Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Advanced Transient Response Tests
For details about our transient response testing, please click here.
In the real world, power supplies are always working with loads that change. It's of immense importance, then, for the PSU to keep its rails within the ATX specification's defined ranges. The smaller the deviations, the more stable your PC will be with less stress applied to its components.
We should note that the ATX spec requires capacitive loading during the transient rests, but in our methodology, we also choose to apply a worst case scenario with no additional capacitance on the rails.
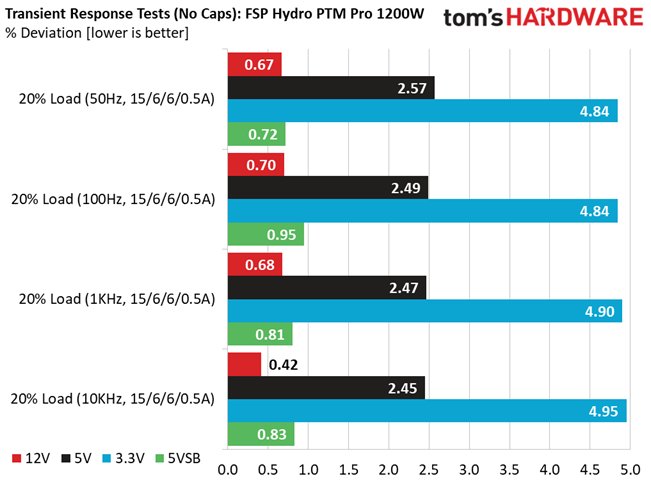
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.075V | 11.994V | 0.67% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.014V | 4.885V | 2.57% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.329V | 3.168V | 4.84% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.033V | 4.997V | 0.72% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 10ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.078V | 11.994V | 0.70% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.016V | 4.891V | 2.49% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.329V | 3.168V | 4.84% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.033V | 4.985V | 0.95% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.079V | 11.997V | 0.68% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.017V | 4.893V | 2.47% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.329V | 3.166V | 4.90% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.033V | 4.992V | 0.81% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.045V | 11.963V | 0.68% | Pass |
