Overclocking: Can Sandy Bridge-E Be Made More Efficient?
Intel's six-core processors are fast, but enthusiasts almost always want to push unlocked multipliers harder. Core i7-3960X can easily exceed 4 GHz, but what happens to power efficiency when clock rates go up? Sandy Bridge-E demonstrates weaknesses there.
Overall Efficiency: Single- And Multi-Threaded
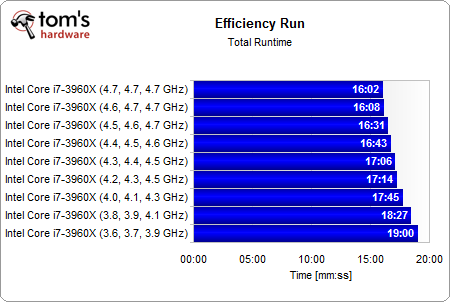
Overclocking from stock up to 4.7 GHz dropped the total run time of our benchmark suite by 16%.
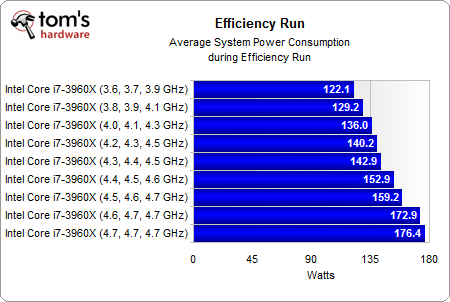
The system needed about 30% more average system power to make this happen, though.
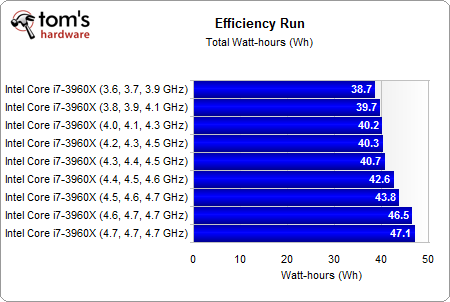
And here, the average energy requirement rose by about 18%
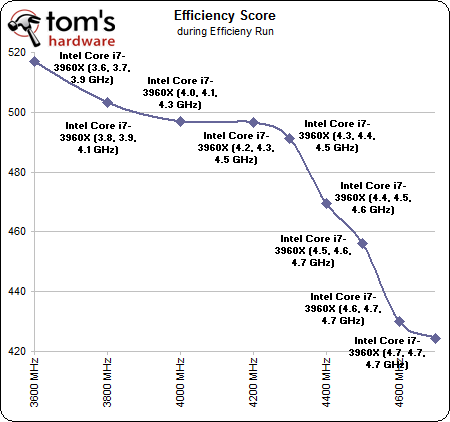
This doesn't always happen, but Intel's Core i7-3960X achieves its best efficiency right at its stock clock rate of 3.3 GHz, with Turbo Boost taking it up to 3.9 GHz in lightly-threaded workloads. Yes, there's plenty more performance to milk from Intel's flagship, but it comes at the cost of even great power use. In the end, a negative impact on efficiency draws the direction of our chart downward.
Then again, if you're spending $1050 on a processor (or even $600, if you want the Core i7-3930K), a few bucks here and there on the power bill probably isn't too big of a concern. Believe us, the point of these chips isn't lost on our enthusiast-oriented minds. But we do find it useful to know exactly what happens as a consequence of tweaking ratios and voltages in the name of more speed.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Overall Efficiency: Single- And Multi-Threaded
Prev Page Efficiency: Multi-Threaded (All Cores Active) Next Page Sandy Bridge-E’s Efficiency Suffers Significantly Overclocked
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.
-
Yargnit What about trying to under-volt it at slight under-clocks to slight-overclocks. How much room is there to reduce it's stock voltage to gain better efficiency?Reply -
billj214 Was there an efficiency chart made for the Core i7 2600k or 2700k?Reply
Nice to know Intel doesn't just set the stock clock speed for just performance! -
Marcus52 ReplyAnd then there's the Core i7-3820, which only sports four cores, but operates at a base clock rate of 3.6 GHz. Although this less-complex chip could probably hit higher Turbo Boost frequencies, Intel limits it to 3.9 GHz to keep it from outshining the top-end Core i7-3960X in single-threaded tasks.
Did someone at Intel tell you that was the reason for a lower Turbo Boost limit, or did you just assume it?
I think we should be careful of this kind of guess at another person's, or company's, reasoning. There could be some other cause for the limit - for example, they will obviously sell it for a lower price, so wouldn't a possible reason be they have looser binning specs to allow for chips that wouldn't make it under more strenuous tests through? (Remember, Intel, or any CPU manufacturer, doesn't warrant the product based on what it can be pushed to, and is generally going to provide it at a clock rate they feel is safe over time to guarantee.)
I'm certainly not saying it is a bad assumption, what you said makes sense to me, but I do think there are enough other reasonable possibilities that I wouldn't have stated it as a fact unless I knew it to be.
;) -
Marcus52 Thanks for the analysis!Reply
I do think articles like this are very important; those of us who overclock, especially when we turn off all the power-saving features in hopes of reaching that max stable a CPU can do, should be aware of how much money we are spending if we keep said OC. It's more than just the high end cooling solution.
The people that bash higher capacity PSUs could also stand to learn a thing or two, here. An overclocked CPU can require a huge amount of peak power over and above what a stock CPU needs (349W measured here). An overclocked Sandy Bridge-E and an overclocked GTX 580 could require a peak power of 650W just considering those 2 components!
A Kill A Watt or similar device is a great way to measure how much you actually spend a month operating your computer. You might be surprised.
;) -
giovanni86 Just a thought, so at 4.7Ghz the performance increase was only 16%? For being such a High overclock i was hoping for more then that. You guys literally upped the bar from stock clock to the OC clock by 1.4ghz, seems like a small increase in performance if you look at the amount of watts it takes.. Well at least its good 2 know my future billing of electricity will sure be expensive.. =PReply -
cangelini Marcus52Did someone at Intel tell you that was the reason for a lower Turbo Boost limit, or did you just assume it?I think we should be careful of this kind of guess at another person's, or company's, reasoning. There could be some other cause for the limit - for example, they will obviously sell it for a lower price, so wouldn't a possible reason be they have looser binning specs to allow for chips that wouldn't make it under more strenuous tests through? (Remember, Intel, or any CPU manufacturer, doesn't warrant the product based on what it can be pushed to, and is generally going to provide it at a clock rate they feel is safe over time to guarantee.)I'm certainly not saying it is a bad assumption, what you said makes sense to me, but I do think there are enough other reasonable possibilities that I wouldn't have stated it as a fact unless I knew it to be.Hence the "probably." Of course, we don't know for sure, nor would Intel ever admit as such, but it's an educated guess nonetheless. =)Reply