Haswell-Based Xeon E3-1200: Three Generations, Benchmarked
Results: Synthetics
We'll see a pattern emerge over the next few pages: mainly, Ivy Bridge improves over Sandy Bridge, and Haswell is faster still. No generation saw the big gains that were evident in the mobile segment, but performance is up even still.
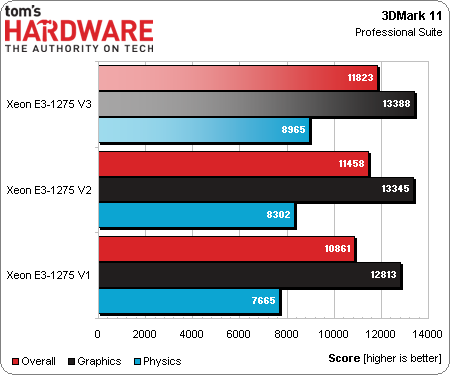
3DMark 11
3DMark 11 is a gaming benchmark, and not a core area of focus for the Xeon E3-1275's more workstation-oriented HD Graphics component. Still, we do see performance improve from one generation to the next.
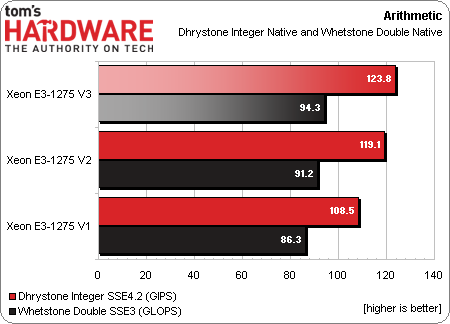
Arithmetic
A look at our Dhrystone and Whetstone benchmarks suggests what we can expect in many of the subsequent benchmarks. Floating-point and integer performance improves in small increments. The other thing we see is that the 100 MHz clock rate difference and memory speed enhancement moving from the original -1275 and -1275 v2 yield an outsized advantage for the v2 part.
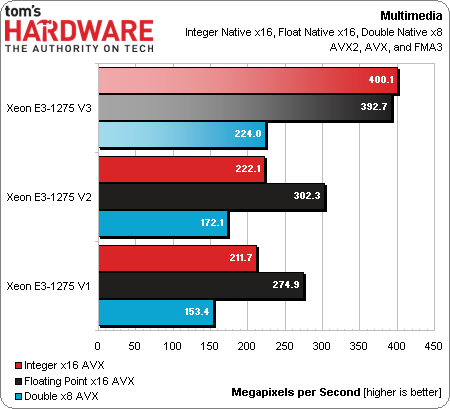
Multimedia
Haswell's AVX2 support translates to big gains in the integer module. That's perhaps the largest theoretical boost we'll see in moving to the -1275 v3, though it necessitates properly optimized software.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
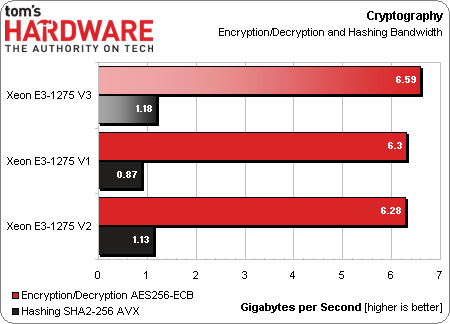
Cryptography
Our cryptography benchmarks are relatively similar from one machine to the next. Of course, because all three setups support AES-NI, they are as fast as their memory subsystems allow them to be. Hashing performance scales more predictably according to the architectural speed-ups from one generation to the next.
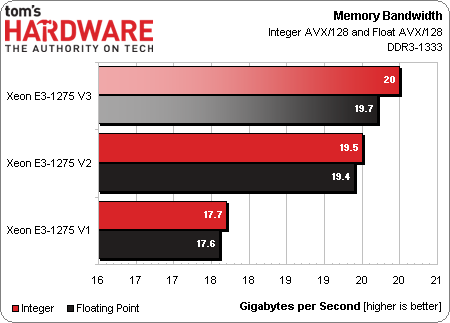
Memory Bandwidth
In terms of memory bandwidth, there is a clear fall-off for the Sandy Bridge part. This can be explained simply. When the Sandy Bridge-based Xeon E3 series launched, Intel validated it with DDR3-1333 memory. The subsequent generations added DDR3-1600 to the mix, even with ECC support.
