FSP Twins 500W Redundant PSU Review
The FSP Twins series combines the usability of a normal ATX PSU and the advanced features of a redundant server unit. The Twins 500W we're evaluating today addresses users that need an ultra-reliable PSU and are willing to pay for it.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
A Look Inside And Component Analysis
Parts Description
Before proceeding with this page, we strongly encourage you to a look at our PSUs 101 article, which provides valuable information about PSUs and their operation, allowing you to better understand the components we're about to discuss. Our main tools for disassembling PSUs are a Thermaltronics soldering and rework station, and a Hakko FR-300 desoldering gun.
| General Data | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer (OEM) | FSP |
| Frame Model | FSP500-70RGHBB1 |
| Single Module Model | FSP520-20RGGBB1 |
| FSP520-20RGGBB1 - Primary Side | |
| Transient Filter | 4x Y caps, 2x X caps, 2x CM chokes, 1x MOV |
| Inrush Protection | NTC Thermistor & Diode |
| Bridge Rectifier(s) | 1x GBU1506 (600V, 15A @ 100°C) |
| APFC MOSFETs | 1x Infineon IPA60R165CP (650V, 13A @ 100°C, 0.165Ω) |
| APFC Boost Diode | 1x Infineon IDH06G65C5 (650V, 6A @ 145°C) |
| Hold-up Cap(s) | 2x Nichicon (420V, 150uF each, 5000h @ 105°C, PT) |
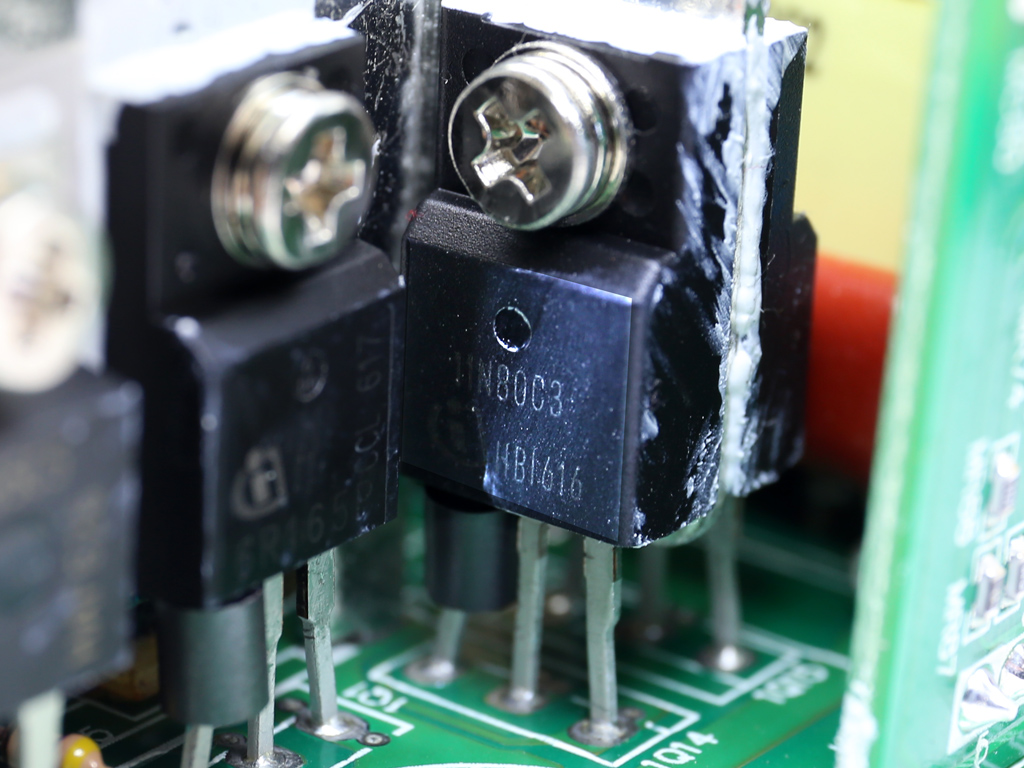
| Main Switchers | 2x Infineon SPA11N80C3 (800V, 7.1A @ 100°C, 0.45Ω) |
| MCU 1 | Texas Instruments MSP430AFE253 (12 MHz, 16-bit, Three-Channel ADC, SPI, UART) |
| MCU 2 | Microchip PIC24FJ32GA (32 MHz, 16-bit, 10-Channel ADC, 2x SPI, 2x UART) |
| Topology | Primary side: Half-Bridge Secondary side: Synchronous Rectification |
| FSP520-20RGGBB1 - Secondary Side | |
| +12V MOSFETs | 2x NXP PSMN2R2-30YLC (30V, 100A @ 100°C, 2.8mΩ) |
| Filtering Capacitors | Electrolytics: Nippon Chemi-Con (KY, KZH, 105°C) Polymers: Nippon Chemi-Con |
| Supervisor IC | HY-510N (OVP, UVP, FPL, PG) |
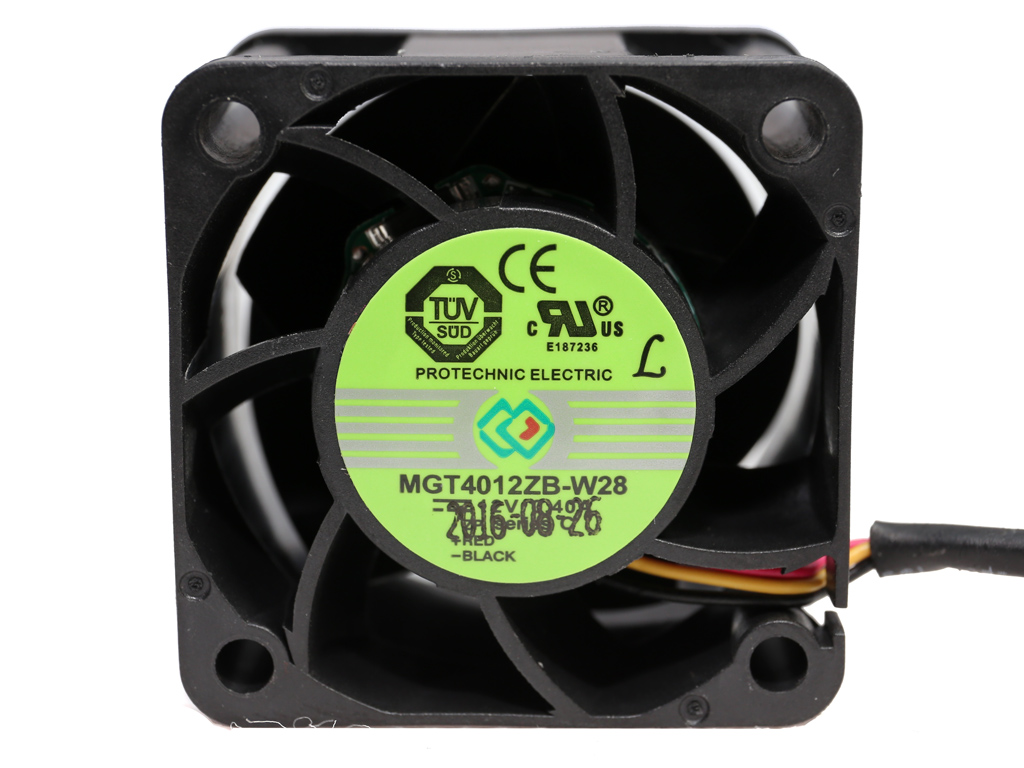
