Corsair Force LE 200 SSD Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
256GB SSD Performance
Comparison Products
There are only a handful of name-brand DRAMless SSDs on the market. Most of the new products we've seen coming from Asia appear to use the DRAMless design, but none of the vendors advertise the products as such. With brand name companies, you find hints at the underlying architecture. Corsair listed the Force LE200's endurance on the specification sheet, but we've found the rating difficult to find for products from smaller companies.
All the DRAMless drives in our tests seem to be on the level. The SanDisk Z410 and SSD Plus both appeared with the OCZ TL100 in our 11-Drive DRAMless Roundup article. The Hyundai Sapphire 240GB sells for roughly $50.
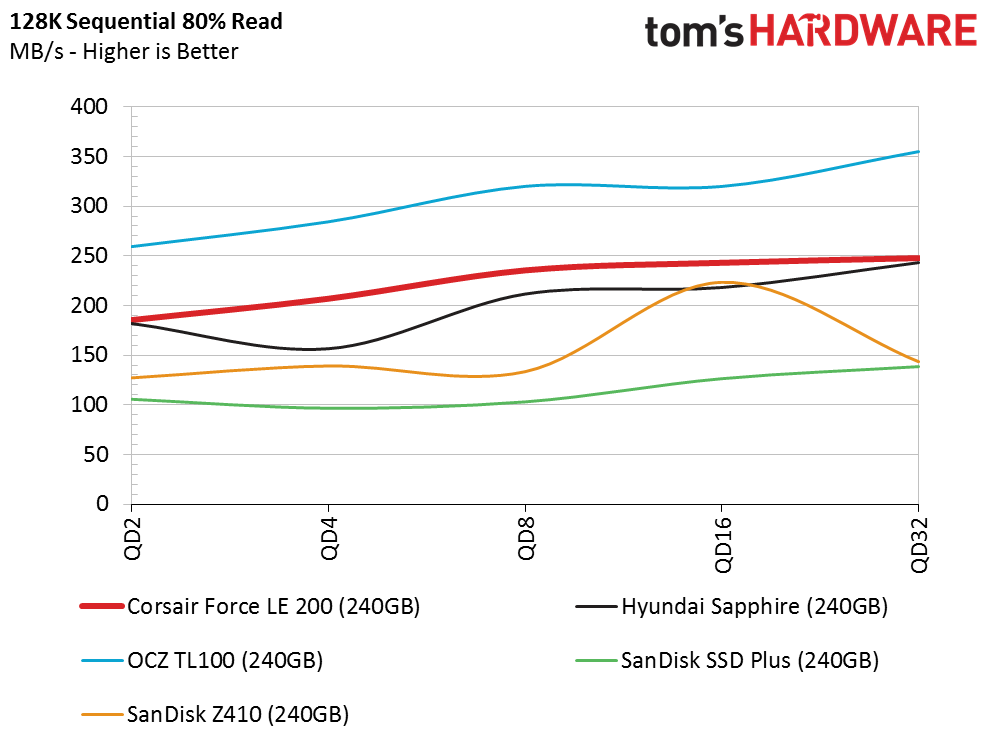
Sequential Read Performance
To read about our storage tests in-depth, please check out How We Test HDDs And SSDs. We cover four-corner testing on page six of our How We Test guide.
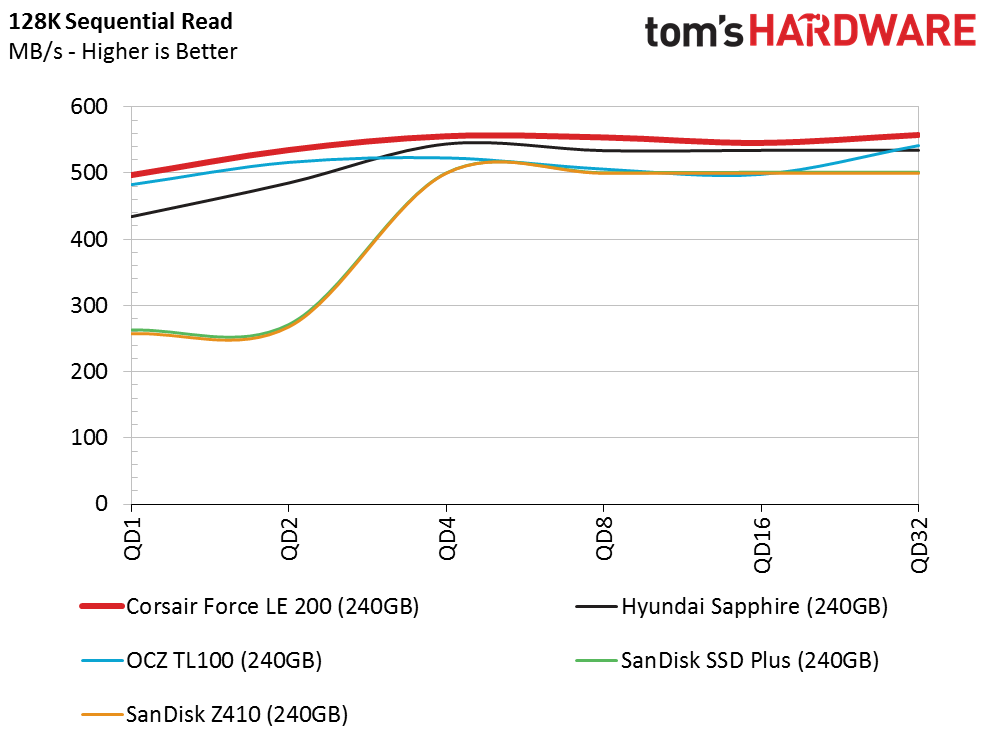
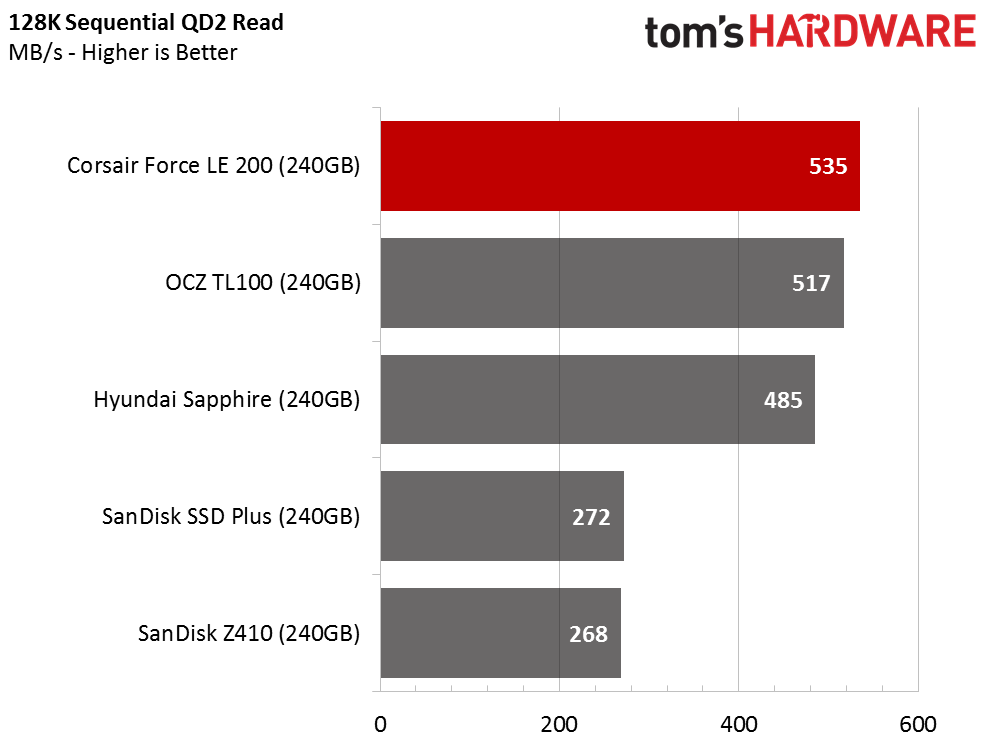
The Corsair Force LE200 has a shot at the title of the highest-performing DRAMless retail SSD. That is due to the other SSDs having very weak performance, rather than the LE200 being an exceptional SSD. The LE200 delivers strong sequential read performance and can sustain the pace at high queue depths. The single-core SSD controller may suffer under heavier workloads, so we'll keep an eye out for issues during our mixed workload testing.
Sequential Write Performance
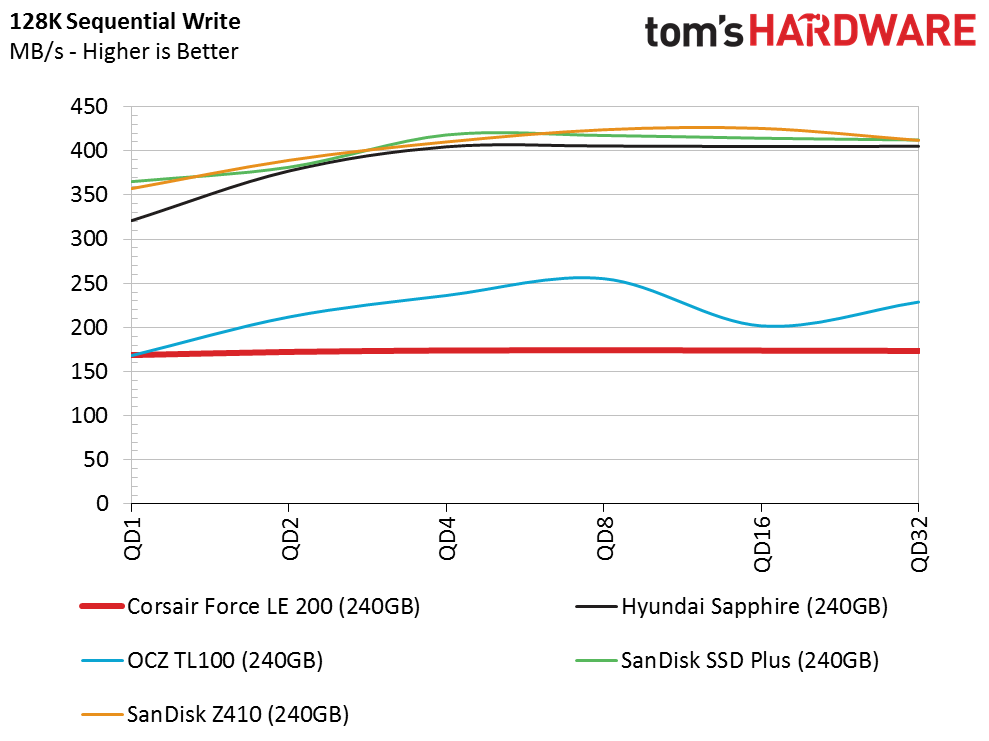
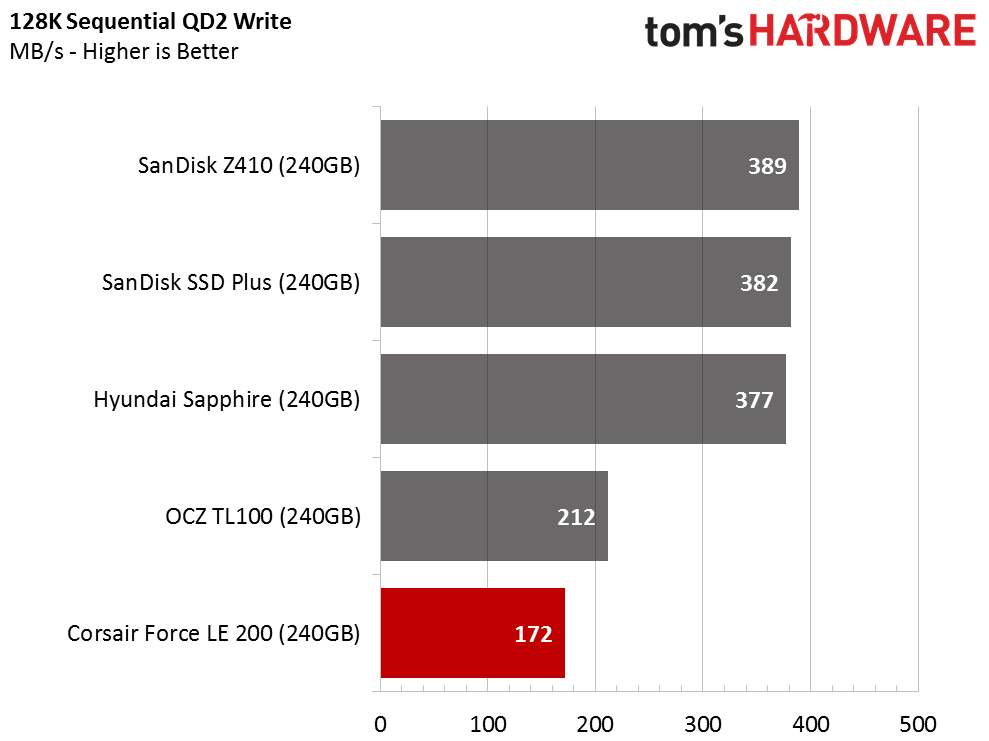
The S11 controller could suffer from performance issues because only one core manages both foreground and background activity. The Force LE200 240GB provided roughly 500 MB/s of sustained sequential write throughput during our initial tests. This phase of testing follows other tests, so the drive has to manage the incoming data while shuffling existing data. Even after a fairly light workout, performance plummets to 300 MB/s.
