AMD Ryzen 3 1300X Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
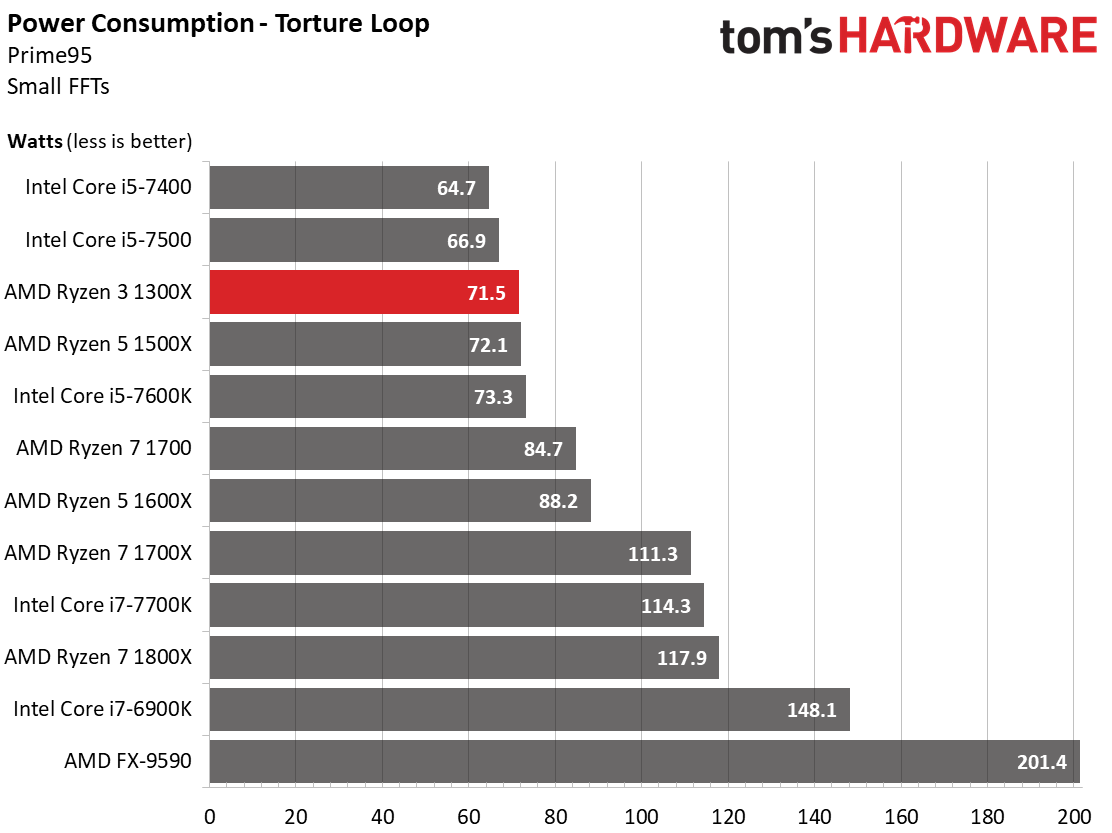
Power Consumption
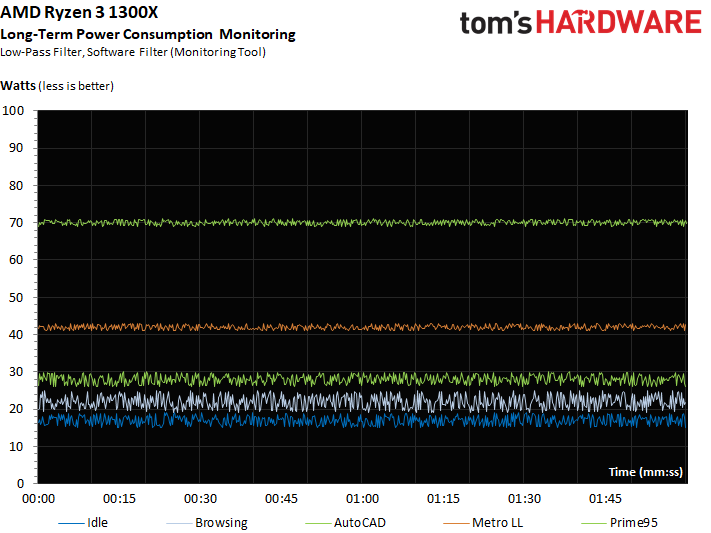
Our power consumption results are based on the sensor readings provided by MSI's motherboard. We use adjusted averages and a special low-pass filter that discards brief peaks and valleys for these runs. The displayed sections show a two-minute window, but the bar graphs include the full 15 minutes that are necessary for precise measurements. We didn't have the i3 and Pentium models in the German lab, but we do have enough comparative data to provide a good sense of the power consumption trends of the Ryzen 3 1300X.
