The 30 Year History of AMD Graphics, In Pictures
AMD Radeon R9 Fury X (2015)
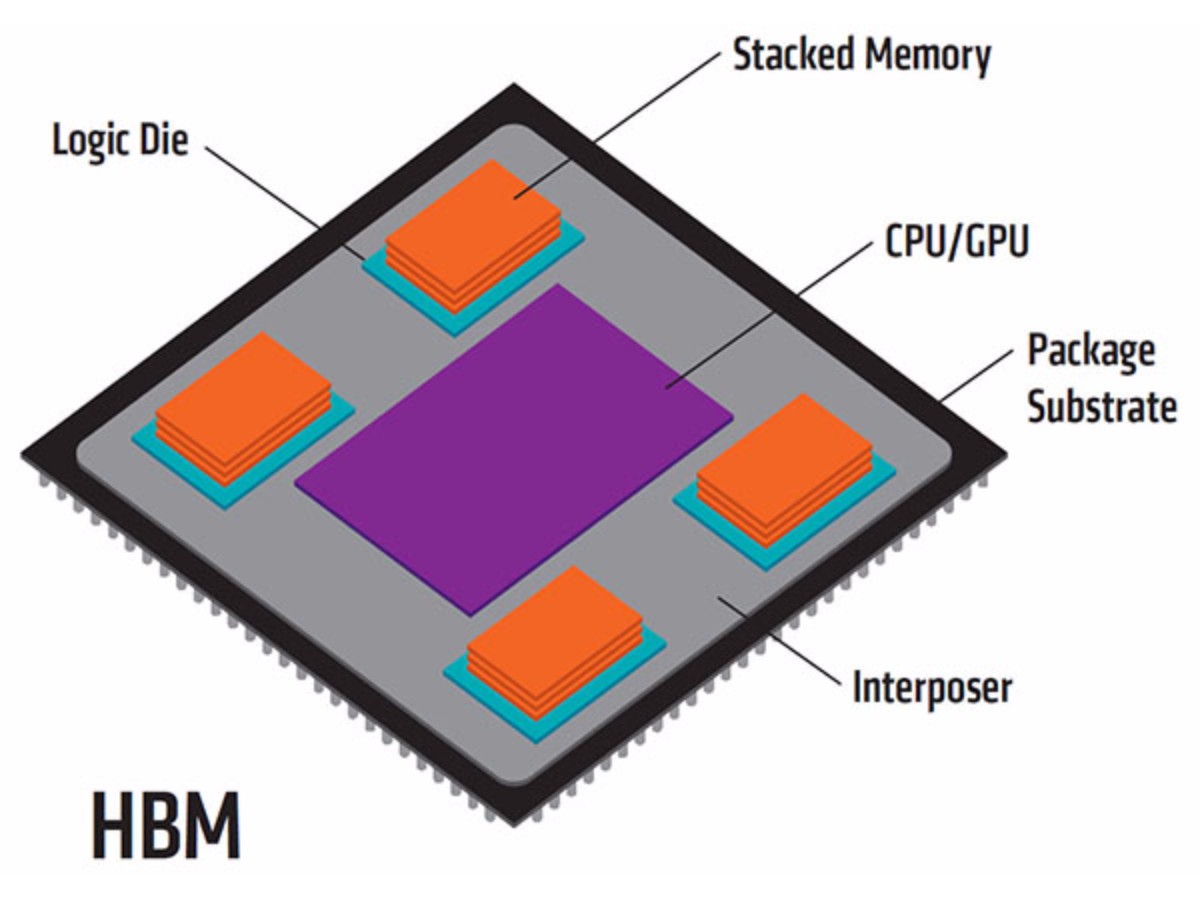
AMD's next flagship also used an updated implementation of the GCN architecture. Its Radeon R9 Fury X sported a Fiji GPU with 8.9 billion transistors, enabling 4096 Stream processors, 256 TMUs, and 64 ROPs. More notable than the massive core, however, was AMD's pioneering introduction of High-Bandwidth Memory. Fiji is fed by 4GB of HBM capable of 512 GB/s over a 4096-bit bus.
Stuck at 28 nm manufacturing and faced with a big, hot GPU, AMD went with liquid cooling to make the Fury X smaller and quieter than would otherwise be possible. The Radeon R9 Fury X outperformed Nvidia's GeForce GTX 980, but traded blows with its GeForce GTX 980 Ti. As a result, determining last generation's king often came down to game selection and quality settings.
AMD Radeon RX 480 (2016)
AMD's Radeon RX 480 is somewhat unique in that it was not designed to be the company's fastest graphics card. Instead, it was built to be an efficient mid-range board. You can expect higher-end solutions based on the same Polaris architecture in the months to come.