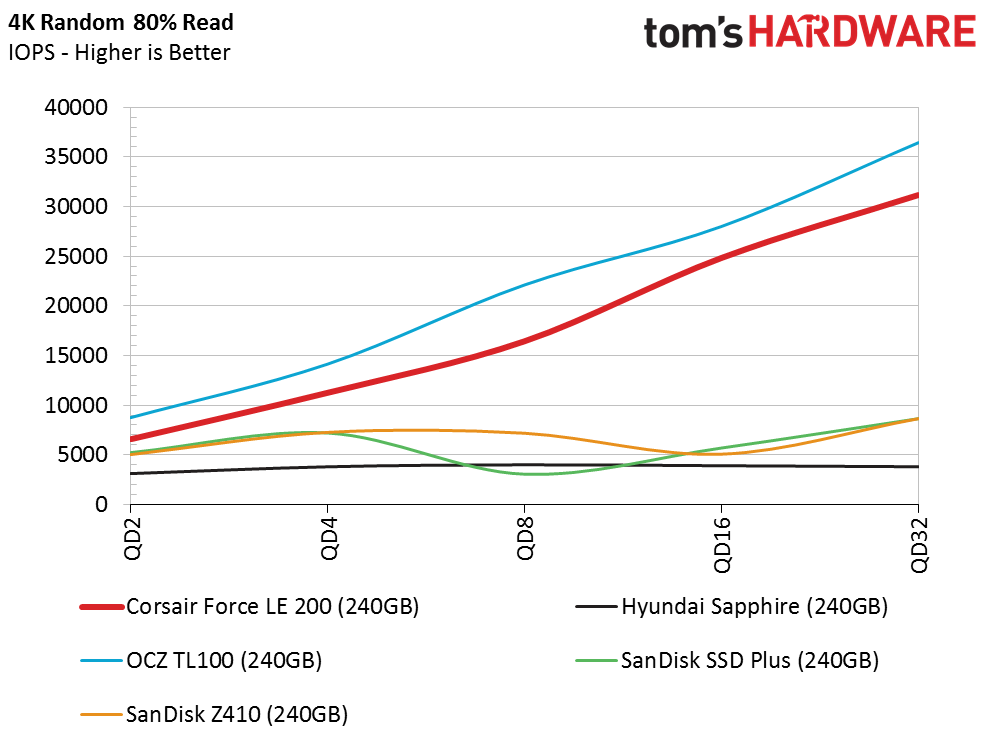
Random Read Performance
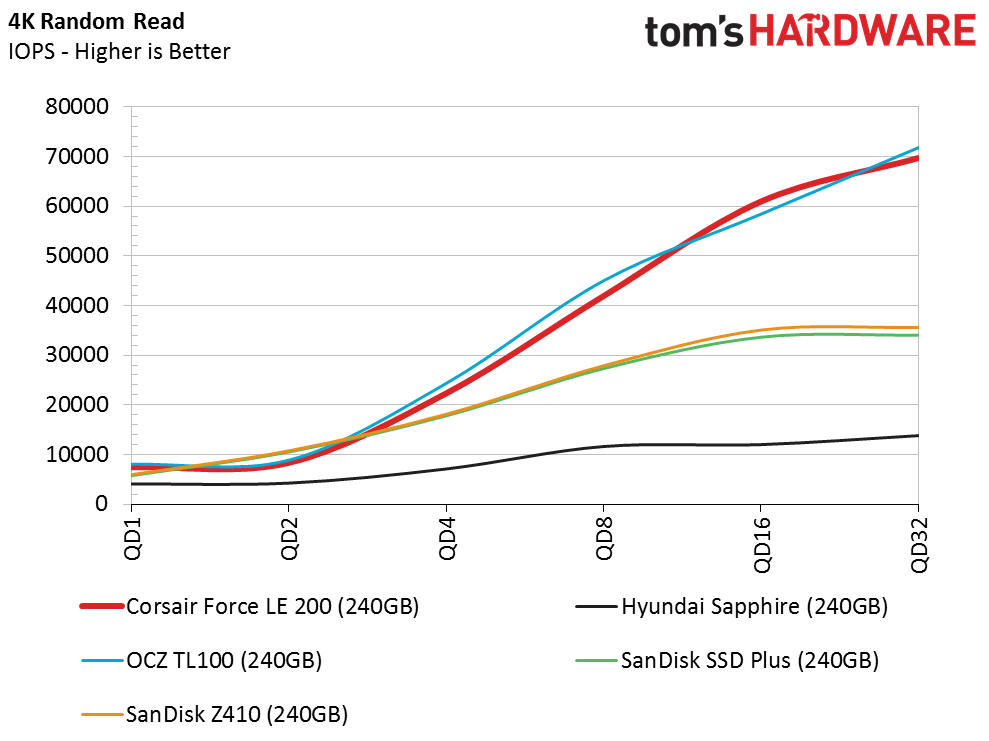
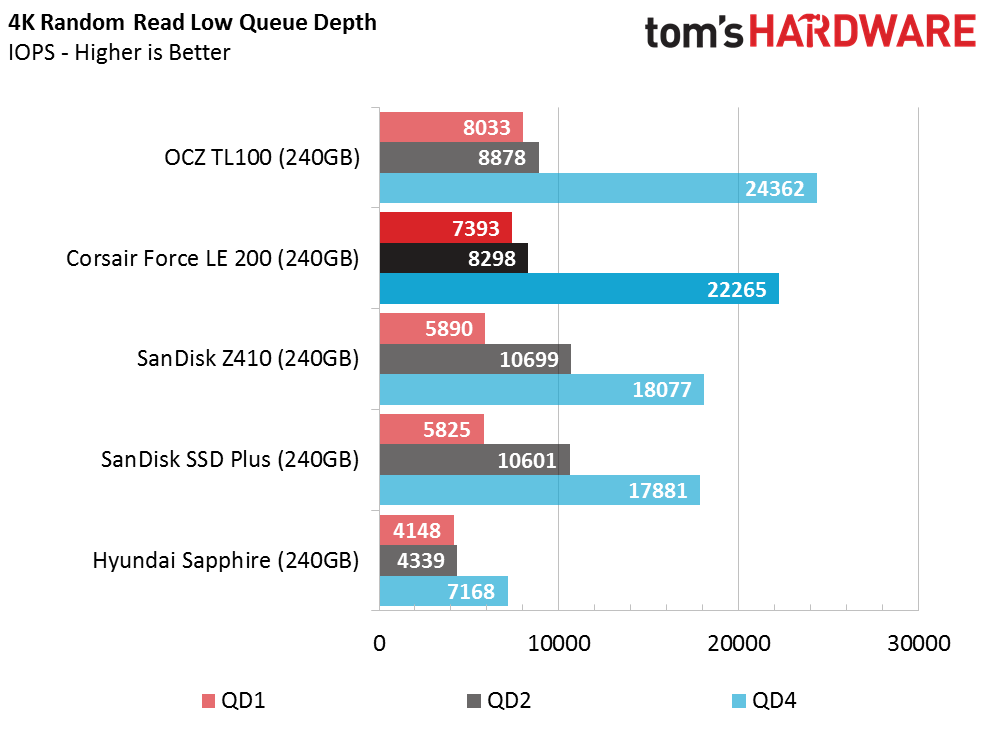
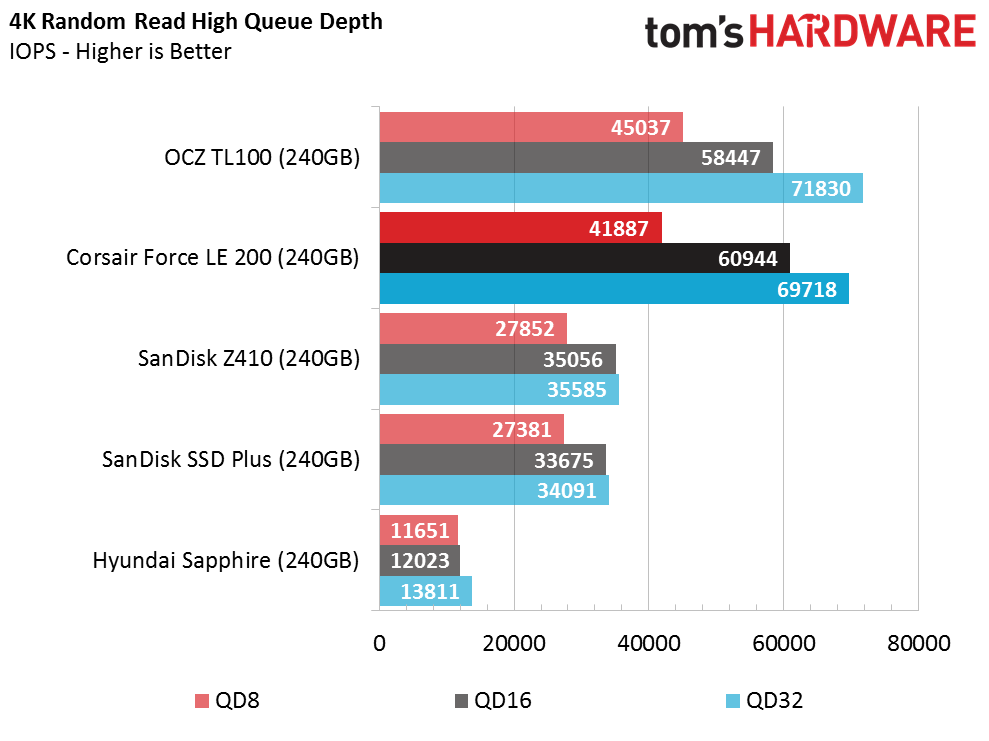
The Phison and Toshiba DRAMless controllers have similar architectures, and although the firmware and underlying IP are different, they are very close in many of the tests. Both drives scale well and offer higher random read IOPS than the other DRAMless SSDs we've tested. Queue depth (QD) 1 performance is the important data point here, though. The Force LE200 provides 7,300 IOPS at this critical measurement. That's a little higher than some TLC-based SSDs with DRAM.