| 5V | 4.999V | 4.874V | 2.50% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.315V | 3.153V | 4.89% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.003V | 4.959V | 0.88% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 10ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.047V | 11.963V | 0.70% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.000V | 4.868V | 2.64% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.315V | 3.156V | 4.80% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.003V | 4.964V | 0.78% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.048V | 11.951V | 0.81% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.001V | 4.874V | 2.54% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.316V | 3.147V | 5.10% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.003V | 4.966V | 0.74% | Pass |
Results 25-29: Transient Response
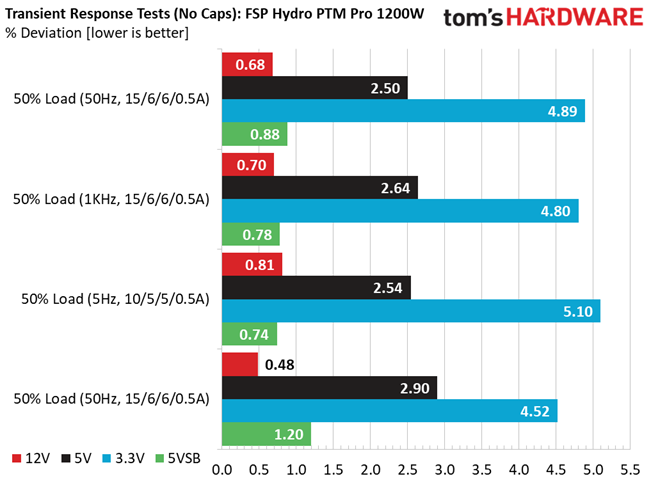
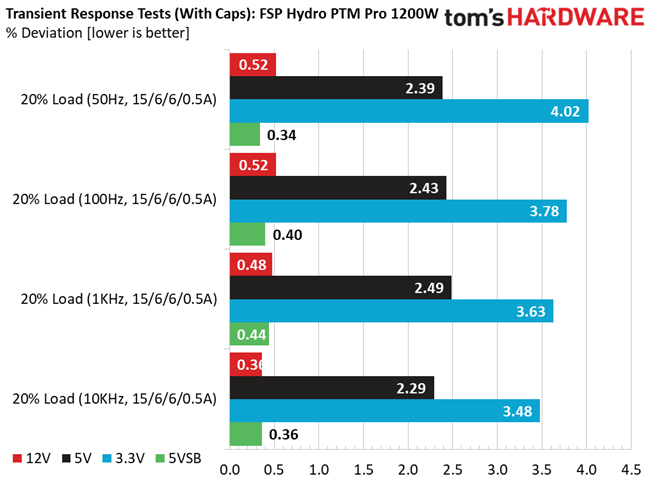
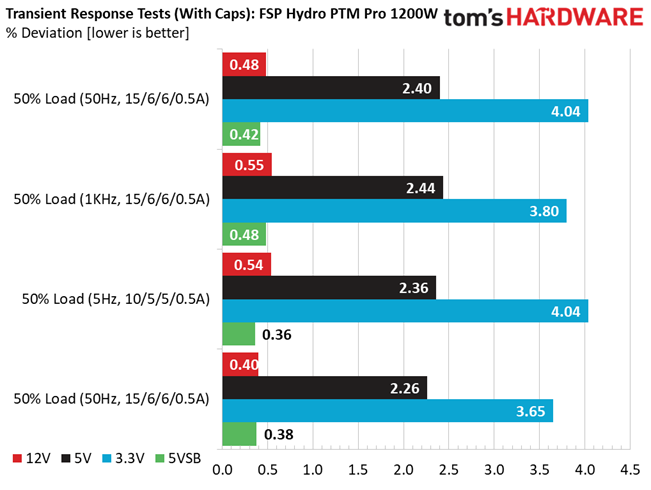
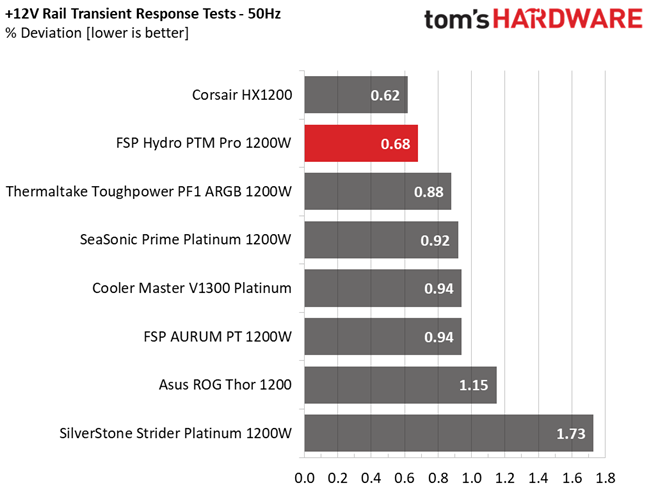
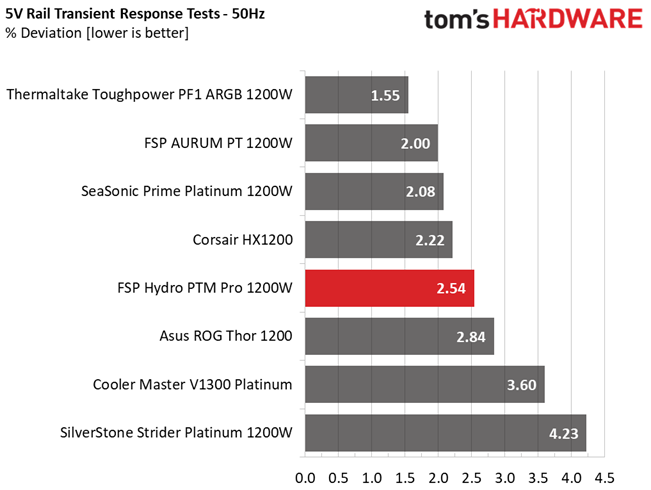
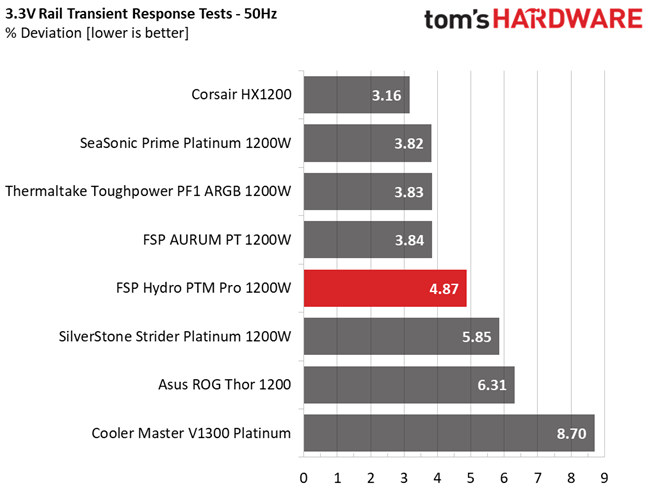
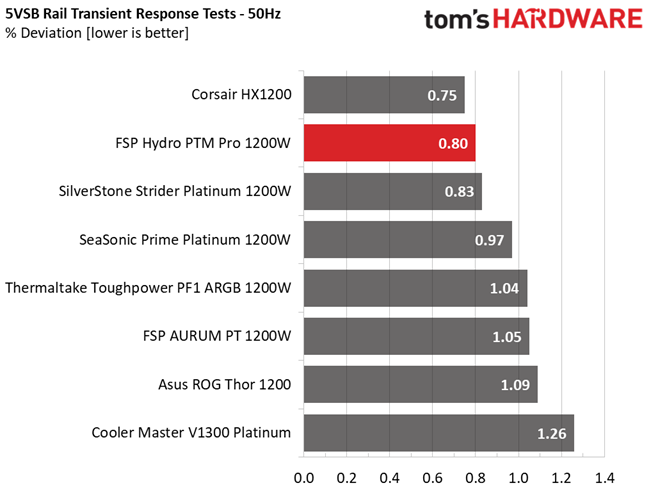
The 12V rail has good transient response. We cannot say the same, though, for the minor rails.
Turn-On Transient Tests
In the next set of tests, we measure the PSU's response in simpler transient load scenarios—during its power-on phase. Ideally, we don't want to see any voltage overshoots or spikes since those put a lot of stress on the DC-DC converters of installed components.
