Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
To learn more about our PSU tests and methodology, please check out How We Test Power Supply Units.
Primary Rails And 5VSB Load Regulation
The following charts show the main rails' voltage values recorded between a range of 40W up to the PSU's maximum specified load, along with the deviation (in percent). Tight regulation is an important consideration every time we review a power supply because it facilitates constant voltage levels despite varying loads. Tight load regulation also, among other factors, improves the system’s stability, especially under overclocked conditions and, at the same time, applies less stress to the DC-DC converters that many system components utilize.
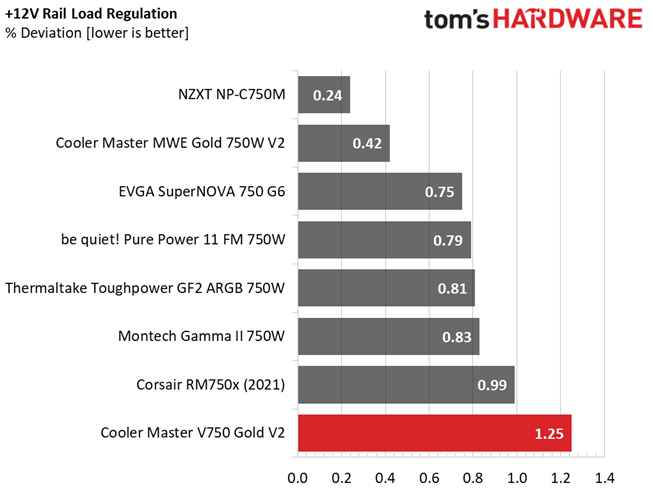
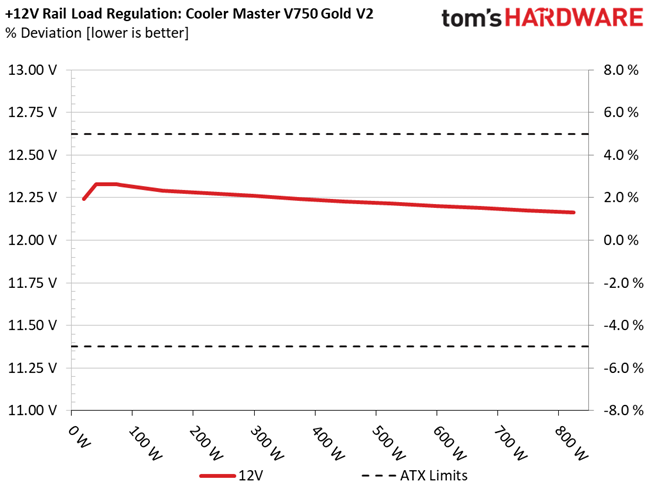
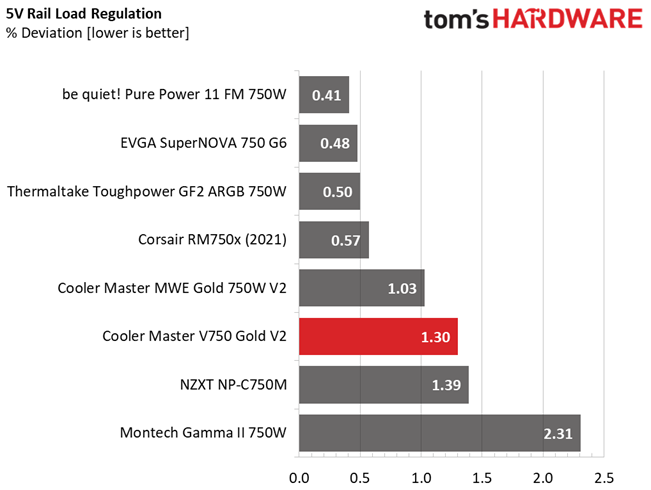
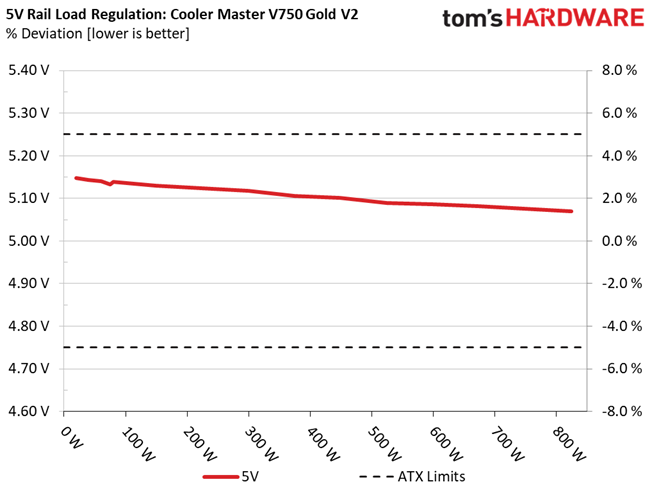
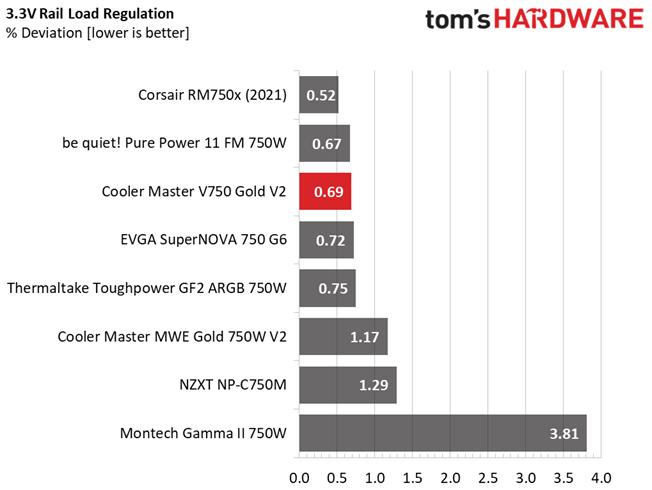
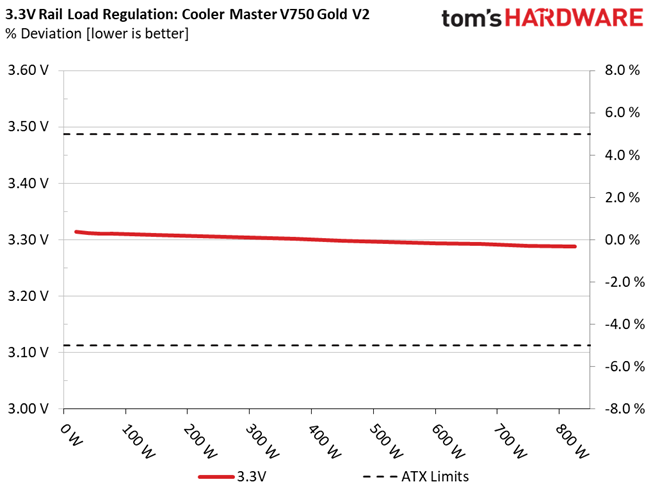
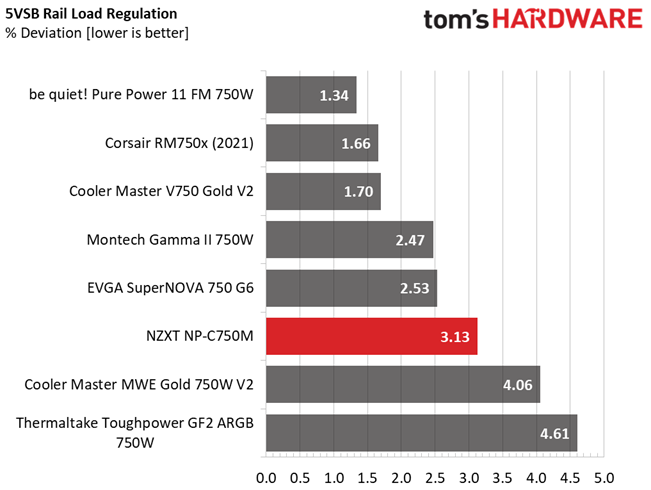
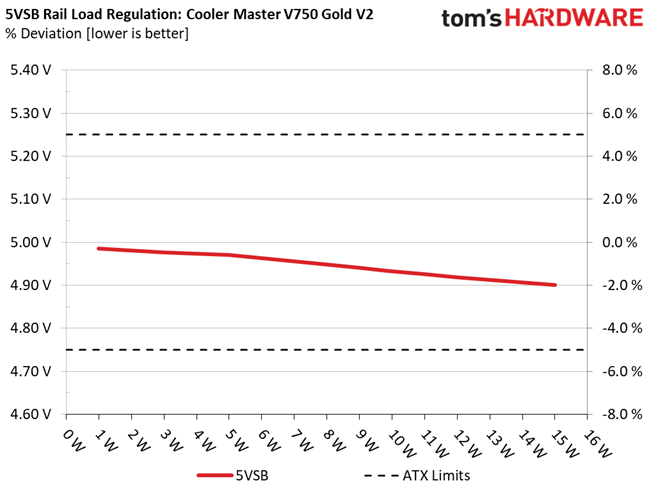
This PSU's load regulation is satisfactory on all rails, but would be ideal if it were within 1% at 12V.
Hold-Up Time
Put simply; hold-up time is the amount of time that the system can continue to run without shutting down or rebooting during a power interruption.
