Asus ROG Strix Radeon RX Vega 64 8GB OC Edition Review: High-End Graphics With Flair
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
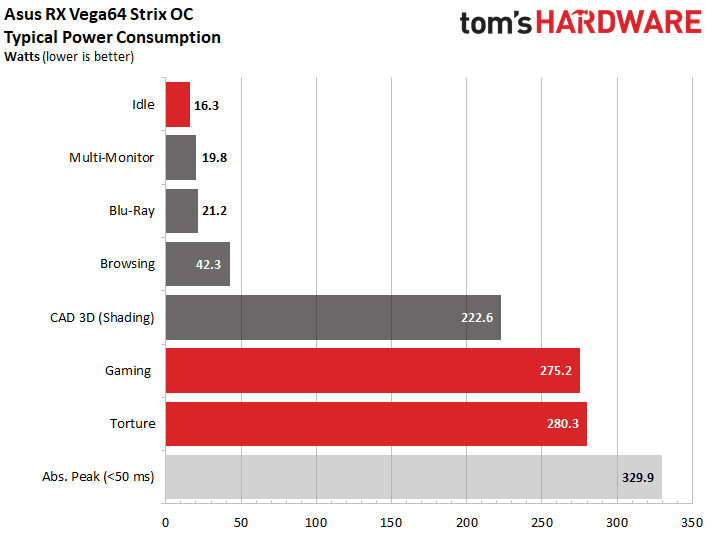
Power Consumption
Power Consumption at Different Loads
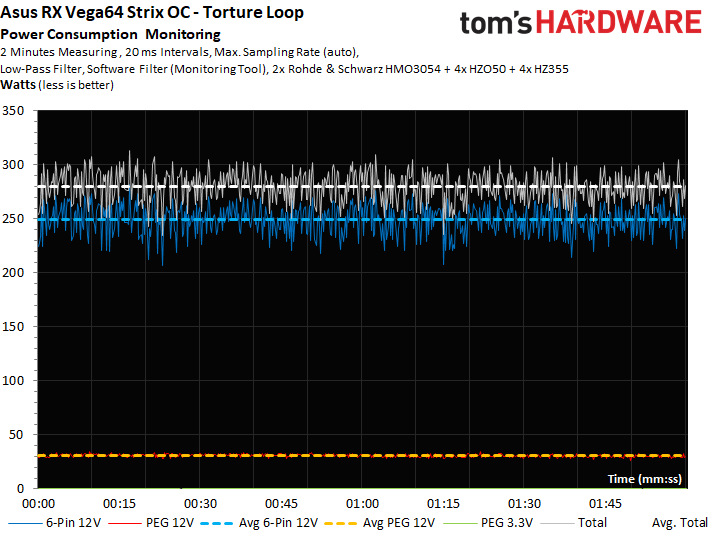
We measured about 275W during our gaming loop using the driver's Balanced power profile. That's about 5W less than AMD's reference model using its default BIOS. This is all the more interesting since Asus' performance is even a bit higher than AMD's. Recent BIOS modifications, including an updated power table, seem to be working well. A 280W measurement in our stress test is also acceptable.
Switching into manual overclocking mode with a 50%-higher power limit pushes us beyond 330W, at which point the thermal solution is overloaded (unless you really crank the fans up). As a result, we decided not to get any more aggressive with our overclocking. Rather, we stuck with the driver's Balanced power profile for testing.