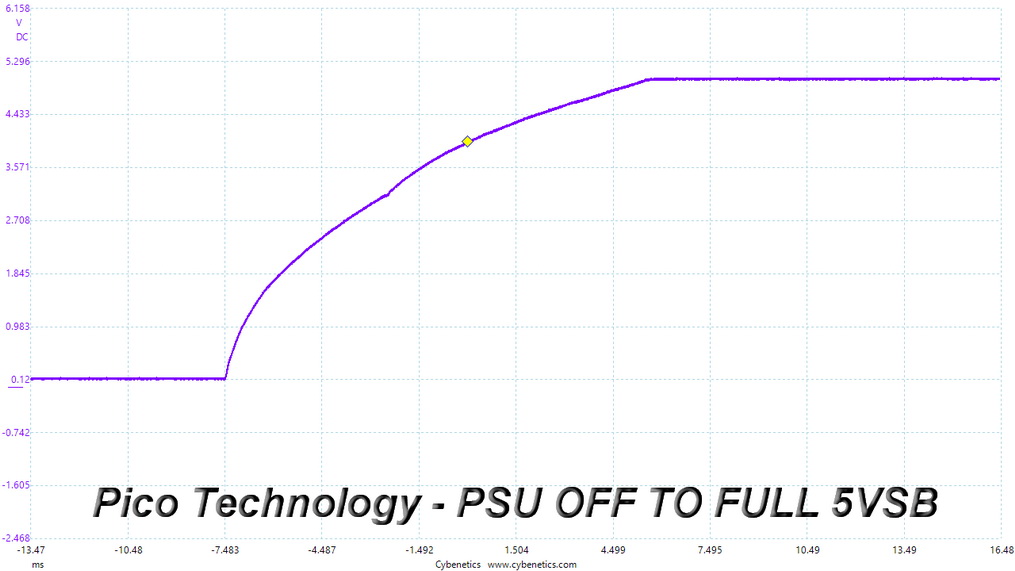
Turn-On Transient Response Scope Shots
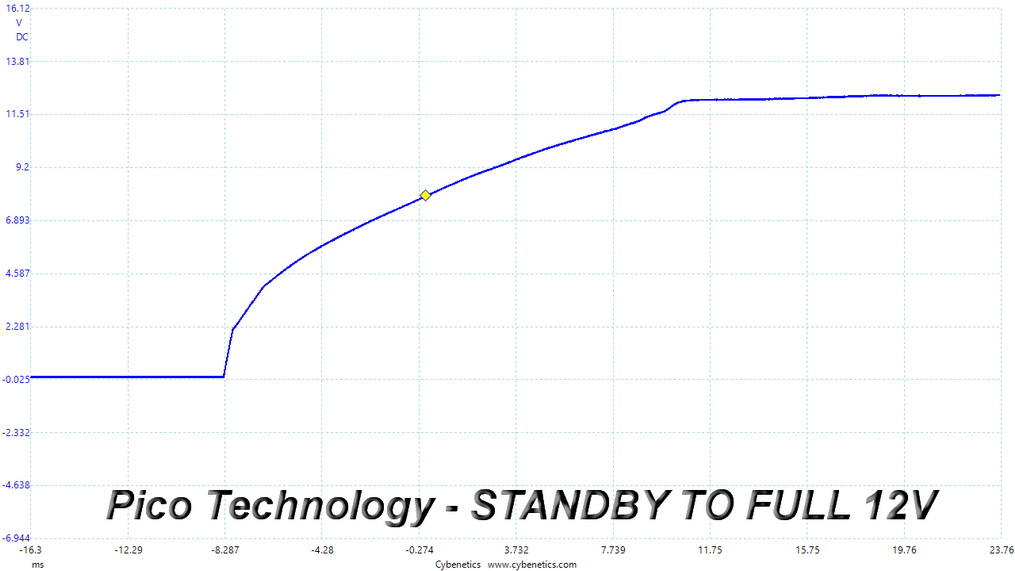
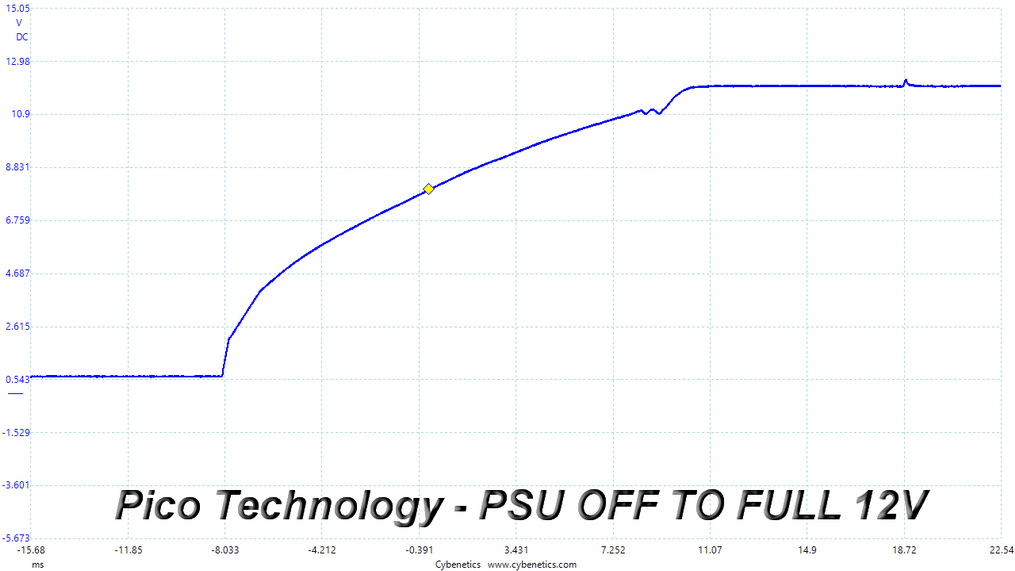
There are no spikes or voltage overshoots in these tests.
Power Supply Timing Tests
There are several signals generated by the power supply, which need to be within specified, by the ATX spec, ranges. If they are not, there can be compatibility issues with other system parts, especially mainboards. From year 2020, the PSU's Power-on time (T1) has to be lower than 150ms and the PWR_OK delay (T3) from 100 to 150ms, to be compatible with the Alternative Sleep Mode.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
| T1 (Power-on time) & T3 (PWR_OK delay) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Load | T1 | T3 |
| 20% | 77ms | 265ms |
| 100% | 81ms | 270ms |
The PWR_OK delay is out of the 100-150ms region, so the PSU does not support the alternative sleep mode recommended by the ATX spec. This is not a major issue since there are no mainboards available yet, supporting this feature. That said, a PSU should be as future-proof as it gets.
Ripple Measurements
Ripple represent the AC fluctuations (periodic) and noise (random) found in the PSU's DC rails. This phenomenon significantly decreases the capacitors' lifespan because it causes them to run hotter. A 10-degree Celsius increase can cut into a cap's useful life by 50%. Ripple also plays an important role in overall system stability, especially when overclocking is involved.