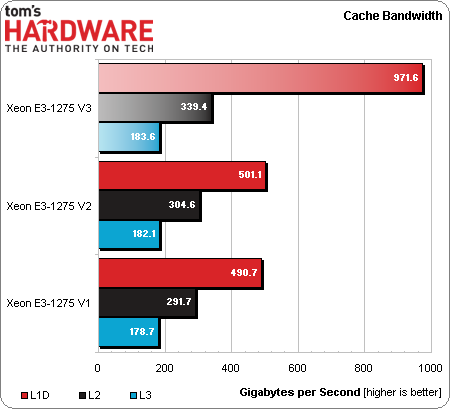
Cache Bandwidth Results
Predictably, Intel's Xeon E3-1275 v3 shows one of its most decisive benchmark victories. The L1D cache results are a direct consequence of a pathway widening to 64 bytes per cycle in Haswell, from 32 bytes per cycle previously.
Current page: Results: Synthetics
Prev Page Hardware Setup And Benchmarks Next Page Results: Adobe CS6-
dgingeri I have two Dell T110 II servers, one with an E3-1230 and one with an E3-1220v2, that cost me less than $800 each. I can tell you, they are great little machines, perfect for self-teaching Windows Server or ESXi. I now have the E3-1220v2 set up as my Windows 2008r2 router/DNS/DHCP/file/print server, and it uses a mere 45W of power when idle. The E3-1230 is my ESXi 5.1 machine right now.Reply -
CommentariesAnd More Best article to say in your face to those who think Xeons are poor performers.Reply -
vmem honestly not surprising at allReply
I think 'meh' will be the overwhelming majority consensus on this chip -
g-unit1111 Reply11571644 said:honestly not surprising at all
I think 'meh' will be the overwhelming majority consensus on this chip
That's kind of the way I see it. I don't think the Xeon is anything to write home about like some people on this board do, but the average user and/or gamer won't notice a lick of difference between an i5, i7, and low end Xeon. I would only recommend them in instances of things like Photoshop and heavy duty CS5 usage, but even then an i7-4770K or i7-4820K would be a better choice. -
InvalidError While ARM chips may be doubling performance on a fairly regular basis, you need to keep in mind that ARM chips are starting from pretty far back. By the time they catch up with mainstream x86 chips, they will most likely hit very similar IPC and frequency scaling brick walls as x86 chips and won't gain much ground beyond that.Reply
The only real threat from ARM is to profit margins: once ARM catches up, it may become more difficult for Intel to maintain the large premiums they currently command across most markets. -
the1kingbob Did Toms looks at the AMD 6100, 6200, and 6300? That would make to be an interesting comparison since the underlying architecture changed from the 6200 to 6300 (i think, maybe 6100 to 6200)Reply -
Amdlova people in my county buy this processor for gaming... need a seriosly test on this. 1230v2 have same price 3570k here!Reply -
dgingeri "I would only recommend them in instances of things like Photoshop and heavy duty CS5 usage, but even then an i7-4770K or i7-4820K would be a better choice." They wouldn't be any advantage in either case. The advantage of the Xeon isn't performance, but stability. It's use of ECC memory makes it much better for purposes like a high end workstation for an engineer or digital artist so their work isn't lost or interrupted by a memory error and crash or in servers where it can stay running reliably for months at a time.Reply
In addition, the chipsets and platforms used with Xeons are more stringently held to industry standards, making them known quantities for device makers. Enterprise raid controllers are frequently unsupported on a standard desktop system with a Core i7 4770 and Z87 chipset, while they would be supported on a Xeon E3-1275v3 with a C226 chipset, even though the actual silicon design is exactly the same between the two.
There really isn't any difference in the silicon itself between a Haswell Core i7 and a Haswell Xeon E3, so there won't be a performance difference. The difference is in the stability of equipment surrounding each. -
pjkenned InvalidError - these are not in the same league as the ARM chips. Avoton and Rangeley are the real ARM competitor. I JUST got two Avoton 8-core platforms in the lab as this article was going live (benchmarks here: http://forums.servethehome.com/processors-motherboards/2444-intel-avoton-c2750-benchmarks-supermicro-a1sai-2750f.html ) If ARM was targeting Centerton (the Atom S1260), they are targeting a platform way behind Avoton and the E3 reviewed above.Reply
the1kingbob - I have AMD Opteron 3000, 4000 and 6000 series chips in the lab and use them daily. The Operton 3300 series would be the closest platform but the performance is significantly behind the Haswell Xeon E3-1275 V3. Those Opterons also do not have integrated GPUs like the E3-12x5 V1 V2 and V3 chips so are hard to compare. -
InvalidError Reply
And I never said they were - at least for now. But ARM might get there if they manage to sustain their current improvement pace for a few years while AMD and Intel remain stuck for most intents and purposes.11572444 said:InvalidError - these are not in the same league as the ARM chips.
Yes, Intel released some cut-down x86 chips to compete with ARM for low-power market segments but this is only a temporary fix since Intel will likely add much of that stuff back in to keep up with ARM as ARM performance ramps up. The interesting part in 3-5 years will be where ARM will go once they hit the same steep diminishing return slope AMD and Intel are on.