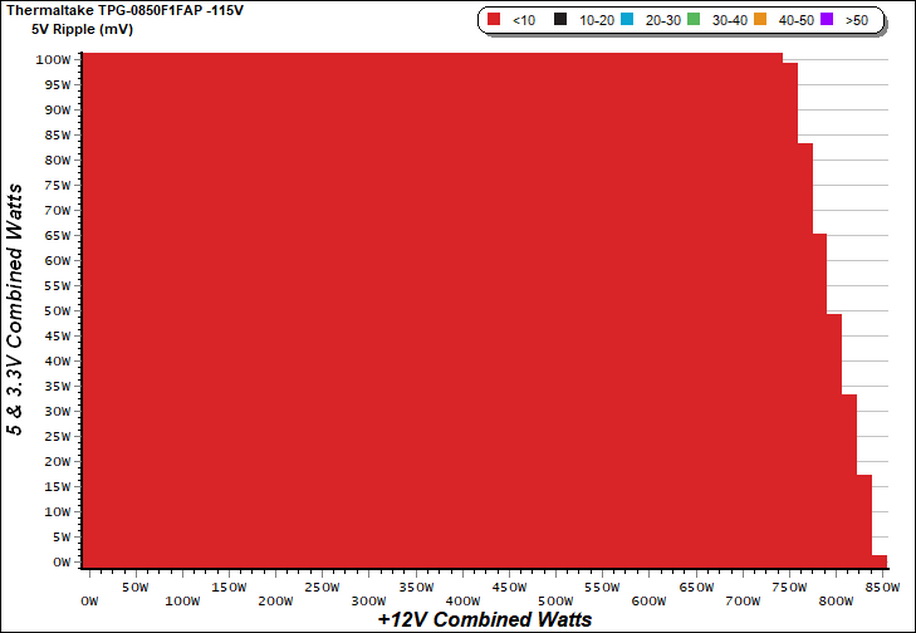
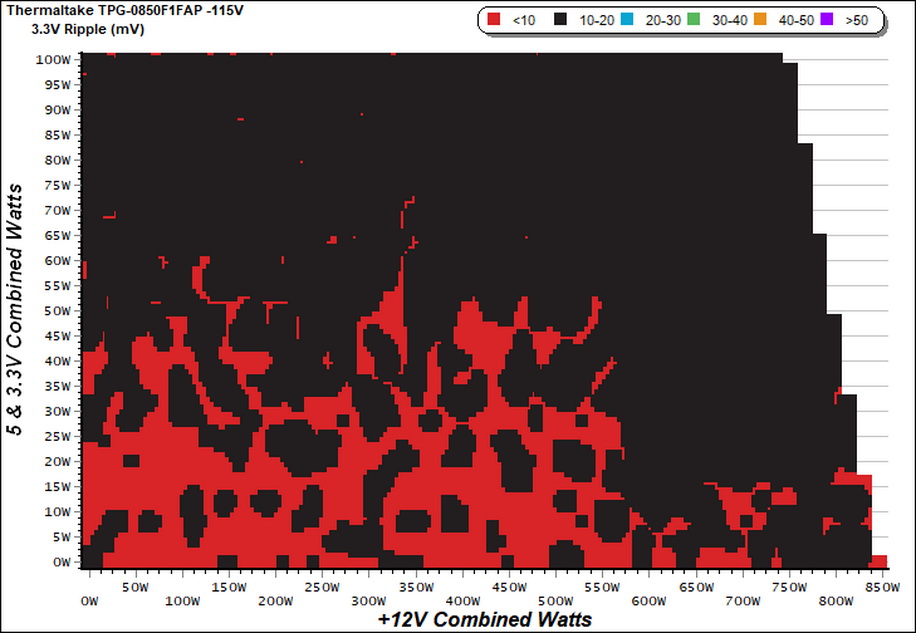
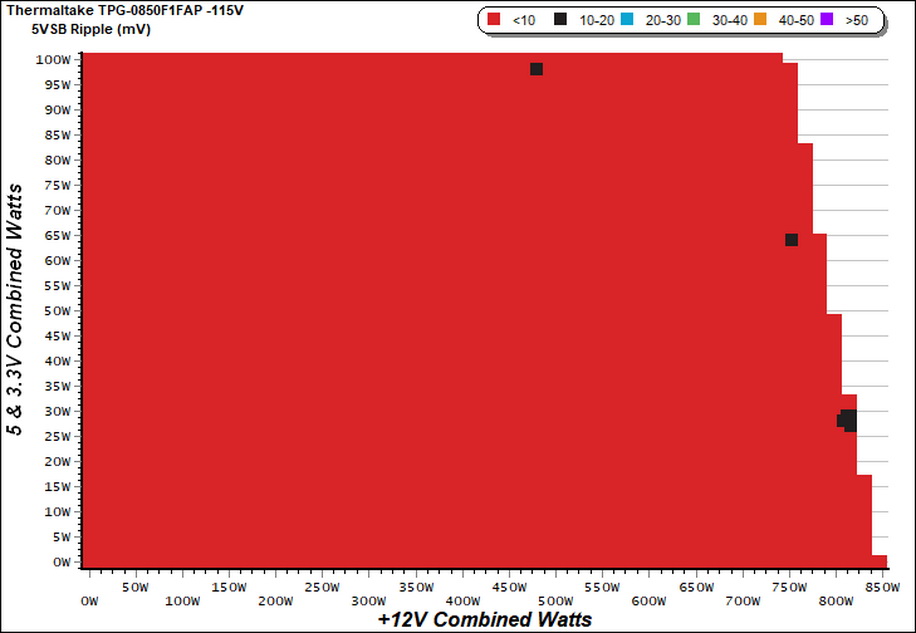
Ripple Charts
The lower the power supply's ripple, the more stable the system will be and less stress will also be applied to its components.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
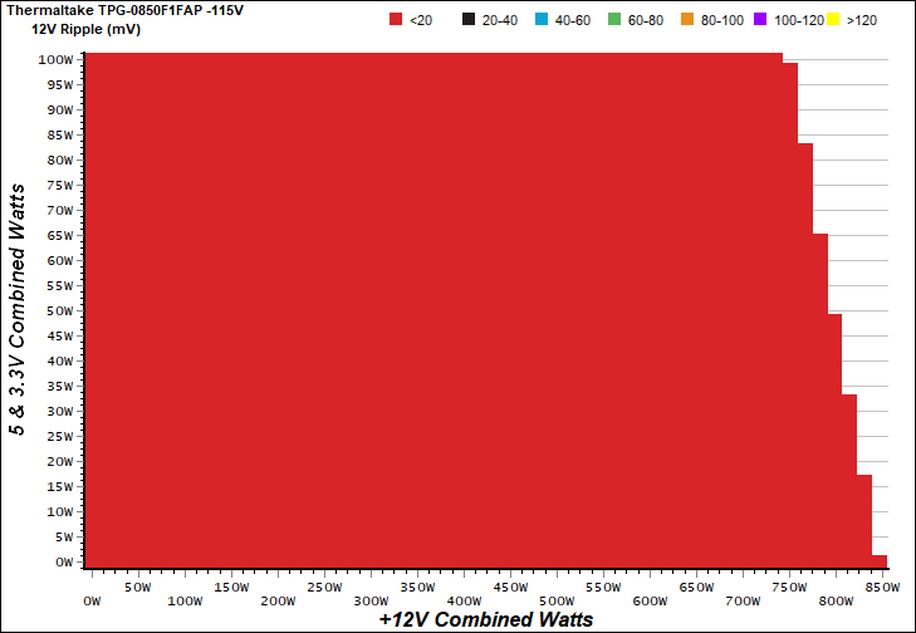
Ripple Suppression Charts
Infrared Images
We apply a half-load for 10 minutes with the PSU's top cover and cooling fan removed before taking photos with a modified FLIR E4 camera able to deliver an IR resolution of 320x240 (76,800 pixels).
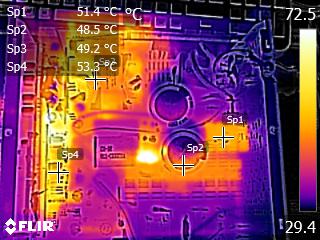
IR Images




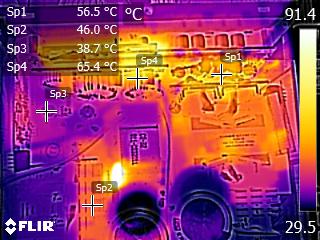
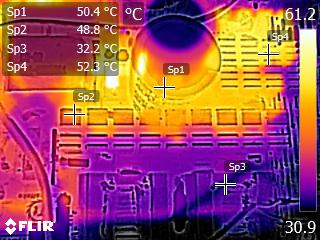
The VRMs get quite hot, and the same applies to the board that hosts the +12V FETs. The latter also increases the operating temperatures of the electrolytic caps, which are installed between the +12V board and the one hosting the modular sockets. CWT used good enough caps (Nichicon HD) in the area. Still, we would prefer to see Chemi-Con's KY line used instead, in such a hot area. This is why CWT had to use a more aggressive fan speed profile, especially at high operating temperatures.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images
Prev Page Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time, Inrush Current, Efficiency and Noise Next Page Transient Response Tests, Timing Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.