The ripple limits, according to the ATX specification, are 120mV (+12V) and 50mV (5V, 3.3V, and 5VSB).
| Test | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Pass/Fail |
| 10% Load | 7.1 mV | 6.8 mV | 17.1 mV | 13.7 mV | Pass |
| 20% Load | 10.0 mV | 7.6 mV | 17.3 mV | 20.3 mV | Pass |
| 30% Load | 11.0 mV | 8.9 mV | 17.3 mV | 23.0 mV | Pass |
| 40% Load | 12.0 mV | 9.0 mV | 17.7 mV | 22.4 mV | Pass |
| 50% Load | 12.8 mV | 10.0 mV | 19.8 mV | 23.7 mV | Pass |
| 60% Load | 10.5 mV | 10.3 mV | 20.6 mV | 24.3 mV | Pass |
| 70% Load | 12.0 mV | 10.8 mV | 21.1 mV | 30.4 mV | Pass |
| 80% Load | 12.4 mV | 11.1 mV | 22.7 mV | 33.1 mV | Pass |
| 90% Load | 13.3 mV | 11.9 mV | 23.2 mV | 33.7 mV | Pass |
| 100% Load | 22.8 mV | 12.6 mV | 26.1 mV | 36.1 mV | Pass |
| 106% Load | 23.1 mV | 12.5 mV | 27.4 mV | 35.3 mV | Pass |
| Crossload 1 | 12.3 mV | 12.9 mV | 20.9 mV | 13.1 mV | Pass |
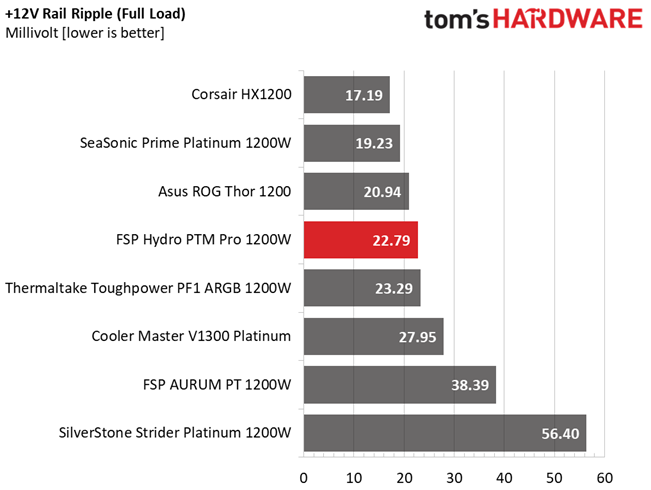
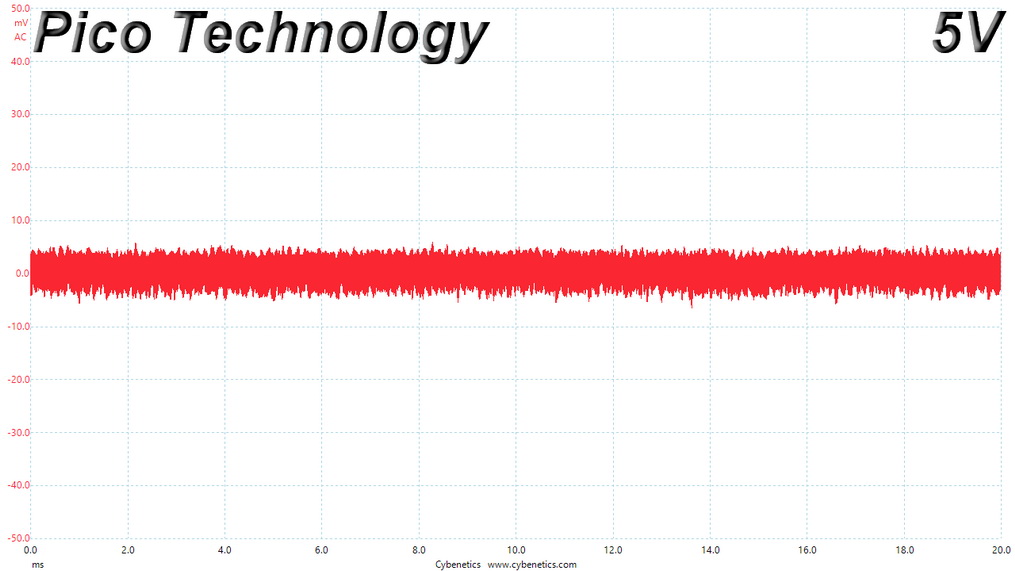
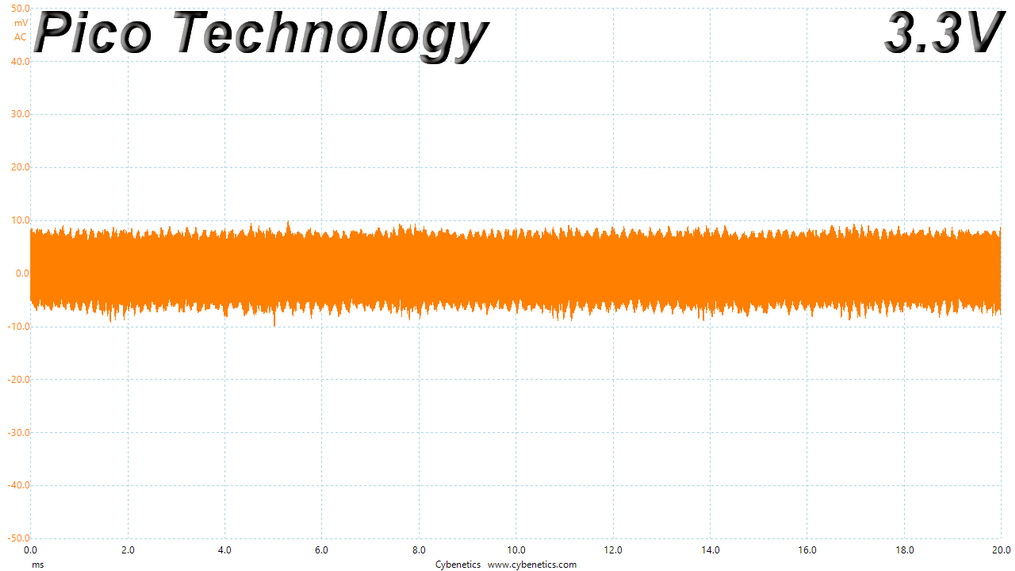
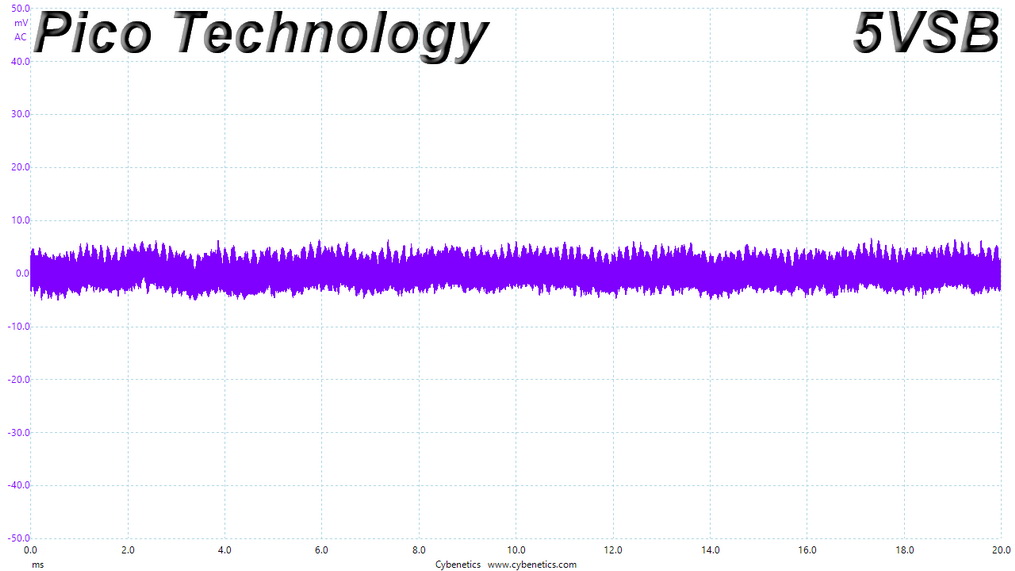
Results 30-33: Ripple Suppression
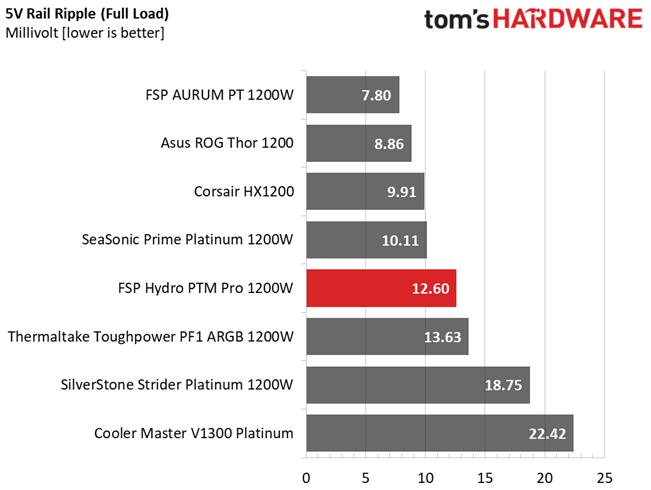
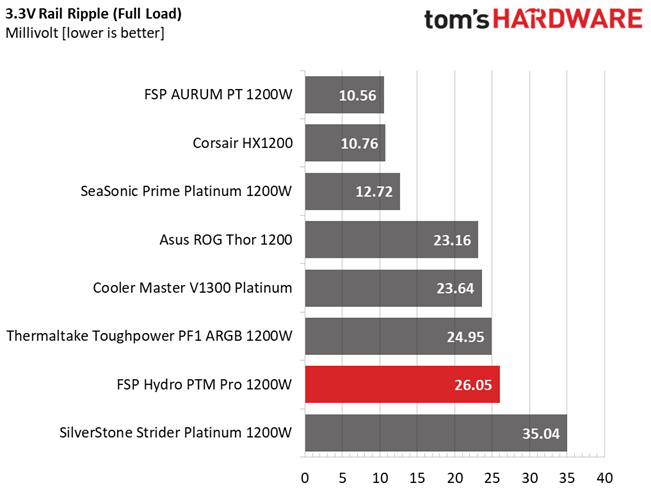
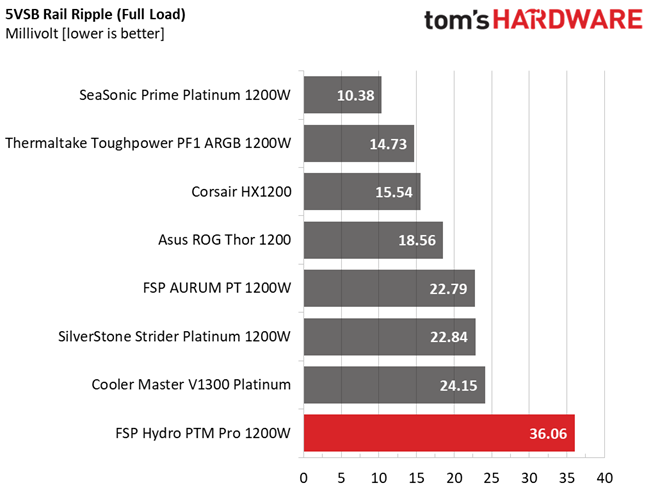
Ripple suppression is good on all major rails. The 5VSB rail registers higher than the competition, ripple. Still, it is way lower than 50mV, which is the limit.
