Asus ROG Strix GeForce GTX 1080 Ti 11GB OC Edition Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Cooling & Noise
Cooling System & Backplate
What makes this solution special is its use of a "sandwich" system, which employs a cooling and stabilizing frame between the board surface and the actual heat sink. Again, it's unfortunate that Asus does not use a dedicated VRM sink built into the cooler to improve thermal performance.
| Cooling Overview | |
|---|---|
| Type | Air-cooling |
| Heat Sink | Nickel-plated heat sink, GPU only |
| Cooling Fins | Aluminum, horizontal orientation Very narrow configuration |
| Heat Pipes | 6x 6mm, nickel-plated |
| VRM Cooling | Via cooling frame Only MOSFETs are cooled |
| RAM Cooling | Via mounting frame, and indirect cooling via heat sink |
| Fans | 3x 9cm fan modules 8.6cm rotor diameter 11 rotor blades Semi-passive regulation |
| Backplate | Aluminum, blackenedDoes not aid cooling performanceIncludes back-lit logo |
The backplate is purely aesthetic. While it does sport a snazzy-looking ROG logo, it does nothing for cooling performance.

Asus' cooling and mounting frame absorbs heat produced by the memory modules and transfers it to the main sink through a layer of thermal pads. The voltage converters are also cooled by this frame; a thick pad facilitates contact with the cooling fins above them. Since those fins aren't angled by 90°, it is reasonable to assume that this solution was an afterthought. To stabilize the contact a bit better, the cooler is placed on a thick adhesive pad.

The heat sink is nickel-plated and very smooth. Six nickel-plated pipes made from a composite material cut through the sink and help dissipate the GPU's waste heat evenly through a pair of fin arrays. Bends in some of the pipes turn out to be relatively large. This, coupled with the small-diameter pipes, helps improve cooling performance.

Fan Speeds And Noise
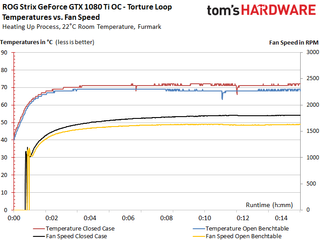
The fan curves indicate a conservative, volume-optimized setup. There's a bit of jittery hysteresis as the fans spin up. However, the number of starting impulses is acceptable without becoming particularly annoying.
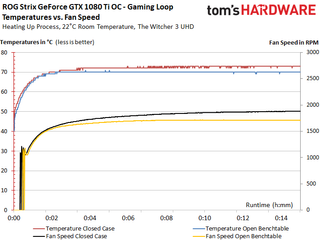
The measurements from our stress test aren't much different. A slight dip in power consumption correlates with lower RPM.
| Fan Speed And Noise Output | |
|---|---|
| Fan Speed (Open Test Bench, Maximum) | 1715 RPM |
| Fan Speed (Open Test Bench, Average) | 1702 RPM |
| Fan Speed (Closed Case, Maximum) | 1884 RPM |
| Fan Speed (Closed Case, Average) | 1874 RPM |
| Noise (Air Cooling, Maximum) | 39.0 dB(A) |
| Noise (Air Cooling, Average) | 38.8 dB(A) |
| Noise ( Air Cooling, Idle) | 0 dB(A) |
| Acoustic Characteristics | Almost no low-frequency bearing noise Very audible motor noise < 1 Hz Discernible oscillations due to slightly different fan speeds Hardly any coil buzzing noise Audible air/tearing noises |
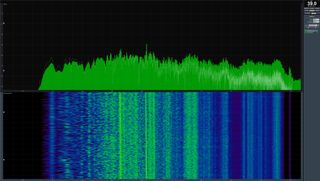
This snapshot illustrates the entire frequency range of our laboratory measurements, adding some data to our subjective observations.
MORE: Best Graphics Cards
MORE: Desktop GPU Performance Hierarchy Table
MORE: All Graphics Content
Stay on the Cutting Edge
Join the experts who read Tom's Hardware for the inside track on enthusiast PC tech news — and have for over 25 years. We'll send breaking news and in-depth reviews of CPUs, GPUs, AI, maker hardware and more straight to your inbox.
-
jasonbgreen83 I'm DISGUSTED that this $750 video card has jumped to $1200 in the last few days just as I was getting the money saved up to add one to my build. I refuse to be a victim of this price gouging greed. I'm sick of these companies pulling this limited stock crap to raise the prices to insane levels. Same thing with Intel and the 8700k. It's DISGUSTINGReply -
dstarr3 Reply20278033 said:I'm DISGUSTED that this $750 video card has jumped to $1200 in the last few days just as I was getting the money saved up to add one to my build. I refuse to be a victim of this price gouging greed. I'm sick of these companies pulling this limited stock crap to raise the prices to insane levels. Same thing with Intel and the 8700k. It's DISGUSTING
If you click the Newegg link it shows a price of $799. I don't know why Tom's is reporting a $1,200 price tag. -
jasonbgreen83 I'm disgusted that this $750 video card has jumped to $1200 dollars in the last few days just as I got the money up to add one to my build. I refuse to be a victim of this price gouging greed. These companies are ridiculous with this limiting third stock crap just to raise the prices. Same thing with the Intel 8700k.Reply -
derekullo Reply20278033 said:I'm DISGUSTED that this $750 video card has jumped to $1200 in the last few days just as I was getting the money saved up to add one to my build. I refuse to be a victim of this price gouging greed. I'm sick of these companies pulling this limited stock crap to raise the prices to insane levels. Same thing with Intel and the 8700k. It's DISGUSTING
I see the confusion.
There are 4 versions of the card.
ASUS ROG Poseidon
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?item=N82E16814126202
$859
ASUS ROG GeForce GTX 1080 Ti DirectX 12 STRIX - Not Overclocked
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?item=N82E16814126187
$759
ASUS ROG GeForce GTX 1080 Ti DirectX 12 STRIX - Overclocked
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?item=N82E16814126186
$1199
ASUS GeForce GTX 1080 Ti DirectX 12 - Blower-cooled design
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?item=9SIA0AJ6E80374
$1299
You can still buy the card for $759 as long as you don't go for the water cooled, overclocked or rear exhaust models.
Less complaining, More research
-
jasonbgreen83 I've had this exact card on my part list on PC partpicker for the last 5 months or so. Been saving up for it. It has been 750-800 for the OC version. In the last 48 hours that has jumped up to over a grand. For the exact same card. I know there are slower ones available, this exact card has jumped up. Now I have to wait for it to come back down.Reply -
The_King Why include a Fury X which is alreay EOL, but not the Vega 56 and 64 in your benchmarks ?Reply -
davidgirgis I own this card.Reply
I have used this card for games daily since it came out last April. It is as fast as Tom's Hardware says it is.
Check out my build:
https://pcpartpicker.com/b/NTCbt6
In August, the card started freezing immediately after I launched Dragon Age: Inquisition or The Division. Asus RMA'ed the card, and the new card works even better.
It is now running 1708 MHz GPU and 11100 MHz VRAM at 120% power target, with a slightly more aggressive fan curve than default. GPU boost does the rest auto-magically. -
a.p.martinez765 WTF 1200 bucks?? Ok this has to stop the PC community cannot afford to pay over a thousand dollars every time a new GPU comes out....Reply -
davidgirgis Reply20278838 said:What is a PCA?
A PCB (Printed circuit board) populated with electronic components is called a printed circuit assembly (PCA), printed circuit board assembly or PCB assembly (PCBA)
Credit: Wikipedia