Random Write Performance
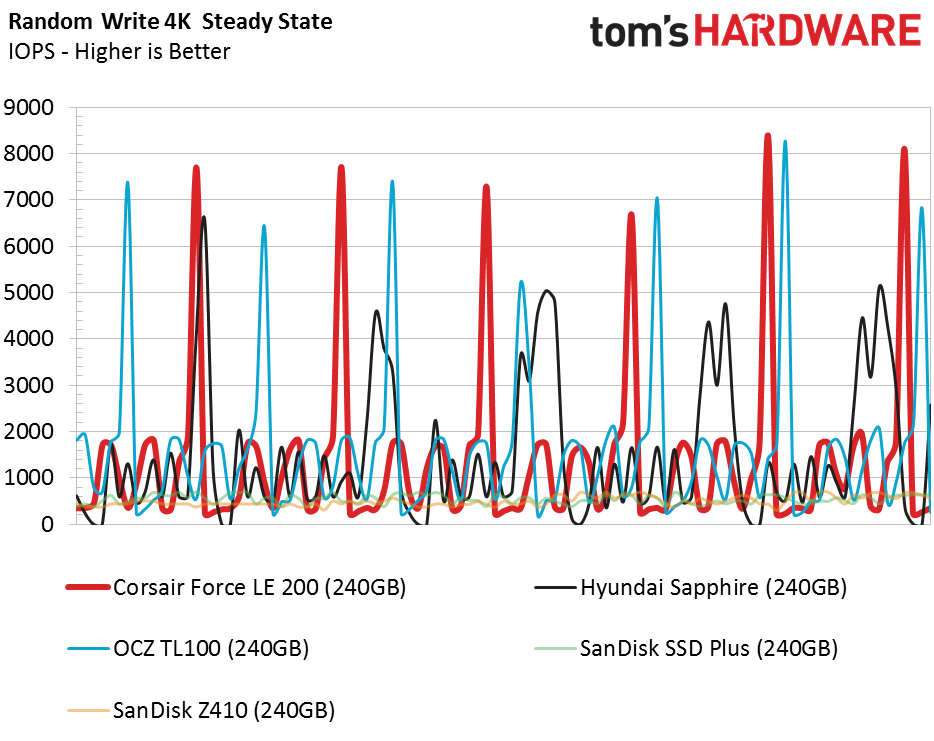
The low-QD random write performance is about half that of a similar SSD with DRAM. You will not use the full capabilities during light workloads but may notice slightly higher latency during longer bursts. This could emerge during several real-world tasks when small data writes occur in rapid succession.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
80 Percent Mixed Sequential Workload
We describe our mixed workload testing in detail here and describe our steady state tests here.
The Corsair Force LE200 sports high sequential read and write throughput, so it naturally delivers a solid result in the mixed workload. The OCZ TL100 scores much better, though. A few years ago, OCZ began focusing on mixed workloads and tuning for real-world software rather than benchmarks. That shift just happened to occur after reviewers began testing mixed workloads.
80 Percent Mixed Random Workload
We observe the same general performance profile with the LE200 and OCZ TL100 during a mixed workload. Both drives scale well as we increase the queue depth, but the TL100 has a performance advantage over the Corsair Force LE200.
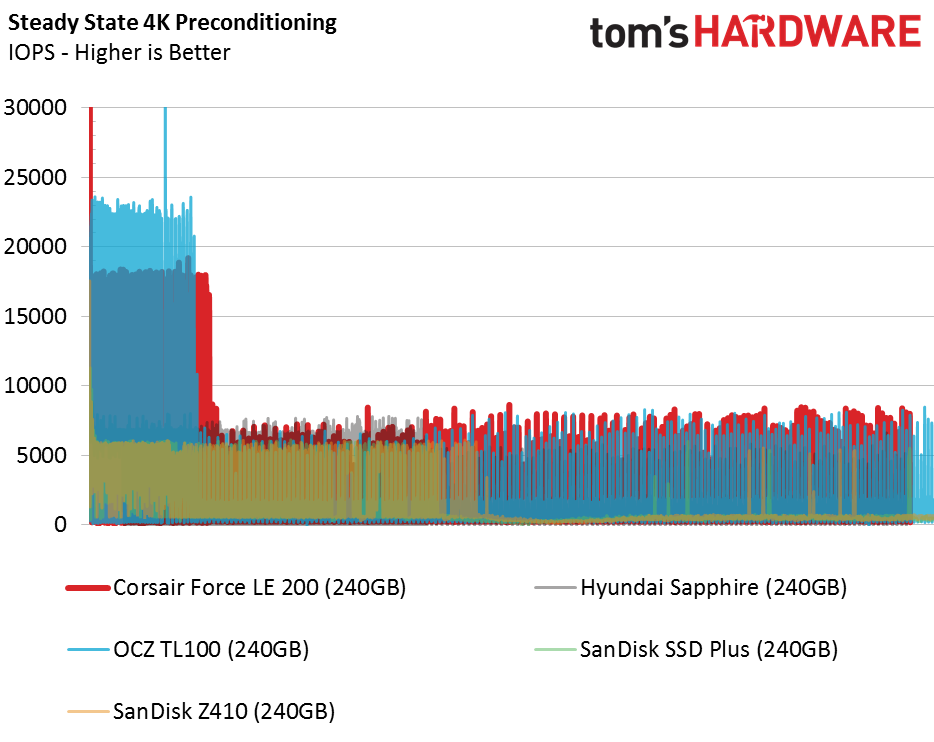
Sequential Steady-State
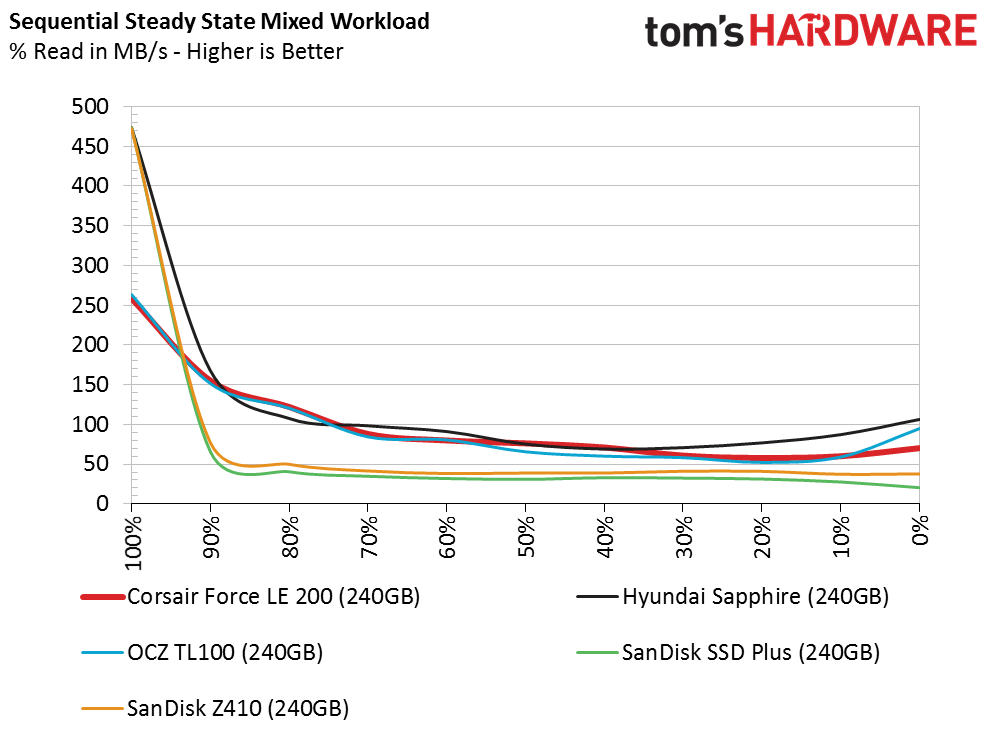
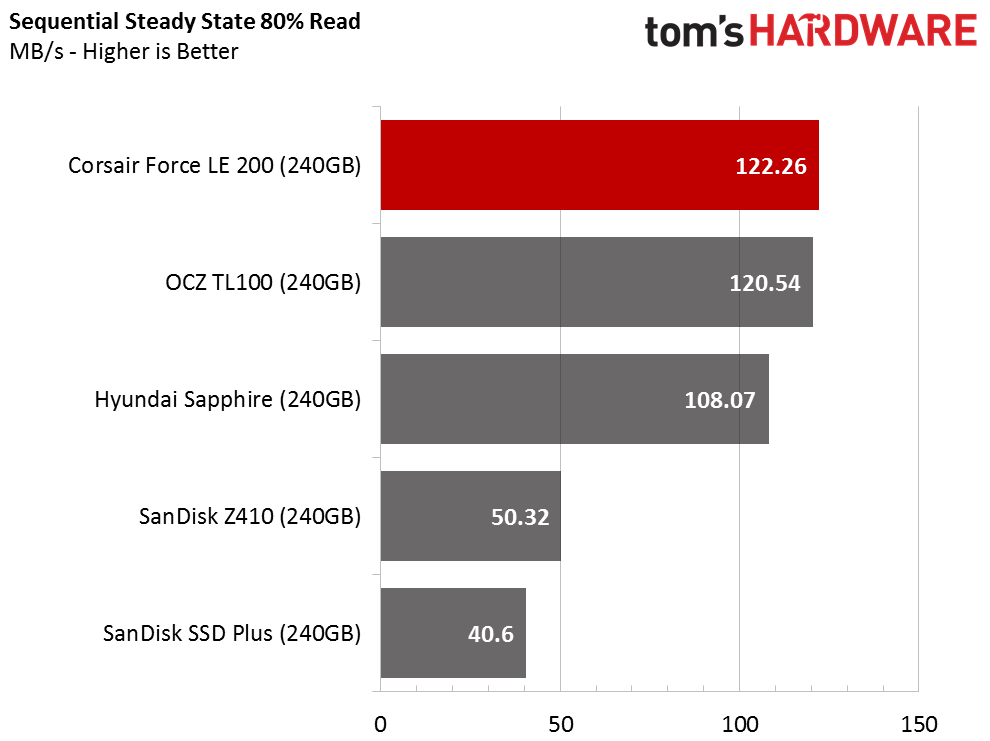
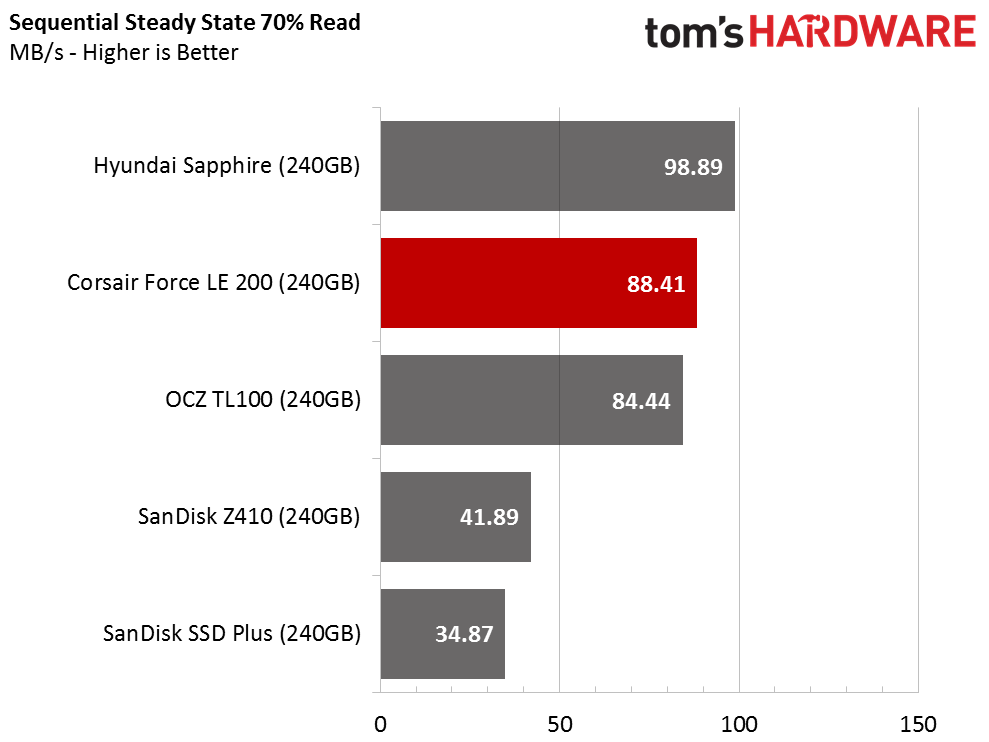
The DRAMless category is the polar opposite of workstation-focused products. Workstation users are more likely to encounter low levels of steady-state performance. DRAMless drives were not designed for these heavy workloads, and you will experience degraded performance if you use the SSD with a lot of data on the drive.