The Radeon RX 480 has 2304 Stream processors, 144 TMUs, and 32 ROPs connected to either 4 or 8GB of GDDR5 on a 256-bit bus. The core operates at a base clock rate of 1120 MHz and can accelerate up to 1266 MHz. The GPU also boasts a large 2MB L2 cache to reduce its dependency on the GDDR5. Officially, the RX 480 is rated for a 150 W TDP. And although it isn't as fast as Nvidia's Pascal-based cards, it does fare well against the GeForce GTX 970.
AMD also produced lower end RX 470 and RX 460 models to handle the budget market. These GPUs use the same architecture as the RX 480, but with fewer cores and reduced memory support.
MORE: Best Deals
MORE: Best Graphics Cards
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
AMD Radeon RX 580 (2017)
In April, 2017, AMD introduced the RX 500 series. Or rather it re-introduced the RX 400 series under a new name. These GPUs are nearly identical to their RX 400-series predecessors. The RX 500 series GPUs, however, feature significant bumps in clock speed and support higher voltage limits. AMD didn't create a reference design for the RX 580, but models produced by OEMs are typically clocked between 100-200MHz above the RX 480. The company also released an RX 570 and plans to release RX 560 and RX 550 models that also have increased clock speeds.
AMD Radeon Vega RX (2017)
AMD designed Vega as a high-performance GPU architecture to run concurrently with Polaris. While the pixel shaders used in Vega and Polaris are relatively similar to each other, Vega has the clear advantage thanks to a significant increase in the number of shaders, plus faster memory. AMD implemented HBM2 memory with Vega, and has announced consumer GPUs with 8GB of GBM2 with a peak bandwidth of 484 GB/s over a 4096-bit bus. The workstation oriented Vega Frontier Edition pushes this up to 16GB of HBM2. AMD also reworked the cache inside Vega to increase bandwidth throughout the core. The render back-end is now a client of the L2 cache, which has increased to 4MB.
Vega also has access to a wide number of new features and processing elements. There is a new programmable geometry pipeline that can render 17 primitives per clock. Vega sports a Next-Generation Compute Unit (NCU), equipped with 64 shaders, which is designed to accelerate game performance.
Vega 64 will compete with Nvidia's GeForce GTX 1080, while a lower-end variant called Vega 56 will do battle with the GTX 1070.
-
adamovera Archived comments are found here: http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/id-3207492/year-history-amd-graphics-pictures.htmlReply -
XaveT I still have a 5870 in production. Great card. And six miniDP ports on one card is great for the workstation it's in. I'm sad to see no current flagships with the same configuration, I may have to do two graphics cards or get an unneeded professional series card at upgrade time.Reply -
Nuckles_56 This sentence doesn't make a lot of senseReply
"All-in-Wonder 8500 close to the performance of AMD's Radeon 8500, which was enough to compete against Nvidia's GeForce 3." -
cub_fanatic I have a couple of those 8500 all-in-wonder cards with the remote, receiver for the remote, the giant dongle, the software and all. A friend had them sitting in his garage and was going to chuck them so I took them home. I believe they were used in a doctor's office or something so that they could have a single display in the room and switch to TV while the patient waited and then back to a desktop to show them x-rays or whatever. I have one hooked up to a Pentium 4 Dell running XP but can't figure out much of a use for it in 2017. Even the tuner is almost useless unless you want to capture a video off of a VCR since they can only handle analog.Reply -
Martell1977 My first ATI discreet GPU was a Radeon 9250, and it was pretty good at the time considering the resolutions of the CRT monitors. My second was a Radeon 3850 AGP, while my brother went with a nVidia card. I sold the 3850 with the other parts, working, on eBay mid last year....my brothers nVidia card barely outlasted the warranty.Reply
Next came my 6870, which I got in 2010 and tried crossfire in 2015, but ended up upgrading to a R9 390 as the 6870's ran into memory issues.
I know a lot of people complain about AMD/ATI drivers, but I've had more issues with nVidia driver (especially recently) than any AMD. Both my laptops have been nVidia GPU's (8600M GT and 1060 3gb).
Awaiting to see what Vega brings, I'm surprised it didn't at least get a tease at the end of the article, but hey, maybe this is a lead up to a Vega release soon? -
I look forward to the next 30 years.Reply
P.S. Maybe eventually heterogeneous compute will work. I doubt it. In any case, they seem back in formation, and charging forward. -
blackmagnum I hate reading this page format on IOS; lots of problems and hangs with page scrolling.Reply -
CRO5513Y You can definitely see the change in Aesthetics, what ever happened to all the fancy details and characters on the cards? :PReply
(I mean to be fair not much room to fit them on cards these days since most have non-blower style coolers). -
LaminarFlow Hard to believe that I've been an ATI user for almost 15 years now. Always had a somewhat limited budget, I picked up a 9600XT in 2003, then X1900 XT in 2006, HD 4850 in 2008 (for $125, that was the best computer part purchased I ever made), and R9 280X in 2013.Reply