| Fan Model | Protechnic Electric MGT4012ZB-W28 (40mm, 12V, 0.40A, Double-Ball Bearing) |
| FSP520-20RGGBB1 - 5VSB Circuit | |
| Rectifier | 1x 30A60CT SBR (60V, 15A) |
| Standby PWM Controller | - |
| FSP500-70RGHBB1 - DC-DC Converters | |
| 5V & 3.3V | DC-DC Converters: 8x NXP PSMN2R2-30YLC (30V, 100A @ 100°C, 2.8mΩ) PWM Controller: APW7159C |
| Filtering Capacitors | Electrolytics: Nippon Chemi-Con (105°C) Polymers: Nippon Chemi-Con, Teapo |
| MCU | Microchip PIC24FJ32GA (32 MHz, 16-bit, 10-Channel ADC, 2x SPI, 2x UART) |
| USB transceiver (HID USB-to-SMBus Bridge) | Silicon Labs CP2112 |
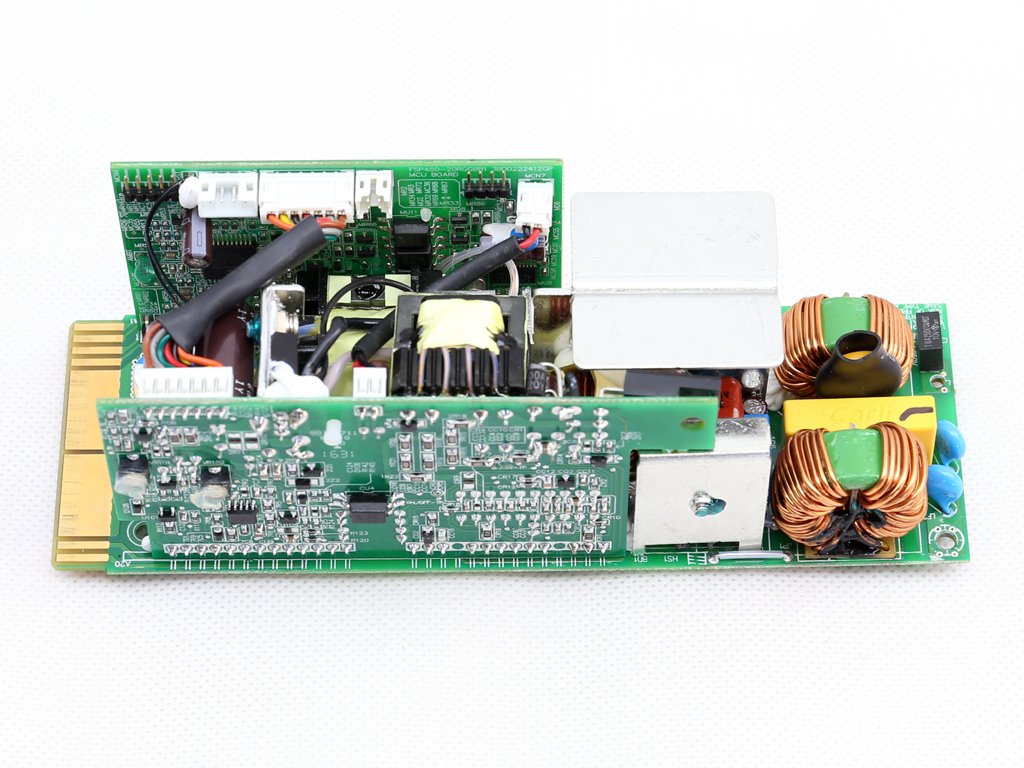
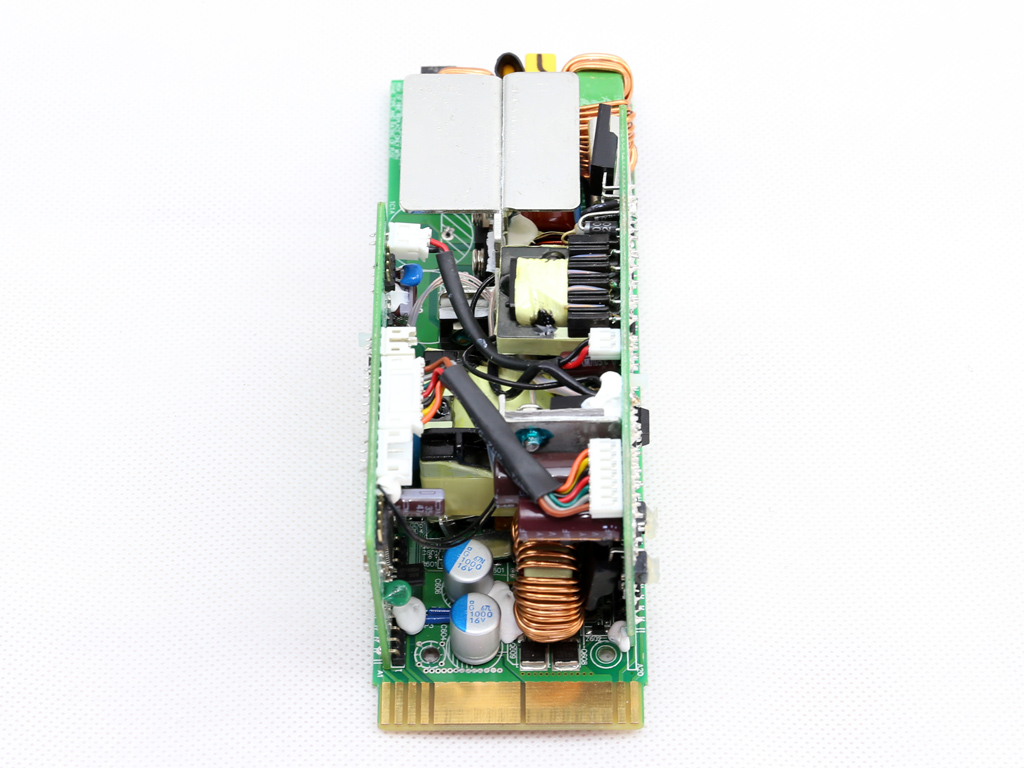
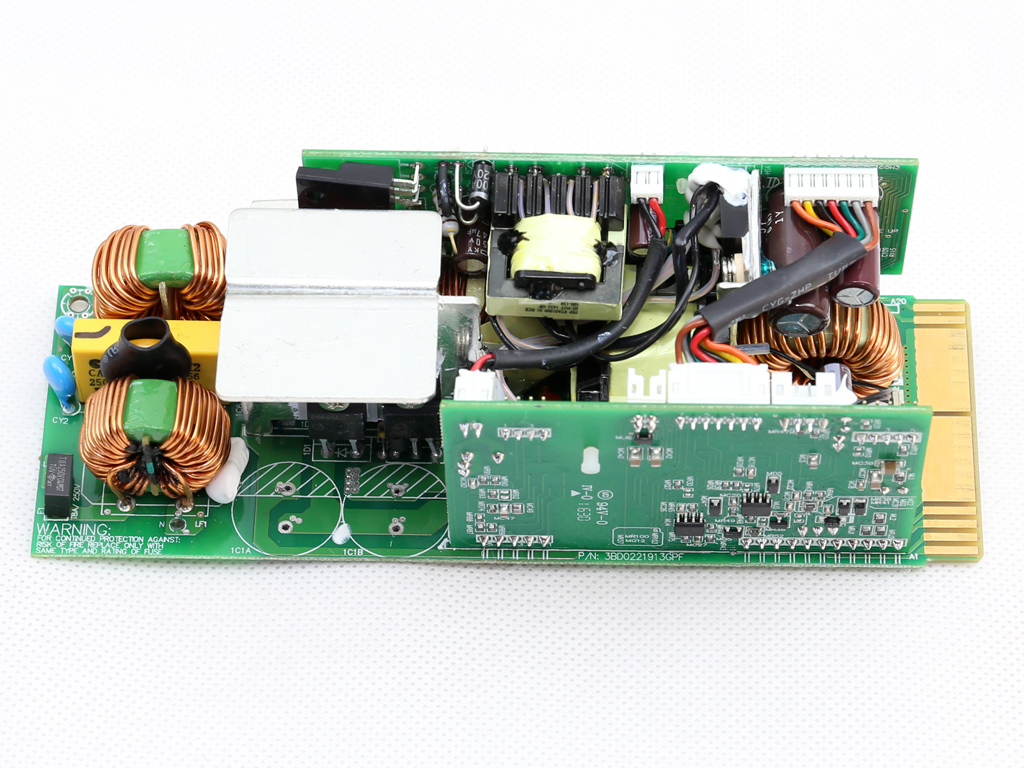
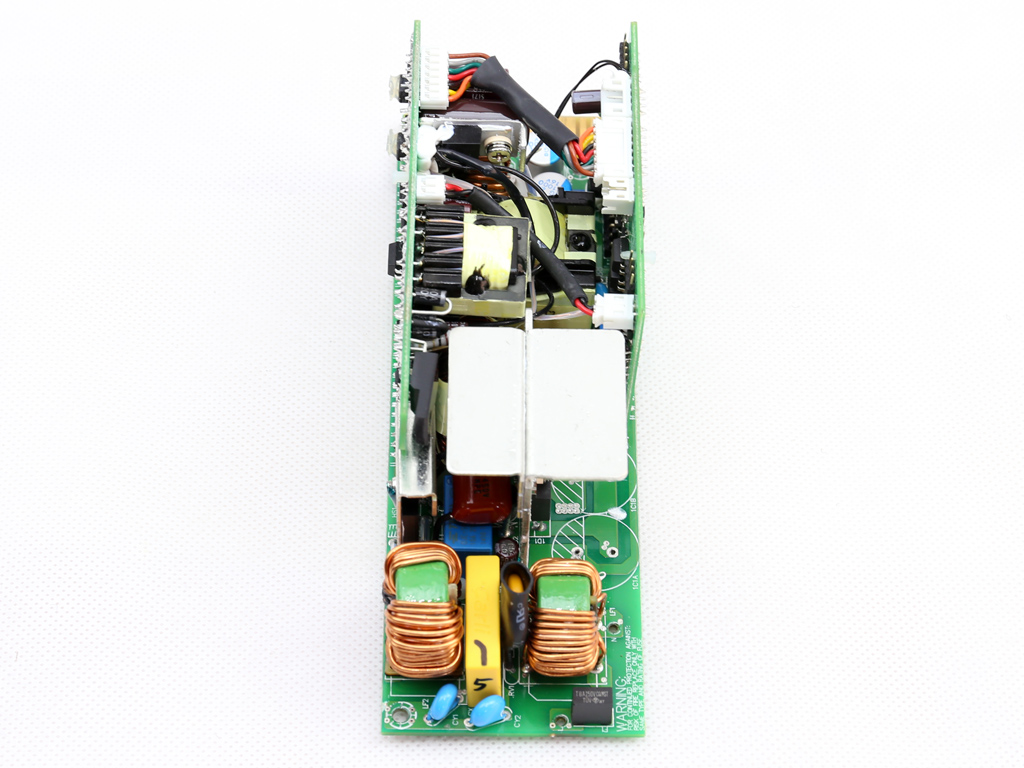
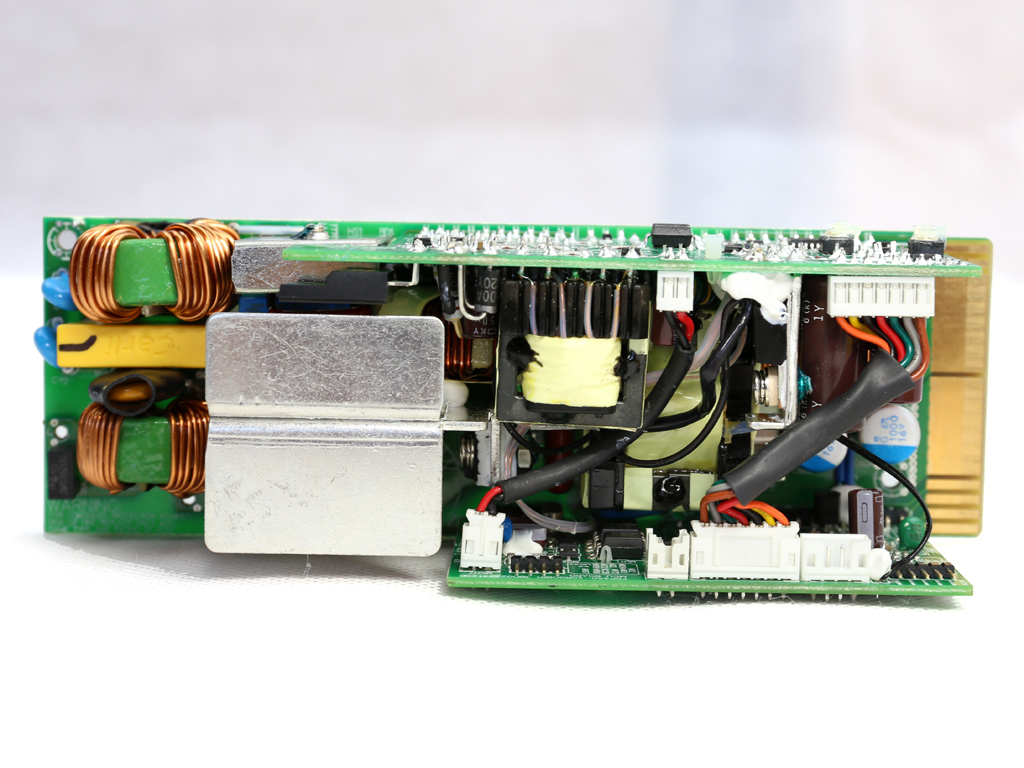
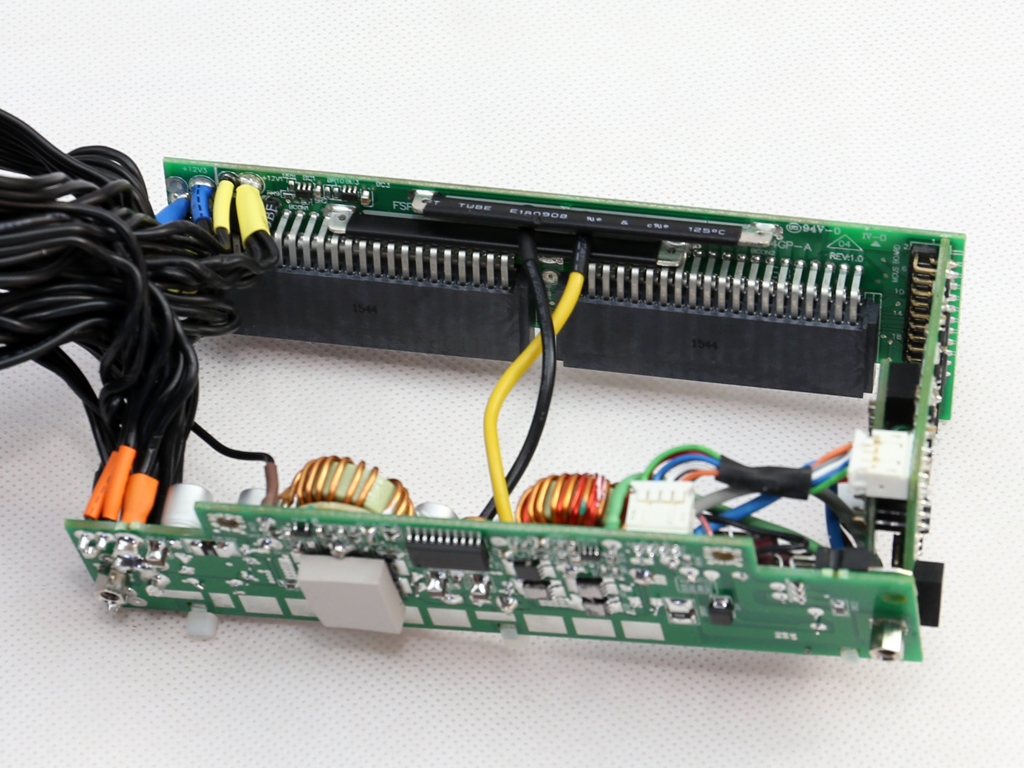
As mentioned, the FSP Twins 500W consists of a frame and a couple of power modules. The frame includes the DC-DC converters that generate the minor rails, along with the -12V regulation and digital communication circuits. The power modules generate the +12V rail and 5VSB output, and feature a digital design with two MCUs handling the control functions. Those MCUs are also responsible for the digital link to the frame.
On the primary side of the modules, a half-bridge topology appears to be used, while on the secondary side a synchronous design is utilized for generating the +12V rail. The modules' filtering caps are of high quality, and in addition to electrolytics, FSP also uses a number of polymer caps for increased reliability.
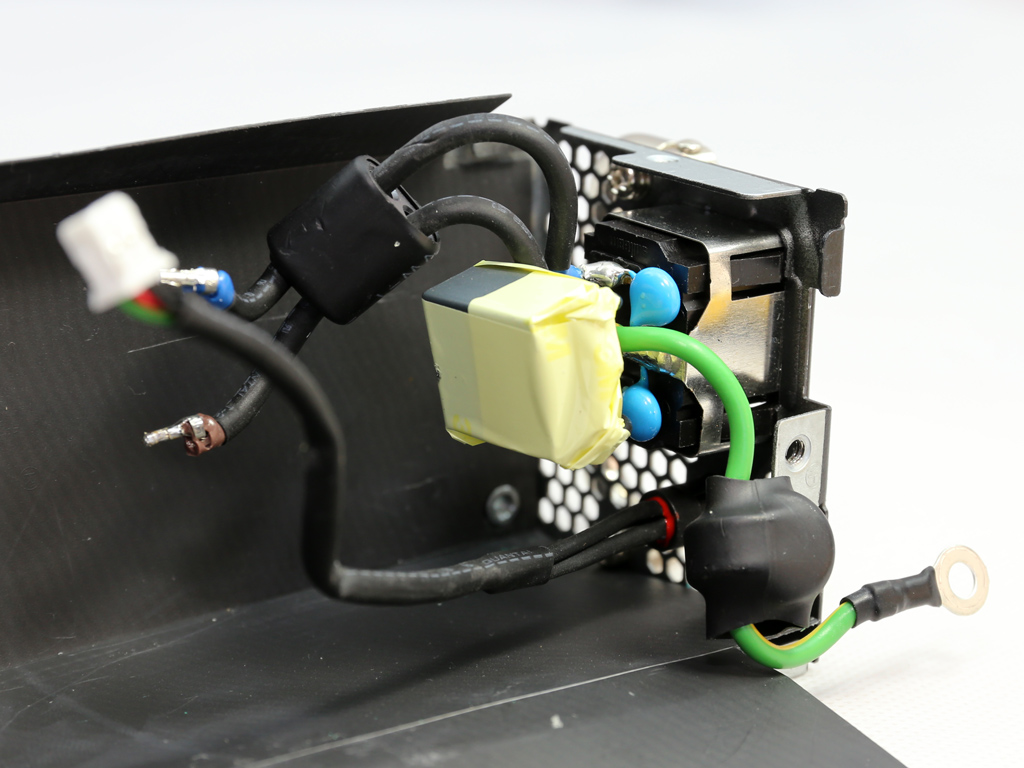
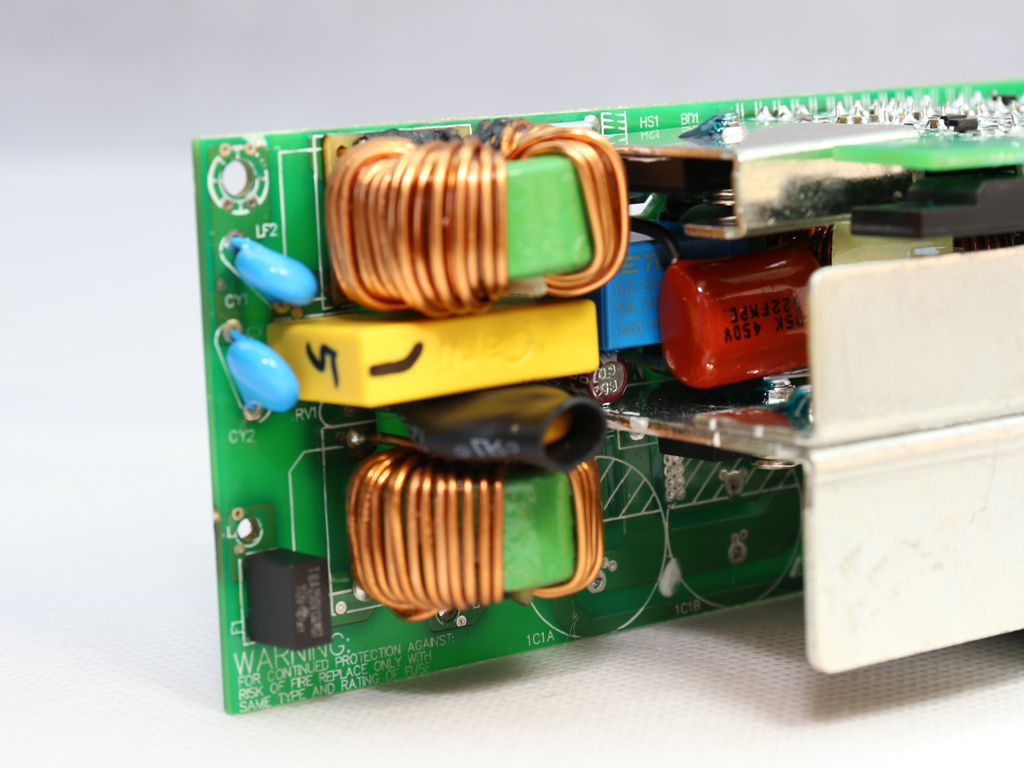
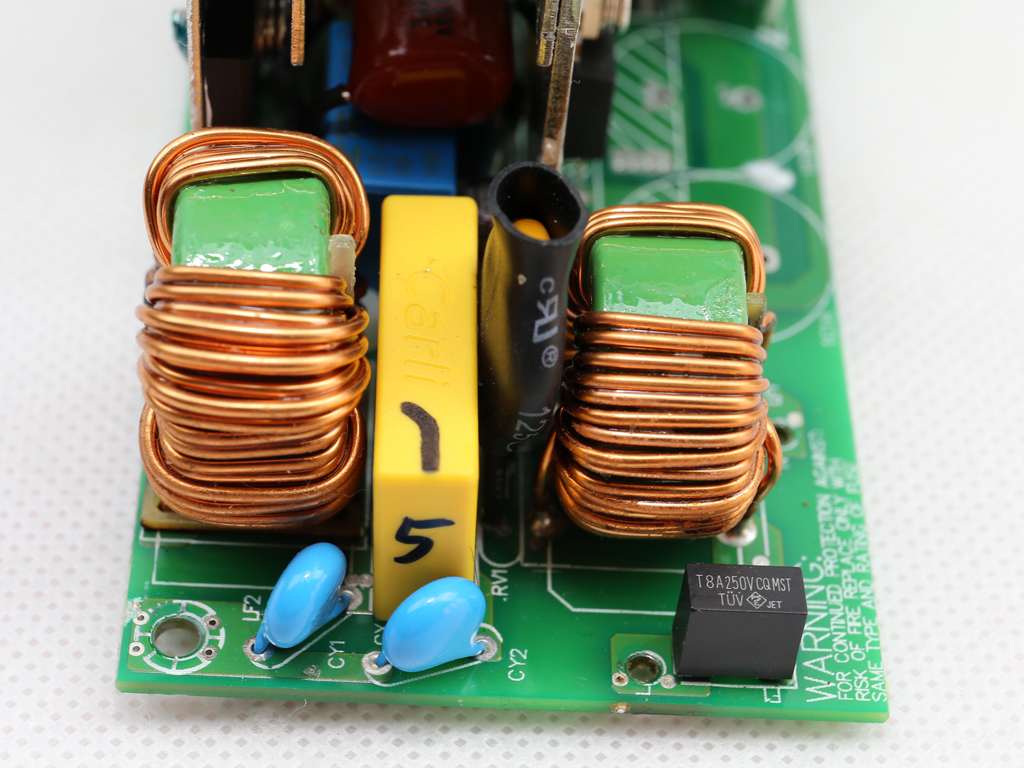
As usual, the transient filter starts at the AC receptacle and, in this case, includes two Y caps and a single X one. It continues on the main PCB with the same amount of Y and X caps, along with two CM chokes and an MOV. There is also an NTC thermistor providing protection against large inrush currents. An electromagnetic bypass relay supports this thermistor.