Random Steady-State


Unlike many of the other DRAMless products we've tested, Phison's superior firmware keeps the Corsair Force LE200 off the bottom of the chart. This workload is well beyond what the drive was designed for, but we still worry when an SSD delivers zero IOPS. It's important to remember the first consumer SSDs didn't have a DRAM buffer, so they gained a reputation for stuttering and system hangs.
PCMark 8 Real-World Software Performance
For details on our real-world software performance testing, please click here.
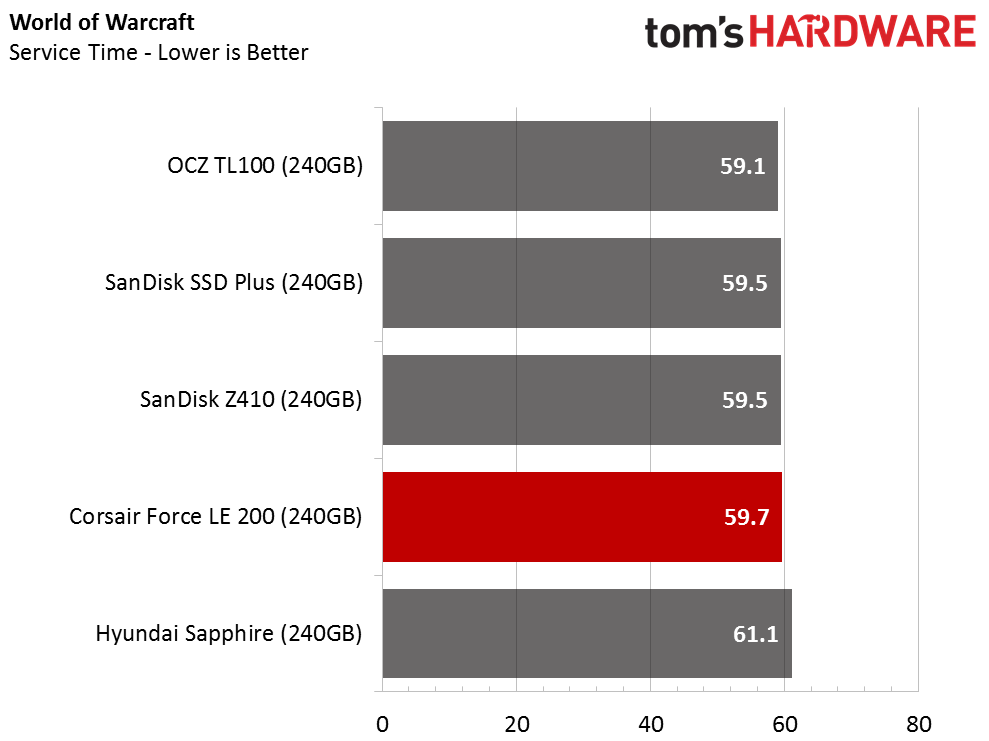
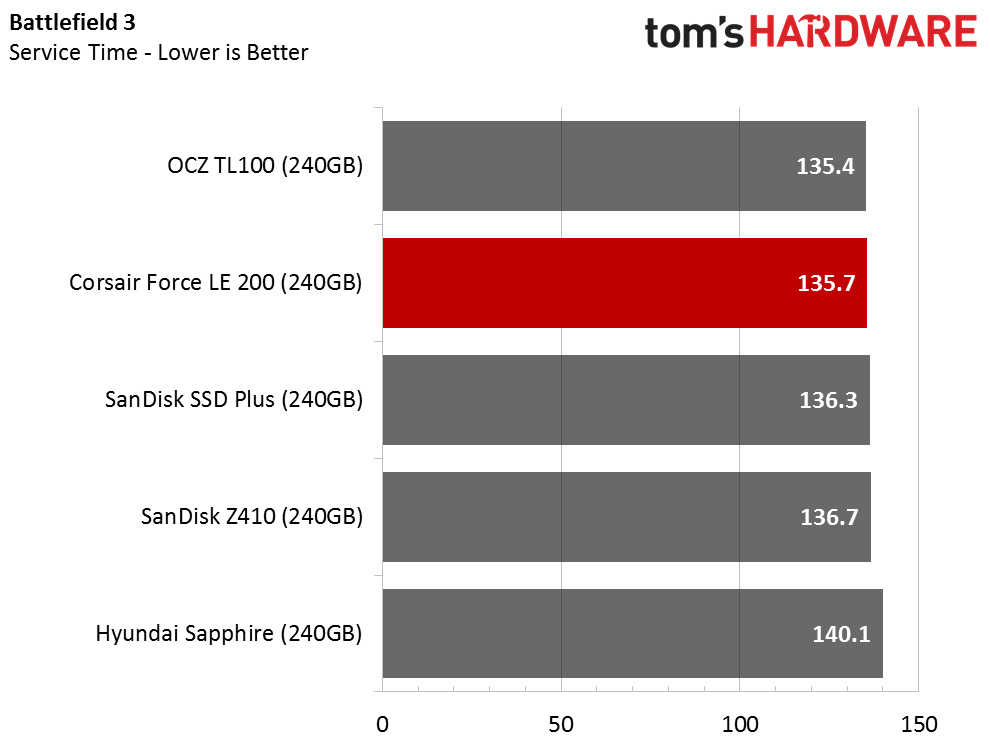
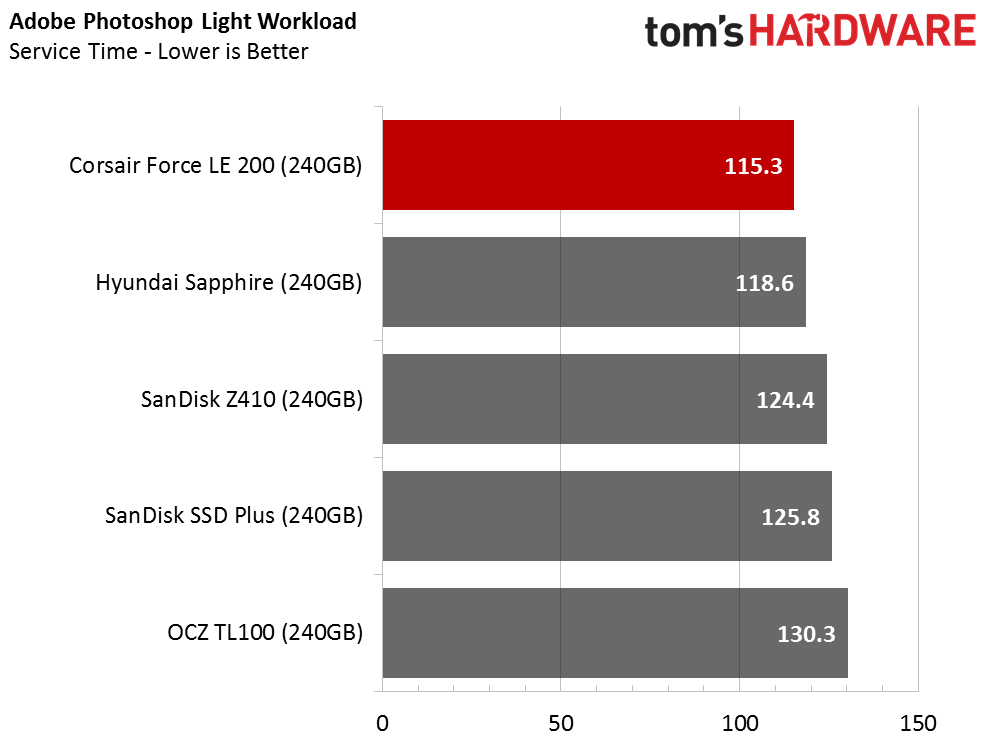
