Intel Cascade Lake Xeon Platinum 8280, 8268, and Gold 6230 Review: Taking The Fight to EPYC
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Sysbench, Stream, C-Ray, 7-Zip
Sysbench CPU
Sysbench is a widely used suite that characterizes CPU, memory, file I/O, mutex, and MySQL performance. We focus on the CPU test, which measures the amount of time required to verify prime numbers in both single- and multi-threaded workloads.
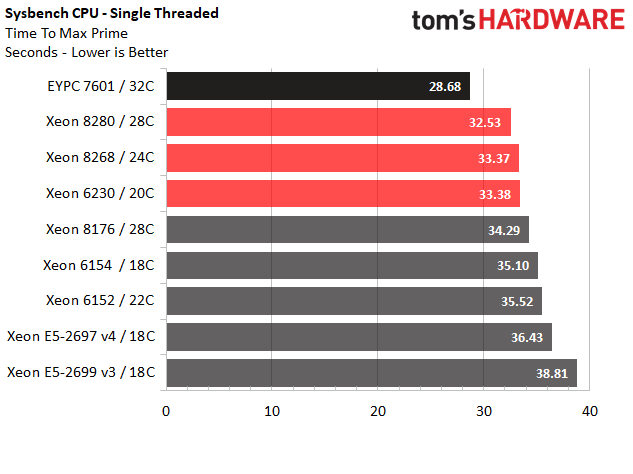
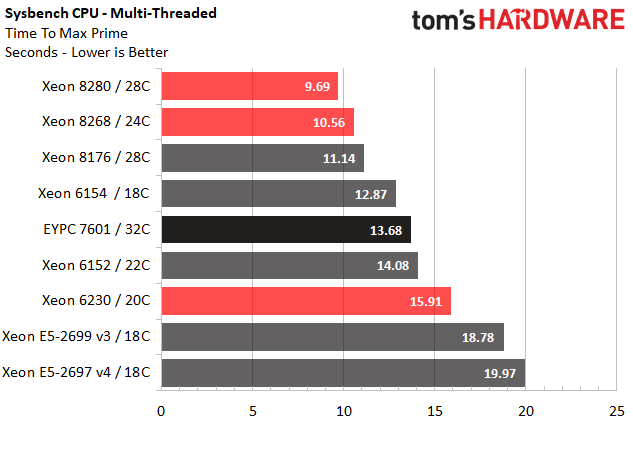
The EPYC 7601's stellar performance in the single-threaded test is impressive given its relatively conservative clock rates. But the chip loses steam during the multi-threaded test, possibly due to architectural influences from the multi-chip module (MCM) design.
The Cascade Lake line-up aligns neatly based on clock rates during the single-threaded test. Then it falls into the expected hierarchy based on core count during the multi-threaded benchmark.
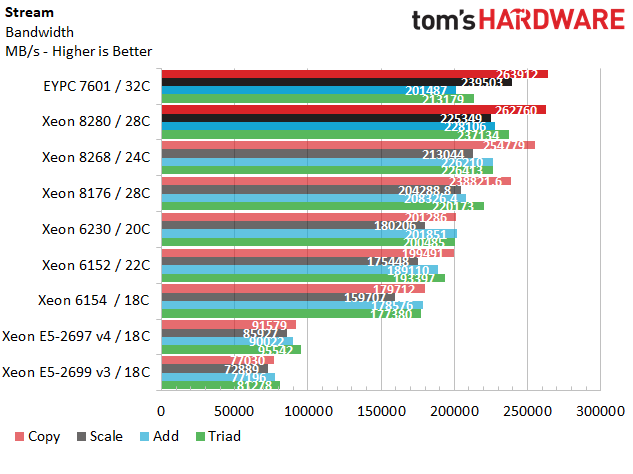
Stream
Stream is a relatively simple test developed by Dr. John D. McCalpin. It measures the sustainable memory throughput of a given system in MB/s.
AMD's EPYC 7601 leads the pack during the copy and scale tests, but it isn't uncommon to see the chip deliver more throughput thanks to its eight-channel memory interface.
The improvement from Intel's Broadwell (quad-channel) to Skylake (six-channel) architectures is impressive. The increased throughput from Skylake to Cascade Lake isn't as significant, though we do see some gains from support for faster DDR4-2966 memory.