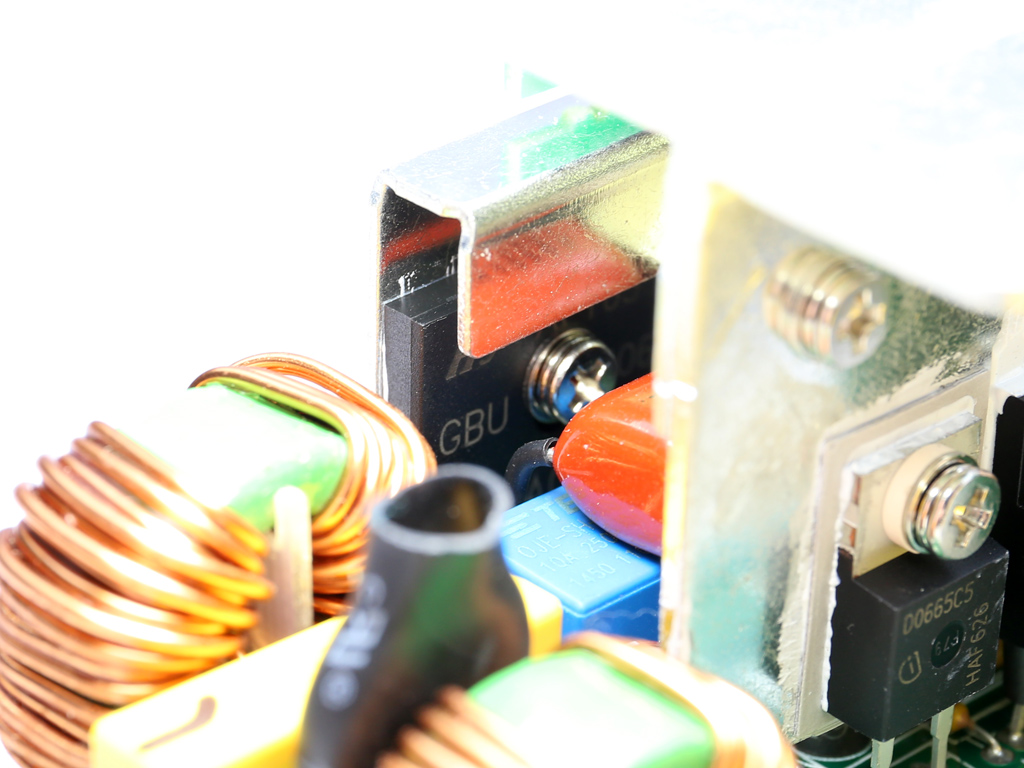

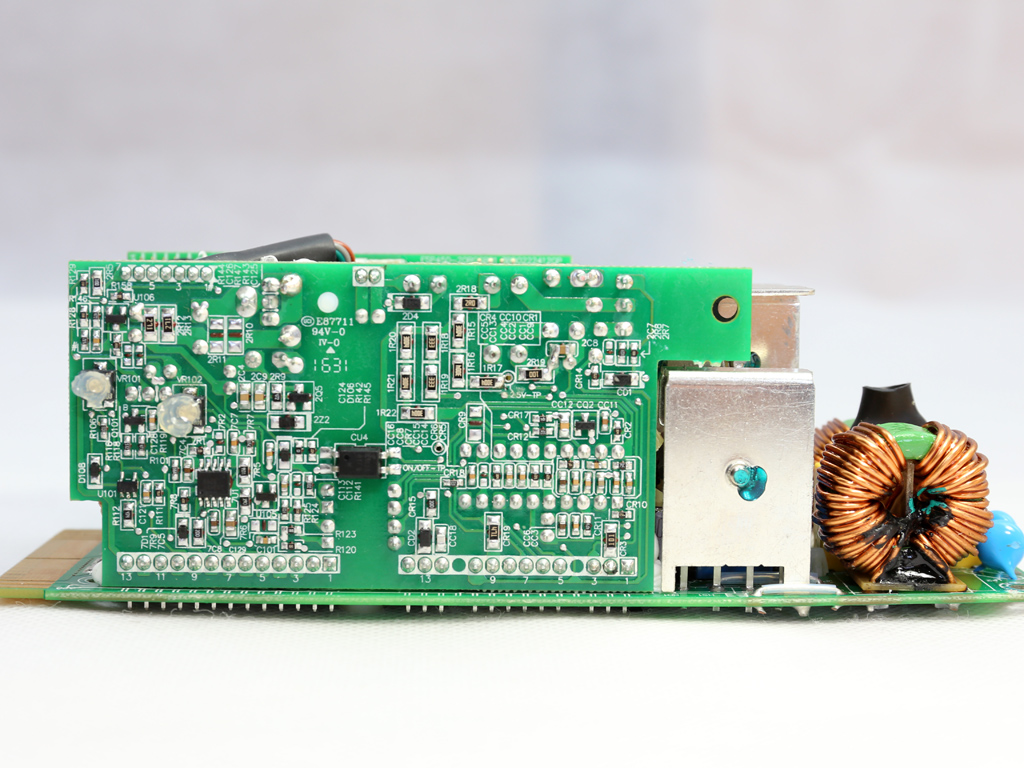
The single GBU1506 bridge rectifier is bolted on a dedicated heat sink.
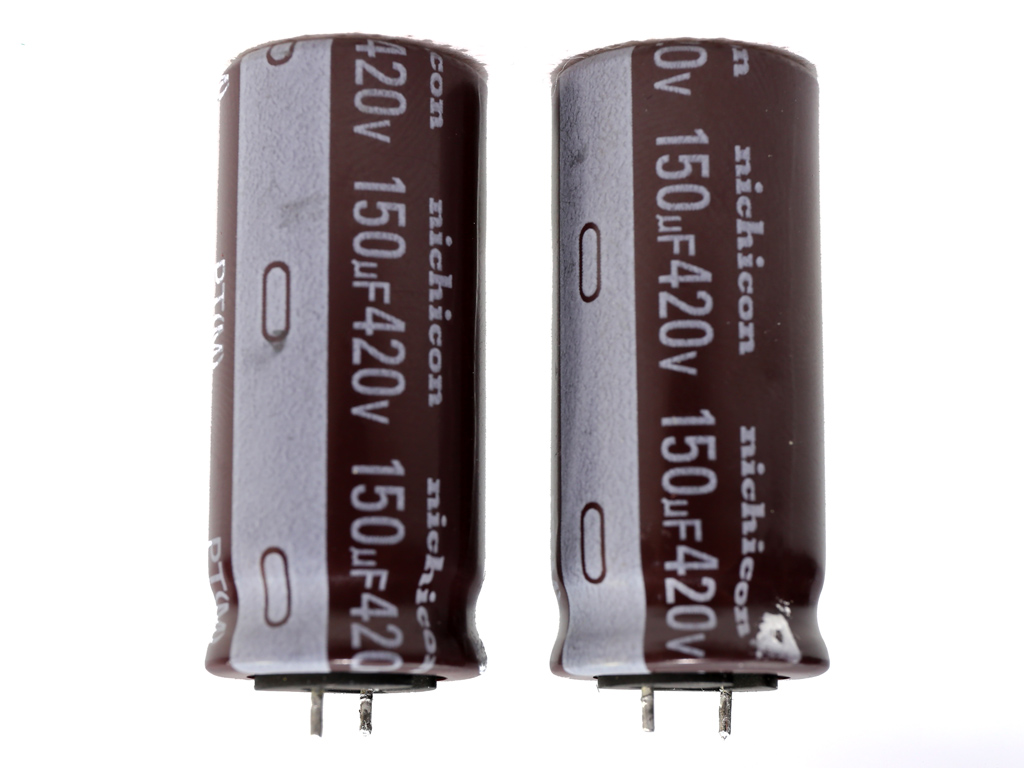
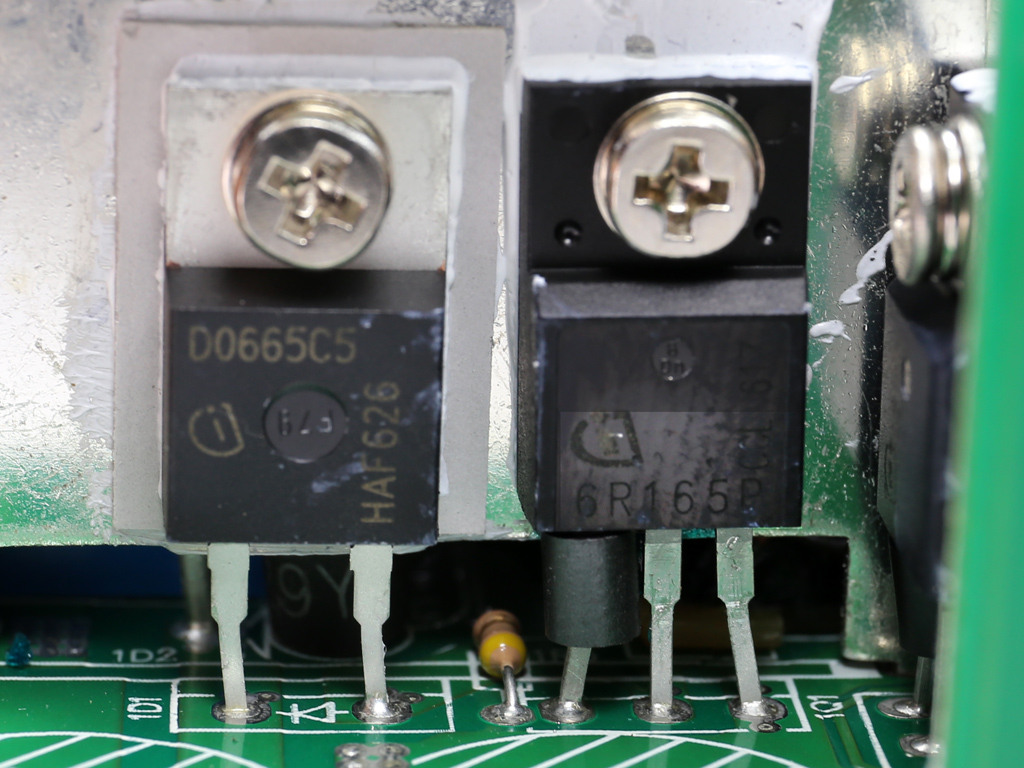
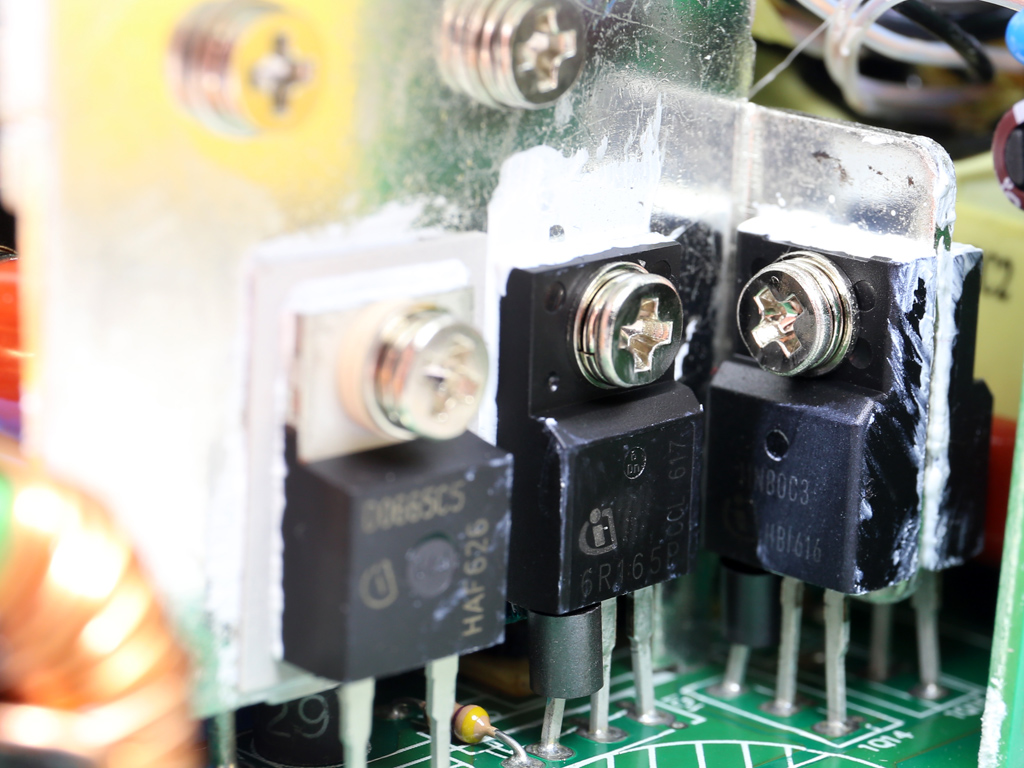

We had to completely remove the bulk caps in order to take a good look at the APFC converter's parts. This wasn't easy due to the limited height of the APFC's heat sink. One Infineon IPA60R165CP FET is used here, along with a IDH06G65C5 boost diode provided by the same manufacturer. The bulk caps come from Nichicon and have 2.5x more lifetime than the bulk caps we usually find in high-end desktop PSUs.
