G31 And E7200: The Real Low-Power Story
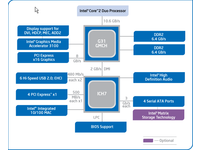
Intel G31 Express Chipset
The diversity in Intel’s chipset portfolio can be difficult to understand, as some features overlap from one model to the next. Picking a higher model number will not necessarily give you a more advanced chipset, either—the G35 offers the more advanced graphics unit, while it does not support DDR3 memory nor the newer ICH9 southbridge like the G33. Intel’s G31, however, is an entry-level chipset indeed and it typically requires the least power.
The G31 is classified as a mainstream desktop chipset, which Intel targets at “essential computing.” This means that the product clearly isn’t suitable for high-end systems and it does not support top notch features. Instead, it was designed to provide a great bang for the buck for average users. Hence it is aimed at hosting a Core 2 processor or Pentium Dual Core or Celeron equivalent based on the Core 2 micro-architecture.
Limited Feature Set
The G31 chipset is limited to 4 GB of memory, while the G33 and G35 support up to 8 GB. The lower-end model also only supports DDR2-800 dual channel memory (though this isn’t a disadvantage compared to DDR3) and it is bundled with the ICH7 southbridge instead of the ICH8, ICH9, or ICH10. This results in only four SATA/300 ports, but it also provides the platform with two UltraATA/100 channels, while the newer chipsets support either one legacy ATA channel or none at all. The G31 with ICH7 sports eight USB 2.0 ports, HD audio, and conventional PCI slots, but only a 100 Mbit network controller. Should you need a quicker Ethernet connection, please look for a motherboard that comes with a PCIe network controller for Gigabit speeds. This is the case for both boards we looked at. Finally, while supporting one x16 PCI Express slot for upgrades, G31 is not PCI Express 2.0-compliant.
Although initially specified for FSB1066 speeds, all the current G31 motherboards we looked at will also support FSB1333 processors. Both boards in this piece support the entire Core 2 processor portfolio, including the Core 2 Quads. Believe it or not, even the three-phase voltage regulator on the Foxconn G31 motherboard is sufficient to operate a Core 2 Quad Q9550 easily, should you decide to ditch a dual-core in favor of a quad-core processor.
GMA3100 Graphics
Integrated graphics solutions will not deliver performance or features anywhere close to those of decent 3D graphics cards such as the Radeon HD4850/4870 or the GeForce 260/280 by Nvidia. Even mainstream graphics cards based on GeForce 9600GT processors vastly outperform integrated solutions. However, we decided to stay with integrated graphics for the sake of maximizing power efficiency.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The G31 chipset includes Intel’s GMA3100 integrated graphics unit, which is based on the GMA3000 core. This is the graphics core that Intel first deployed on the 965 chipset family (called GMA X3000), and although the G965 supports pixel shader model 3.0, the G31, G33, Q35 are limited to SM 2.0, which means DirectX 9.0c capabilities. This is sufficient for all Aero features on Windows Vista, though. Motherboards with the G31 chipset typically include one analog D-SUB15 display output and sometimes a digital DVI output. Since the GMA3100 isn’t suitable for home theater PCs (HTPCs), boards will typically not have any HDMI outputs; don’t expect two digital outputs on these boards, either.
Current page: Intel G31 Express Chipset
Prev Page Performance And Efficiency Basics Next Page Core 2 Duo E7200