Nvidia GeForce GTX 780 Ti Review: GK110, Fully Unlocked
Hot on the heels of AMD's Radeon R9 290X receiving acclaim for a fair price and high performance, Nvidia is launching its fastest single-GPU gaming card ever: GeForce GTX 780 Ti. It's quicker than 290X, but also more expensive. Is the premium worthwhile?
Gaming Power Consumption Details
Measuring Power Consumption
We’re using a current clamp to measure power consumption at the external PCIe power cable and, using a special PCB, directly at the PCIe slot. These measurements are recorded in parallel and in real time, added up for each second, and logged using multi-channel monitoring along with the respective voltages. All of this results in a representative curve over the span of 10 minutes. That's all we really need, since these cards reach their operating temperatures relatively quickly.
The curve isn’t just representative; it's also exact. Measuring system power introduces bias, since a number of factors can affect consumption other than the graphics card. A faster GPU might cause the CPU’s power consumption to go up as well, for example, since a limiting factor holding it back is gone.
We’re including three different GK110-based graphics cards in our measurements. Starting from scratch allows for a comparison that’s as objective as possible. We’re using the new GeForce GTX 780 Ti, the Titan, and Gigabyte's GTX 780 WindForce GHz Edition, which might be able to compete with the two other cards thanks to elevated clock rates.
Let’s first take a detailed look at each of the three cards. We’re benchmarking both boards with Nvidia's reference cooler twice: once with default settings and once at 70 °C GPU temperature. The latter necessitates a manual fan speed increase.
GeForce GTX 780 Ti
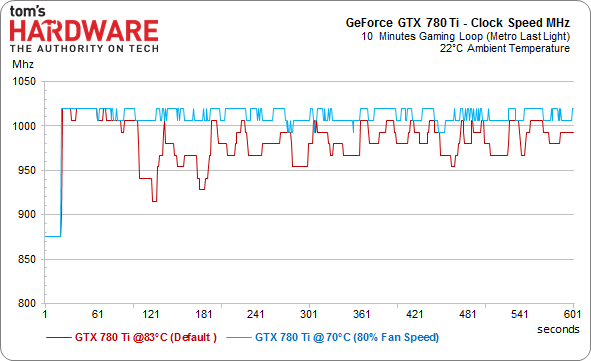
We start with a look at the frequencies, which might help us explain the somewhat unexpected differences in power consumption later.
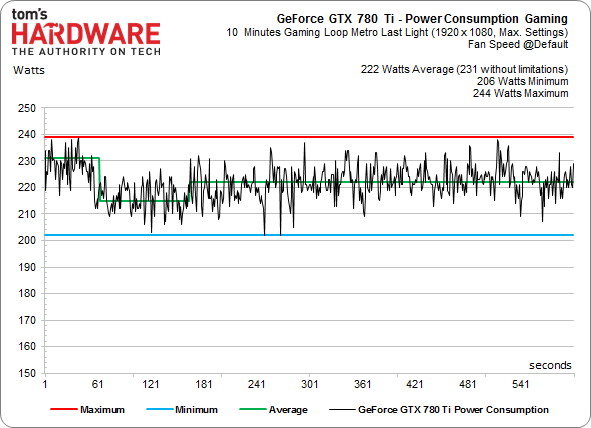
Even under full load, the GeForce GTX 780 Ti balances its frequencies well. Consequently, its power consumption is similar in the two scenarios. Nvidia has raised its target temperature target from 80 to 83 °C, which results in a fan RPM that's a little bit higher. Still, the shape of the curve shows how the power consumption decreases once the card backs off of its GPU Boost clock rates.
