Intel SSD DC S3700 Review: Benchmarking Consistency
With the recent announcement of the SSD DC S3700, Intel is firmly targeting enterprise customers with something not normally seen on spec sheets: performance consistency. Will their latest offering live up to expectations, or fall short? Lets find out.
Results: Enterprise Workload Performance
Our next set of tests simulates different enterprise-oriented workloads, including database, file server, Web server, and workstation configurations.
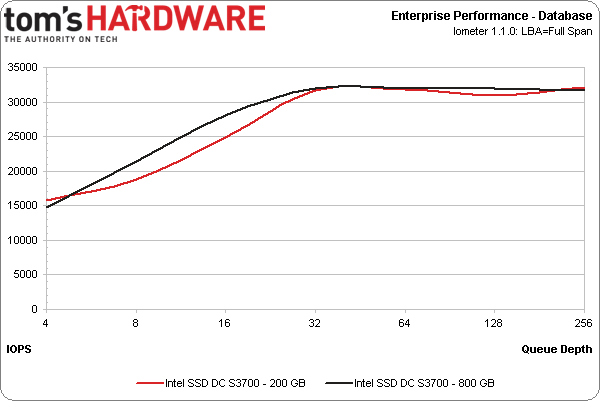
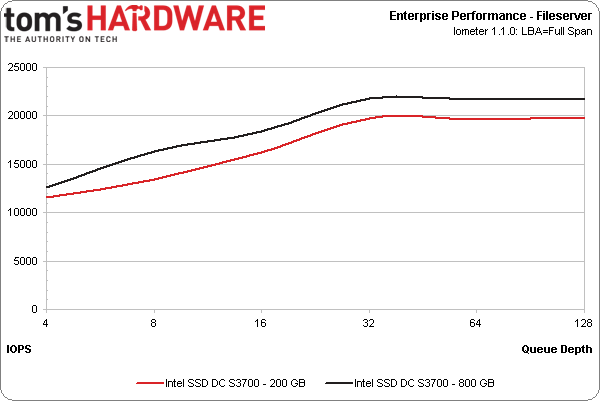
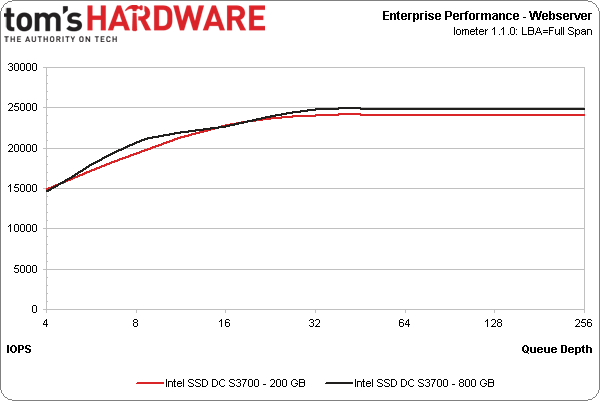
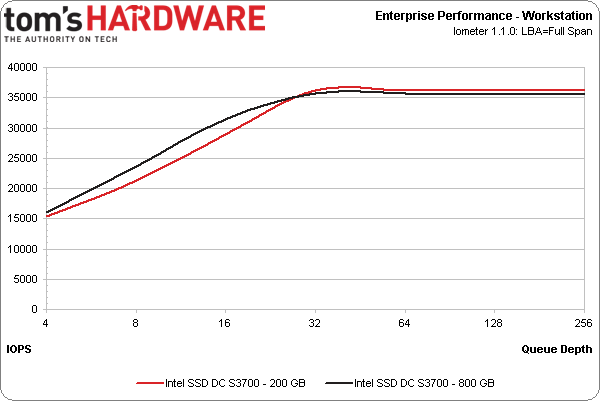
Notice that the results are pretty similar, regardless of whether you're looking at the 200 or 800 GB model. This is the case largely because high-end workloads are generally biased to read operations. Both capacities offer the same read performance, so it's no surprise to see them so close to each other.
At lower queue depths, the 800 GB SSD DC S3700 is consistently faster in each workload. It also exhibits an advantage in the file server workload. However, if your application mostly involves read operations, any of Intel's available capacities should be suitable. Our only warning would be that the 100 GB drive, which we don't have in-house, is rated for significantly lower write performance.
Our database workload (also categorized as transaction processing) involves purely random I/O. Its profile consists of 67% reads and 33% writes using 8 KB transfers.
The file server workload consists of 80% random reads of varying transfer sizes.
The Web server (100% read, varying transfer size) and workstation (80% reads, 80% random) workloads show the same basic trend.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Results: Enterprise Workload Performance
Prev Page Results: 4 KB Random Performance And Latency Next Page Results: Sequential Performance-
merikafyeah Consistency and reliability are always more important to me than speed and capacity,Reply
but it's wonderful when you can have all four.
Kudos to Intel for raising the bar yet again on SSD quality. Eagerly awaiting trickle-down effect. -
InvalidError adgjlsfhkhow does ssd power consumption compare to an hhd's in watts per gigabyte?For conventional 3.5" HDDs, you have 5-8W idle, 10-15W seek and 15-25W spin-up.Reply
For 2.5" HDDs, you have ~1W idle and 2-2.5W seek/spin-up.
I'm a little surprised at how much power Intel's enterprise SSDs are using. I'm guessing a good chunk of the reason comes from having extra circuitry to do the double-conversion from 5/12V to ~30V and then back down to whatever the SSD needs. -
drewriley InvalidErrorFor conventional 3.5" HDDs, you have 5-8W idle, 10-15W seek and 15-25W spin-up.For 2.5" HDDs, you have ~1W idle and 2-2.5W seek/spin-up.I'm a little surprised at how much power Intel's enterprise SSDs are using. I'm guessing a good chunk of the reason comes from having extra circuitry to do the double-conversion from 5/12V to ~30V and then back down to whatever the SSD needs.Reply
You nailed it. If you look at 2.5" 15K and 10K RPM drive, the Intel is better on W/GB, but it is pretty high when compared to other SSDs. -
master9716 Samsung aint gona mess around , they are going to bring this type of performance to Desktops watch .Reply
-
sanilmahambre So this is why they gave up on motherboards and concentrated more on SSD's! Believe me that trick worked wonders and a lot more money.. LOLReply -
mayankleoboy1 adgjlsfhkhow does ssd power consumption compare to an hhd's in watts per gigabyte?Reply
i am not sure if watt/GB is important for storage.
Reason : the new philosophy is to "hurry up, finish the work, and relax".