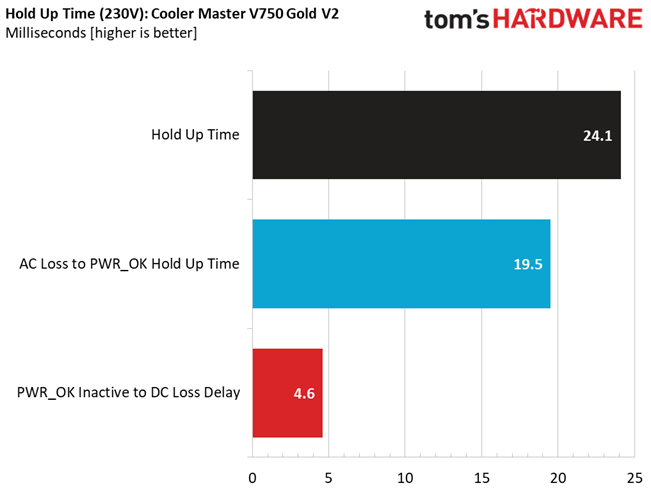
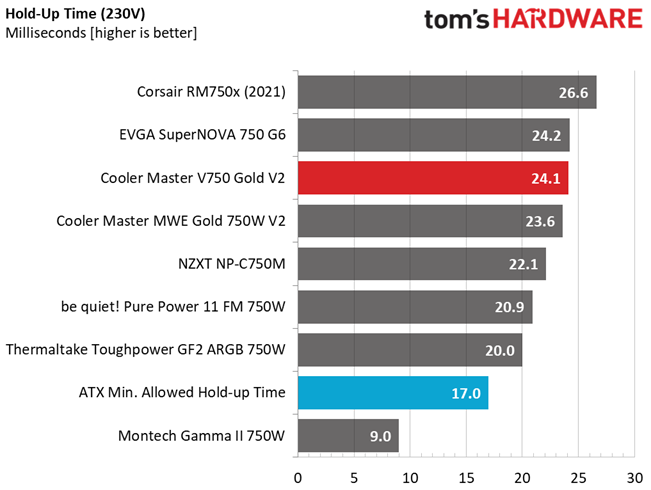
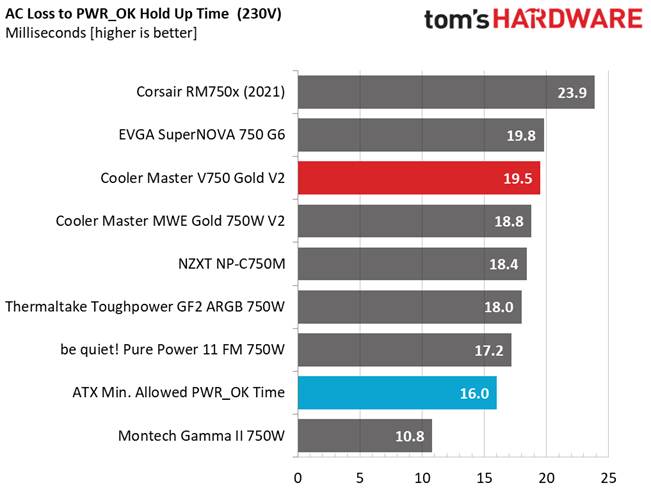
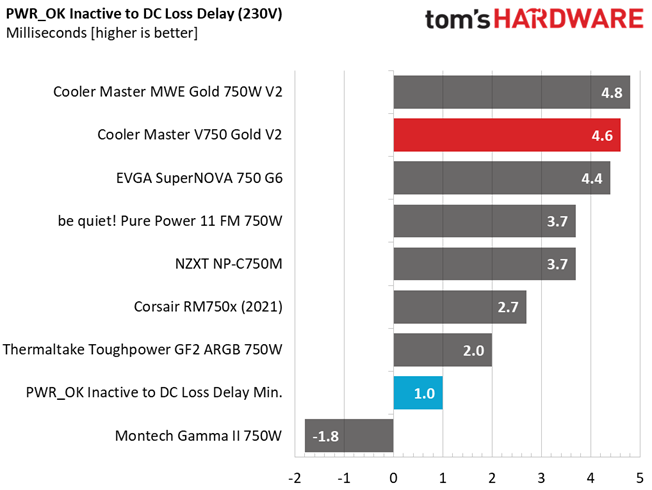
The hold-up time is pretty long here, despite the not so large bulk capacitor.
Inrush Current
Inrush current, or switch-on surge, refers to the maximum, instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when it is first turned on. A large enough inrush current can cause circuit breakers and fuses to trip. It can also damage switches, relays, and bridge rectifiers. As a result, the lower the inrush current of a PSU right as it is turned on, the better.
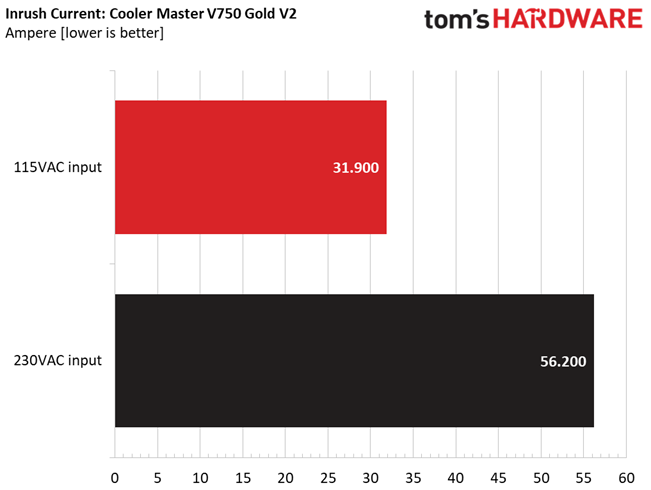
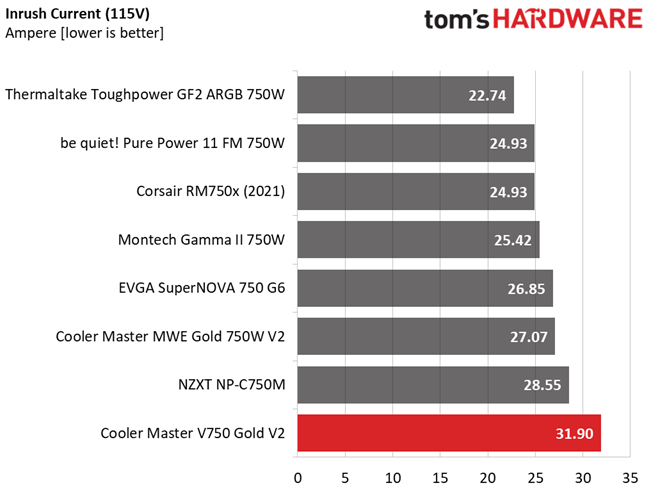
Inrush currents are low on this device, thanks to the large NTC thermistor.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Leakage Current
In layman's terms, leakage current is the unwanted transfer of energy from one circuit to another. In power supplies, it is what happens when the current flows from the primary side to the ground or the chassis, which in the majority of cases is connected to the ground. For measuring leakage current, we use a GW Instek GPT-9904 electrical safety tester instrument.