The primary switching FETs, two Infineon SPA11N80C3s, are configured in a half-bridge topology.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
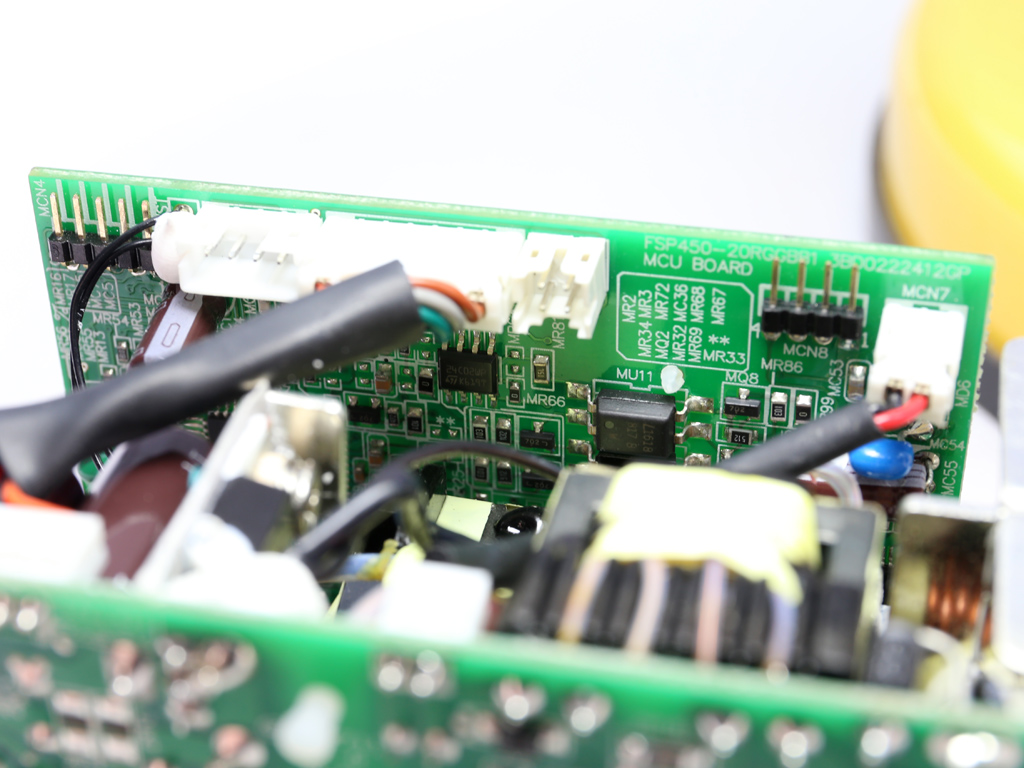
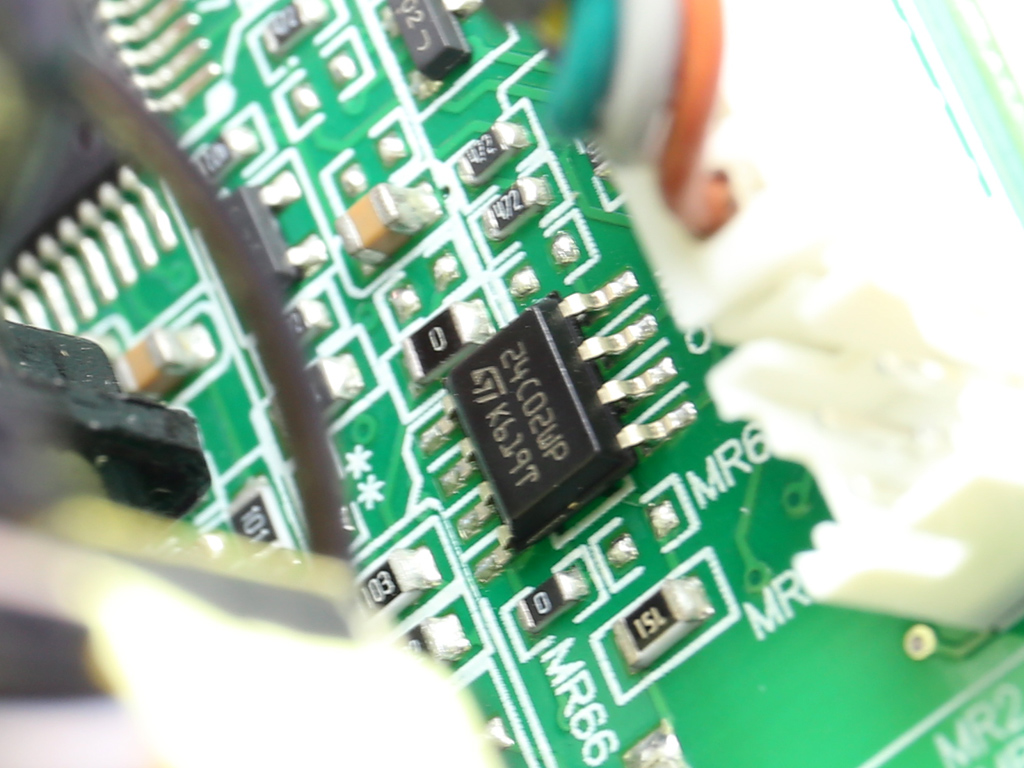
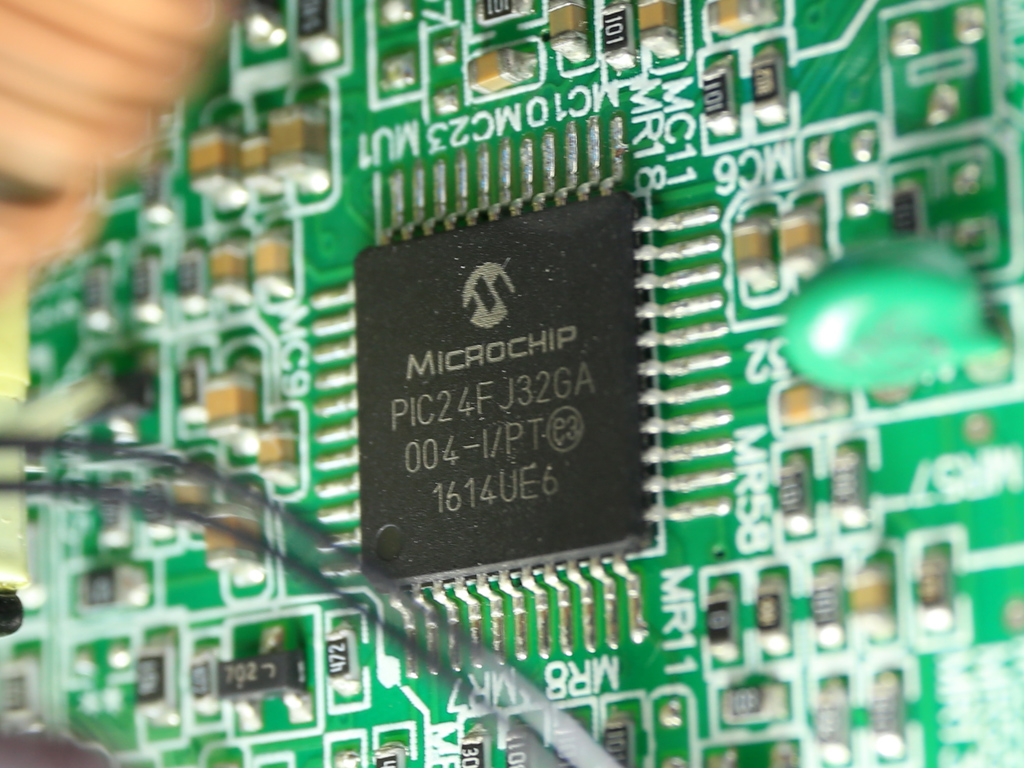
Two MCUs are installed in each of the power modules. One of them handles control functions, while the other one most likely enables a digital link with the frame. The first MCU is a Texas Instruments MSP430AFE253 and the second is a Microchip PIC24FJ32GA.
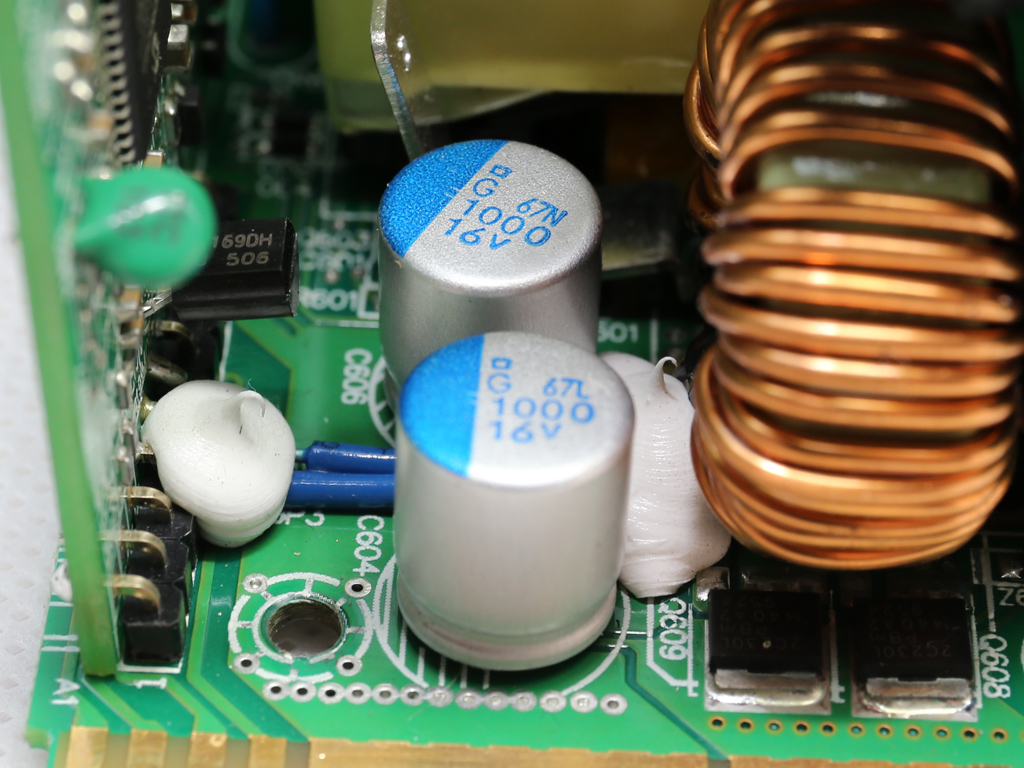
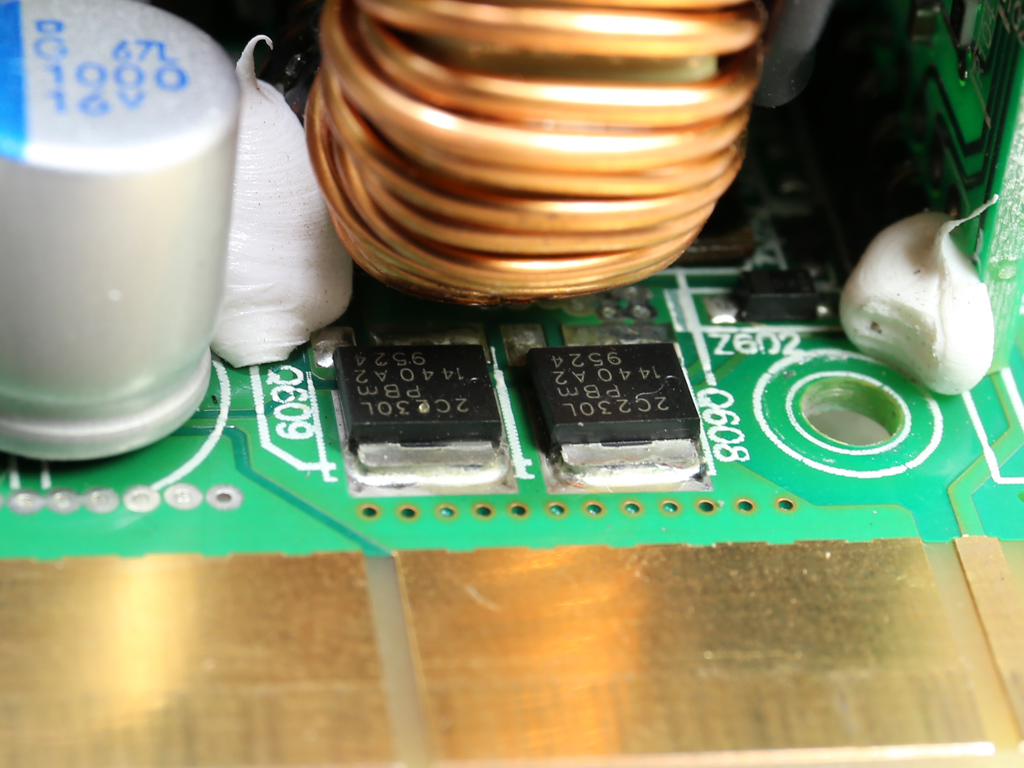
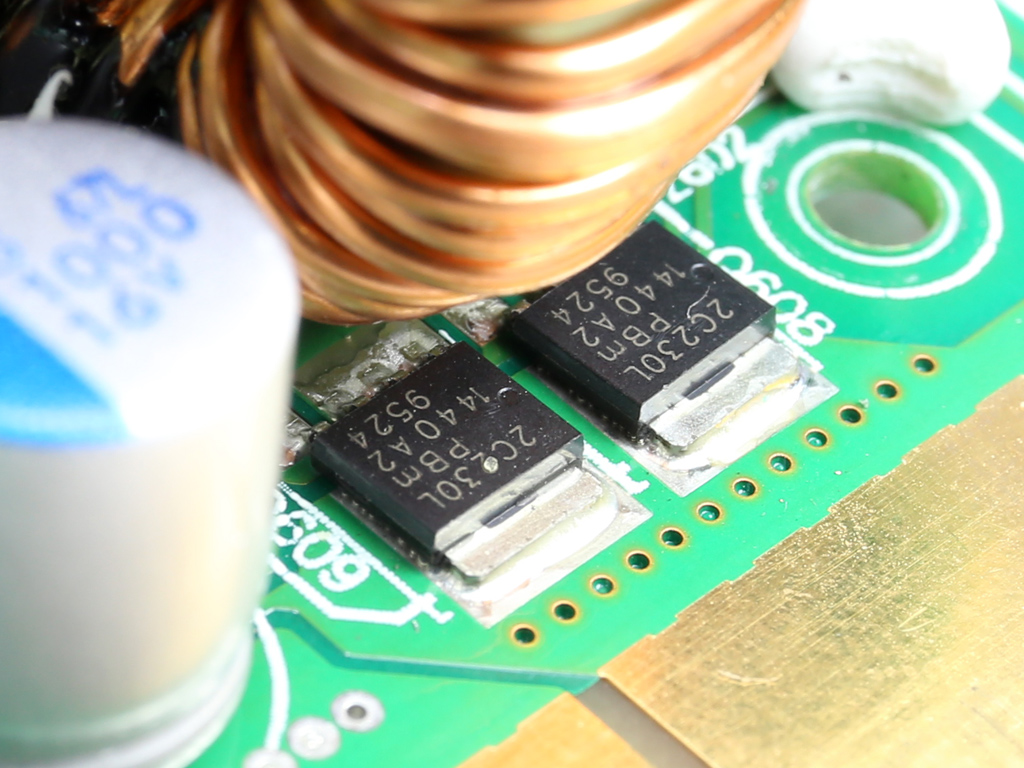
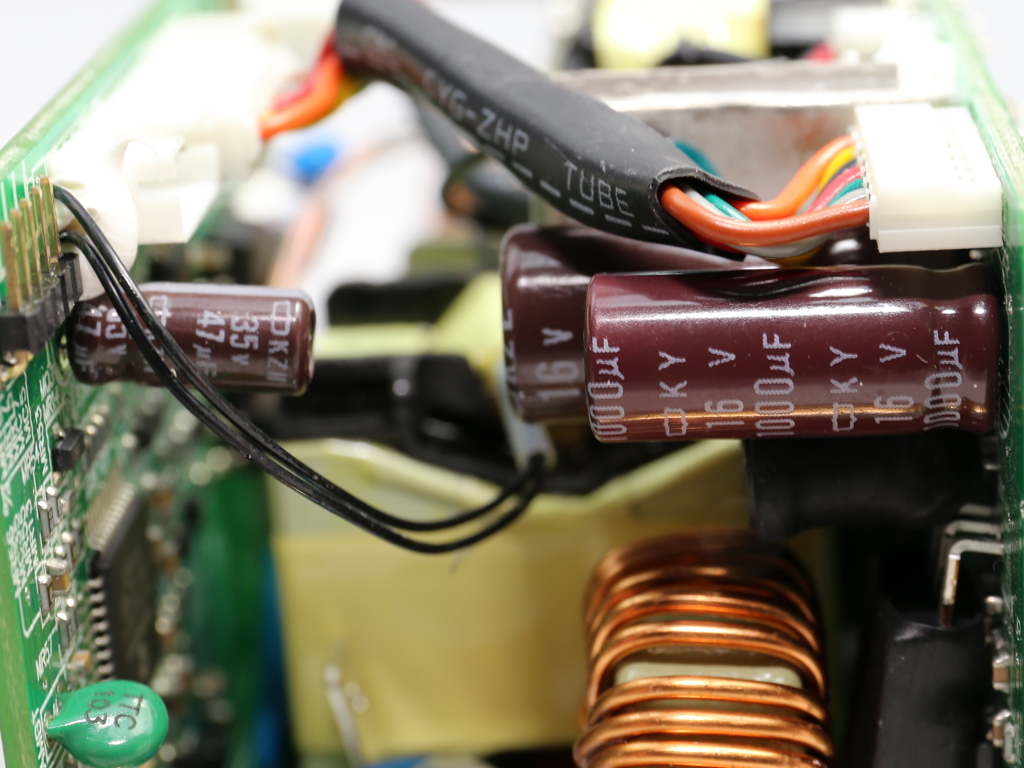

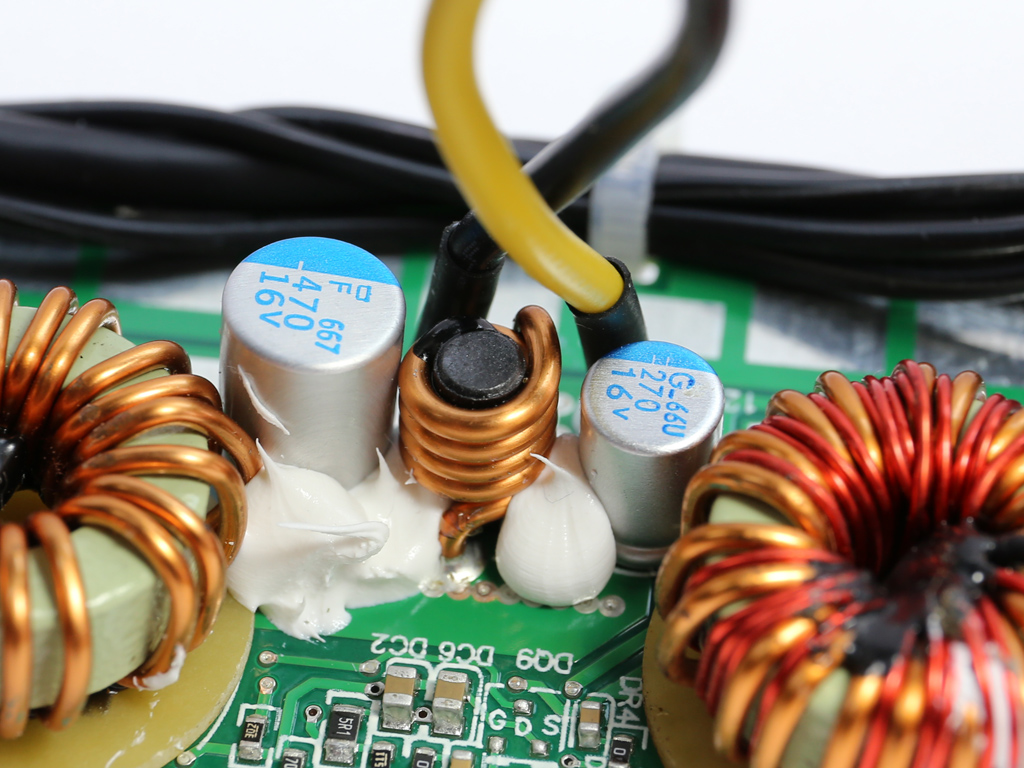