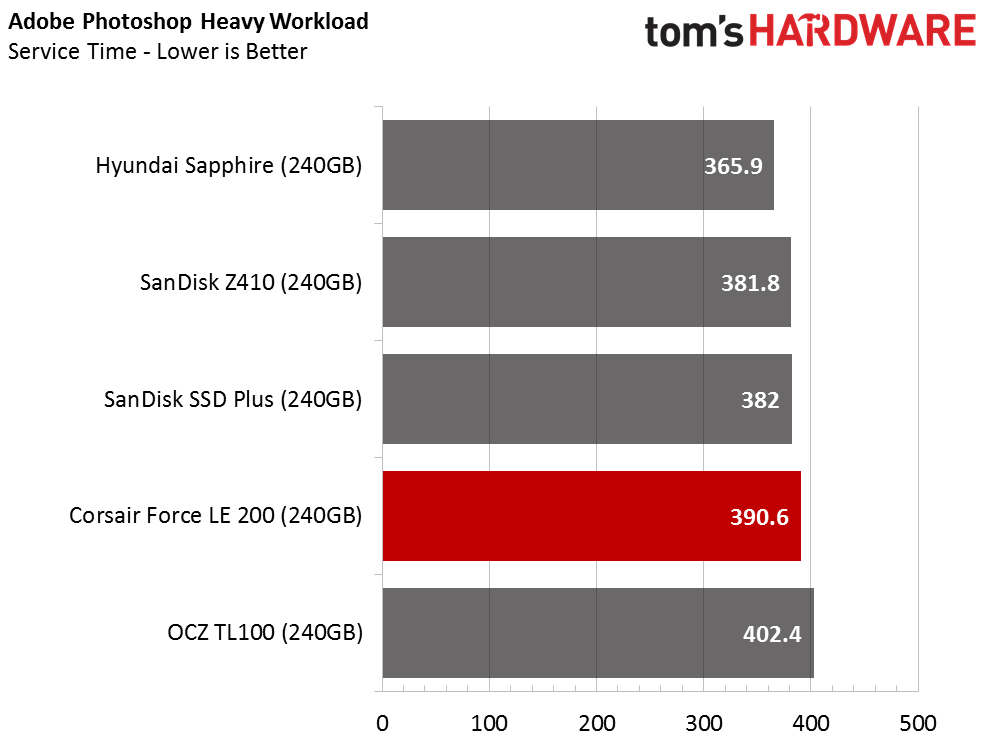
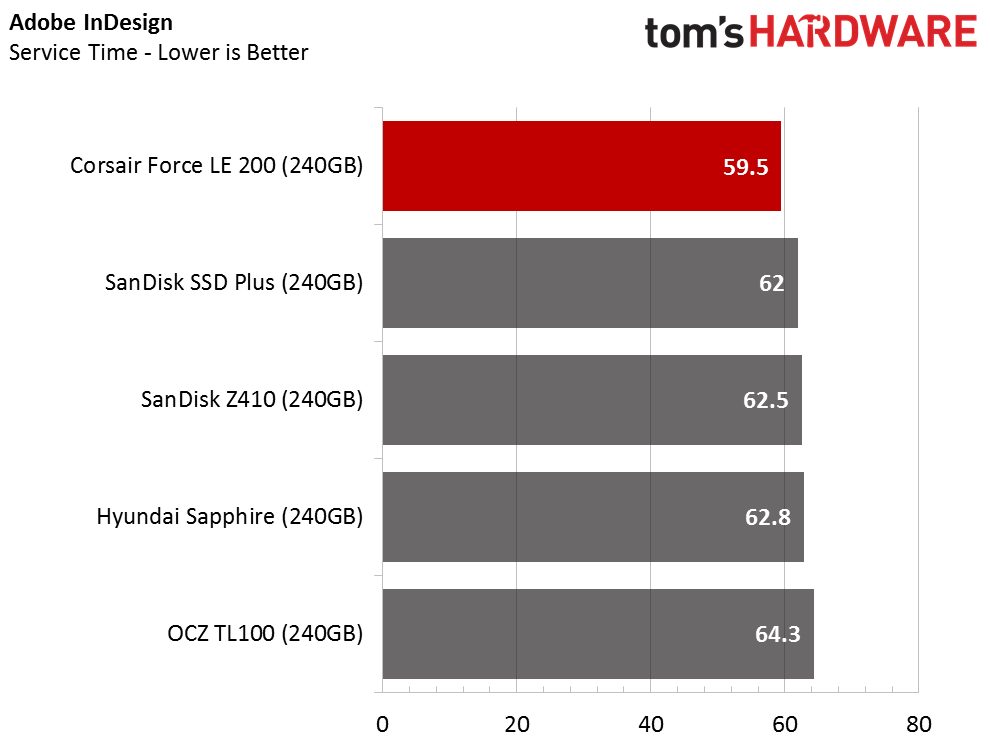
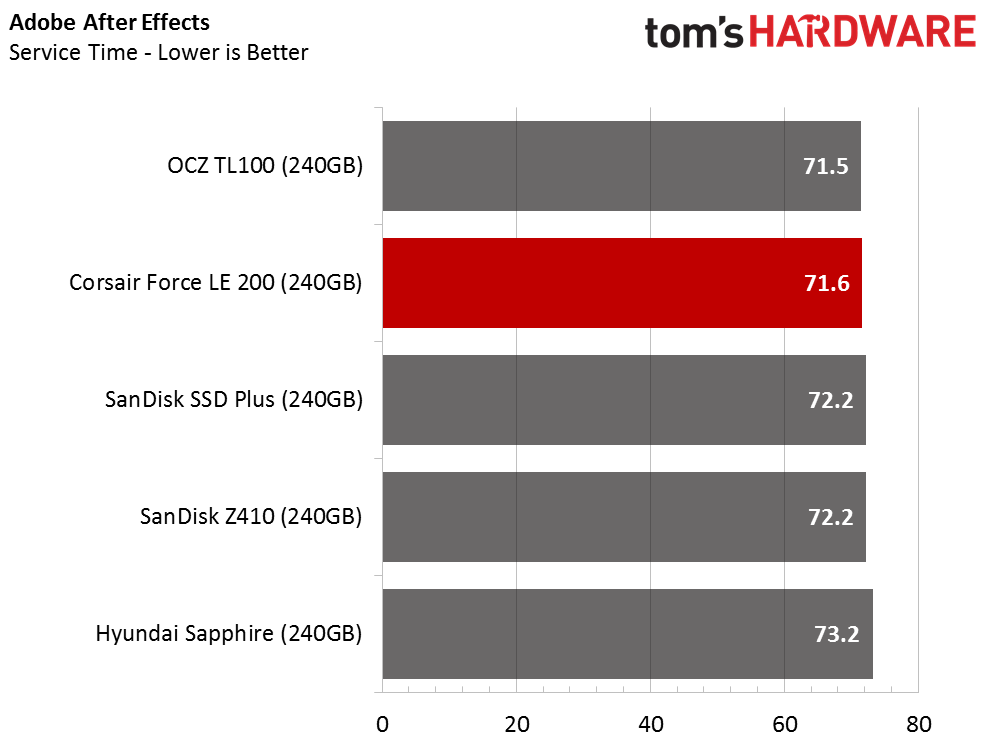
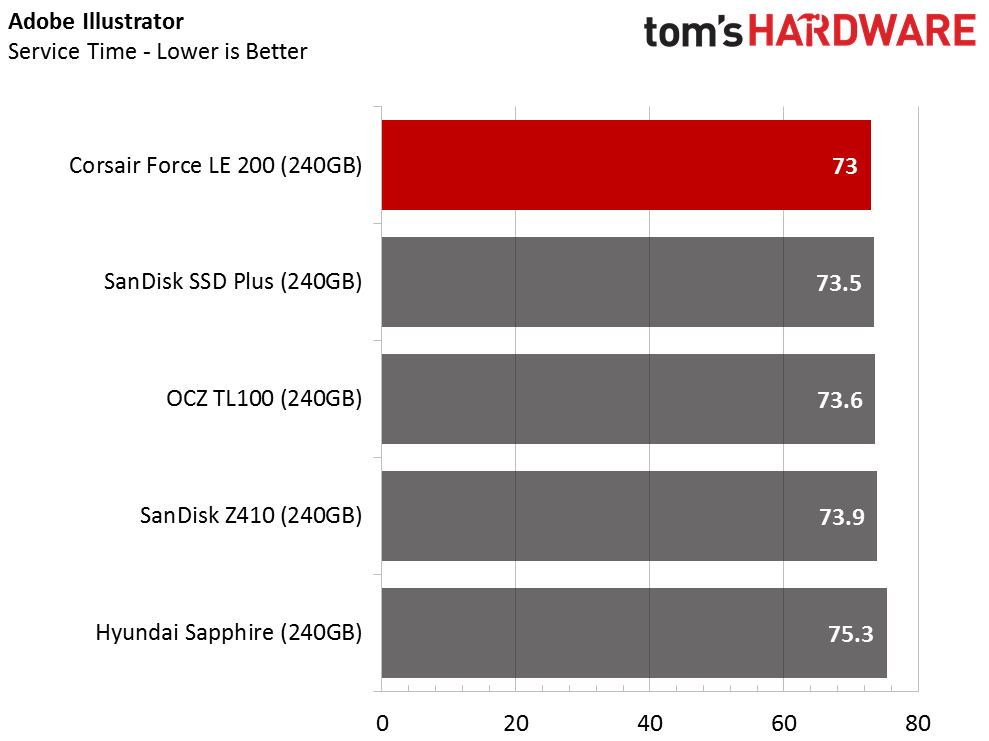
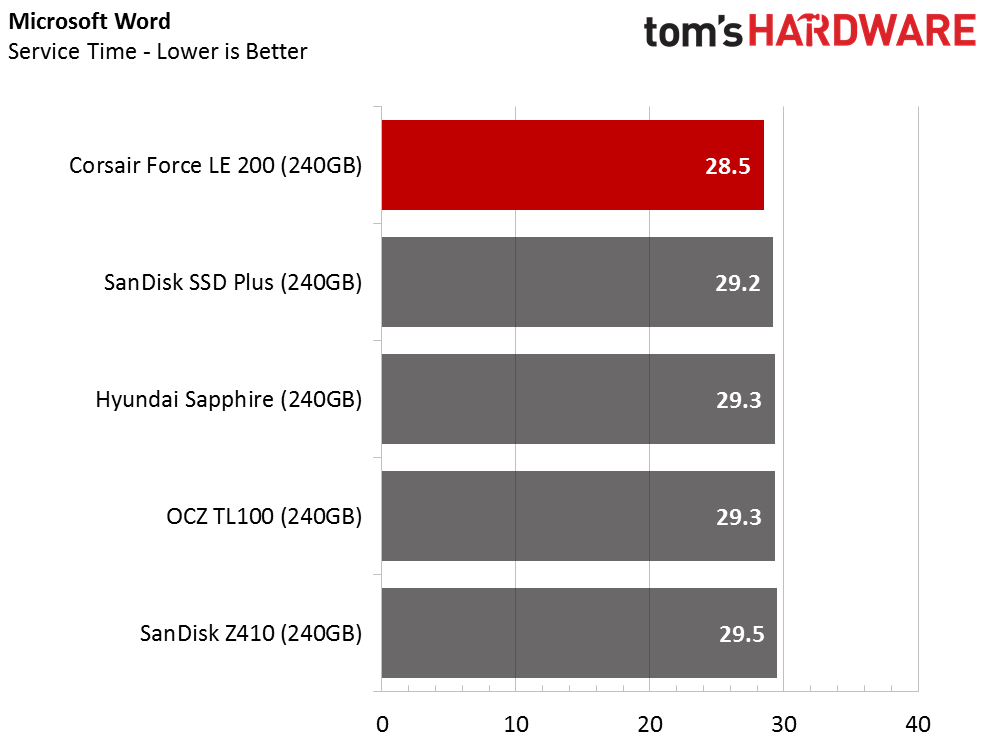
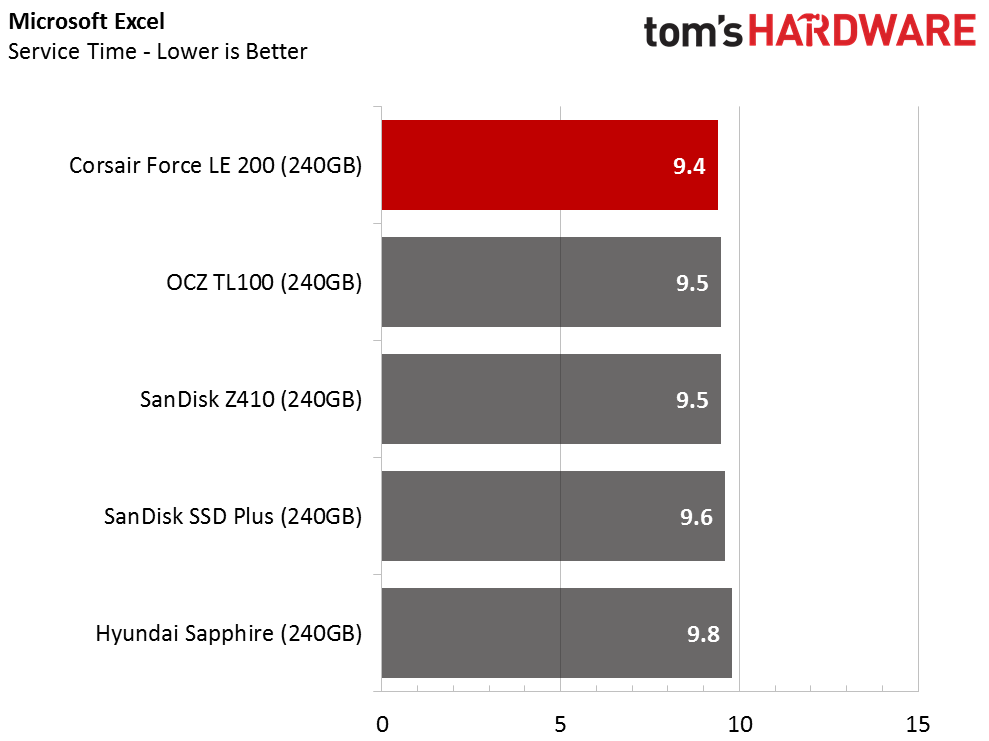
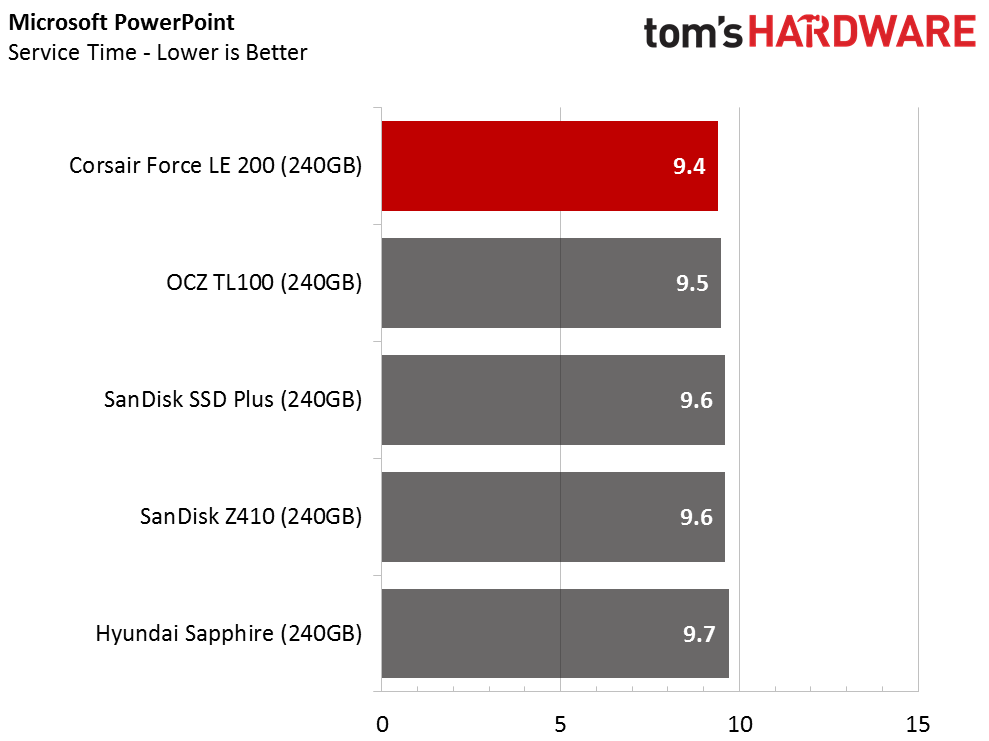
The Corsair Force LE200 performs well against the other DRAMless SSDs, but the results fall well short of traditional SSDs with a DRAM buffer. When the drive wins a test outright, it does so in spectacular fashion. When the Force LE200 loses a test, that is sometimes the case as well.