Our leakage current test is conducted at 110% of the DUT's rated voltage input (so for a 230-240V device, we conduct the test with 253-264V input). The maximum acceptable limit of a leakage current is 3.5 mA (as defined by the IEC-60950-1 regulation), ensuring that the current is low and will not harm any person coming in contact with the power supply's chassis.
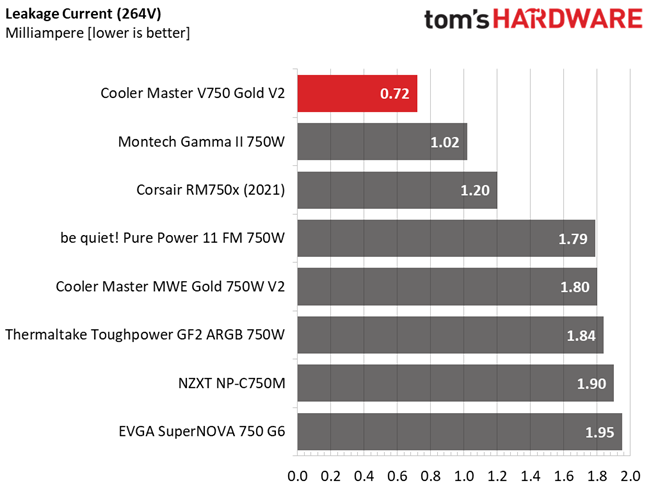
Leakage current here is lower than any of the competition we tested this PSU against.
10-110% Load Tests
These tests reveal the PSU's load regulation and efficiency levels under high ambient temperatures. They also show how the fan speed profile behaves under increased operating temperatures.
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | Temps (In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
| 1 | 4.327A | 1.961A | 1.992A | 1.006A | 74.949 | 86.517% | 0 | <6.0 | 45.63°C | 0.945 |
| 12.329V | 5.102V | 3.311V | 4.971V | 86.629 | 40.20°C | 115.15V | ||||
| 2 | 9.687A | 3.066A | 2.992A | 1.209A | 150.003 | 90.803% | 0 | <6.0 | 46.87°C | 0.961 |
| 12.292V | 4.903V | 3.308V | 4.963V | 165.196 | 40.86°C | 115.15V | ||||
| 3 | 15.387A | 3.620A | 3.494A | 1.412A | 224.998 | 92.179% | 0 | <6.0 | 47.95°C | 0.973 |
| 12.276V | 4.850V | 3.306V | 4.956V | 244.087 | 41.30°C | 115.15V | ||||
| 4 | 21.103A | 3.910A | 3.995A | 1.617A | 300.000 | 92.299% | 0 | <6.0 | 48.87°C | 0.980 |
| 12.263V | 5.118V | 3.304V | 4.949V | 325.030 | 41.82°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 5 | 26.451A | 4.897A | 5.001A | 1.821A | 374.349 | 91.861% | 770 | 27.8 | 42.56°C | 0.979 |
| 12.243V | 5.106V | 3.301V | 4.941V | 407.519 | 50.13°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 6 | 31.850A | 5.899A | 6.004A | 2.000A | 449.146 | 91.518% | 818 | 29.6 | 43.03°C | 0.980 |
| 12.228V | 5.088V | 3.298V | 4.934V | 490.773 | 51.29°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 7 | 37.285A | 6.880A | 7.010A | 2.233A | 524.591 | 91.034% | 899 | 31.2 | 43.82°C | 0.983 |
| 12.216V | 5.089V | 3.296V | 4.926V | 576.257 | 52.48°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 8 | 42.736A | 7.867A | 8.012A | 2.440A | 599.911 | 90.440% | 977 | 34.0 | 44.37°C | 0.986 |
| 12.203V | 5.086V | 3.294V | 4.918V | 663.323 | 53.36°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 9 | 48.554A | 8.360A | 8.504A | 2.442A | 674.400 | 89.915% | 1052 | 34.9 | 44.68°C | 0.988 |
| 12.191V | 5.082V | 3.292V | 4.913V | 750.039 | 54.15°C | 115.14V | ||||
| 10 | 54.199A | 8.901A | 9.026A | 3.061A | 749.565 | 89.258% | 1077 | 36.0 | 45.21°C | 0.990 |
| 12.175V | 5.056V | 3.289V | 4.901V | 839.769 | 55.42°C | 115.13V | ||||
| 11 | 60.432A | 8.877A | 9.030A | 3.062A | 824.723 | 88.603% | 1127 | 37.2 | 46.64°C | 0.991 |
| 12.163V | 5.069V | 3.288V | 4.899V | 930.805 | 57.30°C | 115.12V | ||||
| CL1 | 0.121A | 14.000A | 13.997A | 0.000A | 119.331 | 83.995% | 0 | <6.0 | 50.21°C | 0.959 |
| 12.306V | 5.109V | 3.309V | 4.967V | 142.070 | 42.84°C | 115.15V | ||||
| CL2 | 62.488A | 1.001A | 0.999A | 1.000A | 774.732 | 89.579% | 1142 | 37.3 | 45.31°C | 0.990 |
| 12.185V | 5.090V | 3.293V | 4.931V | 864.859 | 55.55°C | 115.12V |
The PSU manages to keep high-efficiency levels even under increased operating temperatures. The APFC readings should be a bit higher, though.