On the secondary side of the modules, the +12V rail is rectified by a pair of NXP PSMN2R2-30YLC FETs. The electrolytic and polymer filtering caps come from Chemi-Con and are of high quality. We don't find any KZE caps in the Twins, only the better KY and KZH ones. Given the tight space inside each module, which limits airflow, and the overpopulated PCB, it is good to see FSP using electrolytic caps with increased lifetime.
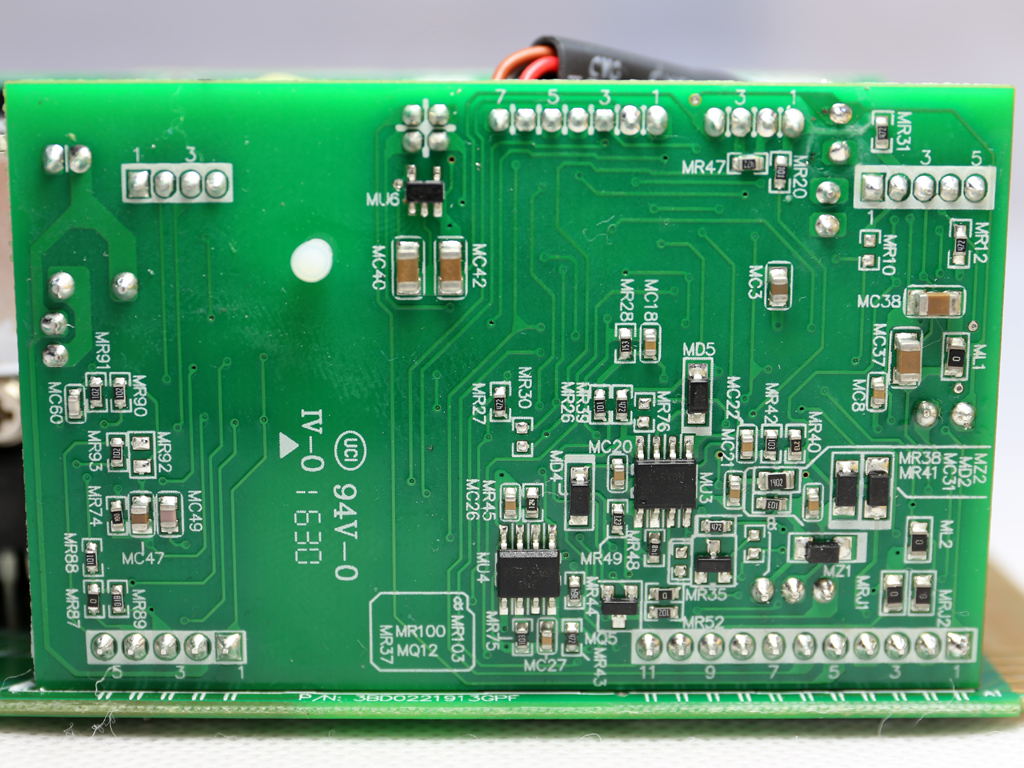
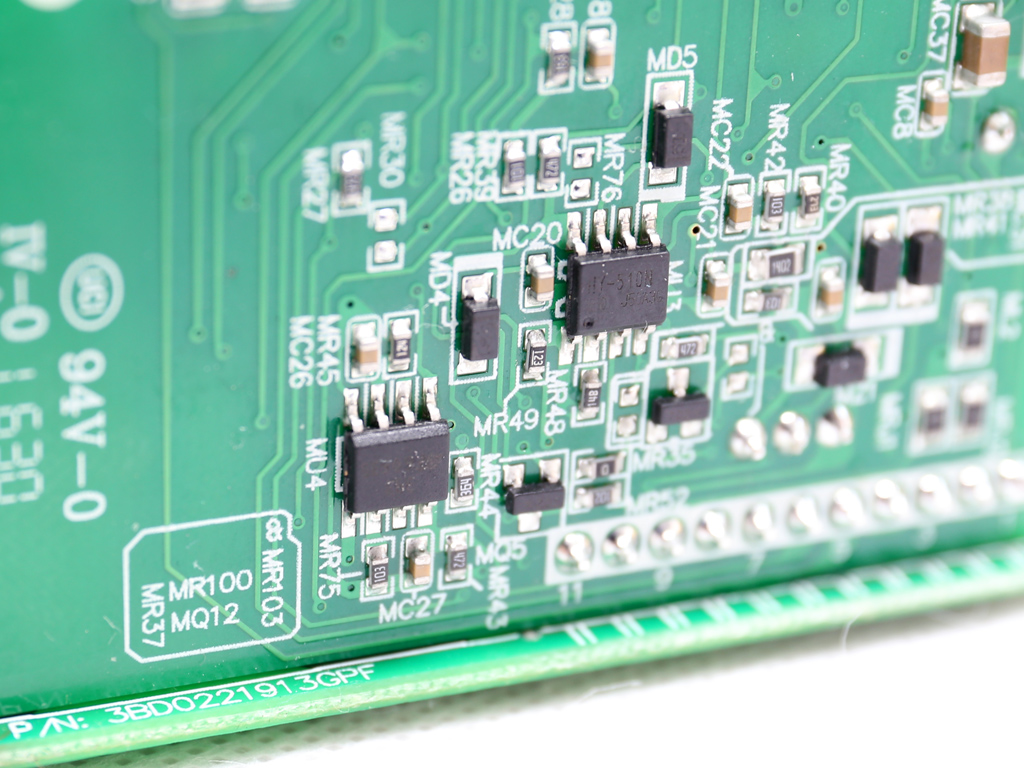
There's a very basic protections IC on this board, a HY-510N. It's probable that one of the MCUs also handles some protection features.
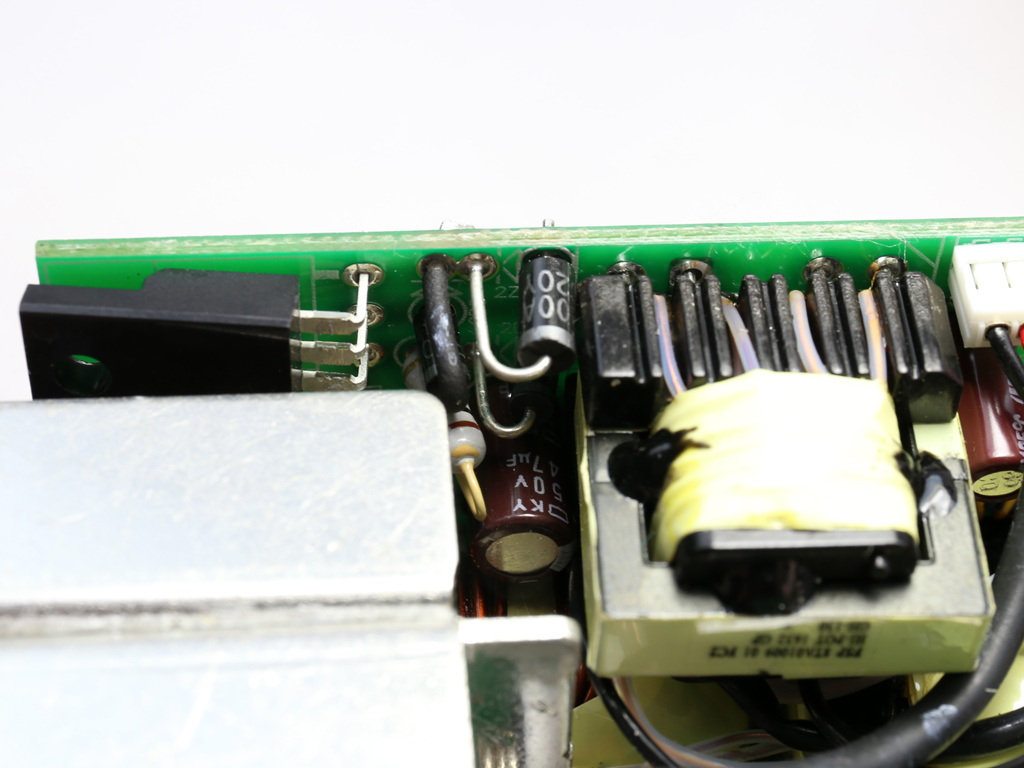

The 5VSB circuit is installed onto a vertical daughterboard. Its main rectifier is a 30A60CT SBR, which is cooled by a small heat sink.