With the DRAMless drives, inconsistent performance is the root cause of poor performance. Our test runs each application three times and averages the results into a final measurement. With this class of products, the numbers can vary widely from one test to the next.
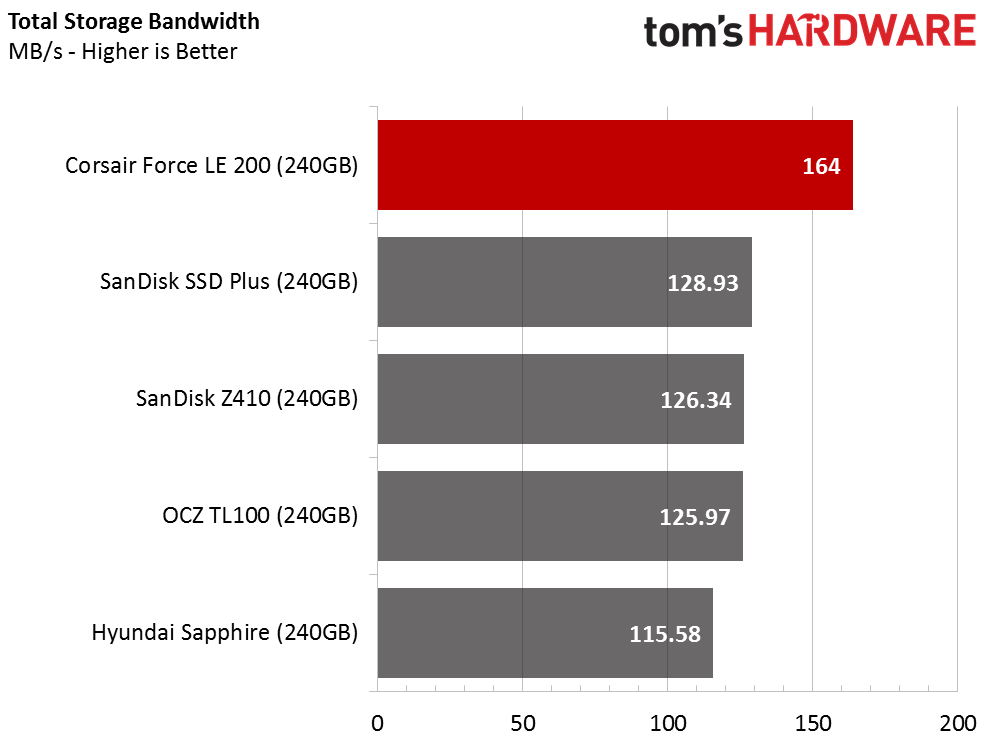
Application Storage Bandwidth
The important thing to keep in mind is that DRAMless SSD performance is much higher than a hard disk drive. To put that into perspective, the Seagate Barracuda Pro 10TB, the fastest consumer HDD on the market, scores 19.65 MB/s during this test. The Corsair Force LE200 240GB averages 164 MB/s.
PCMark 8 Advanced Workload Performance
To learn how we test advanced workload performance, please click here.