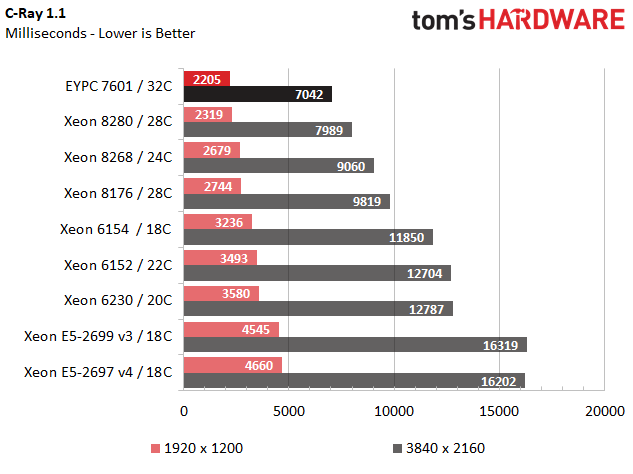
C-Ray 1.1
C-Ray is a ray tracing benchmark designed to reside entirely inside of a CPU's cache, thus eliminating RAM and disk I/O overhead from the measurement. This test focuses purely on floating-point performance during rendering, and it runs across multiple threads.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The ray tracing workload scales nicely based on core count, and AMD's EPYC 7601 shows its chops with 32 cores that carve out a lead. Clock rate clearly plays a role too, as we see the 24-core Xeon 8268 eke out a win over the previous-gen 28-core Xeon 8176. We also notice the Xeon 6154, which has a 900 MHz advantage over the 22-core Xeon 6152, beat its counterpart.
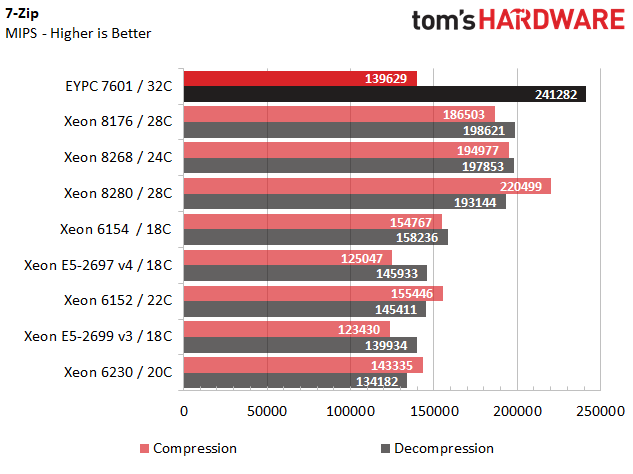
7-Zip
7-Zip is open source software that measures compression and decompression performance, which can be a key capability for storage and networking applications.
As service contracts expire, most enterprises will move up from older Haswell, Broadwell, and Skylake platforms to the Platinum series. This convincing set of benchmarks highlights yet another aspect of day-to-day operations that will benefit from boosted performance.
AMD's EPYC 7601 showcases the Zen architecture's fondness for decompression workloads, while delivering substantially less compression performance.
HardInfo
HardInfo provides granular system information and includes a suite of benchmarks for measuring CPU performance. It's easily accessible and comes as a standard component in many Ubuntu desktop systems. We include these tests because they allow our Linux brethren to easily run comparison data.
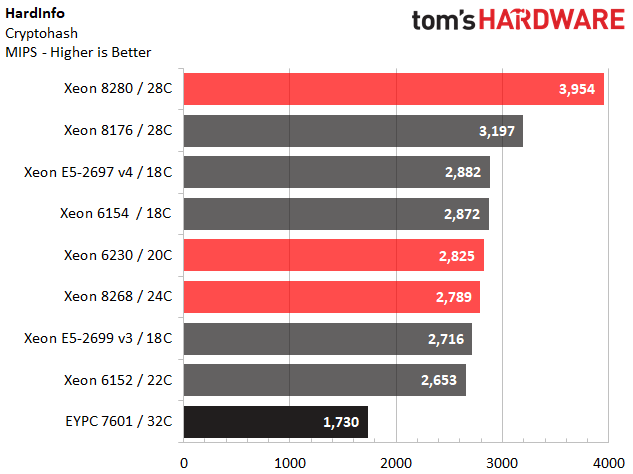
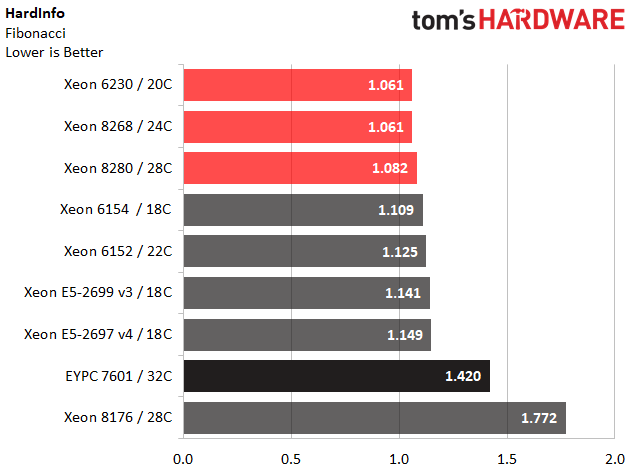
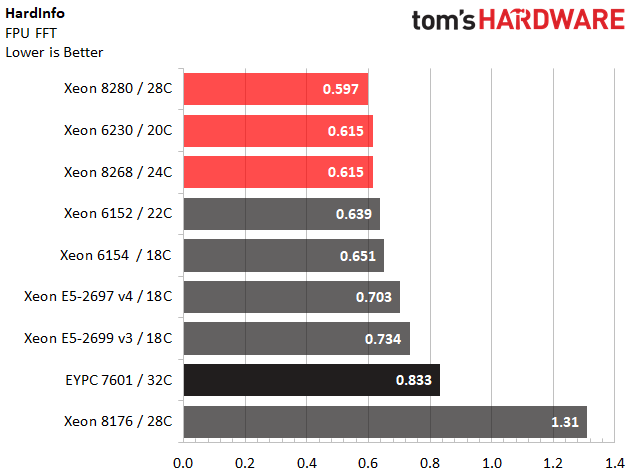
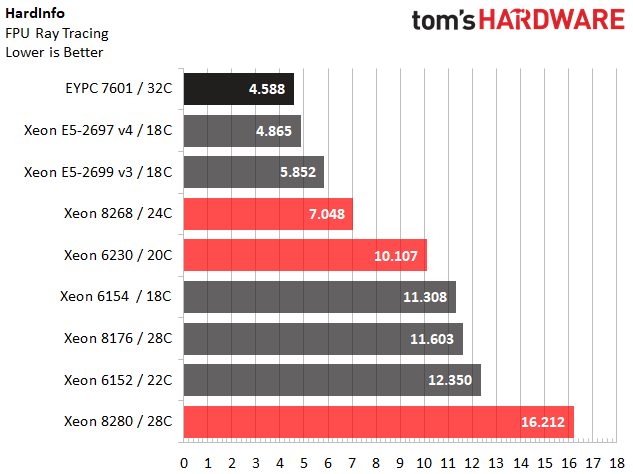
Intel's Platinum 8280 outperforms our expectations in the Cryptohash test. However, we notice reduced performance from the company's LGA 3647 processors during the FPU ray tracing benchmark. Intel informs us that some applications suffer mesh-imposed performance penalties until the software ecosystem adjusts, though we've only found the altered architecture to affect a few enterprise-class benchmarks. We suspect we can add this specific title to the list of applications that might see better performance after optimizations.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPU Content