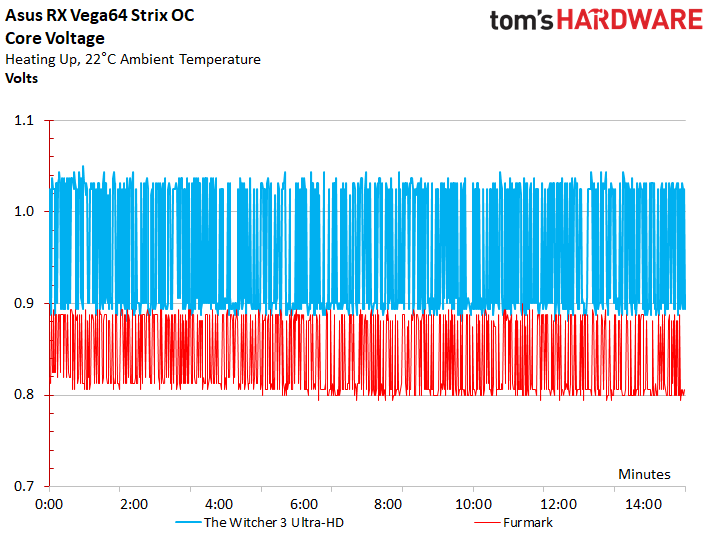
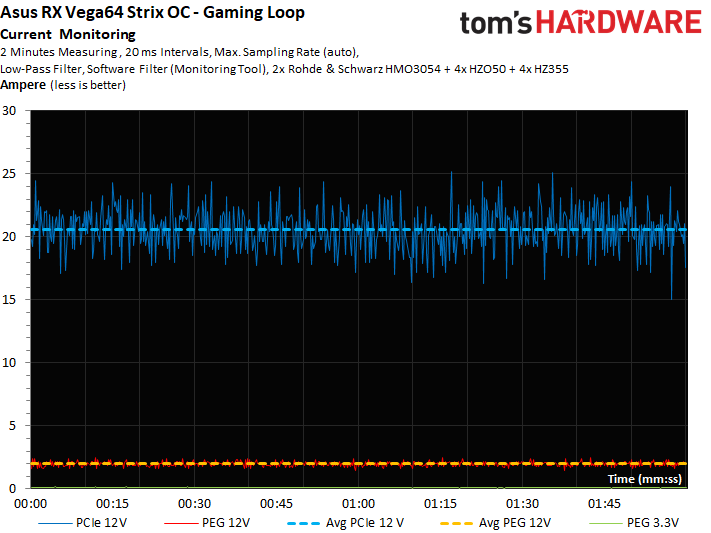
The corresponding voltages for our gaming workload and stress test at Asus' stock settings are plotted in the following graph:
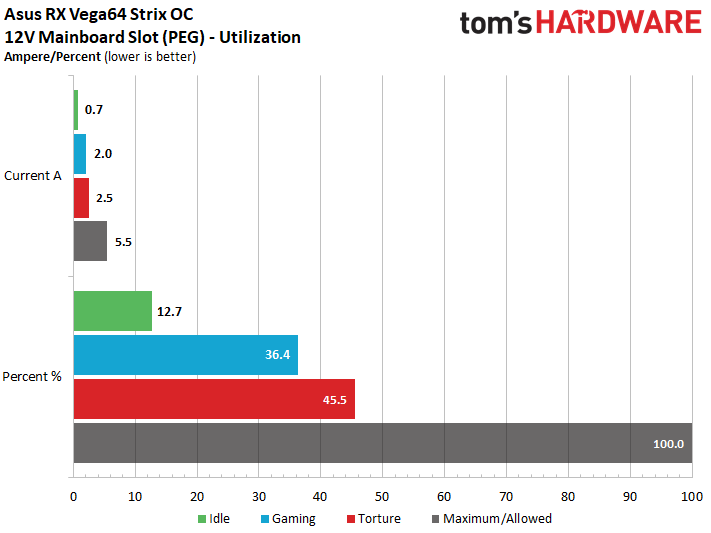
Load On The Motherboard Slot
At a peak of 2.5A through our stress test, Asus' ROG Strix Radeon RX Vega 64 8GB OC Edition falls significantly below the 5.5A ceiling defined by the PCI-SIG for a motherboard's 12V rail. A mere 2A during the gaming loop is even more conservative. Overall, balancing is well-implemented, and the motherboard slot hardly ever experiences serious loads.
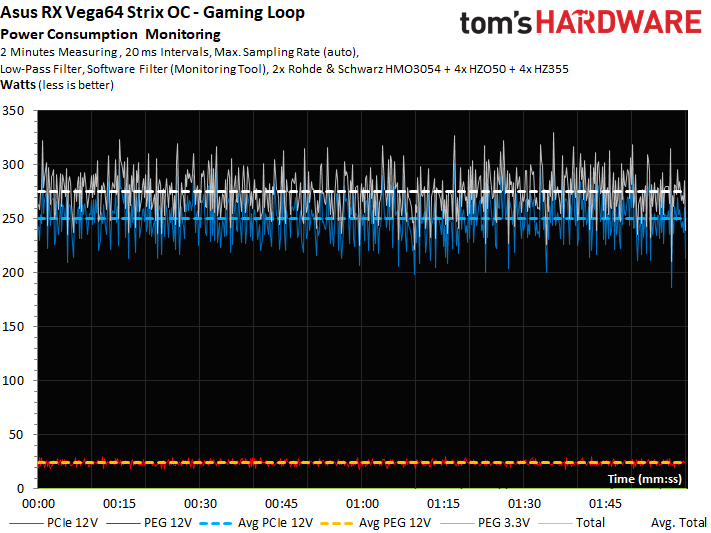
Power Consumption In Detail
The graphs below plot detailed power consumption and current readings in order to illustrate our findings.
Naturally, peaks in power consumption are highest during gaming. But spikes of up to 330W are still acceptable, since they're far too brief to cause a problem.