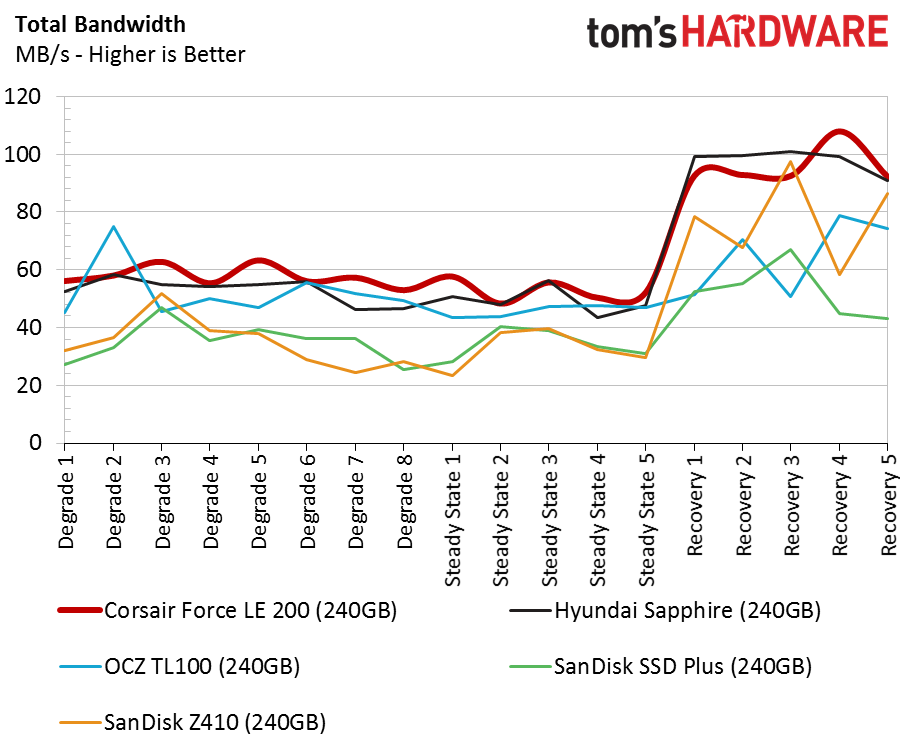
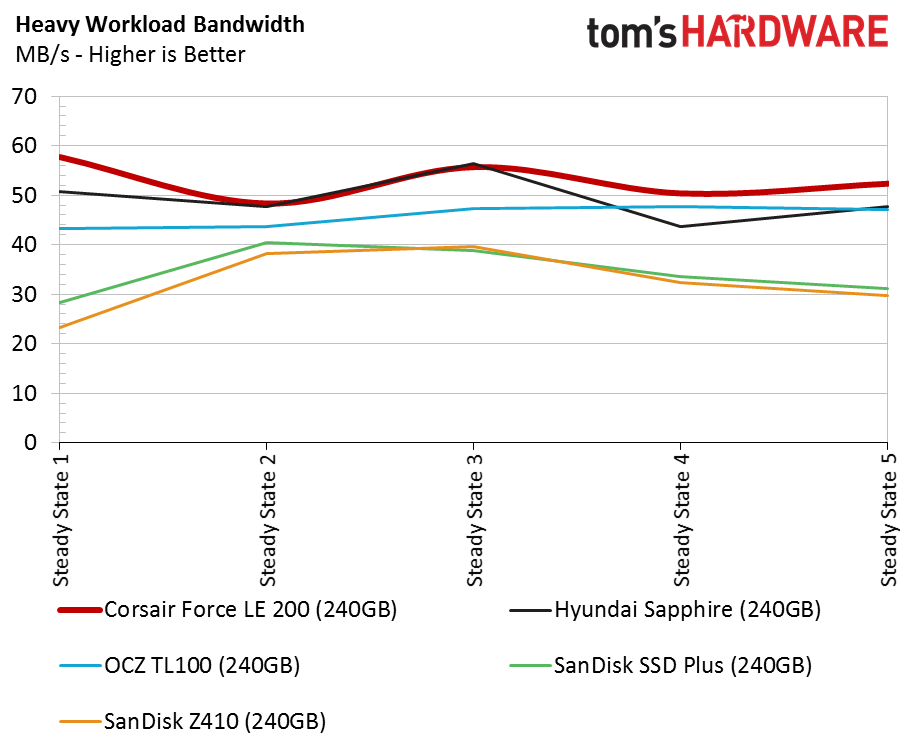
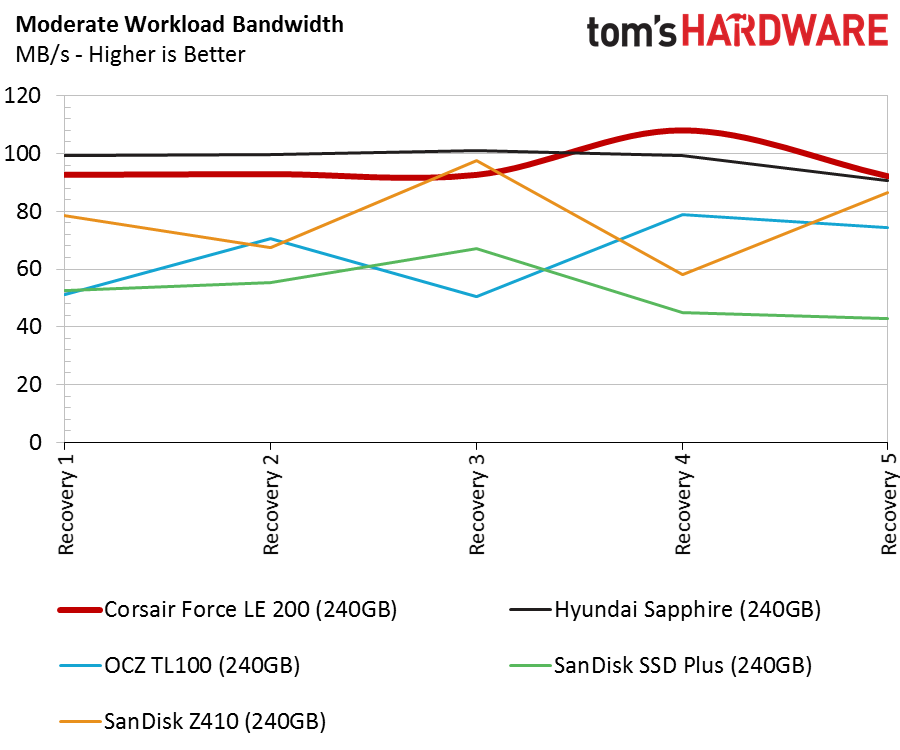
DRAMless products are designed for limited writes and light applications. As such, we only focus on the moderate workload chart and the five recovery stages. The Force LE200 outperforms the other DRAMless SSDs in most of these tests, but throughput results are only part of the story.
Total Service Time
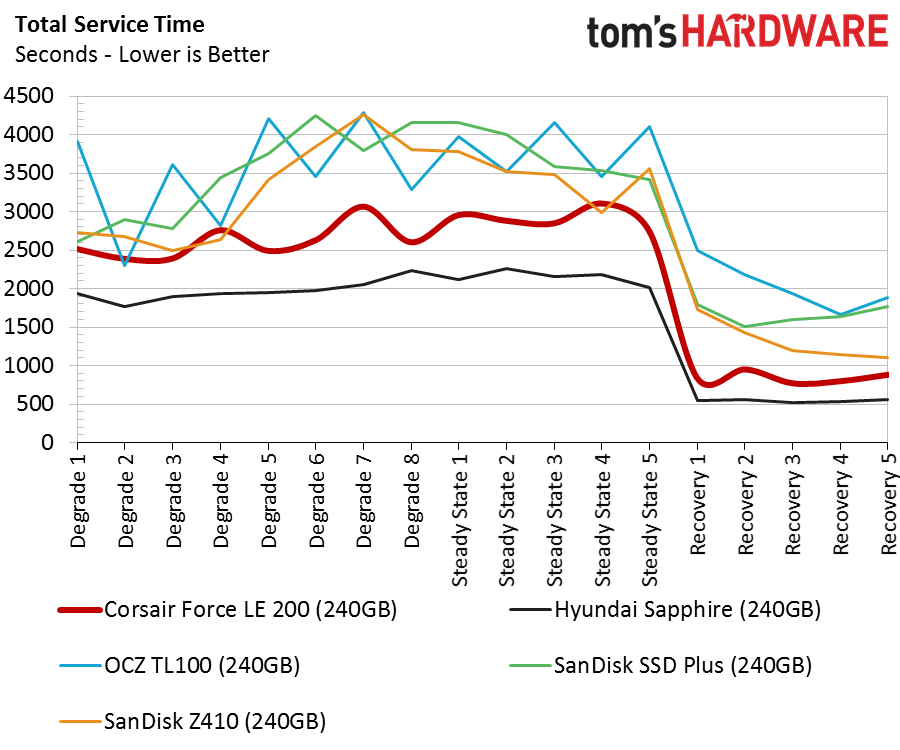
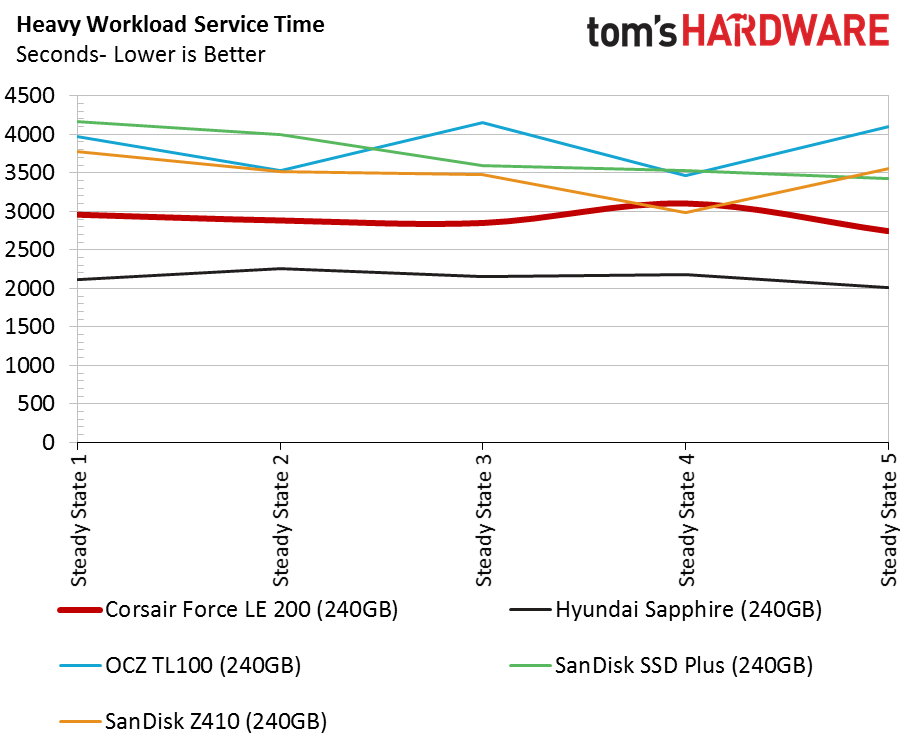
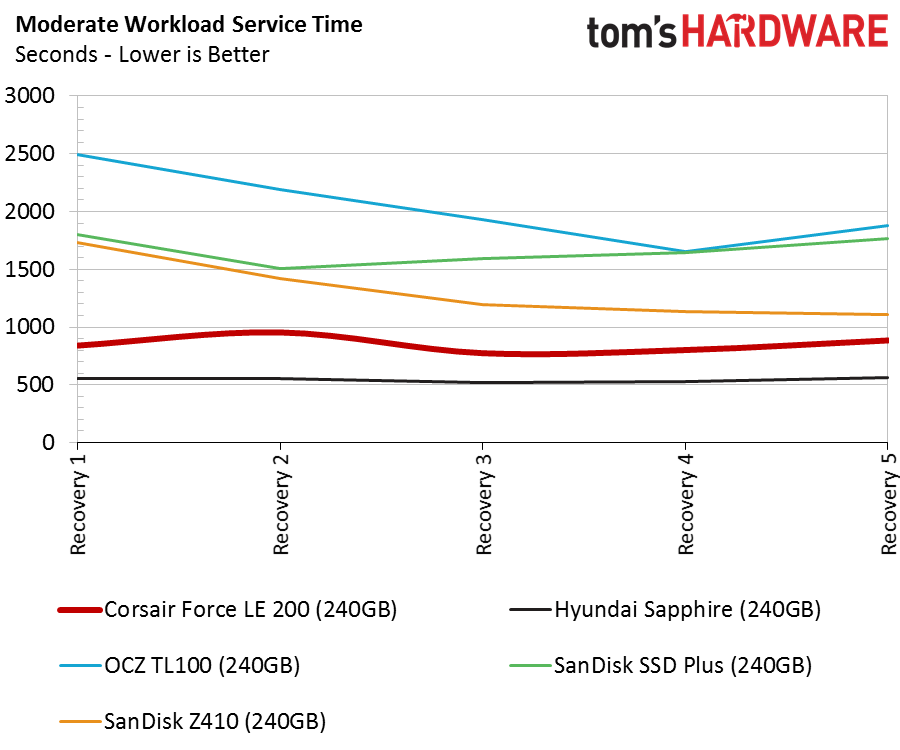
Compared to regular SSDs, all the drives exhibit poor service time metrics in the recovery stages. The SanDisk Extreme Pro, one of the fastest consumer SATA SSDs, scores around 100 seconds during the recovery phases. That is a 5x performance increase compared to the Hyundai Sapphire, and a 10x increase compared to the Force LE200.