Power Consumption Of The Individual Ryzen 3 Processors
Only during the stress test does AMD's Ryzen 3 1300X encounter a significant power consumption increase. Even then, the differences aren’t that large, and almost completely in line with the performance gains.
Power Consumption Comparison For All CPUs
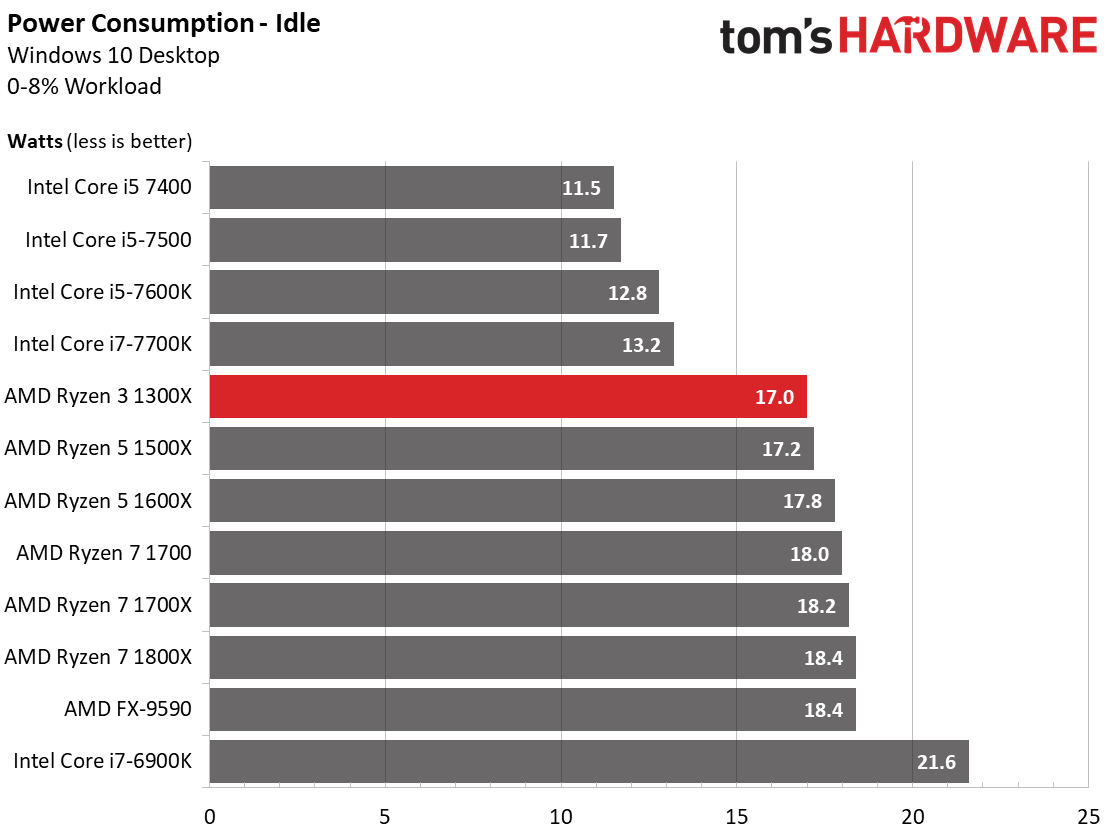
The differences between AMD's Ryzen CPUs at idle are extremely small. It takes a 15-minute test to measure such slight variations reliably. This lends credence to our hypothesis that the models with disabled resources aren't fused off electrically.
It's anyone's guess if there's a way to reactivate those pieces of on-die hardware, though we suspect AMD took measures to make sure it doesn't happen.
