Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Comparison Products
Today, we'll be pitting the Delta Max against a few SATA drives: the Crucial MX500 (SM2258 + Micron 64L TLC), Samsung 860 EVO (Samsung MJX + Samsung 64L TLC), Samsung 860 QVO (Samsung MJX + Samsung 64L QLC), and WD Blue 3D (SM2258 + BiCS3 64L TLC) SATA SSDs. For comparison we threw in a high-end NVMe SSD, the Adata XPG SX8200 Pro (SM2262EN + Micron 64L TLC) and an entry-level Intel SSD 660p (SM2263 + Intel 64L QLC). We also added a 6TB WD Black 7200RPM HDD for some extra perspective.
Game Scene Loading - Final Fantasy XIV
The Final Fantasy XIV StormBlood benchmark is a free real-world game benchmark that easily and accurately compares game load times without the inaccuracy of using a stopwatch.
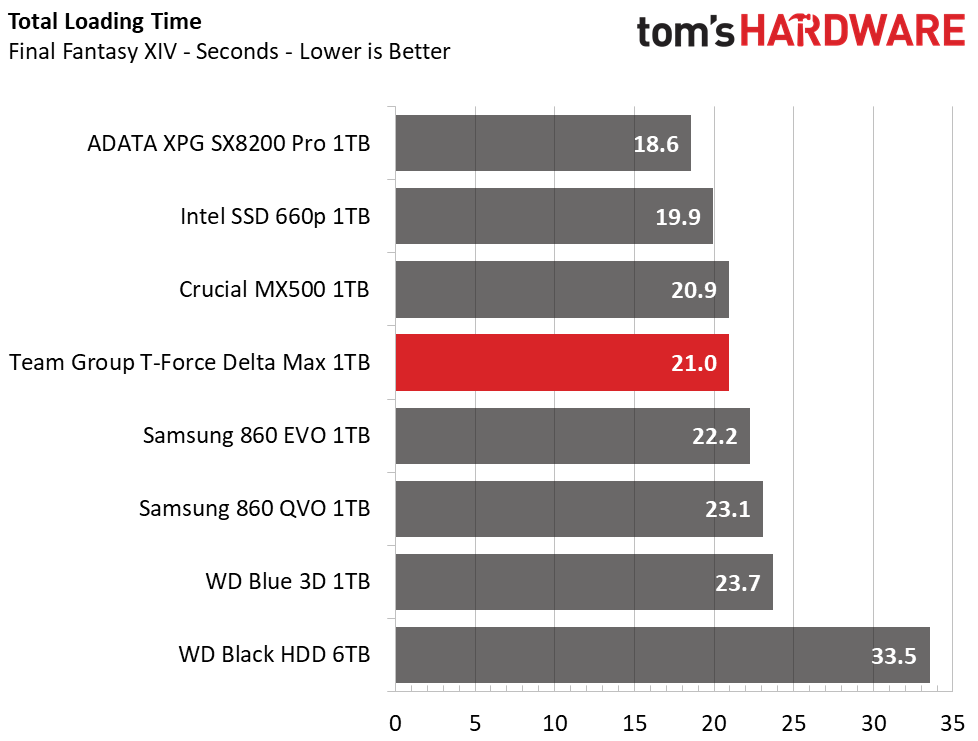
The Delta Max displays very good game loading performance. With a total time of 21 seconds, it is almost as fast as the MX500 and outperforms the Samsung 860 EVO.
Transfer Rates – DiskBench
We use the DiskBench storage benchmarking tool to test file transfer performance with our own custom 50GB block of data. Our data set includes 31,227 files of various types, like pictures, PDFs, and videos. We copy the files to a new folder and then follow up with a reading test of a newly-written 6.5 GB file.
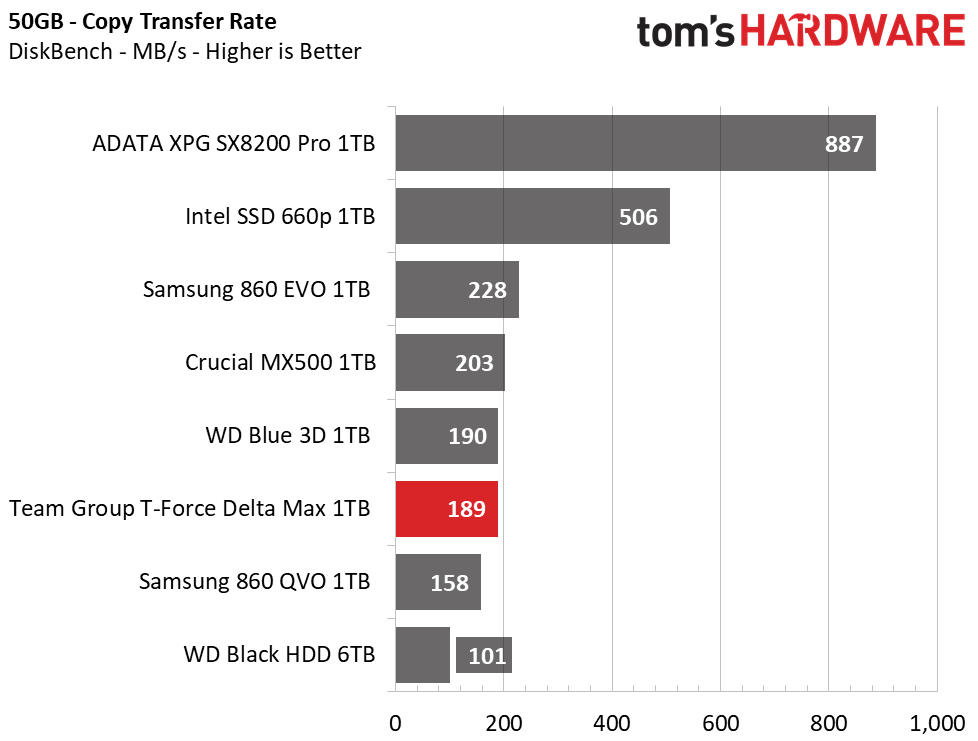
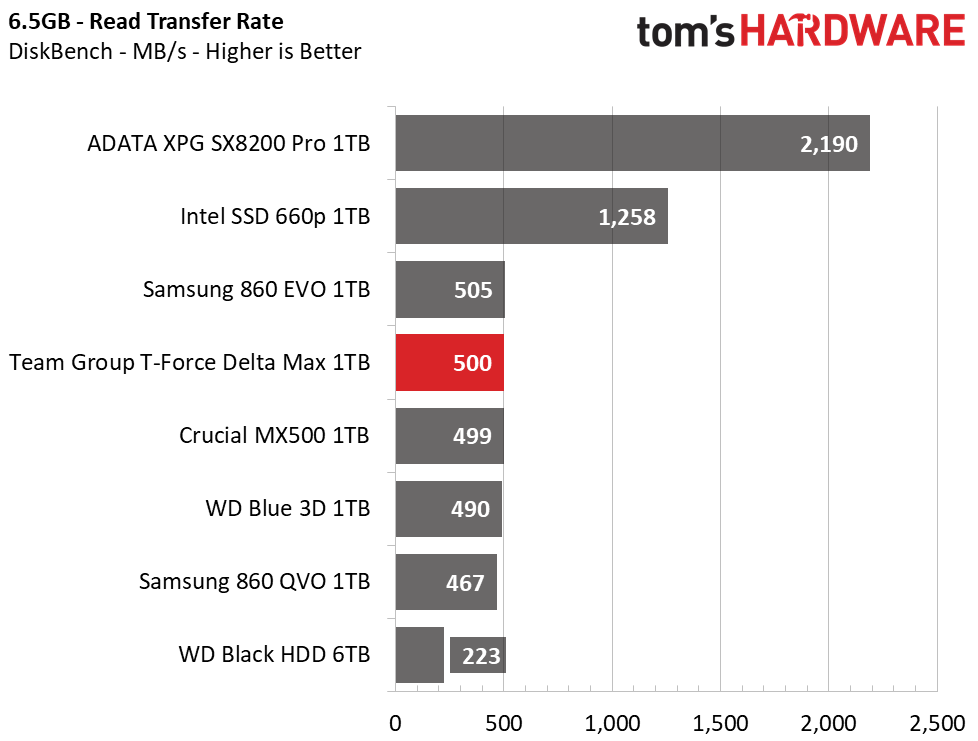
The M.2 NVMe SSDs on the charts take first and second place during our 50GB file transfer. Their extra bandwidth really helps to deliver a more responsive experience. Still, SATA SSDs offer performance that is much faster than any HDD. Team Group’s T-Force Delta Max averages similarly to the other SATA SSDs in the pool and ranks sixth in copy performance and fourth in reading.
Trace Testing – PCMark 8 Storage Test 2.0
PCMark 8 is a trace-based benchmark that uses Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Suite, World of Warcraft, and Battlefield 3 to measure the performance of storage devices in real-world scenarios.