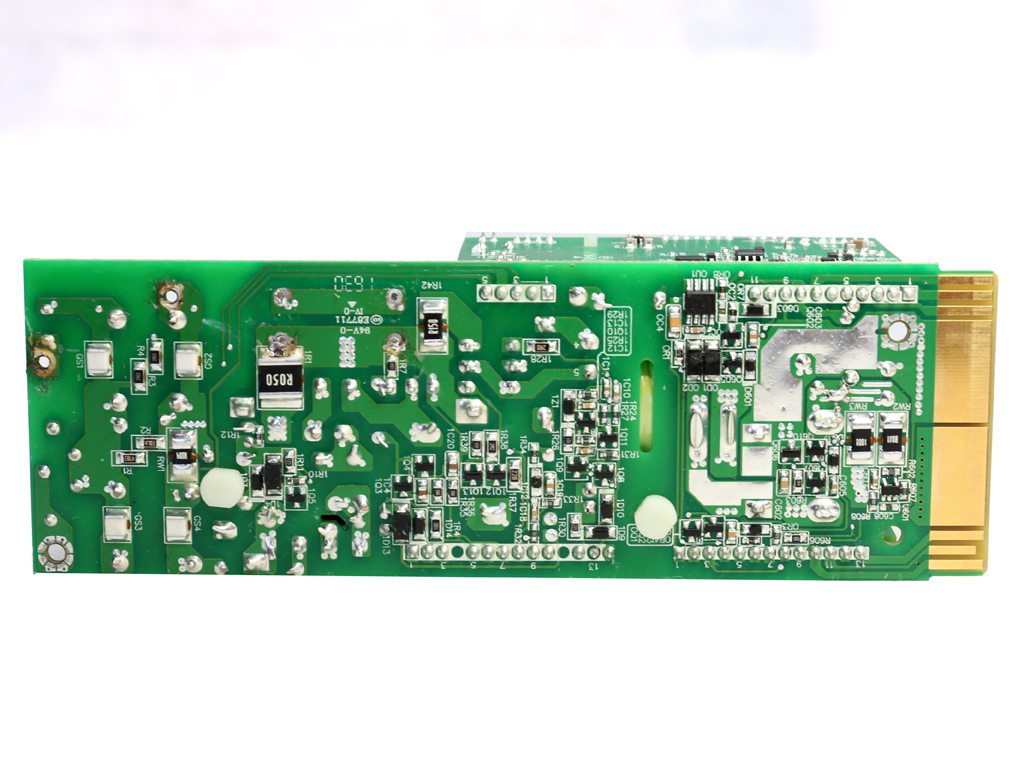
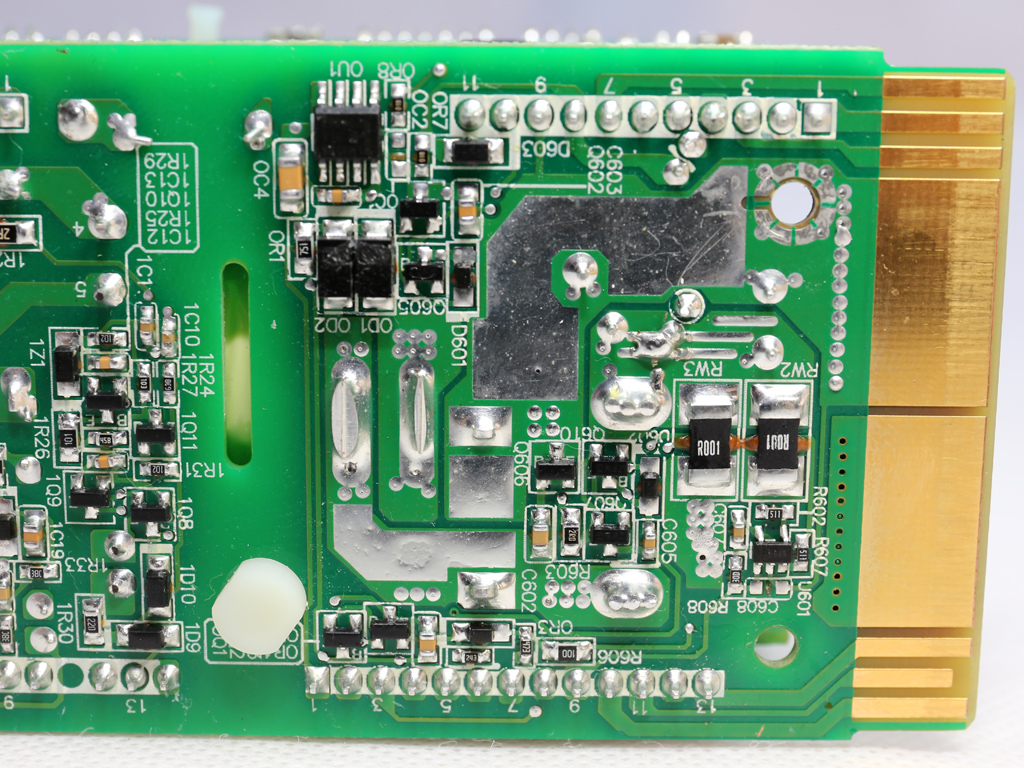
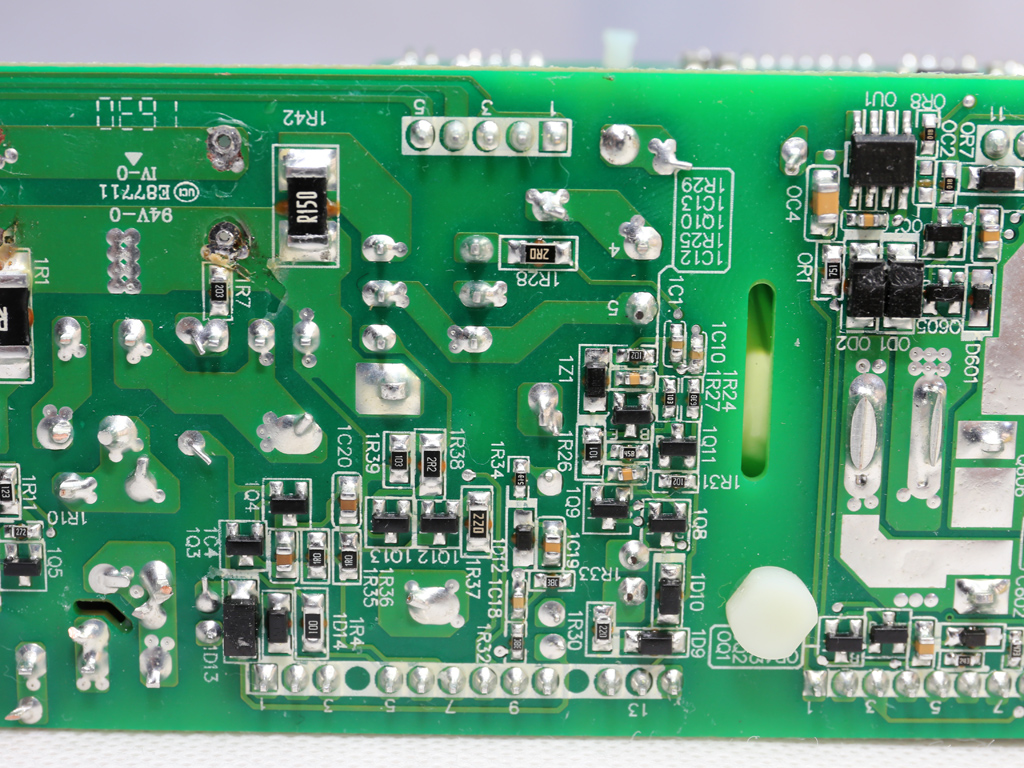
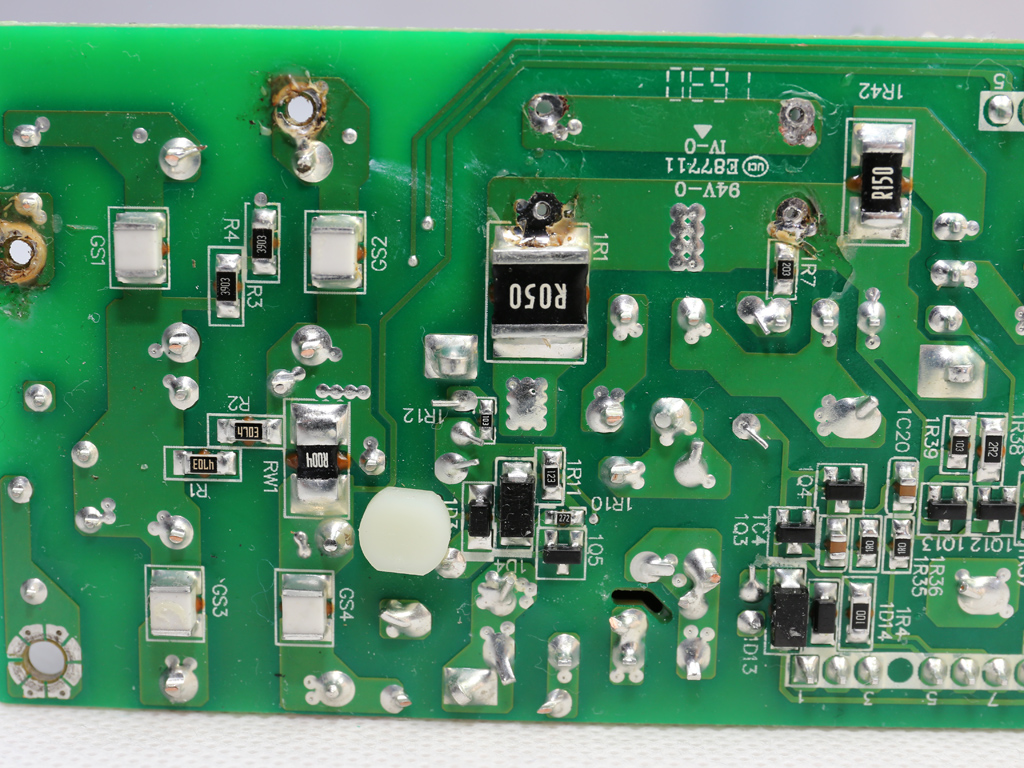
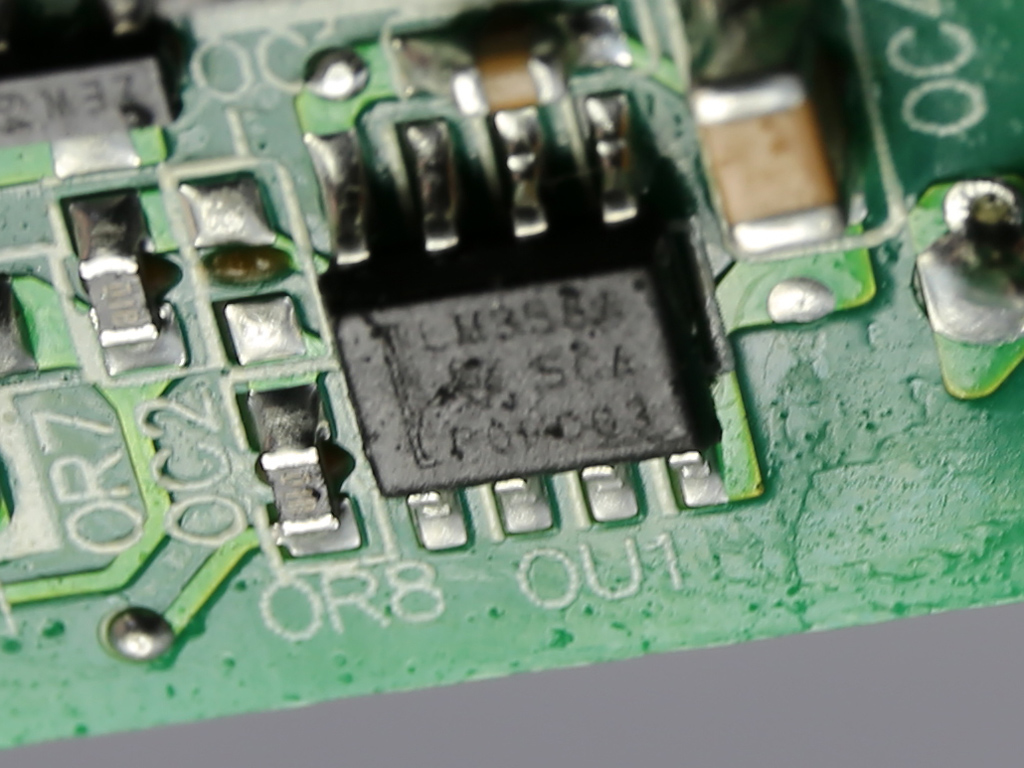
The soldering quality is good, but FSP's PCB isn't as robust. It doesn't cope with the high temperatures of our desoldering tools very well.
A 40mm diameter fan, sourced by Protechnic Electric, cools the module. Its model number is MGT4012ZB-W28 and it uses a dual-ball bearing, so it should last a long time. Expect this ultra-high-speed fan to make a lot of noise if you push the module hard.
Let's take a look at the Twins 500W's frame, which hosts DC-DC converters for the minor rails and the digital interface that facilitates communication between the modules and host system. There are a number of PCBs inside the frame, all of which are connected to each other through cables and pins.