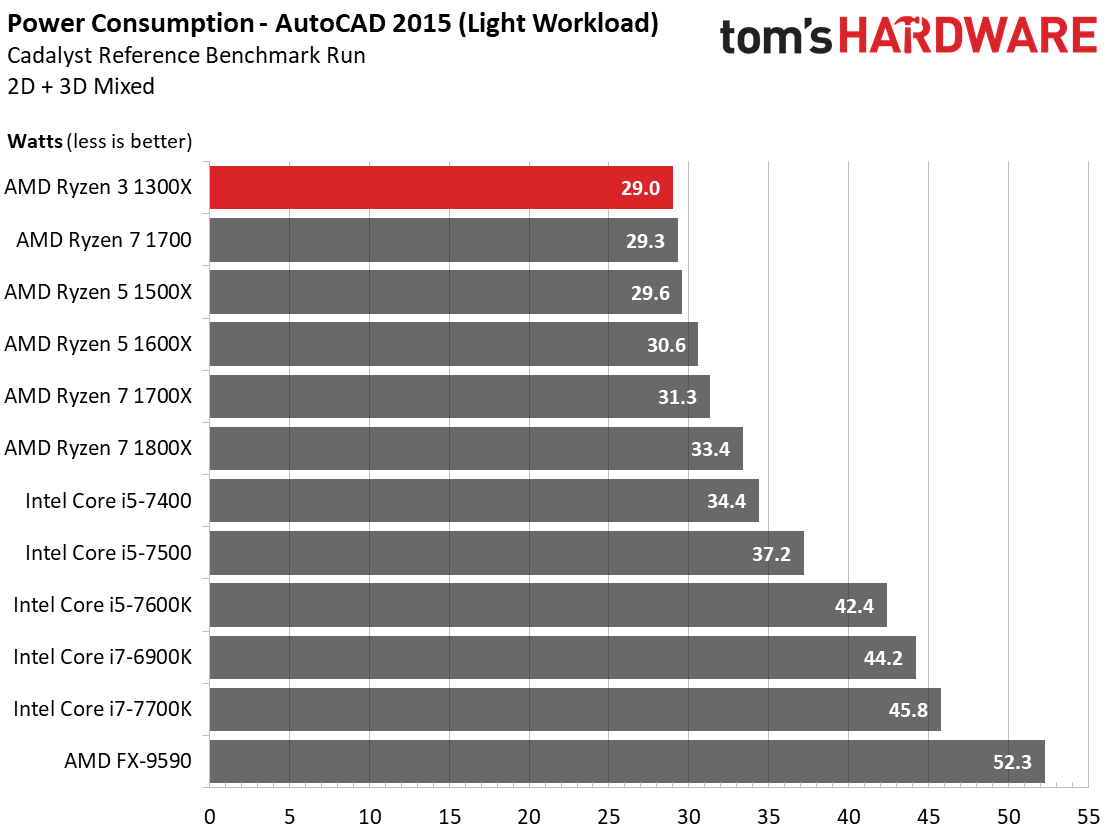
Working with a lightly threaded AutoCAD project doesn’t produce any large differences, either.
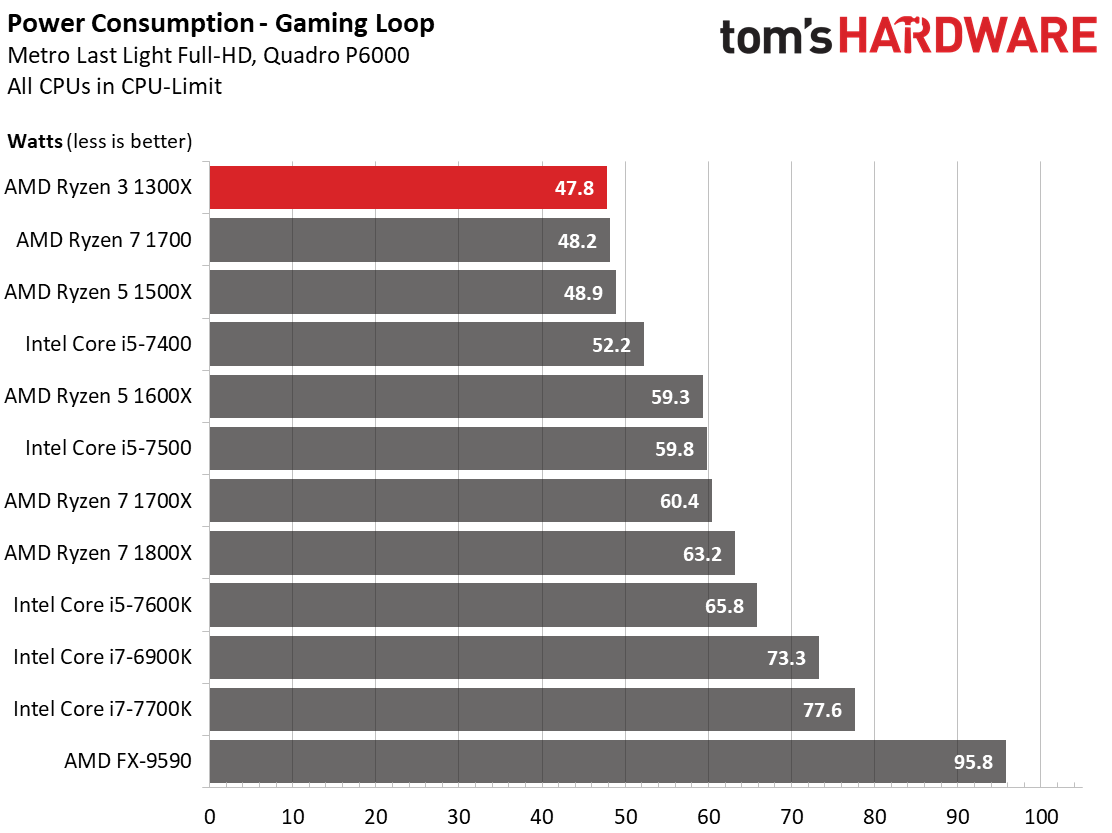
It takes more taxing workload for the higher-end Ryzen model to start drawing notably more power.