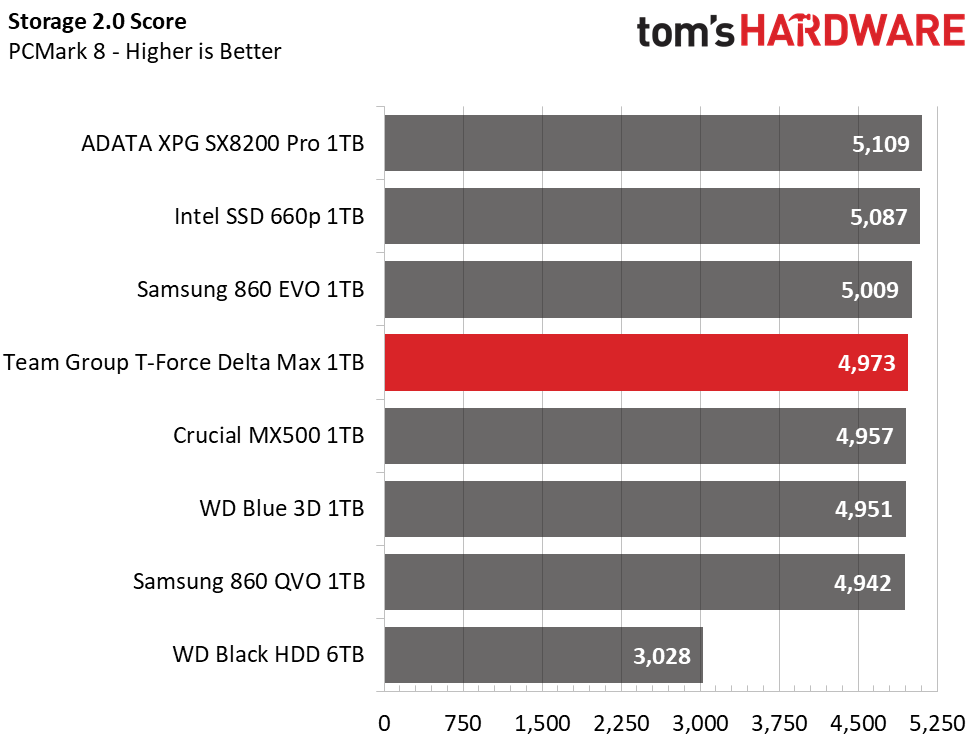
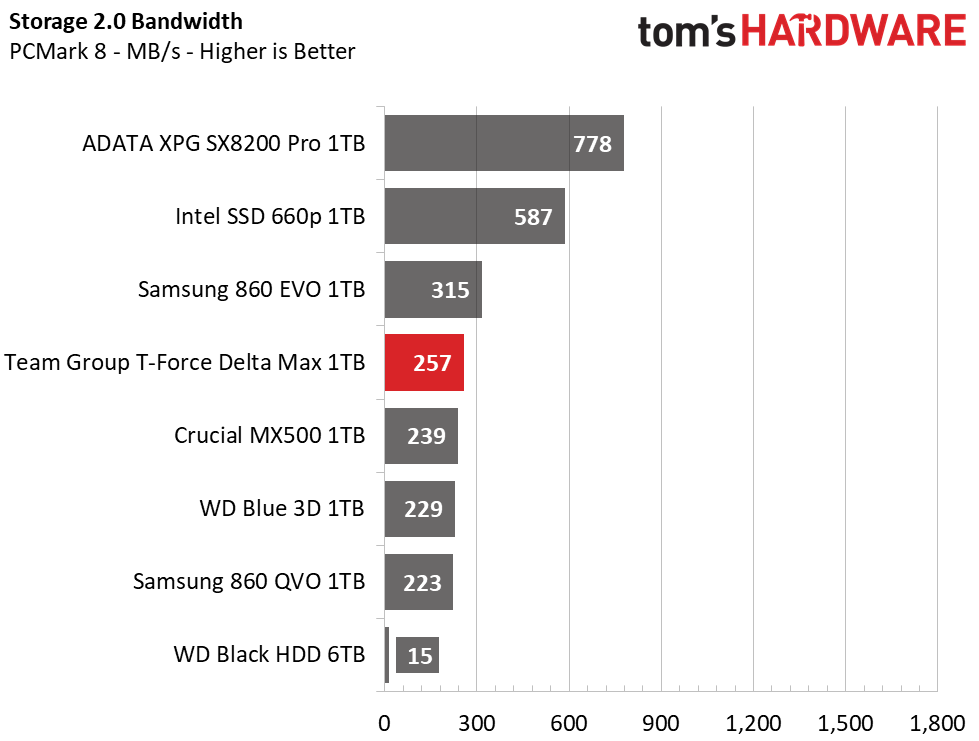
Under some consumer workload testing, again, NVMe proves to have the upper hand. However, the SATA SSDs still provided a responsive experience and scored nearly similarly overall. Team Group’s Delta Max scores fourth place in PC Mark 8, outperforming the Crucial MX500 and lagging the 860 EVO.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Trace Testing – SPECworkstation 3
Like PCMark 8, SPECworkstation 3 is a trace-based benchmark, but it is designed to push the system harder by measuring workstation performance in professional applications. The full suite consists of more than 30 workloads, but