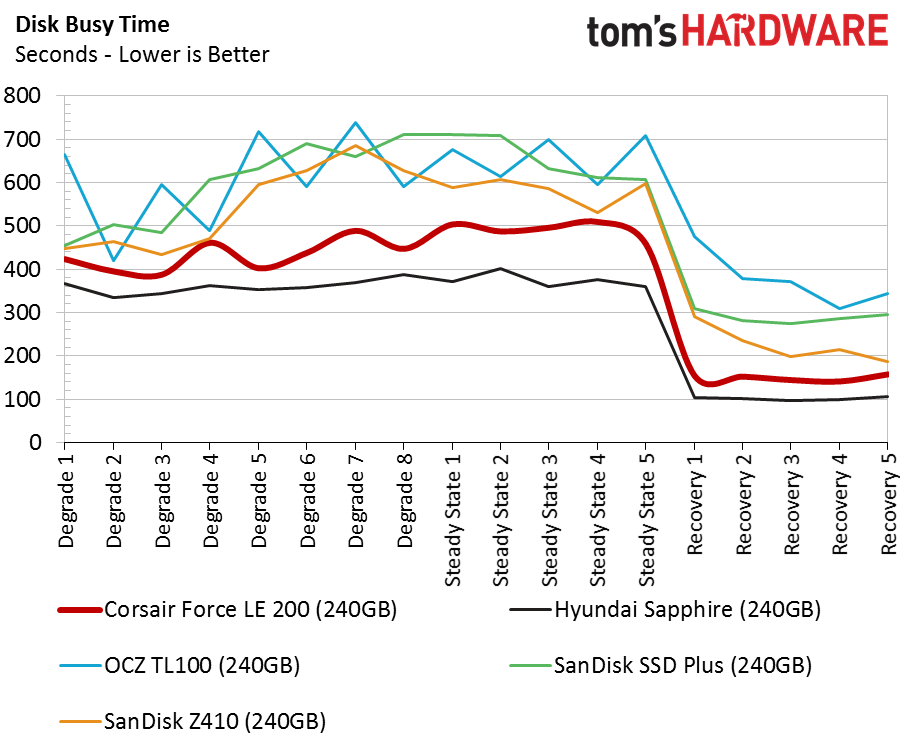
Disk Busy Time
Many have concluded that the difference in performance between SATA SSDs is minimal. That line doesn't work here. DRAMless SSDs are closer to regular SSDs than they are to hard disk drives, but there is still a very wide performance gap between them and regular SSDs.
Responsiveness Test
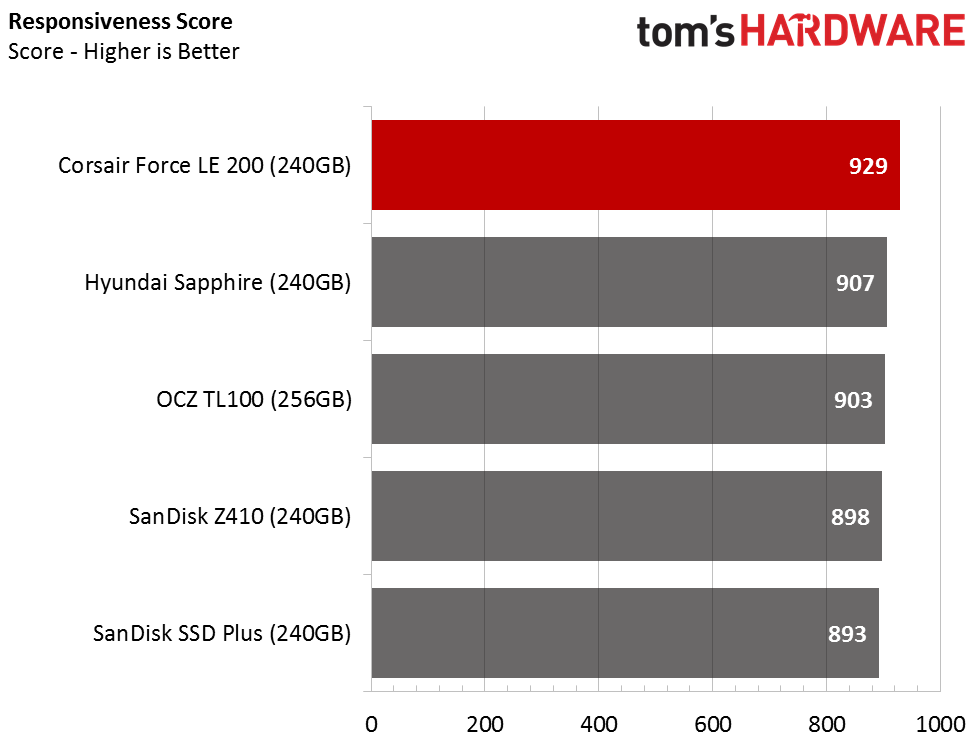
The Responsiveness Score comes from BAPCo's new SYSmark 2014 SE system test. The company added latency measurements generated from real-world software. Of the DRAMless drives, the Force LE200 delivers the best user experience.
Notebook Battery Life
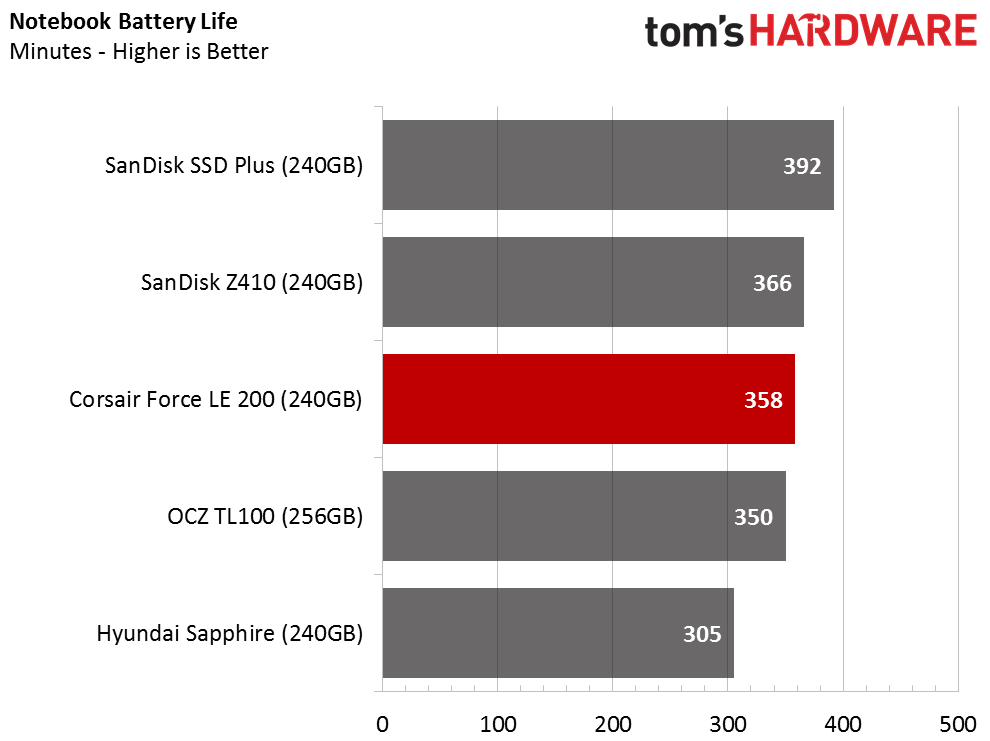
Phison controllers ran into a power issue with the PS5007-E7 NVMe, but that didn't carry over to the S11. DRAMless SSDs can provide very good battery life without a DRAM package consuming extra power, but I don't think many DRAMless products have been fully optimized for this purpose. The Force LE200 doesn't deliver the same battery time as the SanDisk SSD Plus, but the previous tests show that the SSD Plus falls short in other areas.

Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
hdmark Am i missing something or is this pricing way too high even for release? an 850 evo is 8$ more right now on amazon and crucials mx300 275gb is retail at 99$. Shouldnt the initial price have to be much lower considering the performance drop?Reply
the 70$ price by june might make it more reasonable? -
Snipergod87 The product at this price point doesn't make sense when you can an 850 EVO 250 GB for a few dollars more, also the 30TB of endurance is rather weak.Reply -
Andrew_190 ummmm im right there with HDMARK i know SSD (well RAM in general) has gone up for reasons that don't make sense (illuminati) as just a few months ago i was grabbing Crucial 275 drives for around 80 and and there 525GB drives i grabbed for 120. So how is this entry level???????????Reply -
Co BIY Is an NMVe capable SSD that is also SATA backward compatible technologically reasonable or would the cost of two interface capabilities be excessive?Reply
Does the DRAM savings really make that much of a difference ?
How are these DRAMless devices getting so much throughput with a single channel while the high end controllers need eight channels ? Is the scaling on additional channels efficient ? -
3ogdy $100 for 240GB? I know we're in the middle of a NAND shortage, but man...that is a lot for 240GB in 2017. That should be the price of a half-terabyte SSD.Reply -
blazorthon We keep talking about shortages and such, but the simple fact is that you can only have a chip shortage if the companies decide to not make enough to force the price up. If all of them decide to make less than enough at the same time, then it's obviously colusion if there isn't a huge disaster wiping out half of the factories, which there isn't (even the previous situation with hard drives was blown way out of proportion).Reply -
popatim IMO the price to beat is PNY's CS1311 which performs a bit better and at a lower cost...Reply -
Brian_R170 Reply19678120 said:We keep talking about shortages and such, but the simple fact is that you can only have a chip shortage if the companies decide to not make enough to force the price up. If all of them decide to make less than enough at the same time, then it's obviously colusion if there isn't a huge disaster wiping out half of the factories, which there isn't (even the previous situation with hard drives was blown way out of proportion).
All NAND fabs combined can't make enough to satisfy the demand right now. They are all running at maximum capacity. Increasing yields (as mentioned in the article) will be the fastest way to increase supply. They can build more factories, but it takes a couple years and billions of $. They can switch to a better process technology, but that can take even longer and even more $. -
littleleo I think the SK Hynix performs better and is at a great price $95.58 & FREE Shipping on Amazon. I've watched prices increase steadily since October with no end in sight. The shortages are real and the explanations have been given over and over. The Hard Drive factory disaster that hit WD and affected the whole hard drive segment was real too. We saw it coming and went through it and came out the other side.Reply
When I see people still in denial about the Nand shortage, and the HDD factory flooding. I just have to wonder why are they so uninformed to the point I think they must be joking and are just baiting people. -
CRamseyer We just have a few more months....like 6ish. Samsung ramps up a new fab between now and mid-July. Toshiba will have their new fab up between now and the start of next year and IMFT (Micron / Intel) are about to release 64-layer to double capacities again. In just a few short months we should see bit output nearly double. I think we will make a 6 month stop at pre-shortage prices and then the bottom will fall out as yields improve. I think 2TB SSDs will become fairly common by this time next year and 512GB will be the new starting point (where 256GB is today).Reply