JMicron Returns: The JMF667H Controller On Four Reference SSDs
It's rare that we get the chance to test SSDs before they hit production. But after waltzing with Silicon Motion's SM2246EN platform last year, JMicron offered us a handful of reference drives with different types of flash, all driven by the new JMF667H.
Results: Sequential Performance
Fantastic sequential read and write performance is a trademark of modern SSDs. To measure it, we use incompressible data over a 16 GB LBA space, and then test at queue depths from one to 16. We're reporting these numbers in binary (where 1 KB equals 1024) instead of decimal numbers (where 1 KB is 1000 bytes). When necessary, we also limit the scale of the chart to enhance readability.
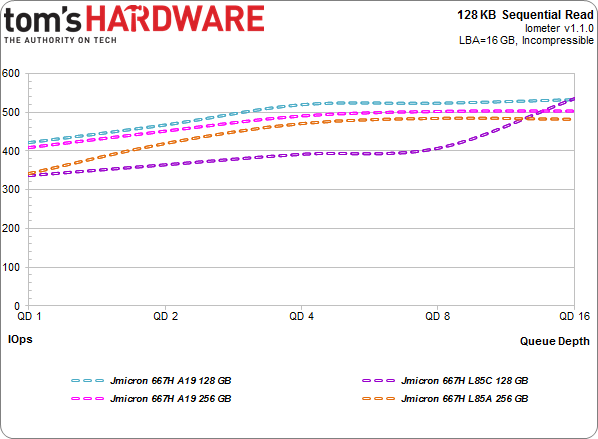
128 KB Sequential Read
Before we get too obscure with the benchmarks, I'll start with the basics. Sequential reads are somewhat mixed between these four reference-class drives equipped with different types of NAND. The SSD armed with Intel's L85C only picks up speed at the end, as queue depth increases. The L85A- and A19-based models get near or pass the 500 MB/s barrier.
Between 520 to 530 MB/s is the practical limit of SATA, and that's where the two ONFi-capable models peak (ONFi stands for Open NAND Flash Interface, by the way, which is a workgroup that created an interface standard for certain flash components). The drives sporting A19 NAND are a little different; they don't demonstrate as high of a read throughput ceiling, which is typically of the Toggle-mode DDR interface. But this will probably be the last time you see the ONFi flash win.
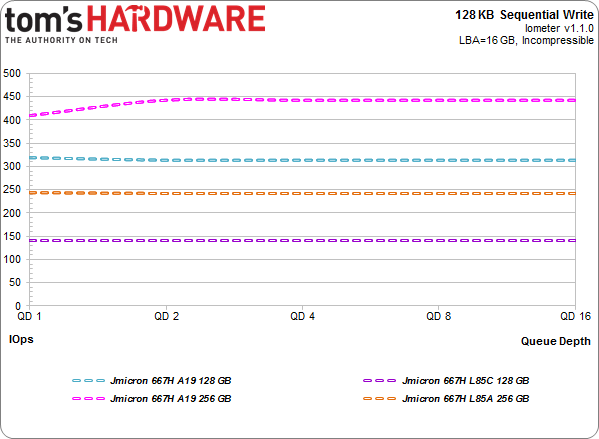
128 KB Sequential Write
Typically, when I test four drives, I get different capacities. Those capacities often behave differently on a benchmark chart due to their die and package configuration. In this case, however, there is significant differentiation from only two capacities. Why? The NAND interface types matter. A lot. The 256 GB model equipped with Toshiba's A19 flash takes top honors by achieving 450 MB/s, followed by the 128 GB drive sporting the same stuff.
Both ONFi-capable drives appear further down the list. Combining JMicron's controller and L85A flash results in just under 250 MB/s, while the 128 GB L85C-armed model falls 100 MB/s behind. Really, these numbers aren't surprising, given fewer die available for interleaving on the SSD with L85C NAND.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Results: Sequential Performance
Prev Page How We Tested JMicron's Reference SSDs Next Page Results: Random Performance-
Snipergod87 Page 6: "For every 1 GB the host asked to be written, Mushkin's drive is forced to write 1.05 GB."Reply
Mushkin drive?, To much copy paste. -
koolkei guys. please take a look at thisReply
http://www.tweaktown.com/reviews/6052/kingfast-c-drive-f8-series-240gb-ssd-review-cheapest-tested-240gb-drive-so-far/index.html
that's an actual SSD using this controller, and the price is........ a little more than surprising... -
pjmelect I remember their USB to IDE SATA chip. It caused data corruption every 4 GB or so when transferring data via the IDE interface. I have always been wary of their products since then.Reply -
tripleX "But we're not going to use theoretical corner cases (the sequential and random 4 KB benchmarks we just ran) to crown one configuration a winner and another a loser."Reply
A corner case is not sequential and random benchmarks. It is an engineering term that means, according to Wiki:
A corner case (or pathological case) is a problem or situation that occurs only outside of normal operating parameters—specifically one that manifests itself when multiple environmental variables or conditions are simultaneously at extreme levels, even though each parameter is within the specified range for that parameter.
-
g00ey JMicron has always made pretty shitty products so I won´'t buy any of these anytime soon...Reply -
2Be_or_Not2Be I, too, find it hard to want to purchase a drive from a manufacturer with such a lackluster history.Reply
One part of this article that also doesn't make sense: "Why four channels and not eight? Efficiency is one key motivator. Fewer channels facilitate a smaller ASIC, which can, in turn, be more power-friendly." Compare the size of the PCB to one like the Samsung 850 Pro. They aren't saving much in real estate (they are actually bigger than the Samsung boards), so it makes it hard to believe they're saving much in power here.