we've opted to only run the storage benchmark which uses only 15 of them and categorizes the results into 5 market segments for scoring: Media & Entertainment, Product Development, Life Sciences, Energy, and General Operations.
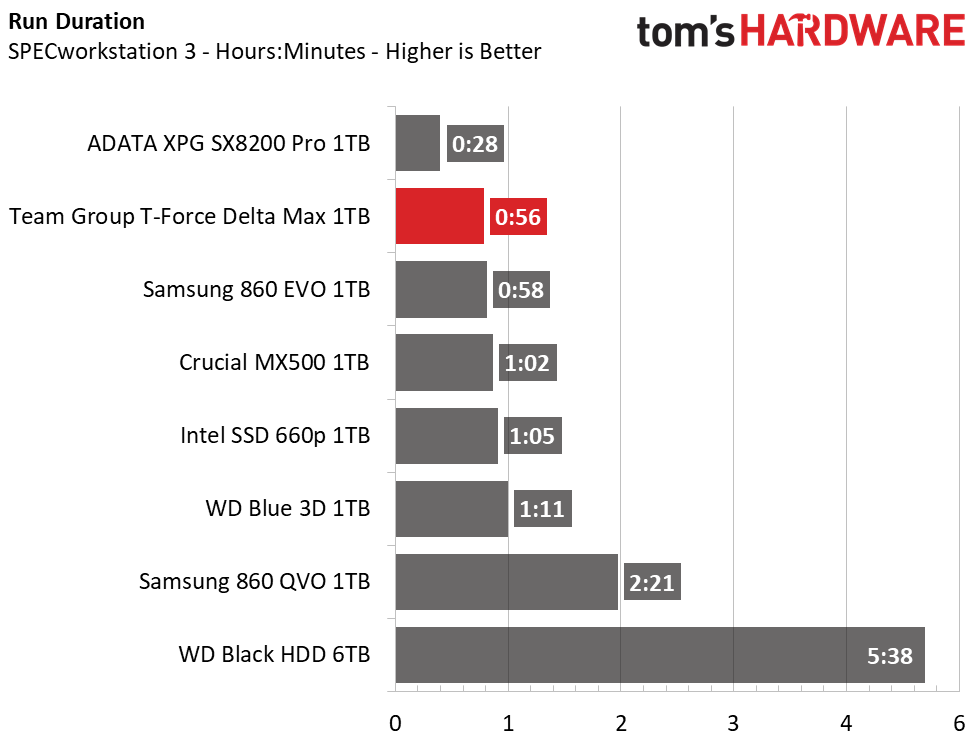
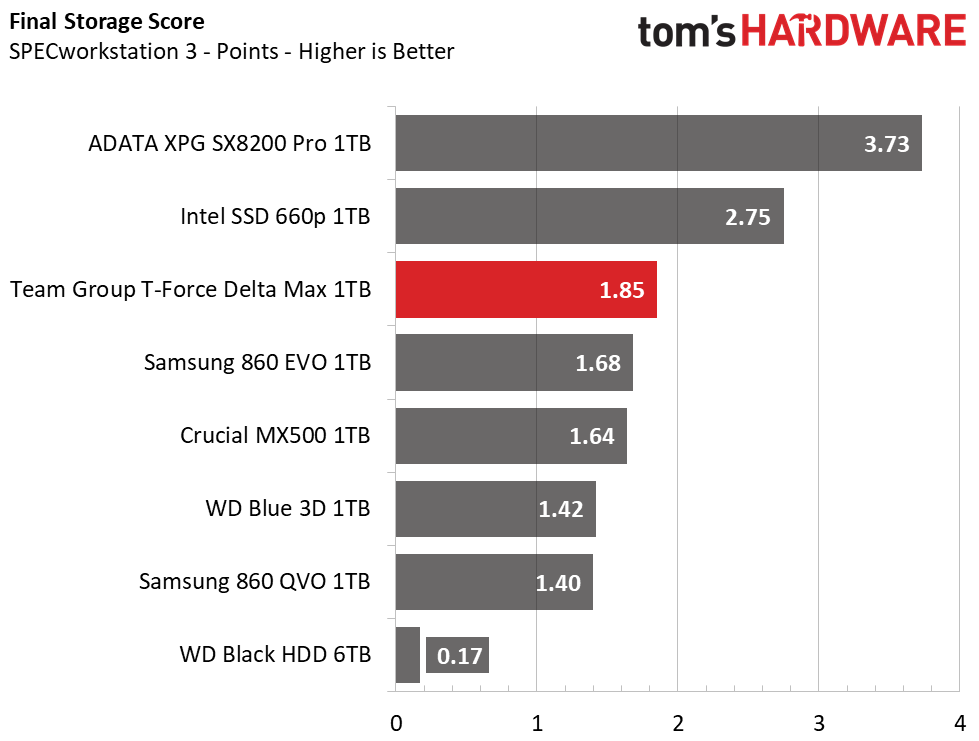
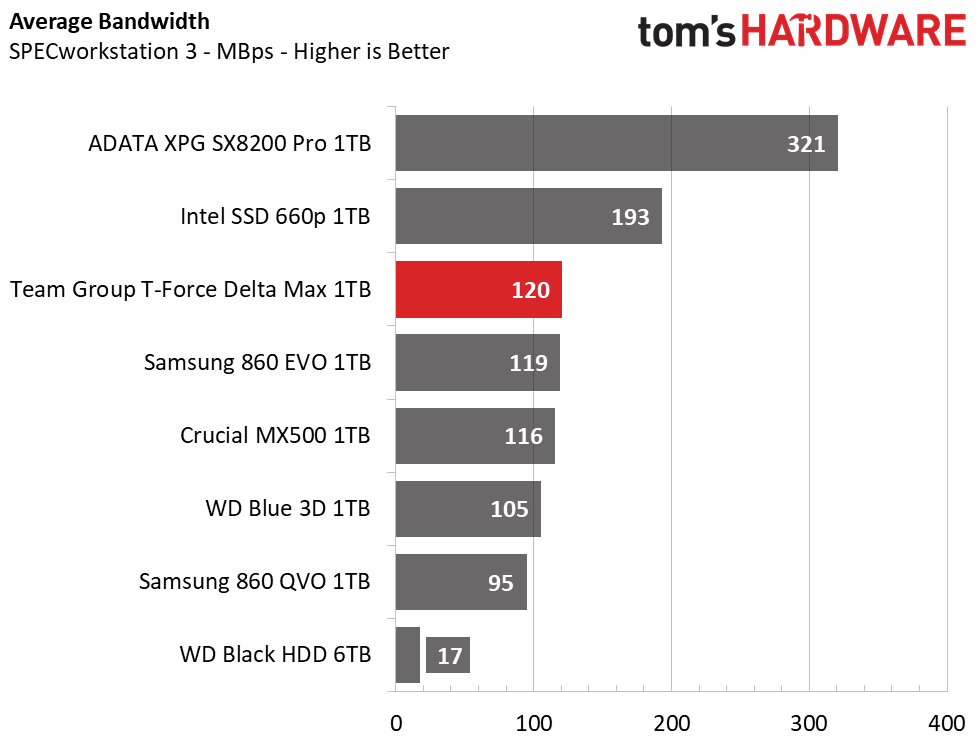
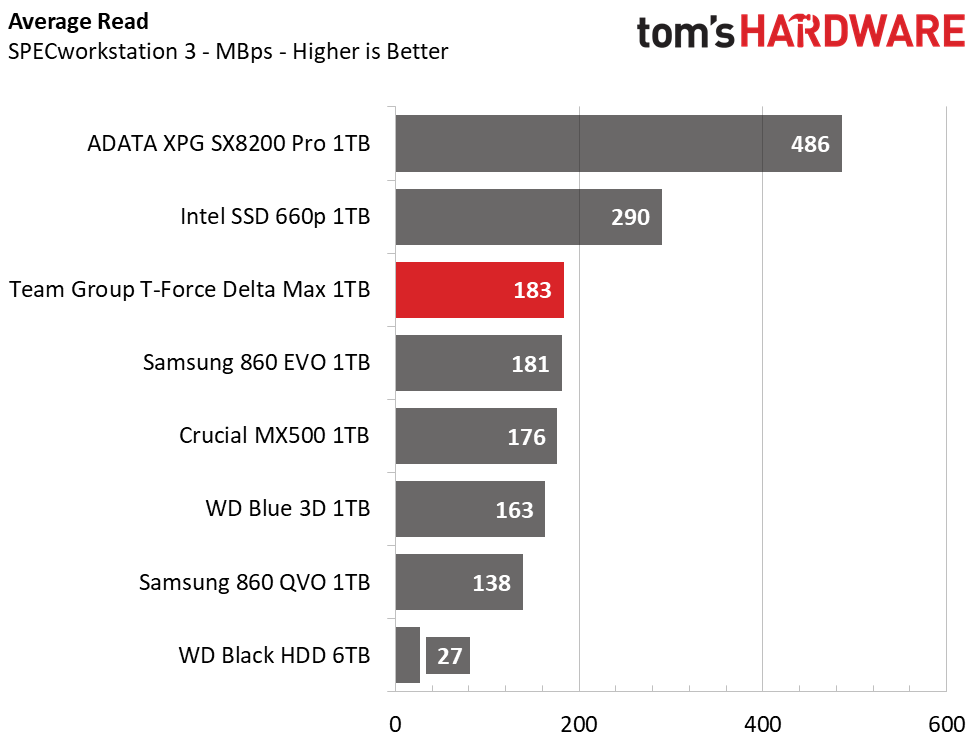
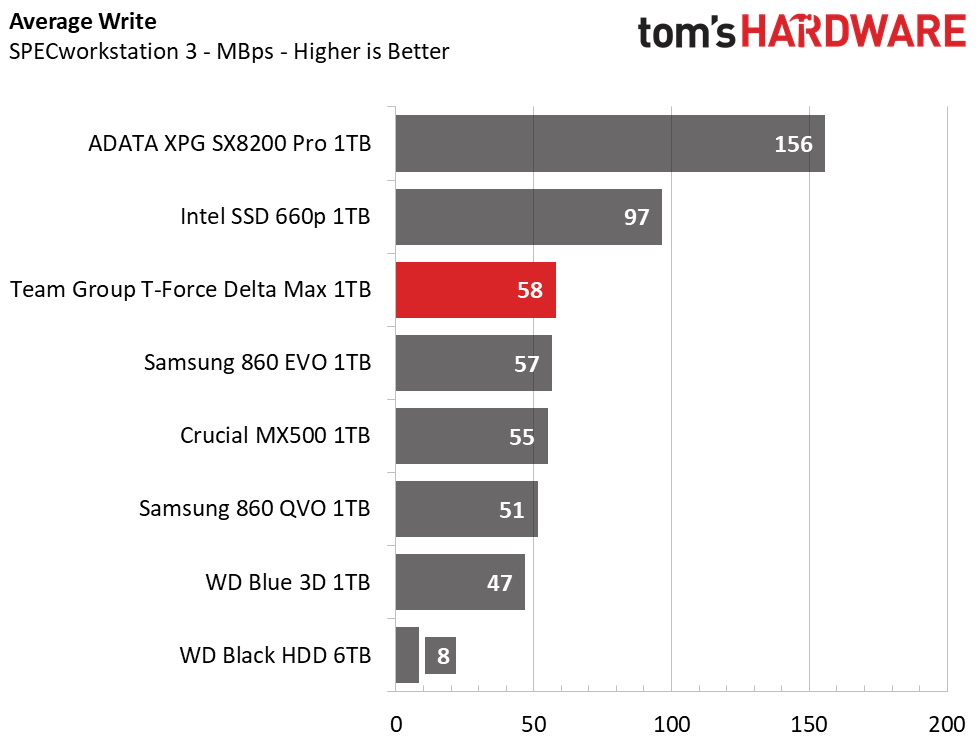
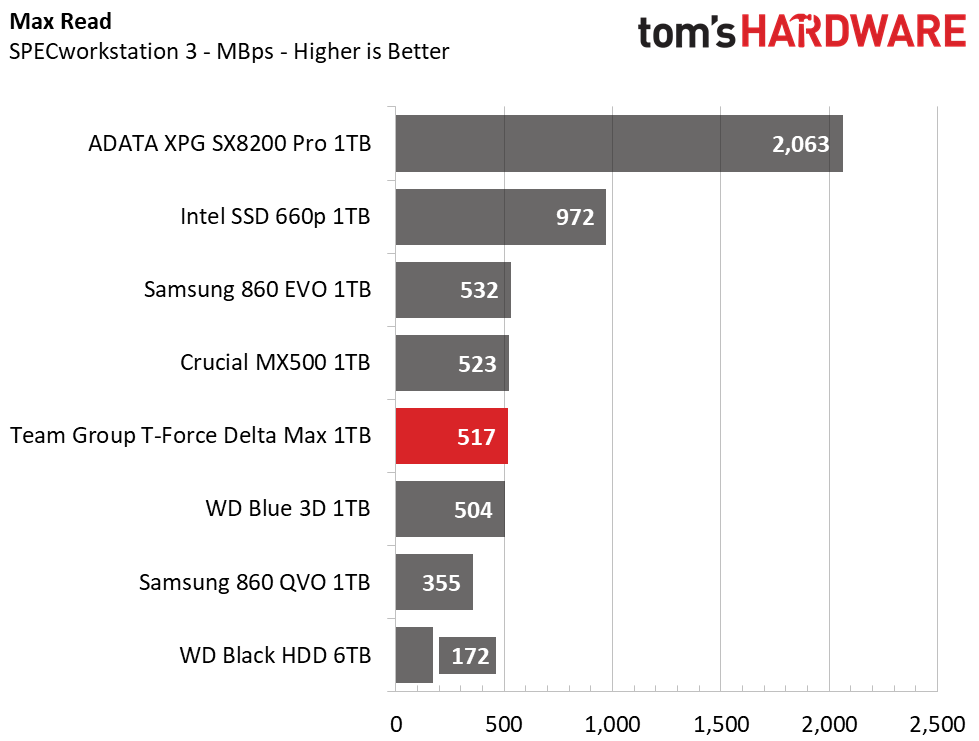
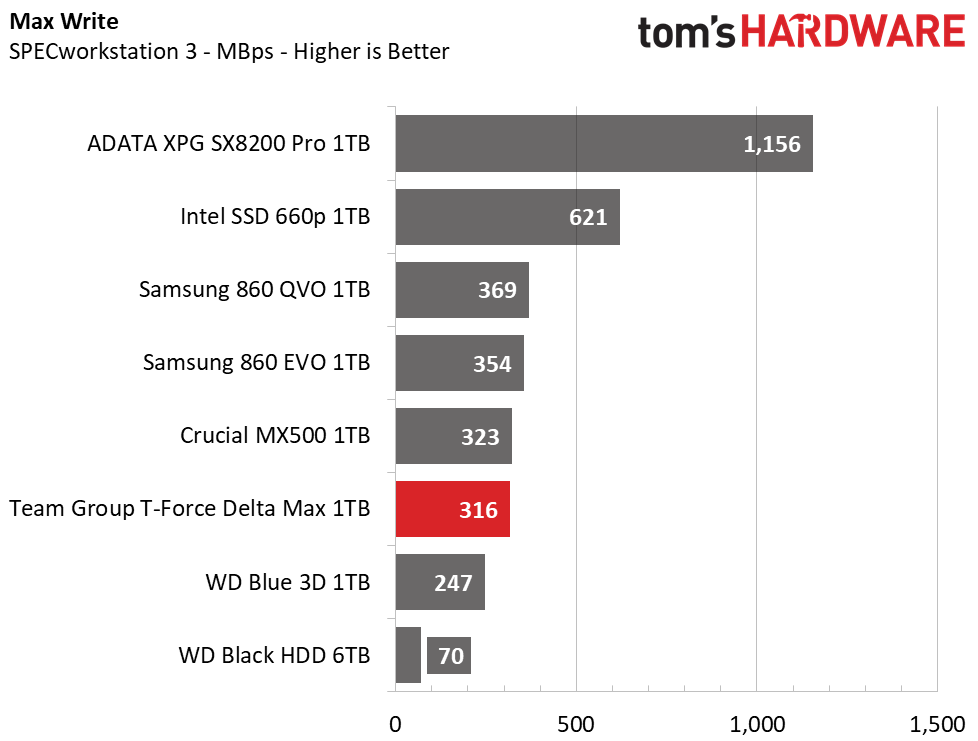
When hit with heavier workloads, the Team Group Delta Max shows the fastest run time out of the SATA competitors. It even outpaces the Intel 660p and leaves the HDD in the dust.