20-80W Load Tests
In the following tests, we measure the PSU's efficiency at loads significantly lower than 10% of its maximum capacity (the lowest load the 80 PLUS standard measures). This is important for representing when a PC is idle with power-saving features turned on.
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | PF/AC Volts |
| 1 | 1.211A | 0.486A | 0.497A | 0.200A | 19.971 | 77.320% | 0 | <6.0 | 0.889 |
| 12.242V | 5.147V | 3.314V | 4.986V | 25.829 | 115.14V | ||||
| 2 | 2.407A | 0.971A | 0.996A | 0.401A | 39.964 | 80.845% | 0 | <6.0 | 0.919 |
| 12.328V | 5.143V | 3.312V | 4.981V | 49.433 | 115.14V | ||||
| 3 | 3.614A | 1.459A | 1.493A | 0.603A | 59.997 | 84.384% | 0 | <6.0 | 0.937 |
| 12.328V | 5.140V | 3.311V | 4.977V | 71.100 | 115.14V | ||||
| 4 | 4.816A | 1.946A | 1.992A | 0.804A | 79.949 | 87.051% | 0 | <6.0 | 0.949 |
| 12.325V | 5.138V | 3.311V | 4.973V | 91.842 | 115.14V |
The efficiency levels are sky high here, so your fan won't need to spin when the PSU is under light loads.
2% or 10W Load Test
From July 2020, the ATX spec began requiring 70% and higher efficiency at 115V input. The applied load for our test is only 10W for PSUs with 500W and lower capacities, while for stronger units, we dial 2% of their max-rated capacity.
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | PF/AC Volts |
| 1 | 1.063A | 0.244A | 0.246A | 0.051A | 15.321 | 73.627% | 0 | <6.0 | 0.891 |
| 12.226V | 5.145V | 3.313V | 4.990V | 20.809 | 115.12V |