The same can be said for our stress test results.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Our findings confirm what we’ve found through our other Ryzen CPU reviews. Ryzen 3 isn’t significantly more efficient at idle and under low loads than Ryzen CPUs with more active cores or threads. This leads us to two conclusions. First, the new chip's quality isn’t worse to the point that it causes lower efficiency and higher power consumption. Second, deactivating parts of the chip doesn’t improve efficiency. In other words, the disabled parts are still, and permanently, supplied with power.
Compared to Intel's equivalent offerings, the power consumption demonstrated by AMD's Ryzen family is acceptable to good. The only exception is idle power consumption. AMD’s efficiency is really no better or worse than Intel's so long as the software you're using (including the operating system) supports Ryzen's power-saving features.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Power Consumption
Prev Page Temperature & Noise (Stock Cooler) Next Page Final Analysis
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
yankeeDDL Wow.Reply
I don't remember when it was last time when we saw a review where, practically, in every chart AMD was at the top, and Intel at the bottom. It is refreshing really. Hopefully this will drive Intel to cleanup the mess it created in 5+ years of unchallenged leadership, and get its acts in order.
I'm enjoying the moment though. With my Ryzen 5 1600 :) -
blackmagnum This is the product segment my slim wallet has been waiting for. I just hope that Intel will fight back with a price war. Now bring in the Ryzen+IGP for office gaming!Reply -
SS_1__ The only mainstream chips Intel makes worth buying are the G4560 and 7700k, AMD has the rest of the product stack.Reply -
mjslakeridge The thing I found interesting from the review is that the disabled cores still receive power (second to last page of the review). Now we just need to figure out how to enable the "hidden" cores!Reply -
bloodroses While I wasn't impressed with the Ryzen 5, their 7 and 3 are really putting the hurt on Intel. Good job AMD for getting back into the race. :) Let's hope they can do the same against Nvidia so true competition will finally be back.Reply -
InvalidError Reply
There isn't a whole lot that Intel can do about it other than drop prices for a given amount of cores and threads, though you can expect Intel to hold on to premium pricing for its IPC, clock frequency and lower power advantages.19988753 said:Hopefully this will drive Intel to cleanup the mess it created in 5+ years of unchallenged leadership, and get its acts in order.
What I'm really curious to see for the mainstream/office segment is the Ryzen-Vega APUs. -
madmatt30 Amd are just absolutely smashing it this year.Reply
Which is a great great thing after Intel's dominance & stranglehold for the last 6 years.
Intel price war ??
No that's not going to happen if it hasn't already ,they're way too arrogant to ever do that.
-
redgarl One of the best CPU of the year with the 1600x. I still take my 1700x over them, but if you are under budget, there is no questions.Reply
Too bad their Vega card seems like another Fury. I sold my stock and wait for the first benches before rebuying it. Also, indication is that RX will cost 600-650$ and barely beating a 1080 GTX. However Vega core are going to be incridilbe with AMD APU on the laptop segment. Nvidia MXM cards are going to be a bad investment and cost a fortune while everything will be on the same chip for AMD. -
dudmont If AMD wants to grab business/oem market, they should come out with a very low end graphics card, something that costs 40$(preferably 20$) or less, that they could bundle with these Ryzen 3s and sell as a one stop solution. So long as it performed similarly to intels IGPs, and the price was competitive, their performance advantage would give them a shot at stealing sales. For them to really get market share, which is where these Ryzen 3s sit, they need to be able to offer something to more than just gamers on a budget.Reply