Synthetic Testing - iometer
iometer is an advanced and highly configurable storage benchmarking tool that vendors often use to measure the performance of their devices.
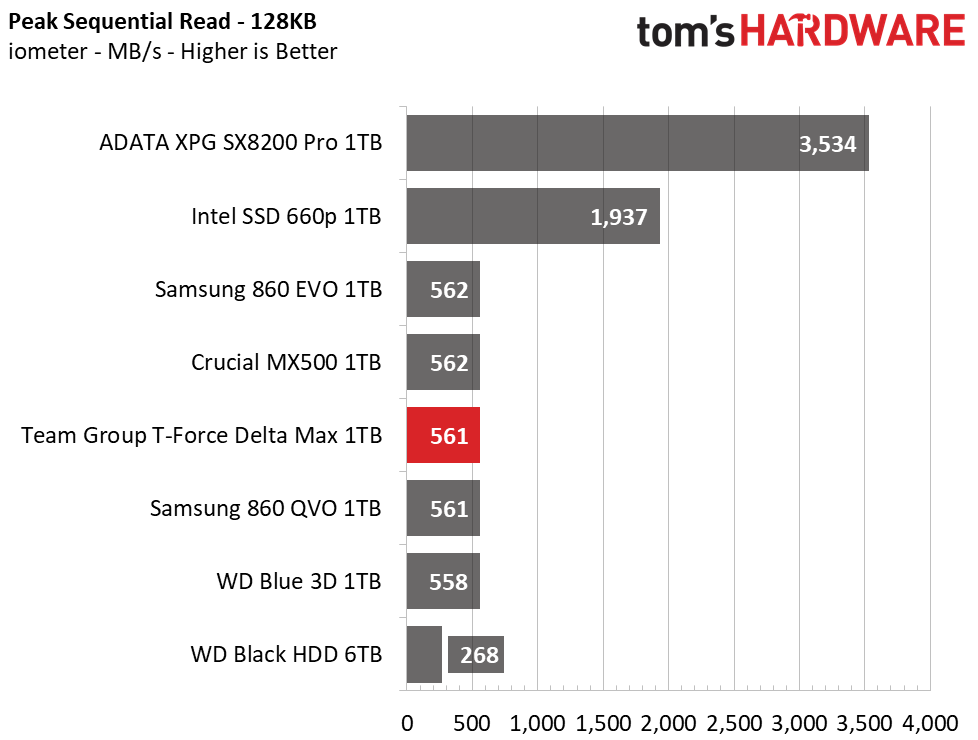
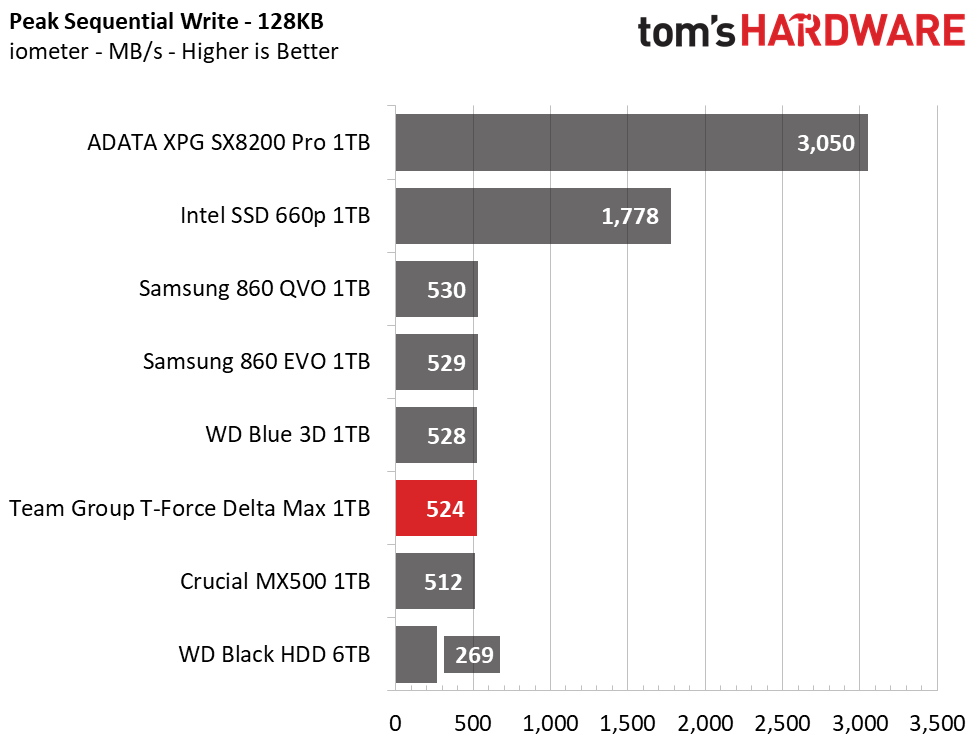
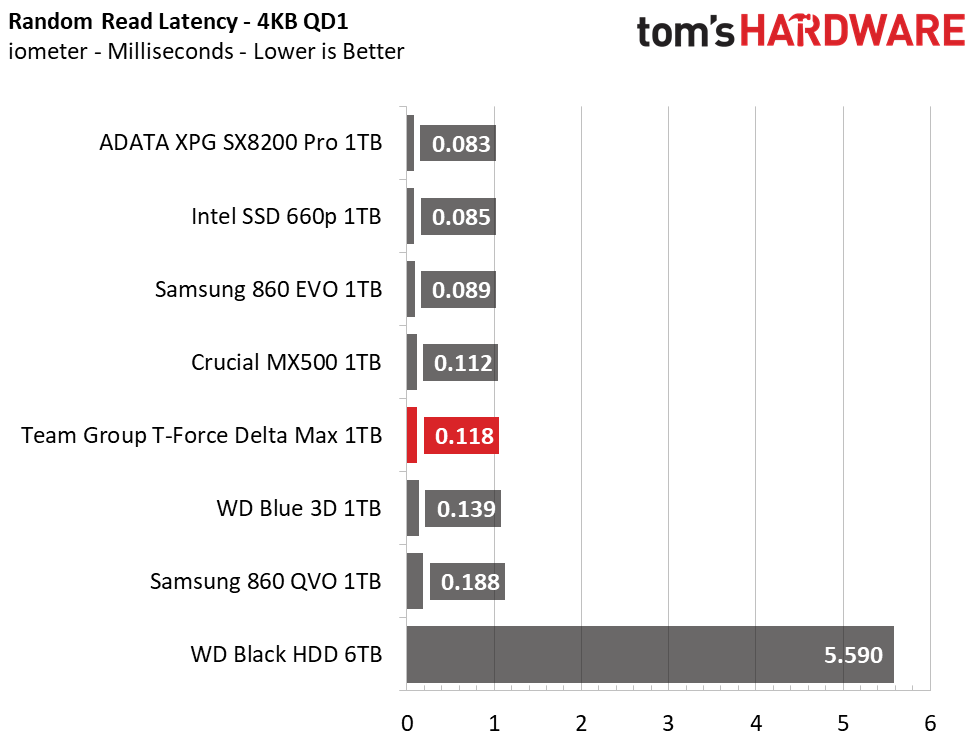
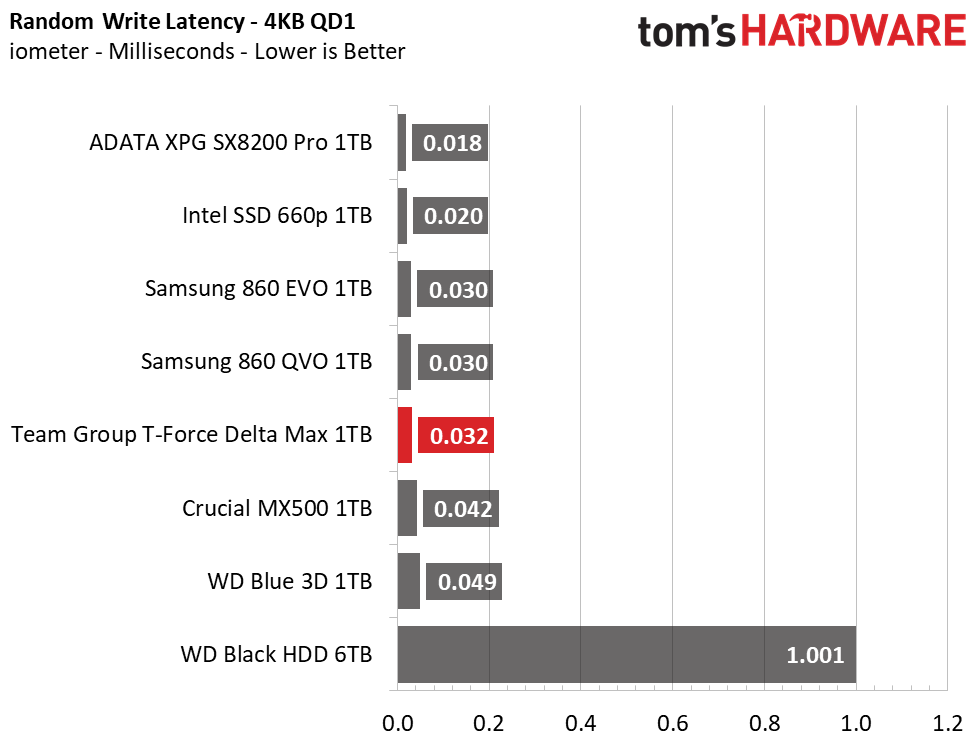
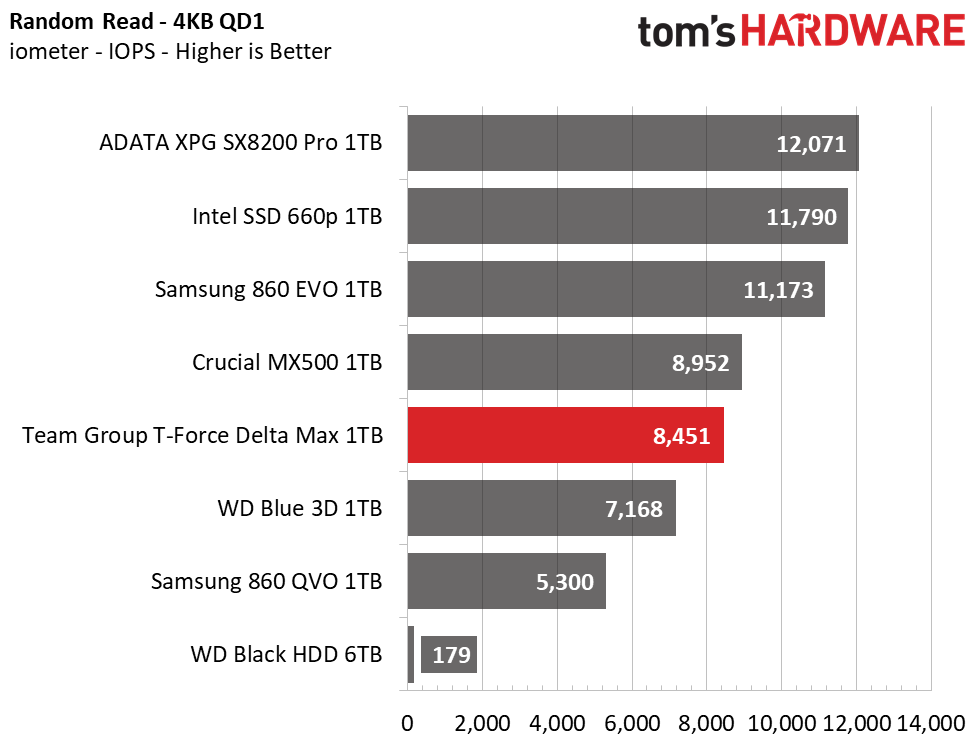
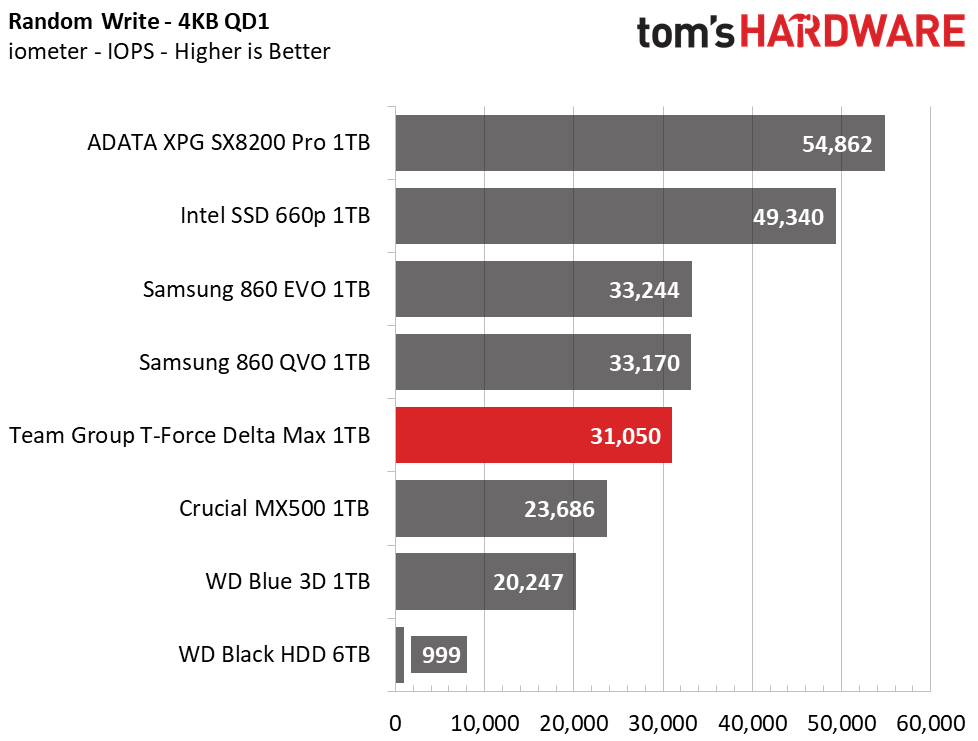
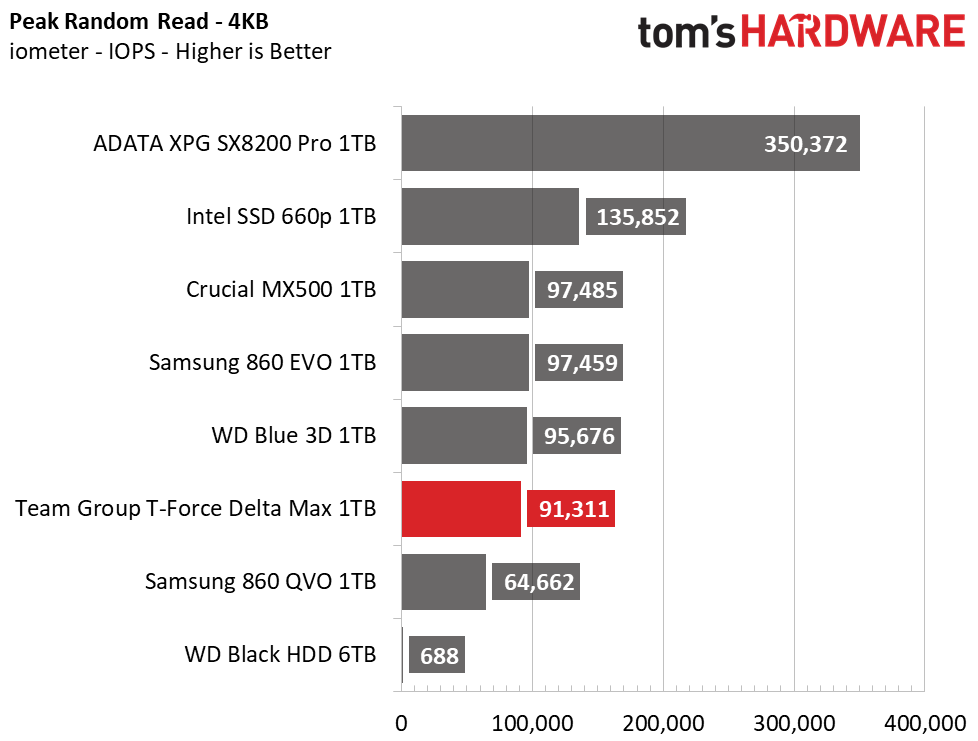