The 70% mark is easy for this platform, with 2% load.
Efficiency & Power Factor
We plotted a chart showing the PSU's efficiency at low loads and loads from 10 to 110% of its maximum rated capacity. The higher a PSU’s efficiency, the less energy goes wasted, leading to a reduced carbon footprint and lower electricity bills. The same goes for Power Factor.
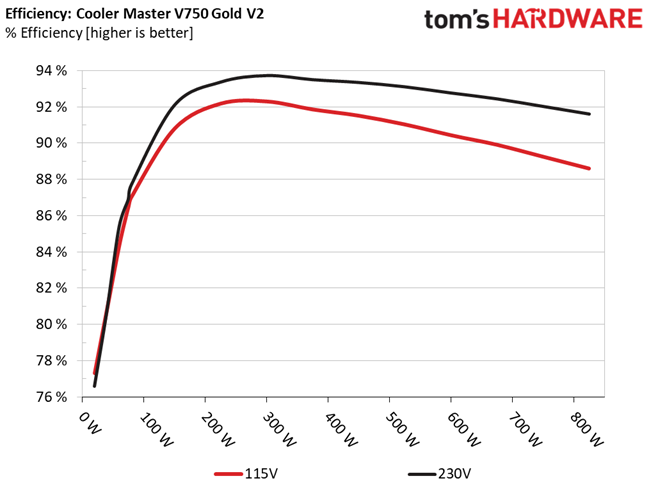
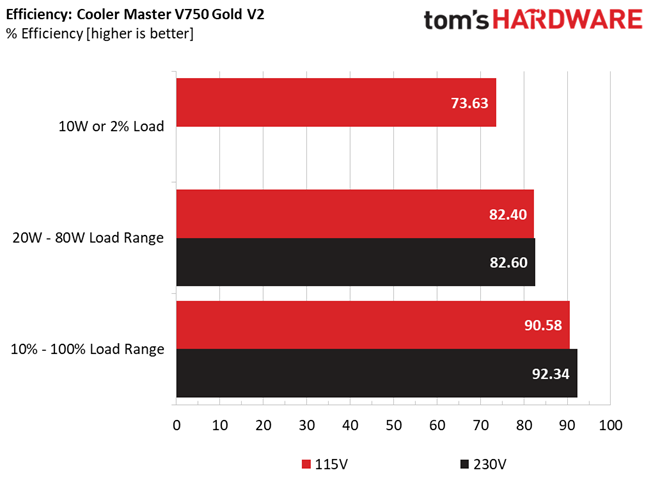
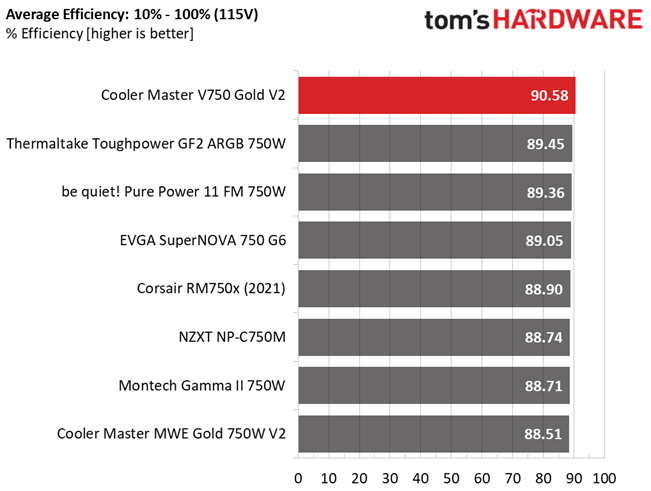
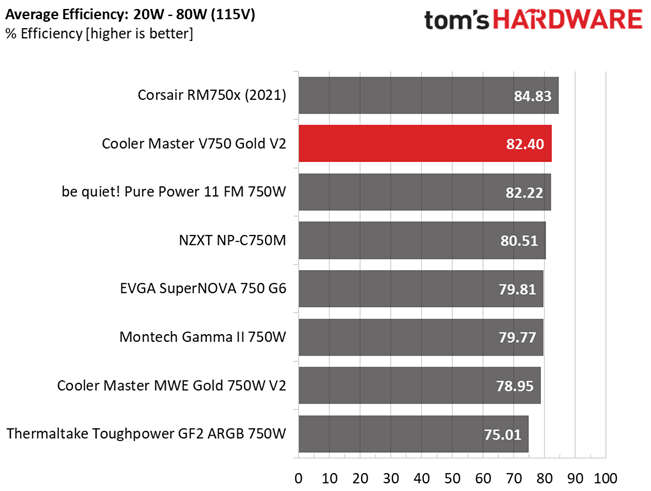
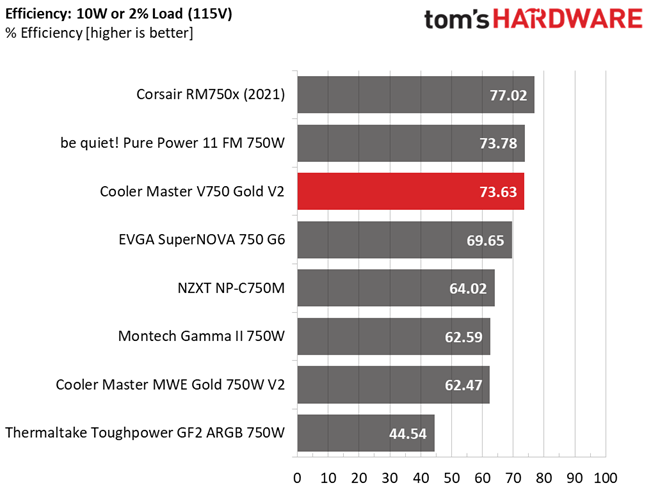
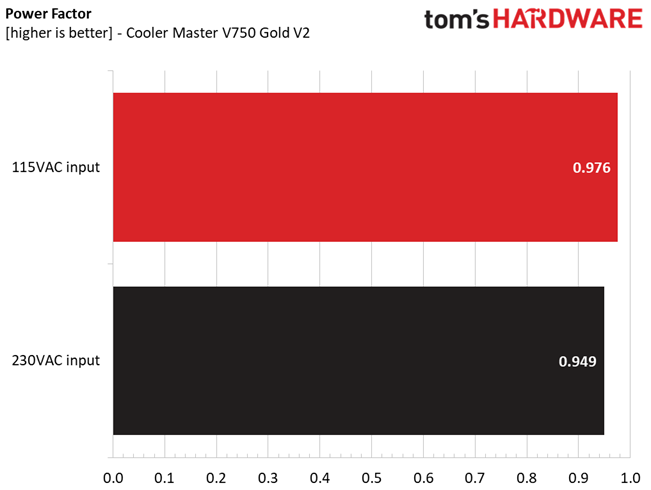
This is a highly efficient platform, which explains why it achieved a Platinum rating in the Cybenetics scale.
5VSB Efficiency
| Test # | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | PF/AC Volts |
| 1 | 0.100A | 0.499 | 76.769% | 0.188 |
| 4.989V | 0.650 | 115.15V | ||
| 2 | 0.250A | 1.246 | 81.491% | 0.417 |
| 4.988V | 1.529 | 115.15V | ||
| 3 | 0.550A | 2.741 | 82.785% | 0.466 |
| 4.984V | 3.311 | 115.16V | ||
| 4 | 1.000A | 4.978 | 82.581% | 0.505 |
| 4.978V | 6.028 | 115.16V | ||
| 5 | 1.500A | 7.458 | 82.464% | 0.529 |
| 4.972V | 9.044 | 115.16V | ||
| 6 | 2.999A | 14.858 | 81.050% | 0.560 |
| 4.954V | 18.332 | 115.16V |
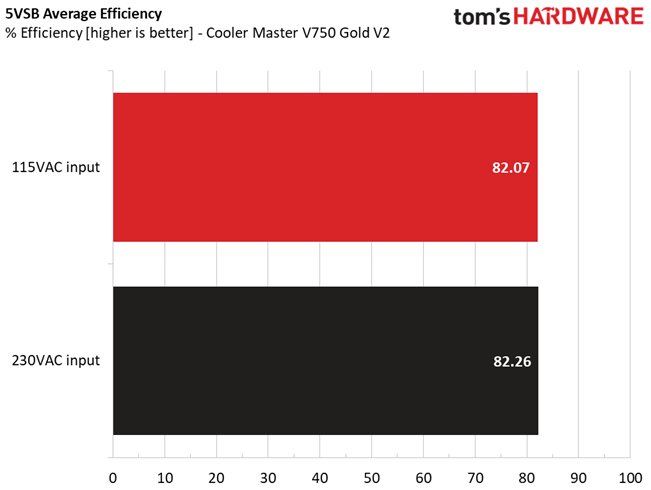
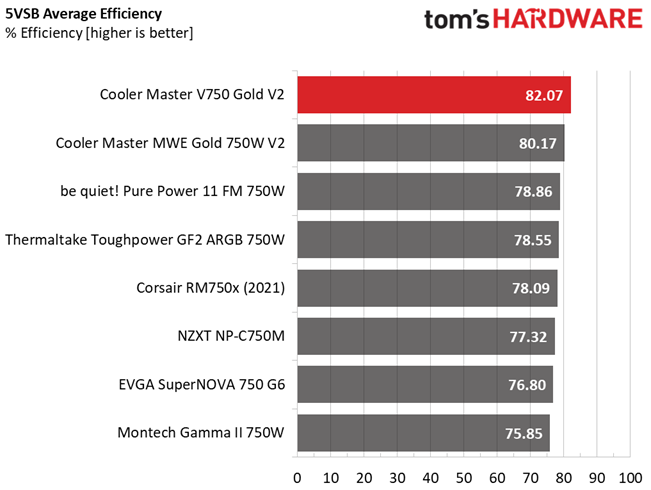
Gospower used a highly efficient 5VSB rail in this platform, which puts to shame the respective circuits of other, similar spec, PSUs.