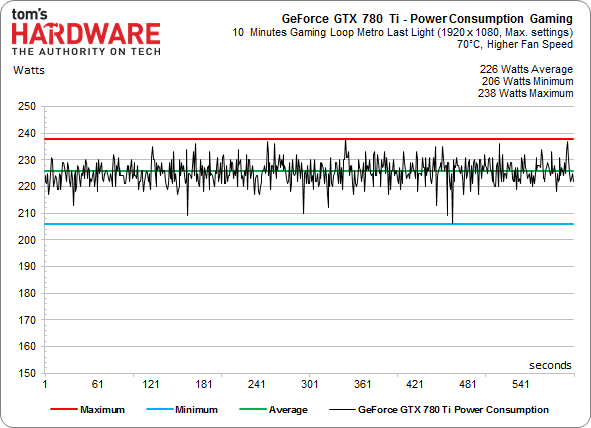
Things look different when the fan RPM is pushed up. We sought to achieve a 70 °C GPU temperature by setting Nvidia's fan speed to 80% duty cycle, which yields additional performance. We’ll take a closer look at this difference a little later in our efficiency section. For now, here’s a nicely shaped curve:
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
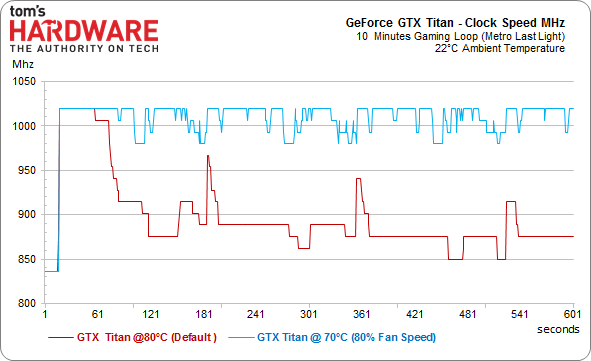
GeForce GTX Titan
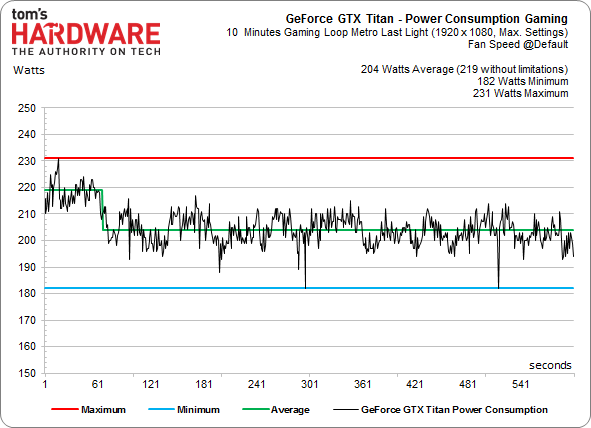
Next up: the former champion. With a temperature target of only 80 °C and a fan that spins only half as fast, the Titan faces an uphill battle. Let’s first take a look at the frequencies:
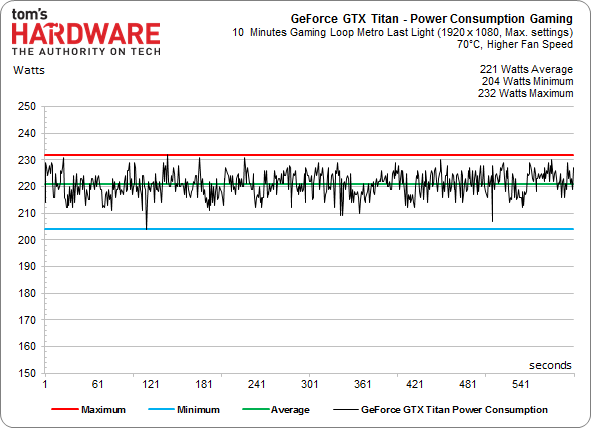
The difference is almost scary to behold, suggesting the Titan's fan could have probably been pushed a little harder. Aiming for a 70 °C GPU temperature using 80-percent fan speed, GeForce GTX Titan lives up to its name and can even show off its GPU Boost feature a bit. So, what does the card’s power consumption look like after its clock rates are uncorked by pushing a lot of air across its heat sink? First, a look at the stock settings:
Power consumption drops alongside clock rate, which also negatively impacts game performance. Again, we'll evaluate this phenomenon's effect on efficiency shortly.
How about when we dramatically ramp up cooling? GeForce GTX Titan puts its pedal to the medal and pulls quite a bit more power.
This is just a look at power, so all we can tell from these charts is that draw increases by 18 W. Our hope would be that you also get a corresponding performance boost, too. We'll see shortly.