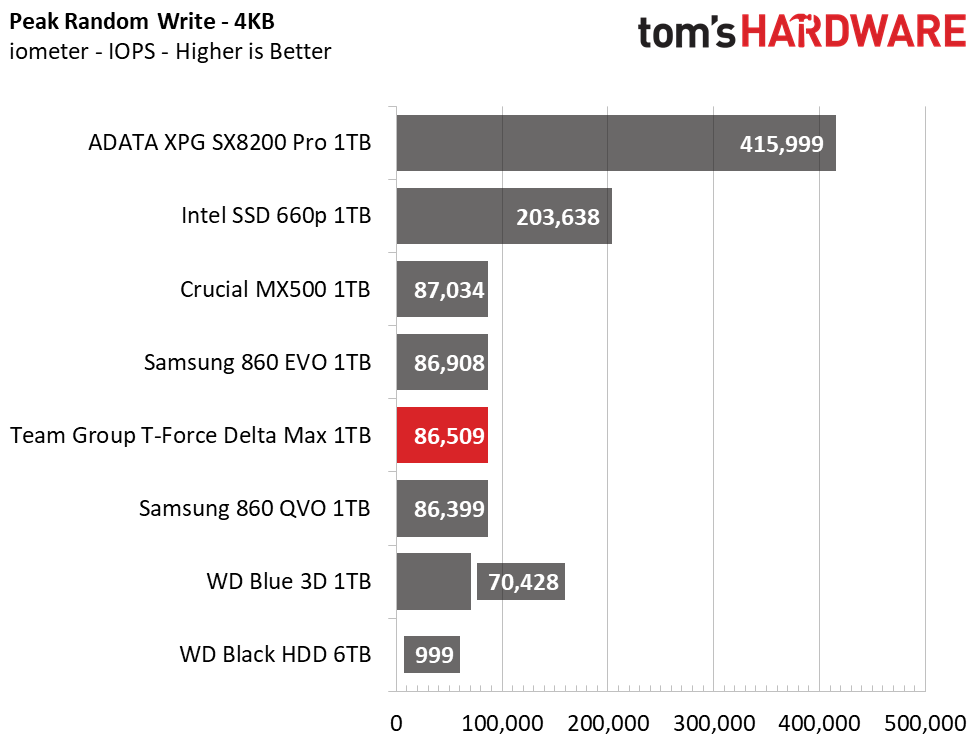
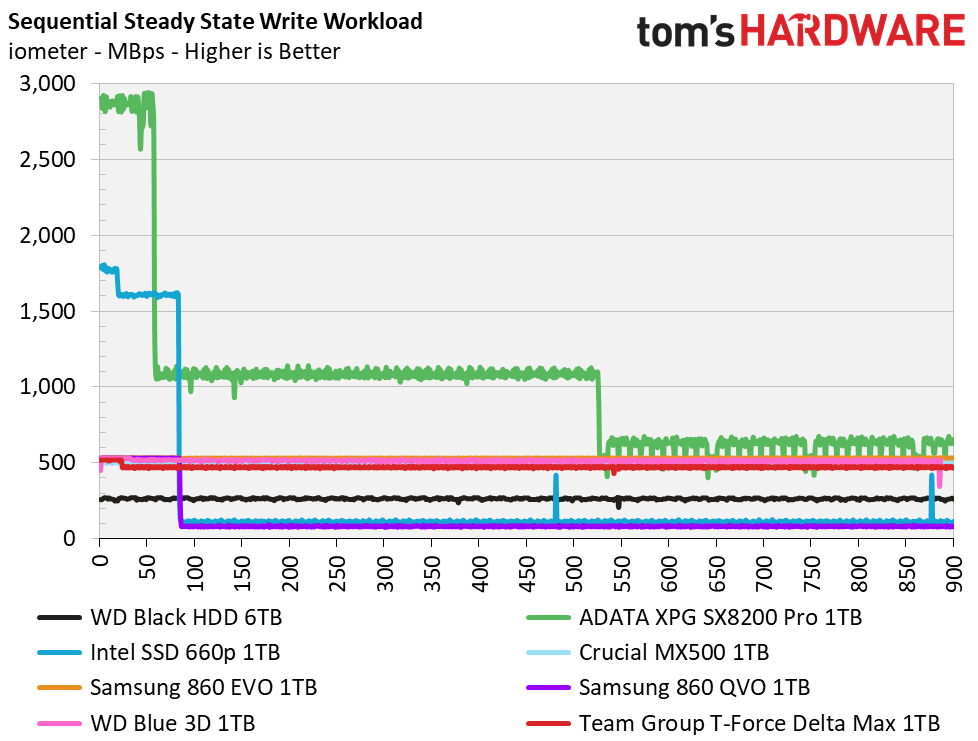
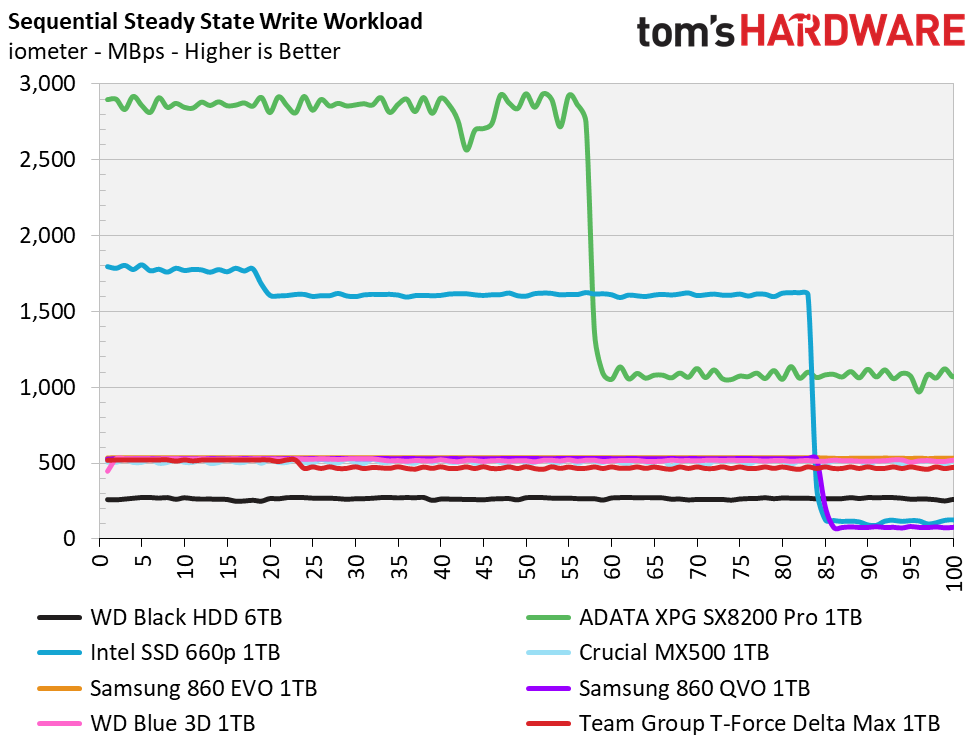
The Delta Max’s peak sequential throughput comes in at 561/524 MBps read/write. Random performance and responsiveness are similar to the other SATA SSDs as well. Maximum IOPS comes in at 91,311/86,509 IOPS read/write.
Sustained Sequential Write Performance
Official write specifications are only part of the performance picture. Most SSD makers implement a pseudo-SLC cache buffer, which is a fast area of SLC-programmed flash that absorbs incoming data. Sustained write speeds can suffer tremendously once the workload spills outside of the pSLC cache and into the "native" TLC or QLC flash. We use iometer to hammer the SSD with sequential writes for 15 minutes to measure both the size of the pSLC buffer and performance after the buffer is saturated.