Power Consumption In Idle And Standby
| Mode | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Watts | PF/AC Volts |
| Idle | 12.216V | 5.146V | 3.312V | 4.992V | 4.001 | 0.646 |
| 115.1V | ||||||
| Standby | 0.040 | 0.239 | ||||
| 115.1V |
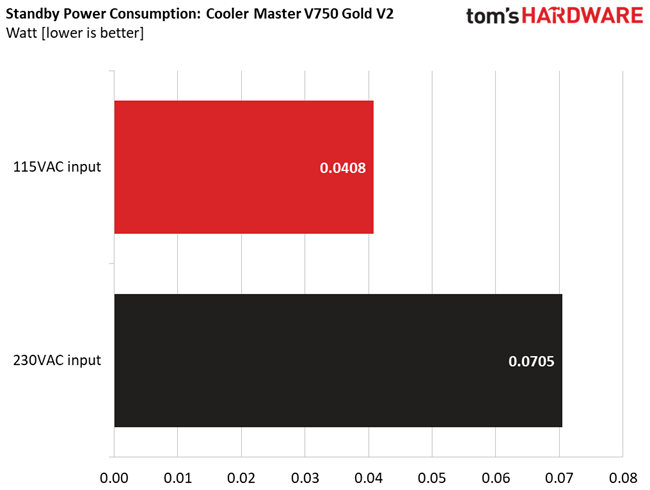
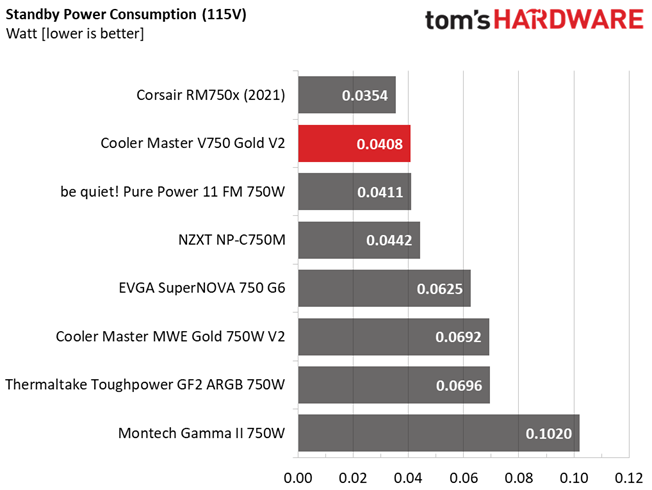
Vampire power is low with both voltage inputs.
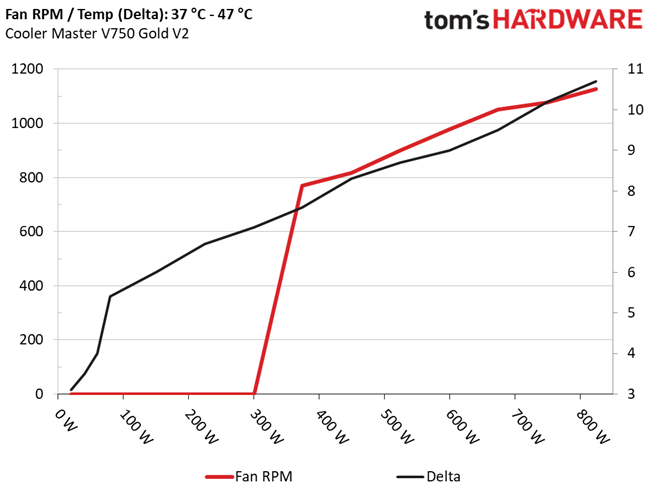
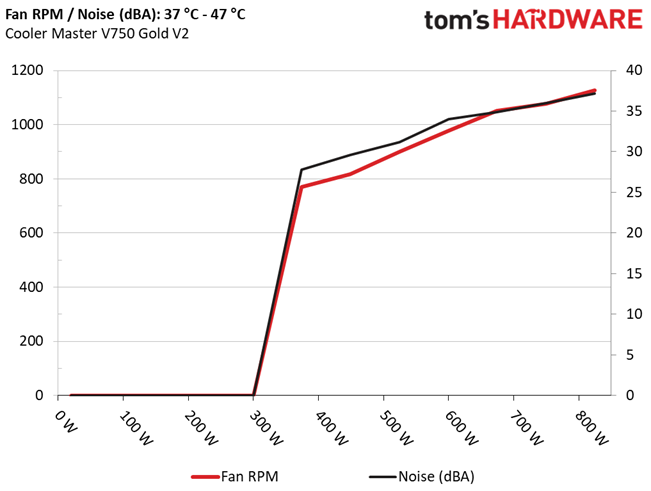
Fan RPM, Delta Temperature, And Output Noise
All results are obtained between an ambient temperature of 37 to 47 degrees Celsius (98.6 to 116.6 degrees Fahrenheit).