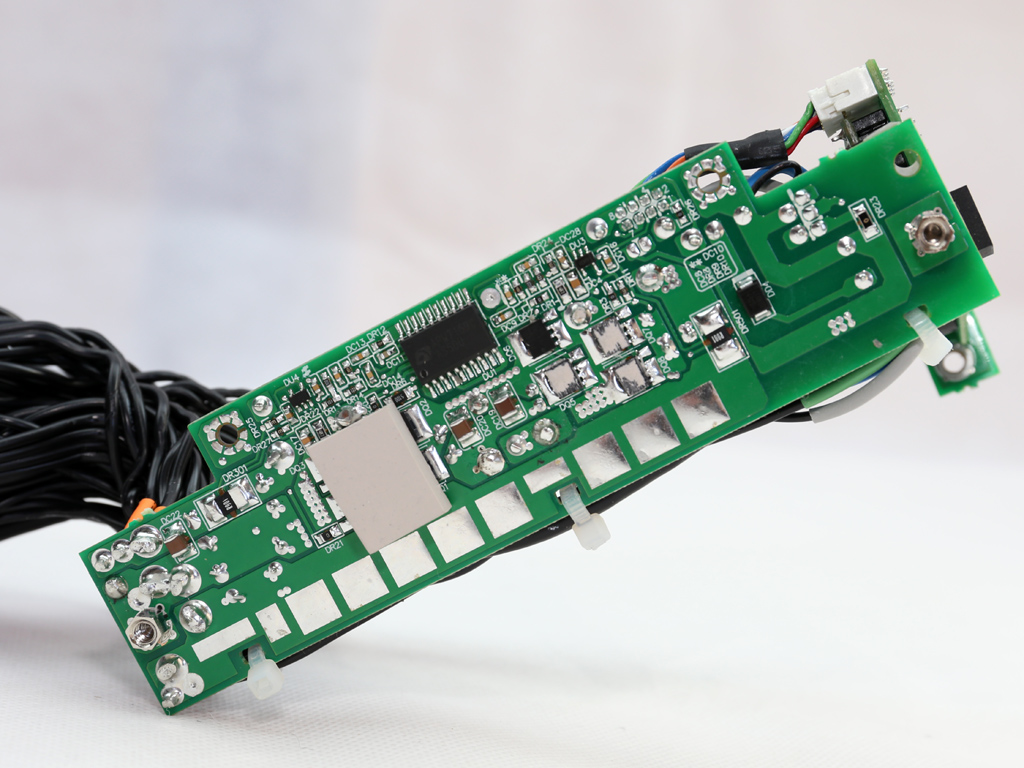
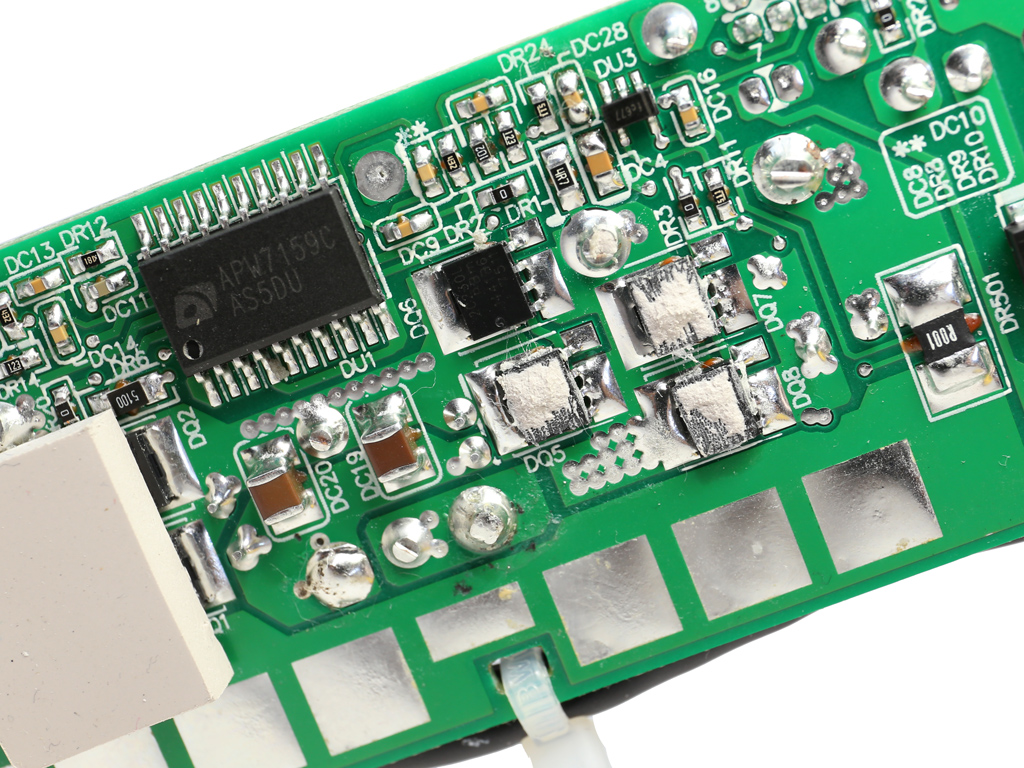
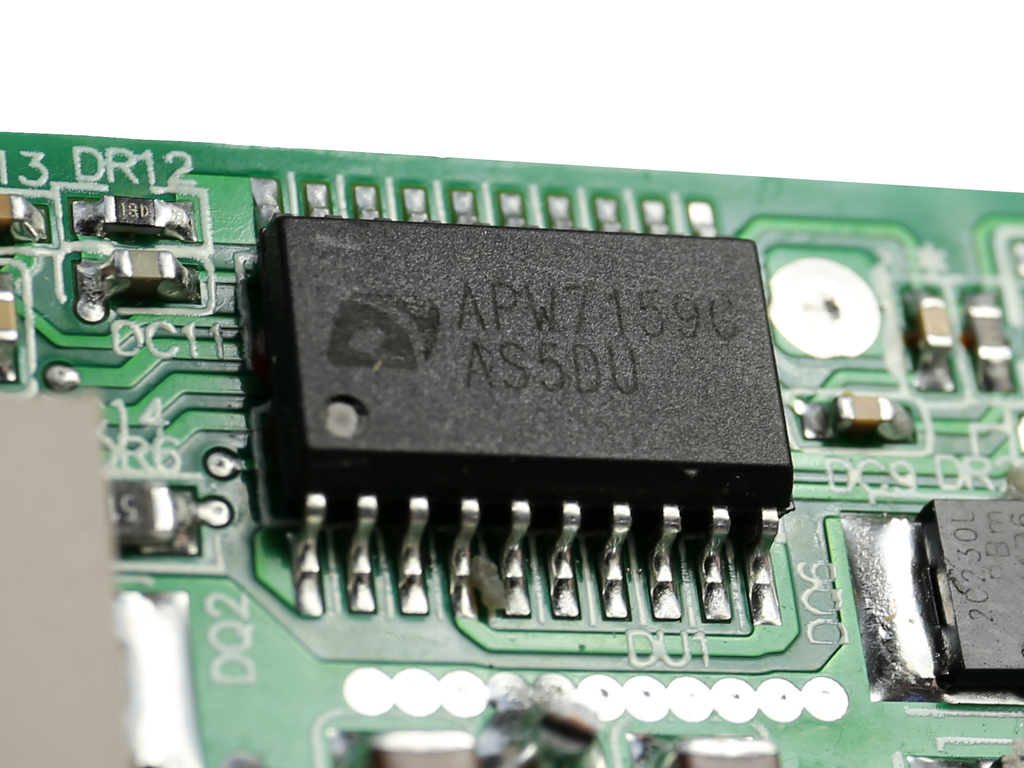
Both DC-DC converters use eight NXP PSMN2R2-30YLC FETs, while the common PWM controller is an ANPEC APW7159C. All of those parts are cooled by the frame's chassis.
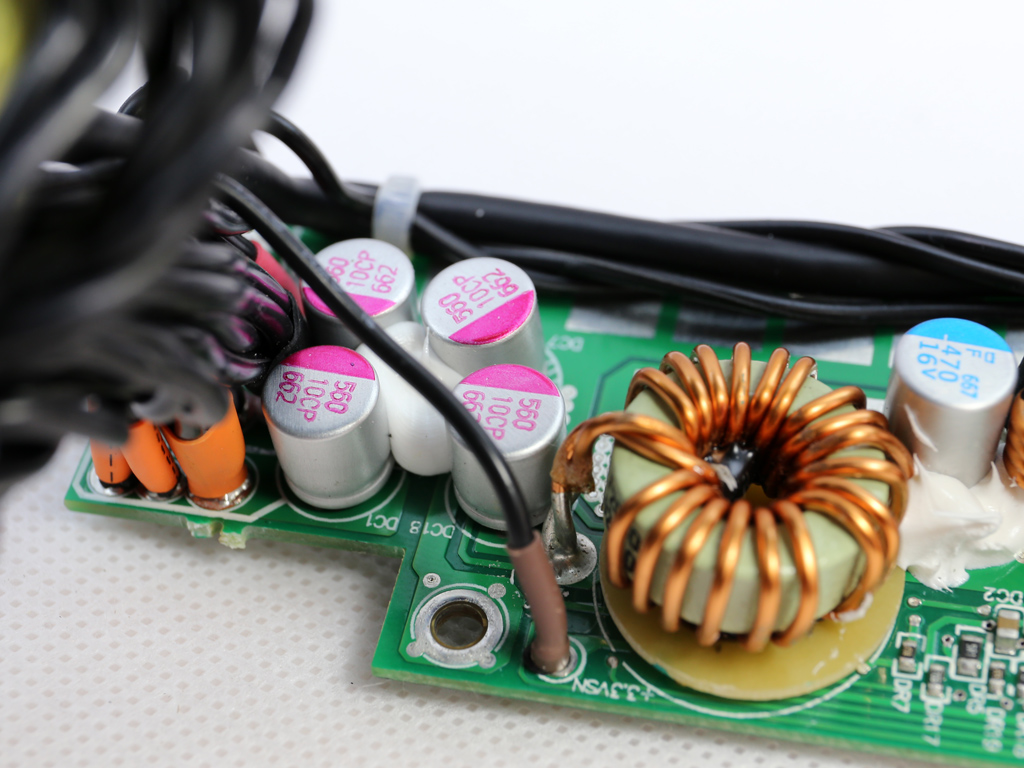
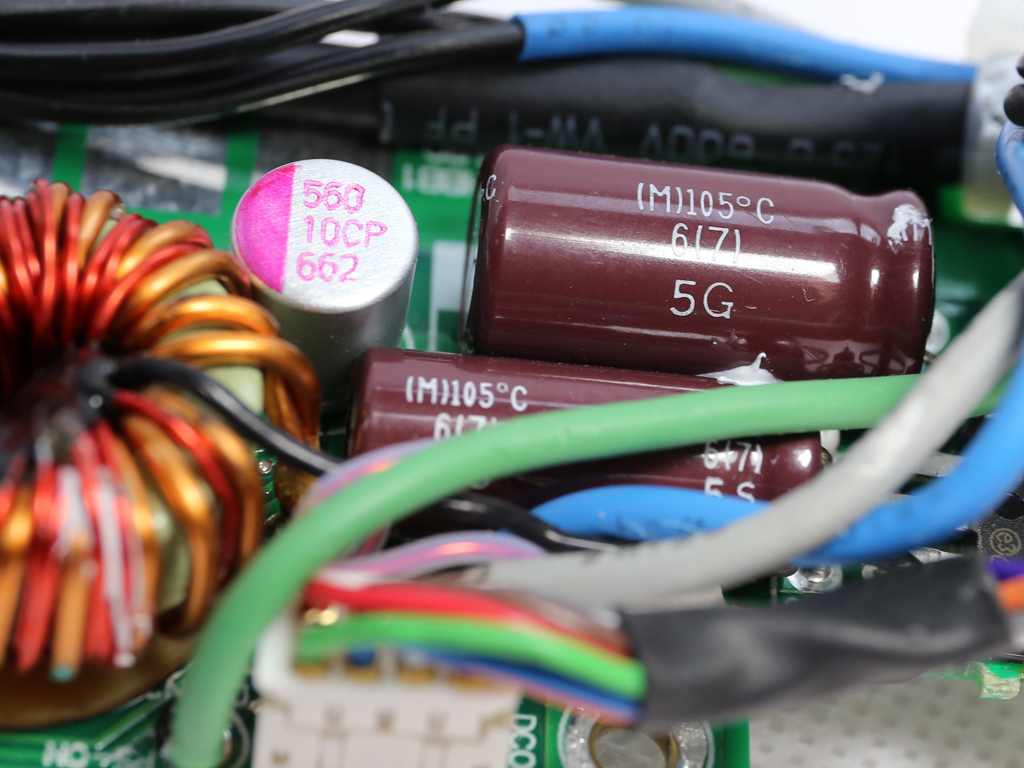
The filtering caps are provided by Chemi-Con and Teapo. All of the electrolytic caps are Japanese, so they should last for a long time.
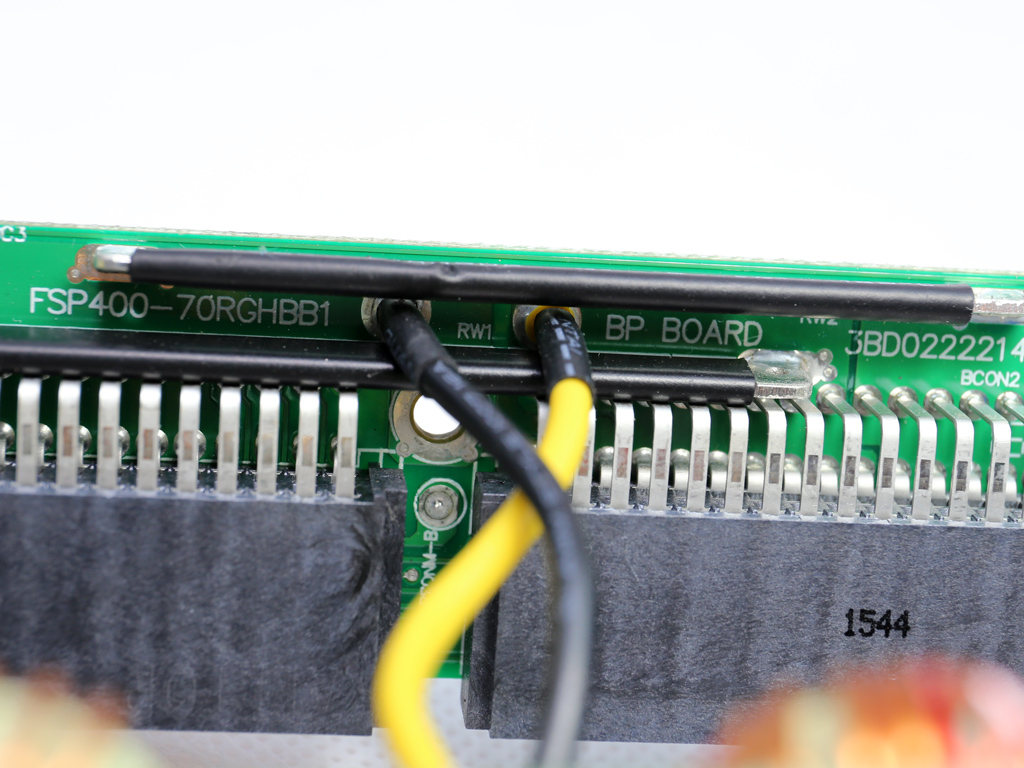

The VRMs are fed from the power modules through a couple of wires.