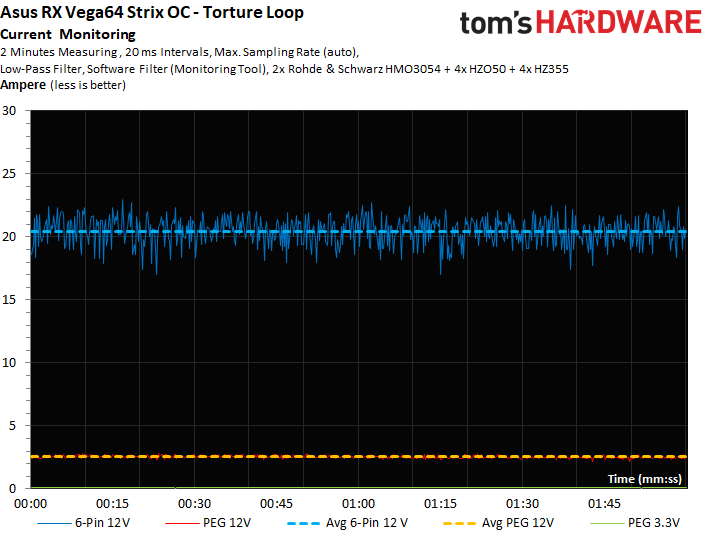
The same goes for the corresponding current measurements:
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
During our stress test, the short-term peaks are significantly less pronounced (even if the power consumption is slightly higher than during gaming workloads).
Again, our current readings follow the graph rather closely and show no abnormalities.
MORE: Best Graphics Cards
MORE: Desktop GPU Performance Hierarchy Table
MORE: All Graphics Content
Current page: Power Consumption
Prev Page Gaming Benchmarks Next Page Temperatures, Clock Rates & Overclocking
Igor Wallossek wrote a wide variety of hardware articles for Tom's Hardware, with a strong focus on technical analysis and in-depth reviews. His contributions have spanned a broad spectrum of PC components, including GPUs, CPUs, workstations, and PC builds. His insightful articles provide readers with detailed knowledge to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape
-
darkchazz "Missing a thermal pad between PCB and backplate"Reply
My Strix GTX 1080 I got in July 2016 also has missing several thermal pads on the GDDR5X modules. Many others reported this issue too and I suppose they still haven't fixed it at the production line. -
Kaziel I just bought one for USD599 on June 6th and waiting for all the parts to arrive. I really hope it'll be okay in an NZXT H500 with the 2x stock fans as exhaust and 2x Noctua NF-A14 as intake.Reply
Do you guys think that my EVGA SuperNova 650 P2 will be able to handle an overclocked R5 2600x and this Asus Strix Vega 64? -
milkod2001 @KAZIELReply
That depends how many other components you also plan to connect: Sound Cards, HDDs, Blue Ray Players, etc, ect but i think it would be OK with 1 SSD and 1 HDD. -
Martell1977 It would have been interesting for Tom's to make the modification of adding the thermal pads and show how much of a difference it would really make. I wonder if ASUS felt it was a acceptable trade off between looks and functionality.Reply -
Kaziel Reply21047426 said:@KAZIEL
That depends how many other components you also plan to connect: Sound Cards, HDDs, Blue Ray Players, etc, ect but i think it would be OK with 1 SSD and 1 HDD.
Still waiting on parts to arrive.
CPU: R5 2600x
Cooling: Noctua NH-U12S, 3x 120 Fans and 2x 140 Fans
Motherboard: Asus Strix x470-F
RAM: Corsair Vengeance RGB 3466 C16 (2x 8gb)
GPU: Asus Strix RX Vega 64
Storage: Samsung Evo 860 (250gb) and Seagate 2TB Barracuda (7200 RPM 64MB Cache)
Planning on just letting Ryzen Master auto overclock the 2600x. For the Vega 64 I plan to do the widely suggested undervolt, +50% power, and overclock HBM2. I have used the calculators and they basically say it's fine, but then again I left everything at stock. Not sure what the values are yet for going about overclocking the two parts so unsure what to put in the calculator. -
tokeylokey66 KekReply
Price had went down a little but still a complete joke of a price. More power and heat than 1080 , cost more, released later. Sry Amd you better figure out better marketing and sale strategies or do better in the tech side of things preferably both. -
alextheblue Wow there's commenters that still don't have a clue about the impact of mining, which lingers on Vega to this day.Reply -
zodiacfml Where the undervolting benchmarks if it is mentioned that it is better for overclocking and the mentioned poor exhaust vents?Reply
I think the critique for most of the Vega 64s are the large PCBs. It deserves smaller PCBs such as found in the Vega 56s to improve cooling. -
bit_user Reply
Nice review, but some Far Cry 5 benchmark would've been nice.21047101 said:...
Newegg now has this card for $599, which I think is pretty close to MSRP.