Game Over? Core 2 Duo Knocks Out Athlon 64
Die Size And Transistor Count
| Processor | Die Size | Transistor Count | Process |
|---|---|---|---|
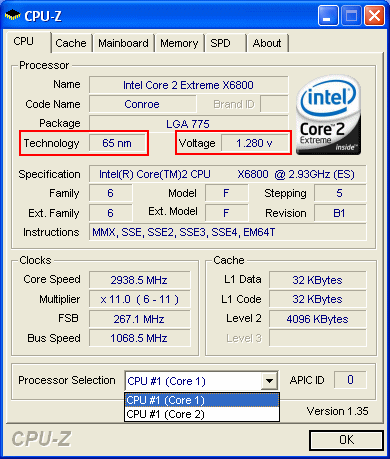
| Core 2 Extreme X6800 | 143 mm² | 291 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Core 2 Duo E6700 | 143 mm² | 291 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Core 2 Duo E6600 | 143 mm² | 291 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Core 2 Duo E6400 | 111 mm² | 167 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Core 2 Duo E6300 | 111 mm² | 167 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Pentium D 900 | 280 mm² | 376 Mio. | 65 nm |
| Athlon 64 FX-62 | 230 mm² | 227 Mio. | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 5000+ | 183 mm² | 154 Mio. | 90 nm |
The transistor count of a Core 2 Duo processor is considerably lower than the total amount required for a dual core Pentium D 900 processor. Thanks to the 65 nm manufacturing, the total die size is reduced as well, since a Pentium D 900 is powered by two Pentium 4 dies.
Power Management & Energy Saving
Intel has learned a lot from its mobility Pentium M processors Banias (90 nm) and Dothan (65 nm) - especially when energy requirements and energy saving are concerned. Most people are very sensitive to unreasonable energy requirements and component heat dissipation, because PCs must neither strain energy bills nor require noisy fans. Intel reacted and introduced a long number of energy management features into its new Core 2 desktop processors. The main hardware fundamentals for an energy efficient processor are the modern 65 nm manufacturing process (low-voltage operation), a reduced transistor count and a reduced die size.
2.93 GHz clock speed at only 1.3 V is impressive.
There are a couple of technologies that need to be mentioned in order to explain Core 2 Duo's energy management meachanisms:
- Intel SpeedStep technology-Technologie
- Ultra Fine Grained Power Control
- Split Busses
- PSI-2
- DTS
- PECI
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Die Size And Transistor Count
Prev Page Power Requirements Next Page Intel SpeedStep Technology
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.