Energy Efficiency: AMD vs. Intel
Constant Operation Under Full Load
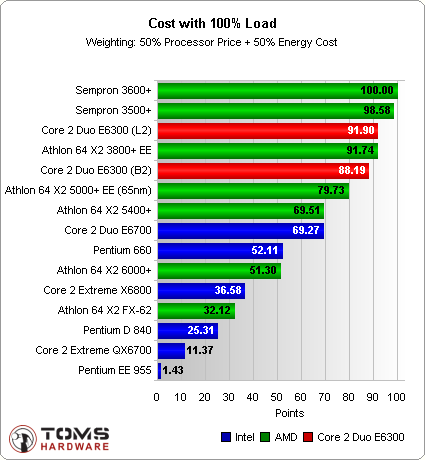
This time, the systems run full tilt the entire time. An example of this usage pattern would be if the computer is only turned on to perform very computationally intensive tasks and is switched back of immediately after completion. Another example could be a system that crunches SETI or BOINC data around the clock.
Under full load, the Core 2 Duo with the L2 stepping is tied with EE variant of the Athlon 64 3800+.
Drawing a Balance: Core 2 with L2 Stepping Disappoints
Since the Core 2 Duo E6300 with L2 stepping costs the same as its B2 brethren and consumes only slightly less power, it only shows a marginal improvement when judged using our index system. It's a good thing that Intel's Celeron processor based on the Cedar Mill core does not feature in our charts - it wouldn't exactly improve the picture for Intel with its high power consumption.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Constant Operation Under Full Load
Prev Page Idle Next Page Energy Efficiency: AMD vs. IntelTom's Hardware is the leading destination for hardcore computer enthusiasts. We cover everything from processors to 3D printers, single-board computers, SSDs and high-end gaming rigs, empowering readers to make the most of the tech they love, keep up on the latest developments and buy the right gear. Our staff has more than 100 years of combined experience covering news, solving tech problems and reviewing components and systems.