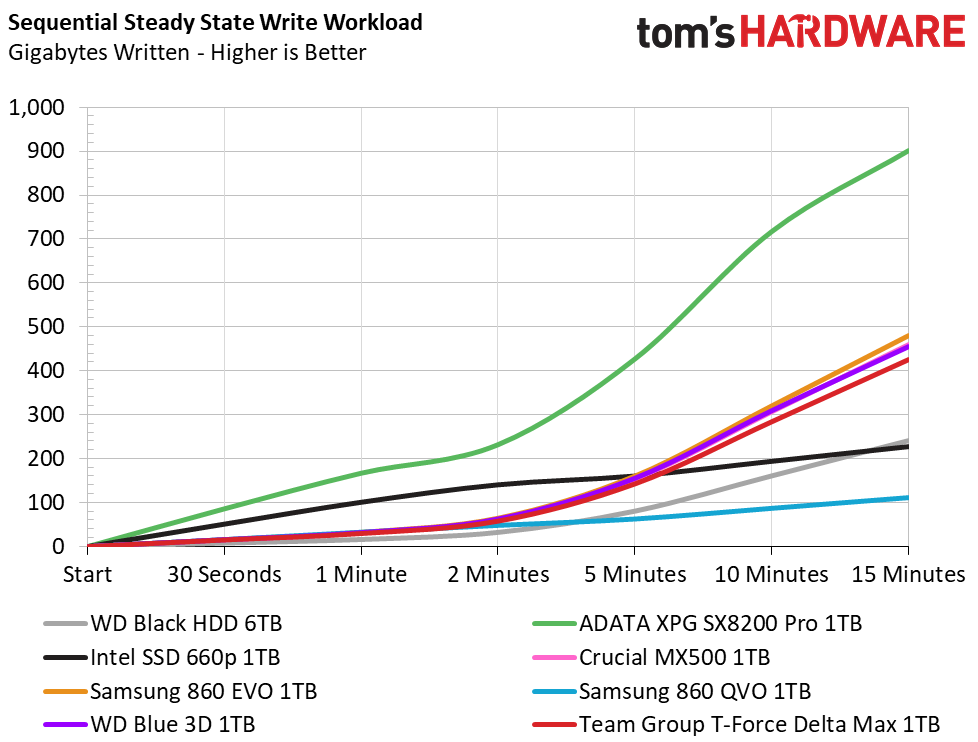
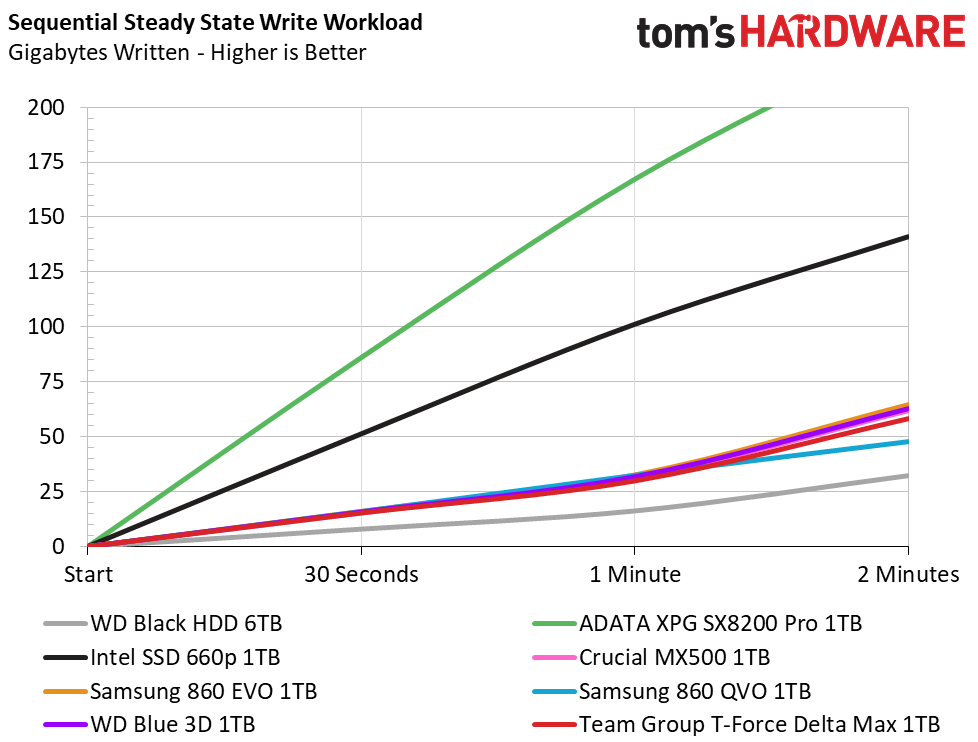
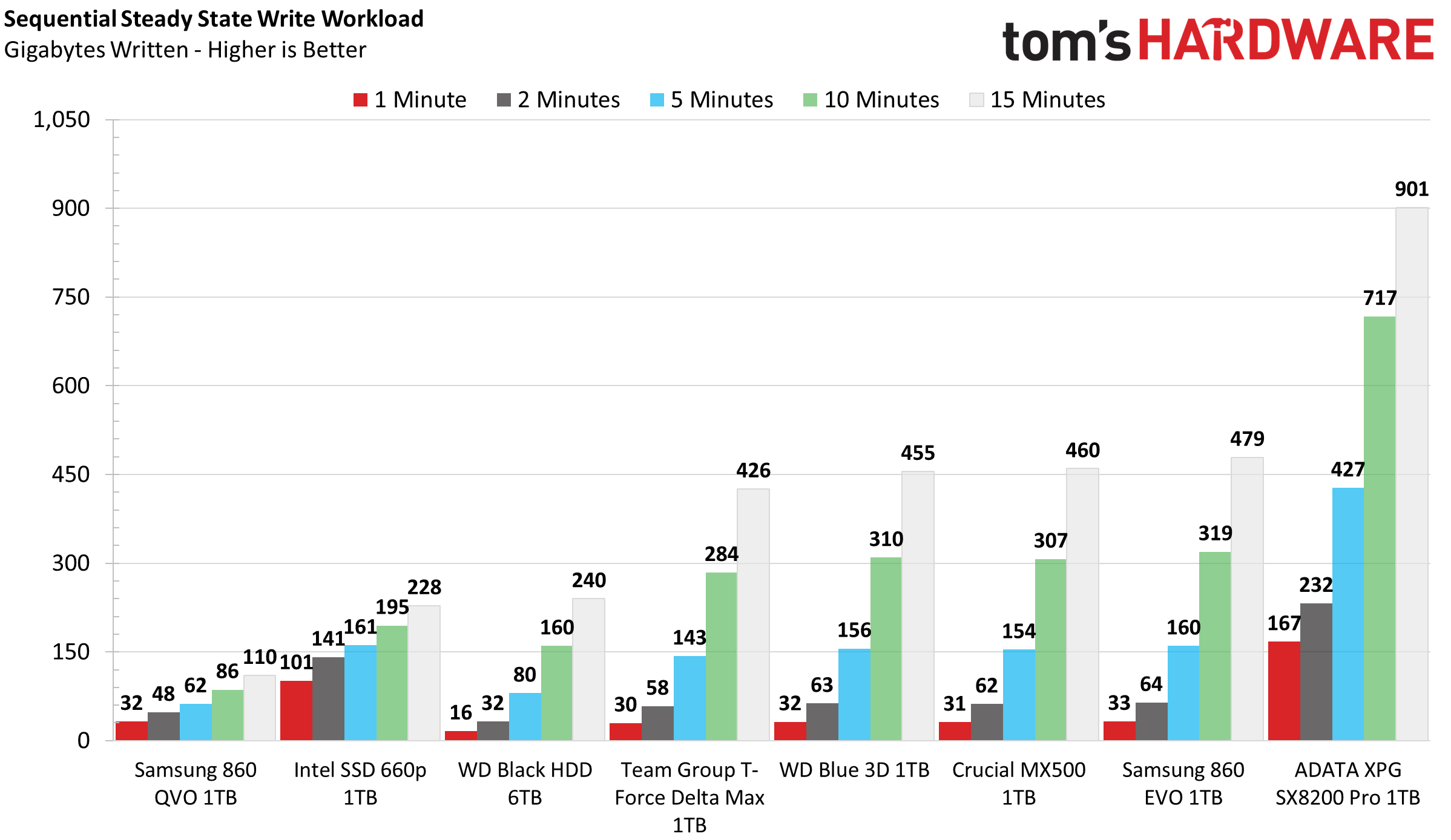
Team Group’s T-Force Delta Max utilizes a pseudo-SLC write cache to achieve its peak sequential write performance. After writing 12GB to the drive, write speeds degrade from 522 MBps down to 471 MBps. This places it just behind the WD Blue 3D in write performance overall. This performance also places it significantly ahead of the QLC-based SSDs after 5-10 minutes of writing.
Power Consumption
We use the Quarch HD Programmable Power Module to gain a deeper understanding of power characteristics. Idle power consumption is a very important aspect to consider, especially if you're looking for a new drive for your laptop. Some SSDs can consume watts of power at idle while better-suited ones sip just milliwatts. Average workload power consumption and max consumption are two other aspects of power consumption, but performance-per-watt is more important. A drive might consume more power during any given workload, but accomplishing a task faster allows the drive to drop into an idle state faster, which ultimately saves power.