Current page: Sysbench, Stream, C-Ray, 7-Zip
Prev Page Linux Compile, Unix Bench, NASPB Next Page Power Consumption
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
Murissokah In the first page there's a paragraph stating "Like the previous-gen Xeon Scalable processors, Intel's Cascade Lake models drop into an LGA 4637 interface (Socket P) on platforms with C610 (Lewisburg) platform controller hubs, and the processors are compatible with existing server boards."Reply
Wouldn't that be LGA 3647? And shouldn't it read C620-famliy chipset for Lewisburg? -
JamesSneed It just hit me how big of a deal EPYC will be. AMD is already pulling lower power numbers with the 32 core 7601 however AMD will have a 64 core version with Zen2 and has stated the power draw will be about the same. If the power draw is truly is the same, AMD's 64 core Zen2 parts will be pulling less power than Intel's 28 core 8280. That is rather insane.Reply -
Amdlova lol 16x16gb 2666 for amdReply
8x32gb intel 2400
12x32gb intel 2933
How To incrase power compsumation to another level. add another 30w in memory for the amd server and its done. -
Mpablo87 The promise or realityReply
Cascade Lake Xeons employ the same microarchitectur as their predecessors, but, we can hope, it is promising!) -
The Doodle Slight problem this author fails to tell you in this article and that's OEM's can only buy the Platinum 9000 processor pre-mounted on Intel's motherboards. That's correct. None of the OEM's are likely to ship a solution based on this beast because of this fact. So at best you will be able to buy it from an Intel reseller. So forget seeing it from Dell, HPE, Lenovo, Supermico and others. your in white box territory.Reply
Besides, why would they? A 64C 225W AMD Rome will run rings around this space heater and cost a whole lot less.