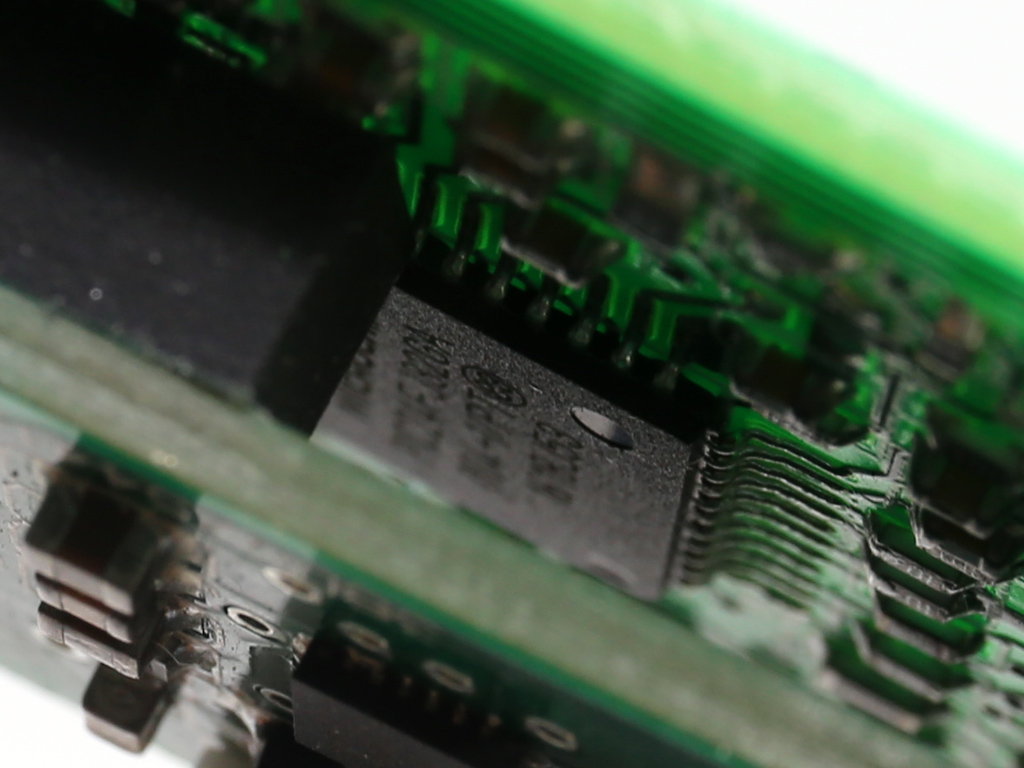
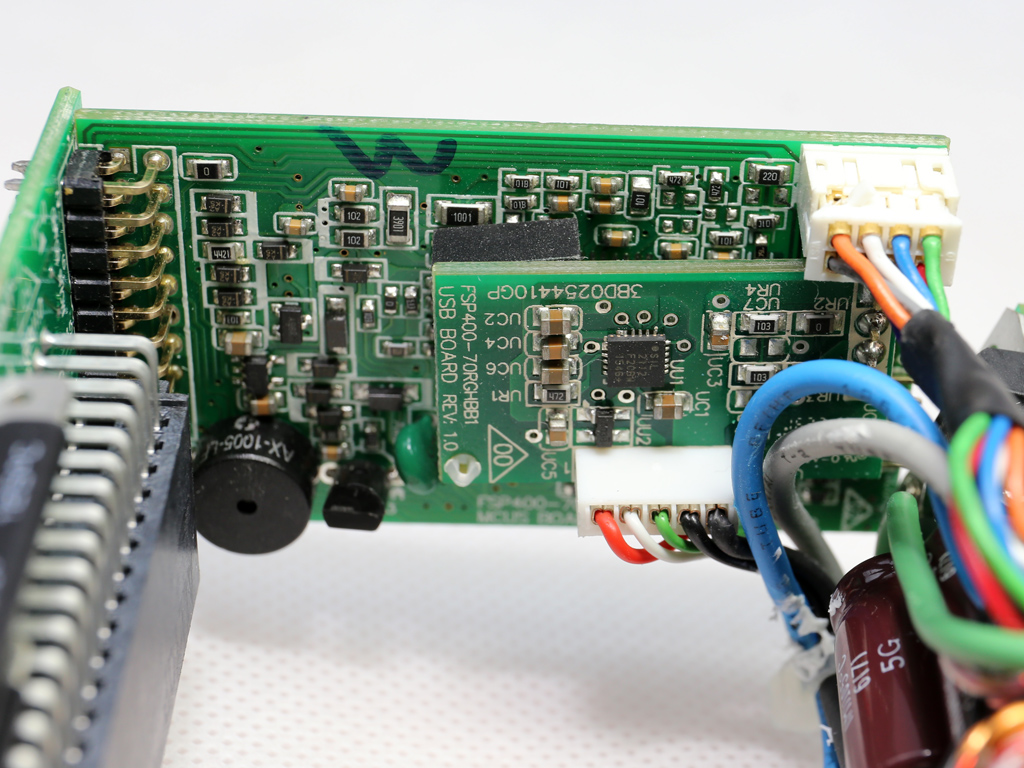
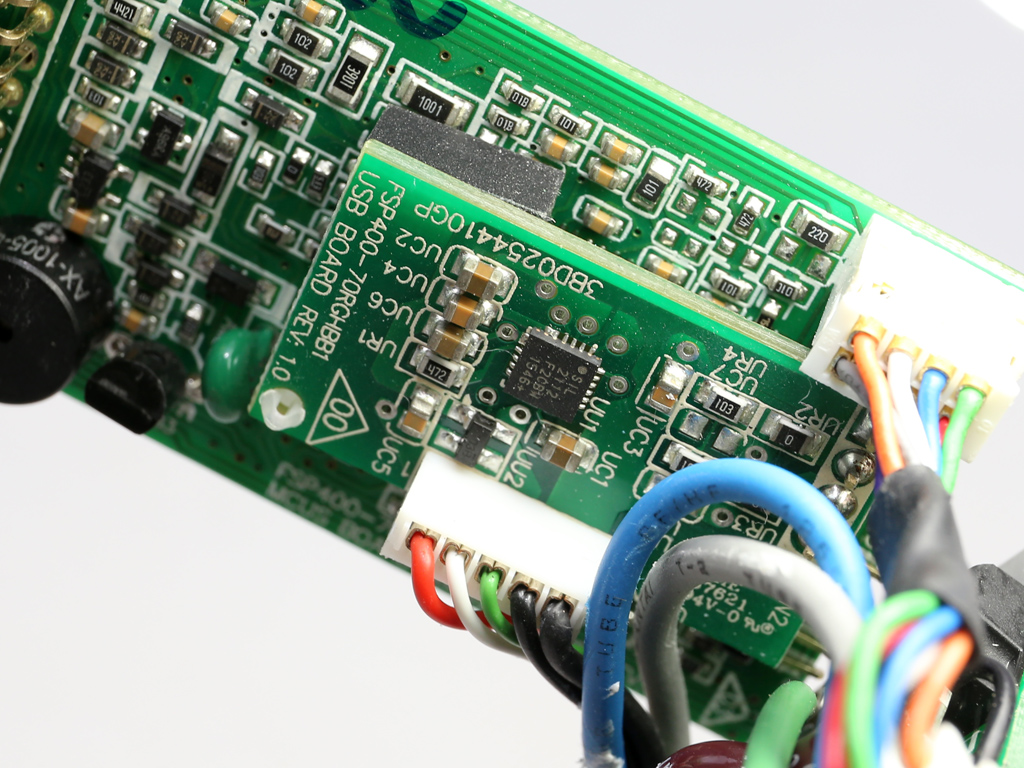
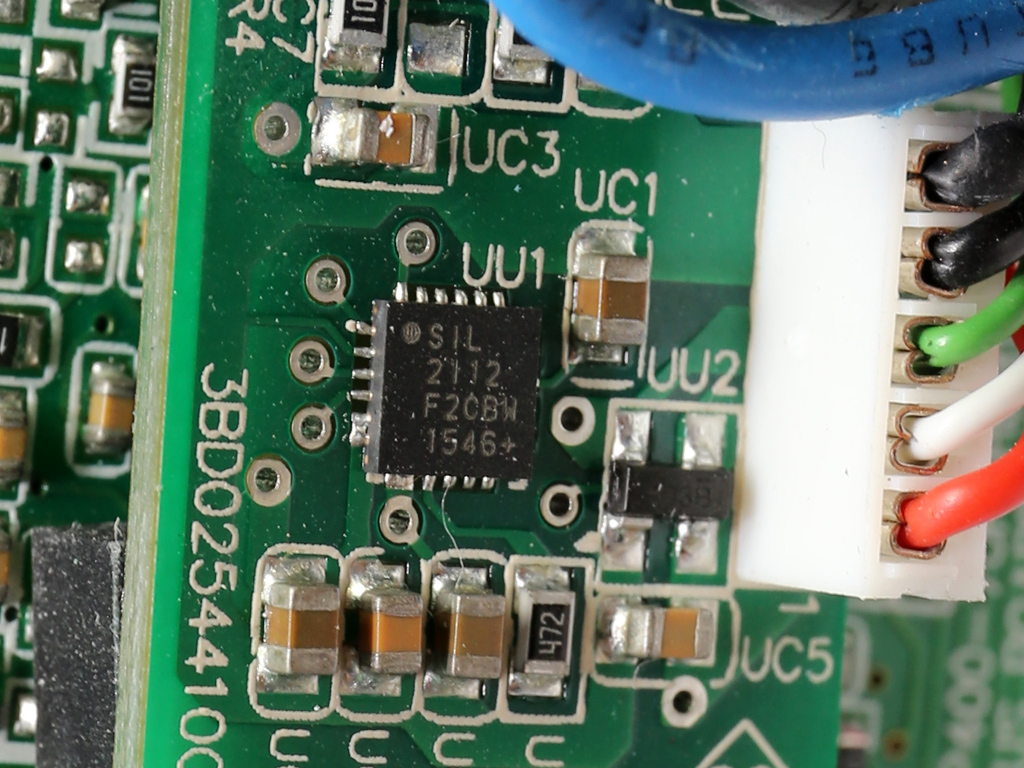
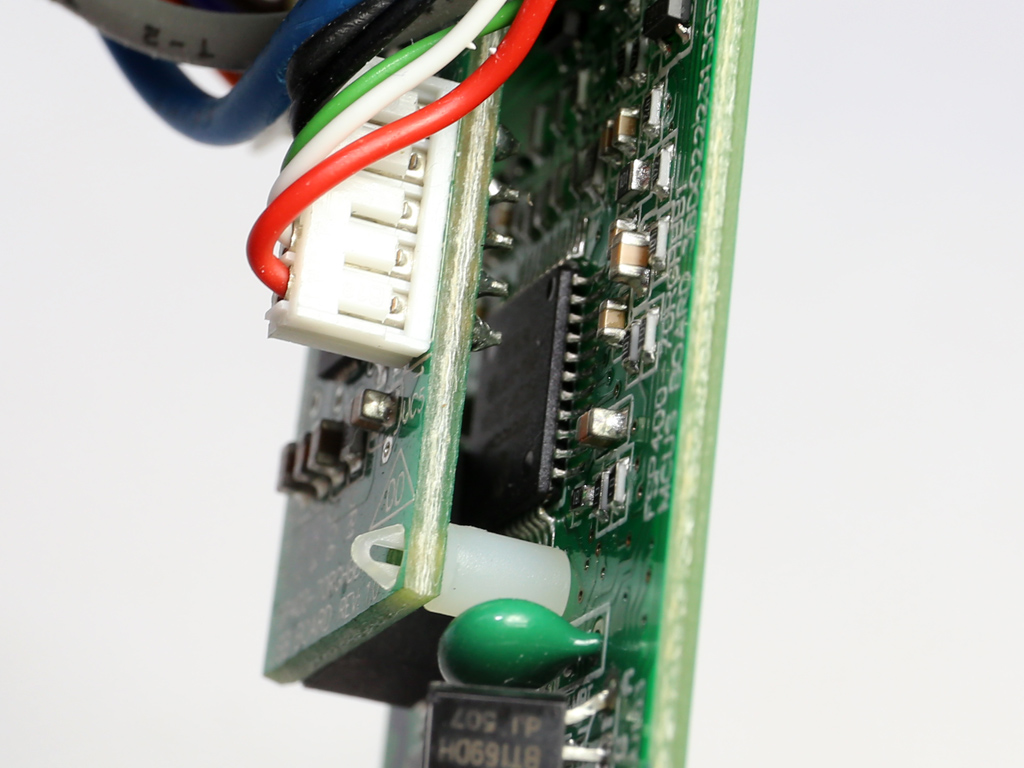

This pair of boards hosts the MCU (Microchip PIC24FJ32GA) and USB transceiver, a Silicon Labs CP2112 IC.
Current page: A Look Inside And Component Analysis
Prev Page Packaging, Contents, Exterior, And Cabling Next Page FSP Guardian Software
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
shrapnel_indie ReplyPros
Full power at 45°CAll cables are fixed, and because this is a server-like product, its maximum operating temperature for continuous full power delivery is 50°C.
Please explain to me why these numbers don't seem to match up properly. (THB, I may have missed it.)
-
dstarr3 I really wonder what a consumer could possibly want this for. What is an ordinary consumer doing that they absolutely cannot risk any downtime whatsoever on their rig?Reply -
nzalog I know freenas can be configured to work faster if you can for sure trust the system from not having RAM errors (covered by ECC) and if you can guarantee there is no unexpected shutdown (covered by dual power and ups). However the reliable power is not really required because a SSD as an SLOG device will cover for it, but then the SSD becomes the bottleneck for writes.Reply -
firefoxx04 I build several file servers a month for clients. Low end enough to where pre built solutions are not an option. This power supply would be a good fit but it is useless, imo, without some sort of email alert option. Maybe I missed that?Reply
When I deploy file servers for clients, I always setup some sort of alert system for raid failures so I can fix the problem. What is the point of redundancy if the user has no idea a problem has occurred? Yes i know that this PSU makes a "loud buzzer noise" but I cant have that either. The user needs to continue to use the system and they cannot if it is screaming 100% of the time.
Send me an email alert. Its easy to implement. -
Rookie_MIB One thing I'm curious about - what if one unit does fail? Are they bog-standard replacement parts where you can go and buy a similar hot swap redundant power supply or is the system proprietary. If it's the latter, then I don't see many people lining up for this one...Reply -
apache_lives A PSU is but one part of a "reliable" machine, to me this will not increase up time or do anything of any value, seems more like a "makes me feel better" part.Reply -
Aris_Mp about the first comment, the PSU is certified for up to 50C ambient full power delivery, but I choose to test up to 45C every PSU that passed from my test bench (since I also have to evaluate 40C rated units and I need to keep the same conditions for all).Reply -
shrapnel_indie Reply19144735 said:about the first comment, the PSU is certified for up to 50C ambient full power delivery, but I choose to test up to 45C every PSU that passed from my test bench (since I also have to evaluate 40C rated units and I need to keep the same conditions for all).
While I'm glad for that, It's also nice to know if a unit rated at 50°C operation will deliver on its "promise" though. (If you exceed the "promised" rating, like the 40°C rated units @ 45, well, it delivered on its promise and then some.)
-
Pompompaihn Newegg has several server chassis for sale that come WITH redundant 500w+ PSUs for less money than just this power supply. Given that the market is low end commercial/prosumer, and it's not going to be for gaming or HTPC, why wouldn't you just buy the whole thing for cheaper?Reply