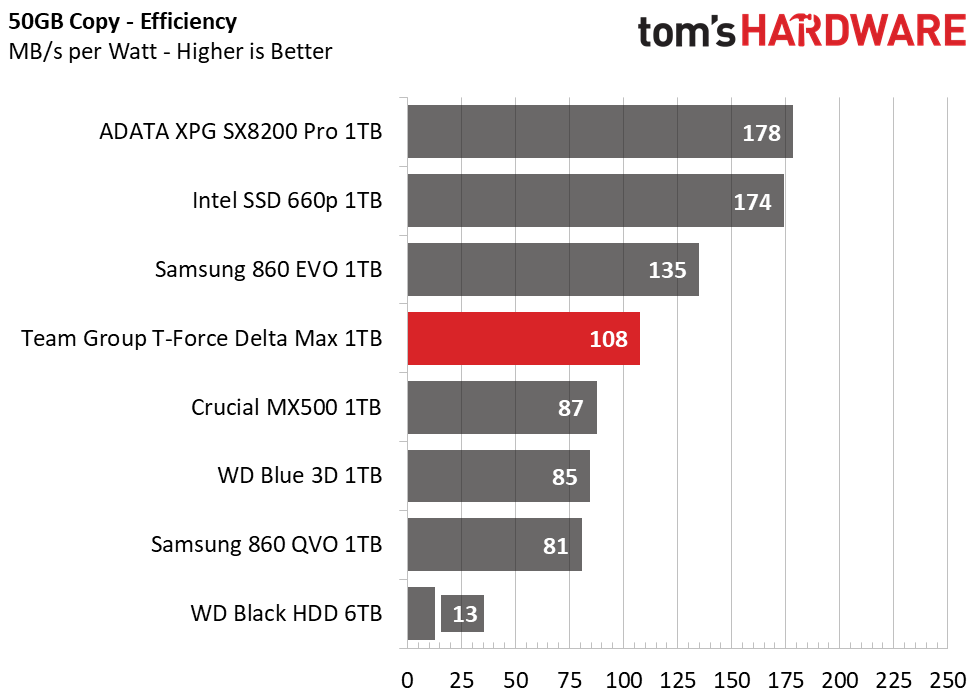
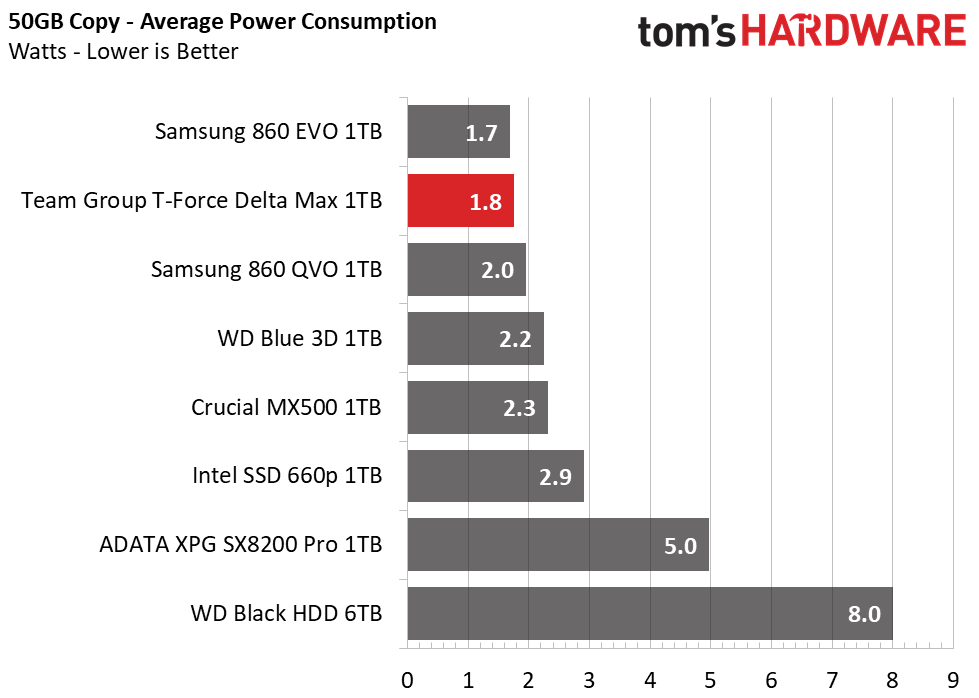
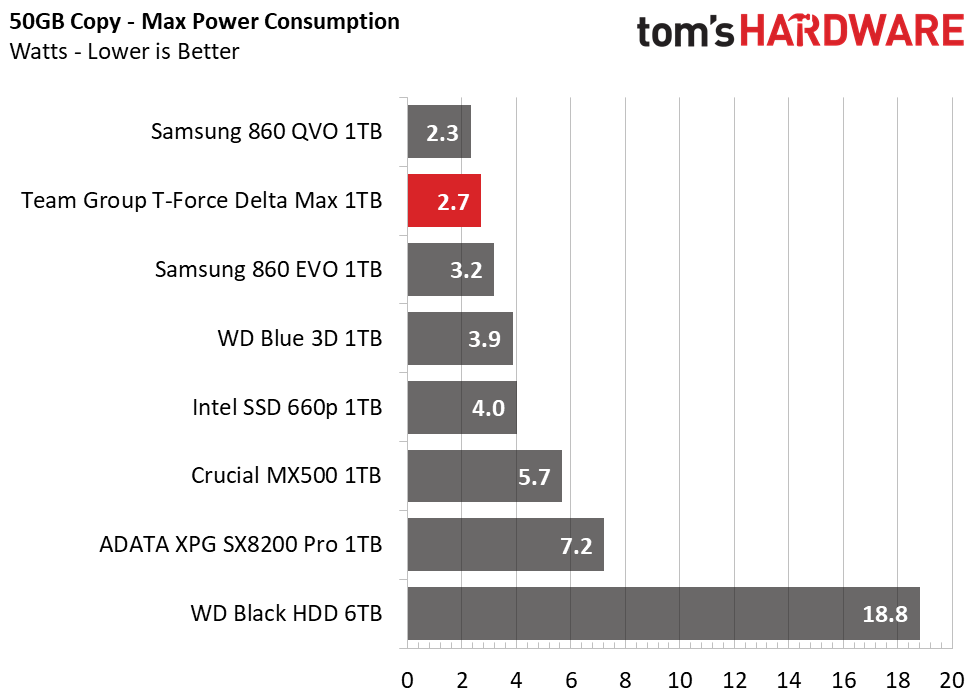
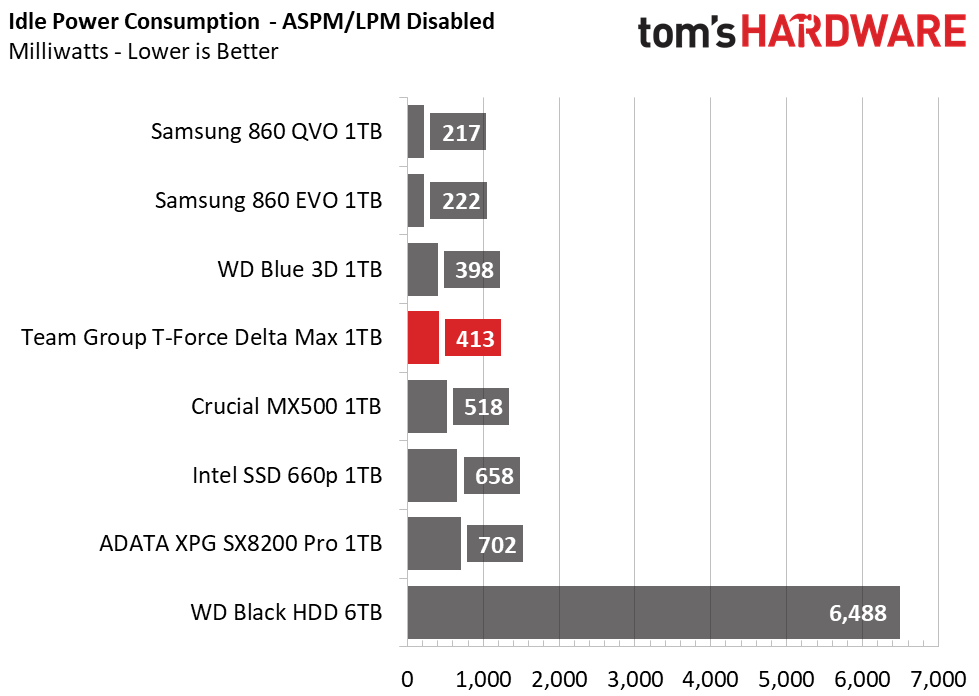
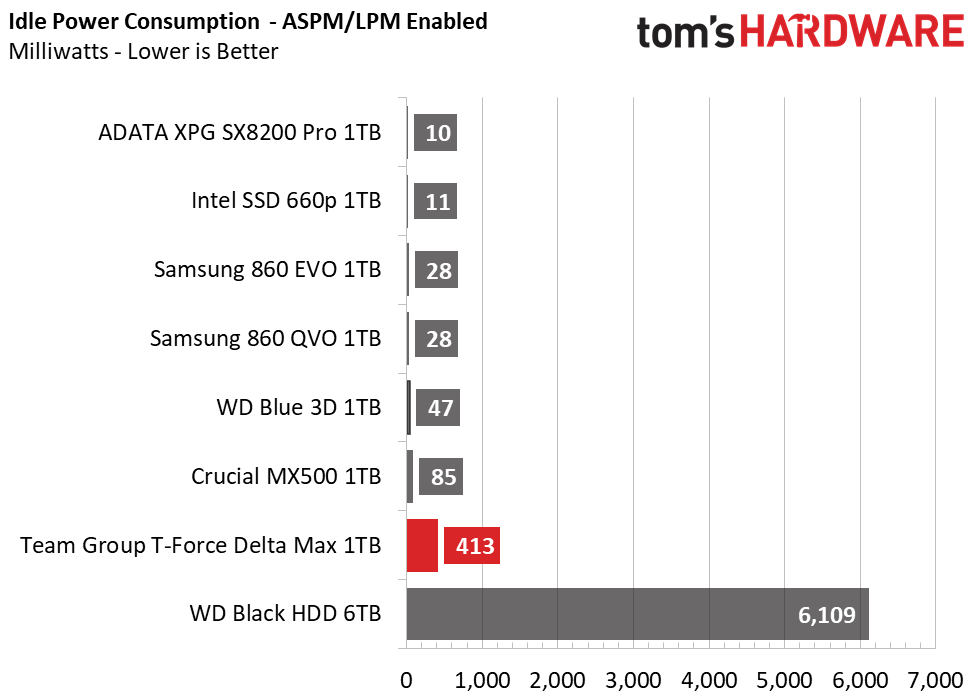
Team Group’s Delta Max is quite efficient, with its Samsung V-NAND. Averaging nearly as low power as the Samsung 860 EVO, overall it ranks fourth in power efficiency. It does't seem to respond to any power management settings, however.
Idle power consumption is higher than most SATA SSDs when doing nothing. That would be bad for laptop users in particular, but given this drive's RGB exterior and thicker-than-average shell, this drive is solely aimed at the desktop.
MORE: Best SSDs
MORE: How We Test HDDs And SSDs
MORE: All SSD Content

Sean is a Contributing Editor at Tom’s Hardware US, covering storage hardware.