The fan speed profile is relaxed even under stressful conditions. The highly efficient platform helps with this, since it keeps thermal loads low.
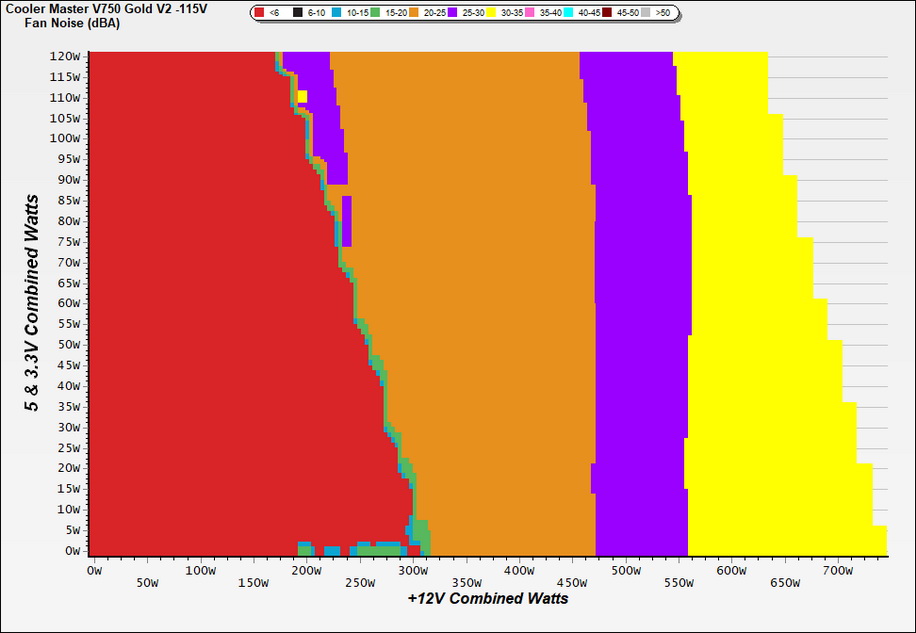
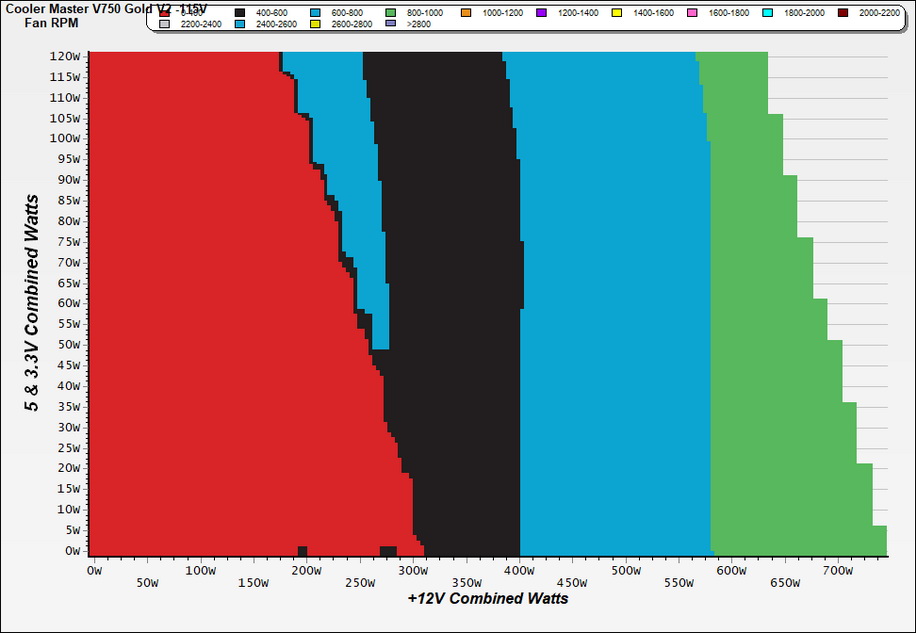
The following results were obtained at 30 to 32 degrees Celsius (86 to 89.6 degrees Fahrenheit) ambient temperature.
At normal operating temperatures, close to 30 degrees Celsius, the PSU will be dead silent with up to 300W loads, and you will barely hear its fan spinning at up to 475W. It exceeds 30 dBA at loads that are more than 550W, but it doesn't go above 35 dBA in any case.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time, Inrush & Leakage Current, Efficiency and Noise
Prev Page Specifications and Part Analysis Next Page Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
helper800 A good Cooler Master branded PSU? Wow good on CM to find a good manufacturer. On a side-note what determines whether a product gets an editor's choice award from Toms? Aris seemed pretty happy with the PSU. Lets hope CM keeps using manufacturers that use modern PSU platforms.Reply -
jayjr1105 Great review. nice to see another OEM with 10 year warranty worthy build quality and parts.Reply
Any plans on doing some of the very affordable Superflower Leadex III units?