Gigabyte GTX 780 Windforce GHz Edition
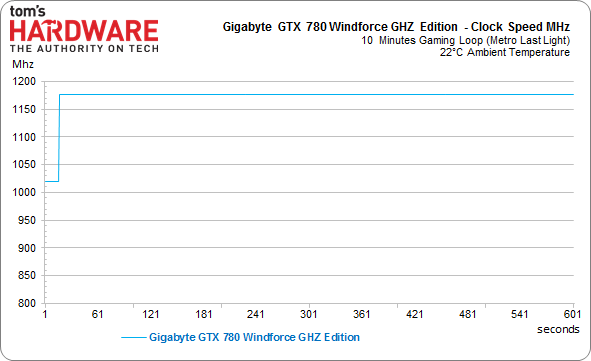
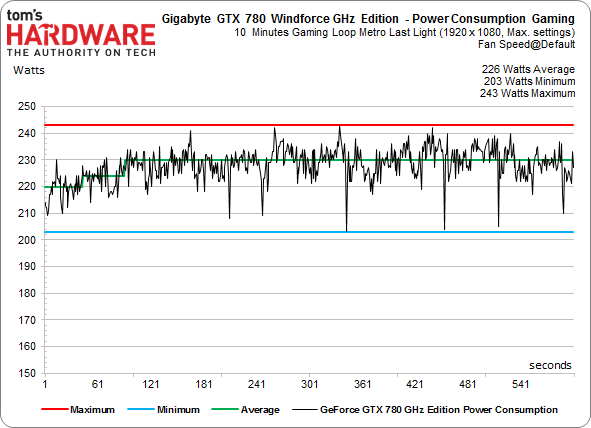
The round-up of GK110-based boards is completed by Gigabyte's brand new GTX 780 WindForce GHz Edition. This card features fewer CUDA cores, but they're running at higher clock rates. Is that enough of a compromise to keep a lower-cost, overclocked graphics card competitive? We've seen in the past that GK110’s sweet spot is under 1000 MHz. However, there's also a new stepping of the chip available, and Gigabyte's offering does facilitate a completely consistent frequency, even under load, thanks to its excellent cooler. The card is naturally more expensive than other GTX 780 boards, so the company has to hope it does battle based on elevated clock rates.
Gigabyte's GTX 780 WindForce GHz Edition manages to hold a core frequency of almost 1180 MHz. This is reflected in our power consumption measurements, though.
We see an average power draw of 226 W, putting the Gigabyte card at the same level as our more aggressively-cooled GeForce GTX 780 Ti, and 4 W beyond the 780 Ti's stock configuration.
Current page: Gaming Power Consumption Details
Prev Page Results: CUDA Benchmarks Next Page Detailed Gaming Efficiency Results-
faster23rd My heart broke a little bit for AMD. Unless AMD's got something up their sleeve, it's up to the board manufacturers now to get the 290X in a better competitive stance than the 780 ti.Reply -
tomc100 At $700, AMD has nothing to worry about other than the minority of enthusiast who are willing to pay $200 more for the absolute fastest. Also, when games like Battlefield 4 uses mantle the performance gains will be eroded or wiped out.Reply -
expl0itfinder Keep up the competition. Performance per dollar is the name of the game, and the consumers are thriving in it right now.Reply -
alterecho I want to see cooler as efficient as the 780 ti, on the 290X, and the benchmarks be run again. Something tells me 290X will perform similar or greater than 780ti, in that situation.Reply -
ohim Price vs way too few more fps than the rival will say a lot no matter who gets the crown, but can`t wonder to imagine the look on the face of the guys who got Titans for only few months of "fps supremacy" at insane price tags :)Reply -
bjaminnyc 2x R9 290's for $100 more will destroy the 780Ti. I don't really see where this logically fits in a competitively priced environment. Nice card, silly price point.Reply -
Innocent_Bystander-1312890 "Hawaii-based boards delivering frame rates separated by double-digit percentages, the real point is that this behavior is designed into the Radeon R9 290X. "Reply
It could also come down to production variance between the chips. Seen in before in manufacturing and it's not pretty. Sounds like we're starting to hit the ceiling with these GPUs... Makes me wonder what architectural magic they'll come up with next.
IB -
bjaminnyc 2x R9 290's for $100 more will destroy the 780Ti. I don't really see where this logically fits in a competitively priced environment. Nice card, silly price point.Reply -
Deus Gladiorum I'm going to build a rig for a friend and was planning on getting him the R9 290, but after the R9 290 review I'm quite hesitant. How can we know how the retail version of that card performs? Any chance you guys could pick one up and test it out? Furthermore, how can we know Nvidia isn't pulling the same trick: i.e. giving a press card that performs way above the retail version?Reply