Ripple At Full Load
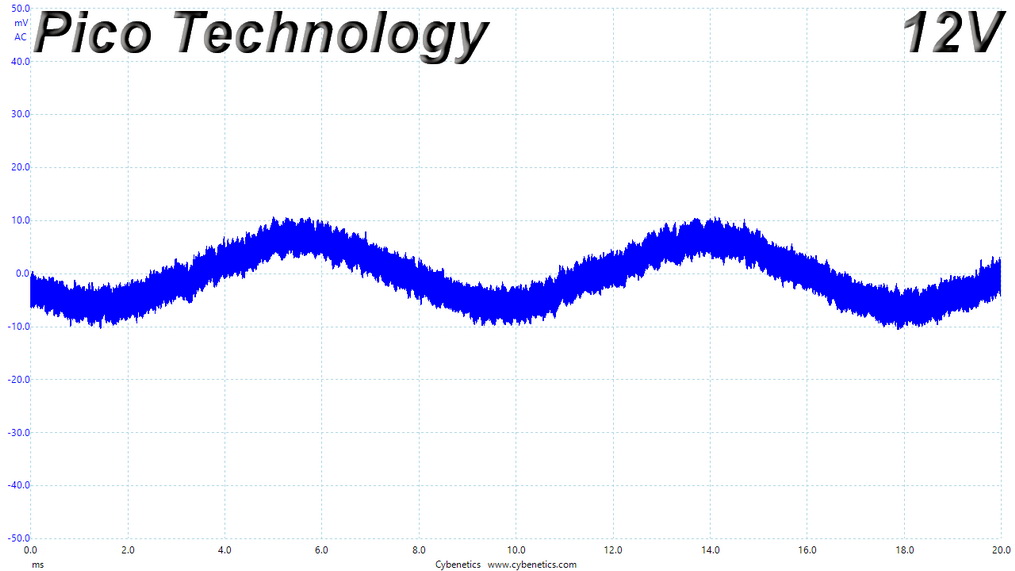
Ripple Full Load Scope Shots

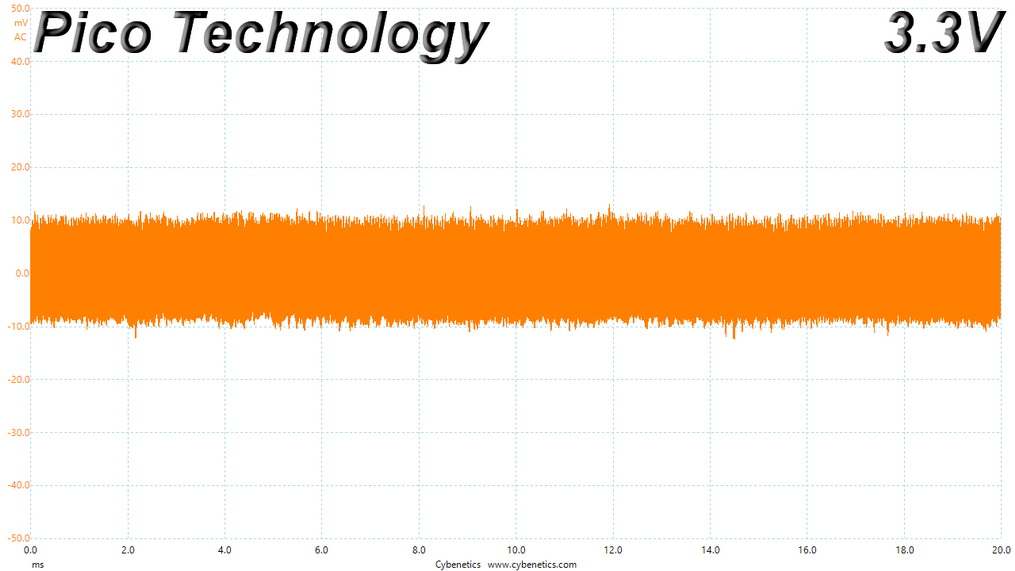
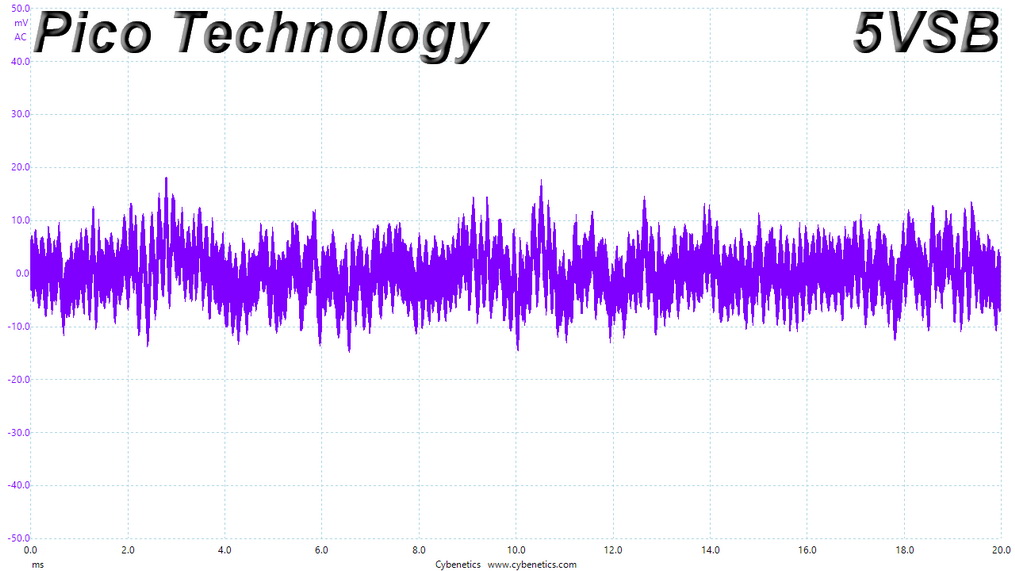
Ripple At 106% Load
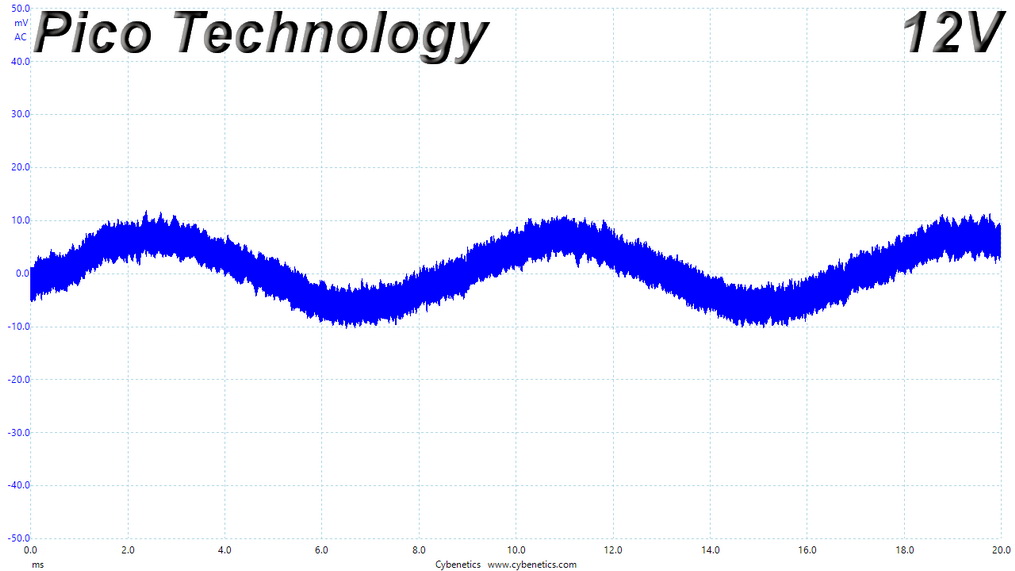
Ripple 110% Load Scope Shots
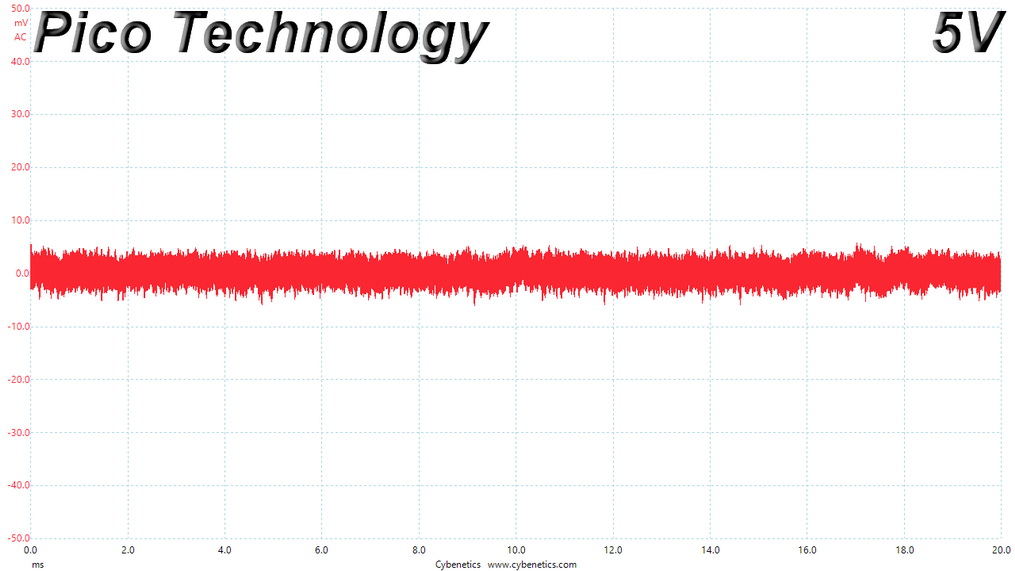
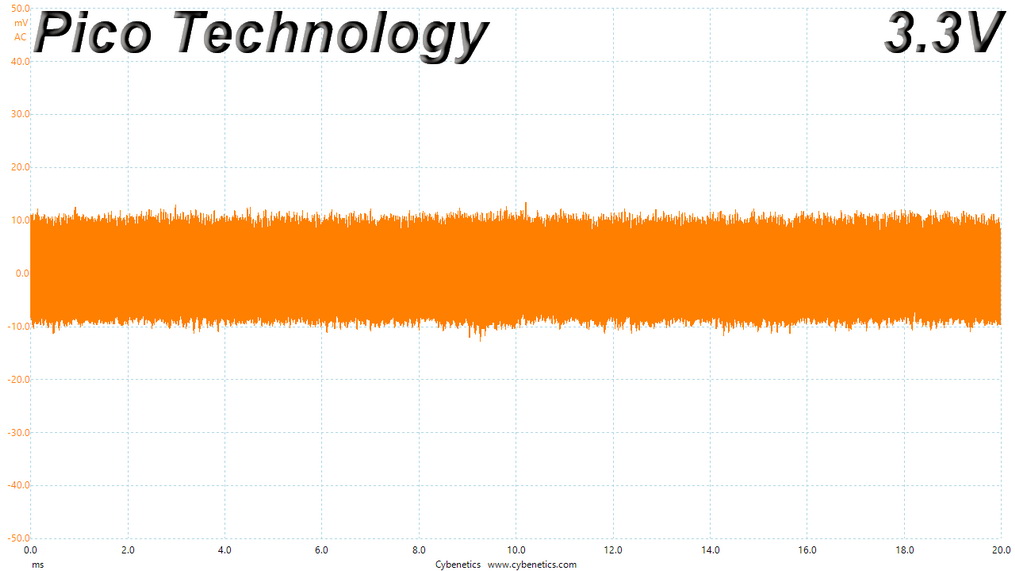
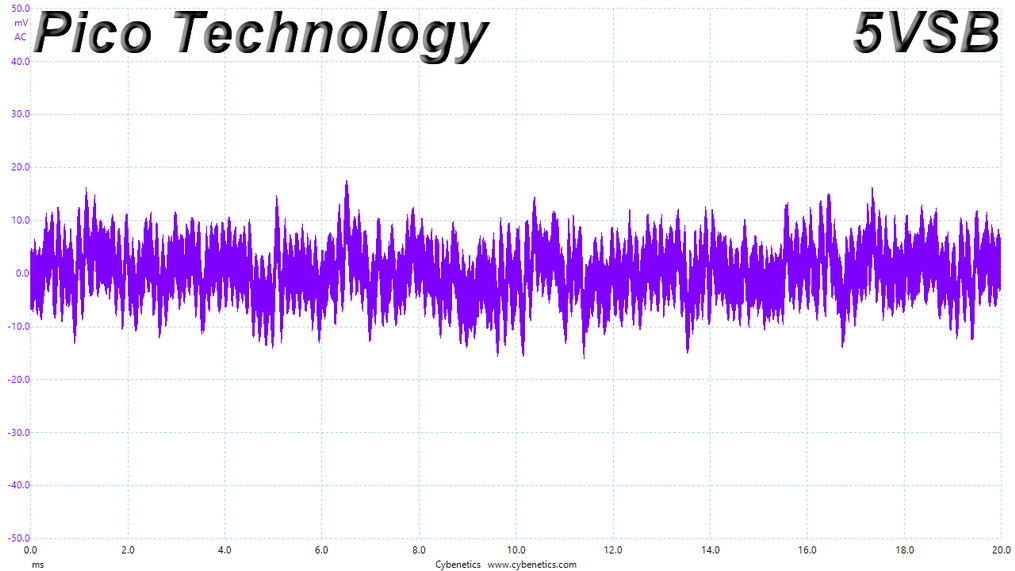
Ripple At Cross-Load 1
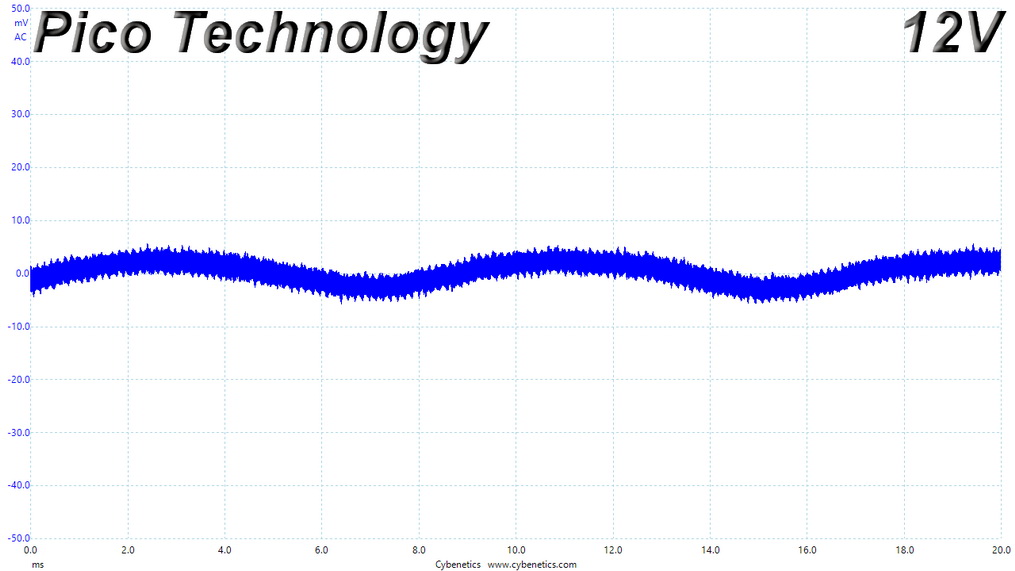
Ripple CL1 Load Scope Shots
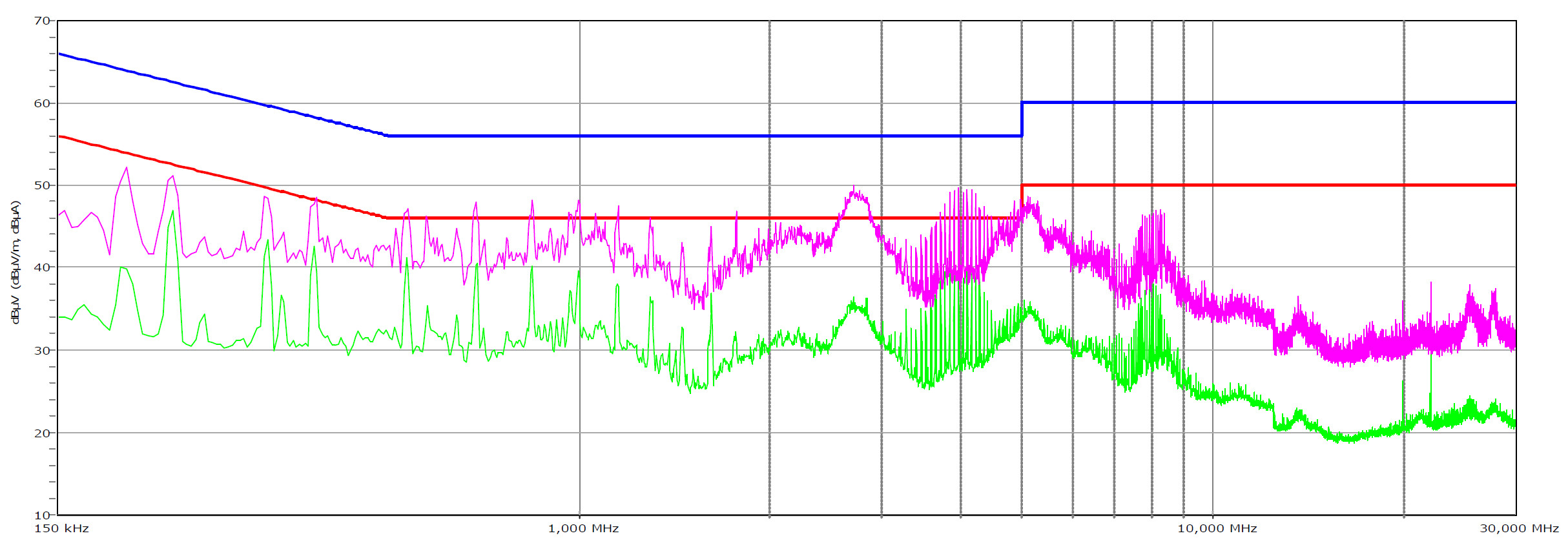
EMC Pre-Compliance Testing – Average & Peak EMI Detector Results
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device to operate properly in its environment without disrupting the proper operation of other nearby devices.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) stands for the electromagnetic energy a device emits, and it can cause problems in other nearby devices if too high. For example, it can be the cause of increased static noise in your headphones or/and speakers.
There are no EMI emissions issues, even with the Peak detector that we tried first, which is much faster than the Quasi-Peak detector. If we spotted any higher than the corresponding limit spur with the Peak detector, we would rerun the test with the QP detector to confirm if the spur indeed exceeds the limits.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Transient Response Tests, Timing Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Prev Page Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images Next Page Performance, Noise, Efficiency and Power Factor
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
Co BIY I would be interested in the reviewer's opinion of the conformal coating and anything he saw related to humidity-proof claims.Reply
Was it visible in the tear down ? is it actually different than other products ? -
Jeremy.L Reply
The conformal coating is hardly to find unless you use some devices to scratch the surface of the PCB board. Its overall performance is beyond my expectation.Co BIY said:I would be interested in the reviewer's opinion of the conformal coating and anything he saw related to humidity-proof claims.
Was it visible in the tear down ? is it actually different than other products ?