Tom's Hardware Verdict
Micron’s new 9300 is a top-notch enterprise SSD with almost everything you could ask for. It’s efficient, spacious, has incredible endurance, and delivers tremendous performance to accelerate today’s largest workloads. The drive is also affordable with flexible pricing to fit your needs.
Pros
- +
Solid performance at QD4 and beyond
- +
3.5 GB/s in both sequential reads and writes
- +
Supports up to 32 namespaces
- +
Capacities up to 15.36TB
- +
Price-per-GB
Cons
- -
Latency under light load
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Micron’s New Heavy Hitter
NVMe devices have taken off these past few years, but adoption is accelerating in 2019. They now surpass both SAS and SATA as the preferred interface and are getting faster with each generation. That's a trend that won’t go away any time soon because we are currently creating over 2.5 exabytes of data a day, and by 2025, the global datasphere is predicted to hit upwards of 175 zettabytes. We once made data lakes; we are now making data oceans.
In fact, that brings us to today’s review. Micron has updated its 9300 series of enterprise-class NVMe SSDs to boost capacity and performance to help handle the explosion of data.
Micron's main goal was to improve the drive's write speed and achieve balanced sequential throughput by tweaking the firmware for the monstrous Microsemi NVMe controller under the hood. As a result, the new 9300 series SSDs hit 3.5 GB/s in both sequential reads and writes over its PCIe 3.0 x4 U.2 connection. Micron also reduced power consumption by 28% on average over the previous-gen model, and the drives are less expensive per gigabyte of storage than the prior-gen models, too.
Finding Balance
Why did Micron focus on achieving a balanced read and write speed? It is what today’s workloads demand, and it enables more efficient utilization of resources.
In today’s markets, data-driven decision making is increasingly important. The 9300 series devices will usually find themselves used as caching devices in AI, machine learning, deep learning servers, or similar database or block- and object-acceleration scenarios. In many of these workloads, the applications need high-performance storage so that they can ingest the data from huge data lakes and then export back out as fast as possible. That allows GPUs and other accelerators to read the data as fast as possible to process and extract any valuable data.
But it’s not just about sheer speed – efficiency is a big factor in enterprise storage. The 9300 series comes in capacities of up to 15.36TB, which a 40% increase over the previous generation and essentially ties with the most capacious HDDs. But these SSDs come in a compact U.2 form factor so you can fit many more into the same space, or use fewer racks and save on overall power consumption. The 9300 drives also support 16 power states ranging from 10W up to 25W. (We tested ours at the stock 25W mode)
Micron's flex capacity feature allows IT admins to configure capacity to match their application’s workloads and requirements. Some users demand a cost-sensitive approach for upgrading their infrastructure for their workloads, while others need the fastest drive they can get. No one solution can satisfy every need, but a flexible one might be able to satisfy most.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Customers are demanding storage tuned just for their needs. That’s where Flex Capacity comes into play. It gives the customer cost flexibility and the ability to adjust write endurance, performance, and consistency, along with capacity, for their applications. In fact, both the Micron 9300 PRO and MAX have the same hardware through and through. The MAX is simply preconfigured with more over-provisioning.
We don’t have official pricing from Micron, but the PRO sells from ~$0.19 -$0.20 per GB online, while the MAX sells for ~$0.24 - $0.26 per GB depending on the capacity point. This gives customers the option to save a few bucks by buying the PRO, but remember, while it won’t be an upfront cost, it will take some time to reconfigure the drives in the field, if needed.
Furthermore, Micron enabled the option to define up to 32 namespaces on a drive. This allows the drives to accommodate multitenancy deployments in hyperscale data centers and cloud infrastructure and enables more parallel sessions for single storage devices, which improves elasticity and application utilization. But while these features are awesome in their own way, note that Micron states that Flex Capacity and manual Namespace Management are not intended to be configured together and should be implemented independently.
Specifications
| Product | 9300 PRO 3.84TB | 9300 PRO 7.68TB | 9300 PRO 15.36TB | 9300 MAX 3.2TB | 9300 MAX 6.4TB | 9300 MAX 12.8TB |
| Pricing | $775.00 | $1,475.00 | $3,000.00 | $828.51 | $1,550.00 | $3,150.00 |
| Capacity (User / Raw) | 3.84TB / 4.096TB | 7.68TB / 8.129TB | 15.36TB / 16.384TB | 3.2TB / 4.096TB | 6.4TB / 8.129TB | 12.8TB / 16.384TB |
| Form Factor | U.2 15mm | U.2 15mm | U.2 15mm | U.2 15mm | U.2 15mm | U.2 15mm |
| Interface / Protocol | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 | PCIe 3.0 x4 / NVMe 1.2 |
| Controller | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 | Microsemi PM8607 NVMe2016 |
| DRAM | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 | DDR4 |
| Memory | Micron 64L TLC | Micron 64L TLC | Micron 64L TLC | Micron 64L TLC | Micron 64L TLC | Micron 64L TLC |
| Sequential Read | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s |
| Sequential Write | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s | 3,500 MB/s |
| Random Read | 850,000 IOPS | 850,000 IOPS | 850,000 IOPS | 850,000 IOPS | 850,000 IOPS | 850,000 IOPS |
| Random Write | 105,000 IOPS | 145,000 IOPS | 150,000 IOPS | 210,000 IOPS | 310,000 IOPS | 310,000 IOPS |
| Power Consumption Read | 14 W | 14 W | 14 W | 14 W | 14 W | 14 W |
| Power Consumption Write | 21 W | 21 W | 21 W | 21 W | 21 W | 21 W |
| Power Consumption Idle | 6.65W (Measured) | 6.65W (Measured) | 6.65W (Measured) | 6.65W (Measured) | 6.65W (Measured) | 6.65W (Measured) |
| Security / Encryption | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Endurance | 8.4 PB / 1 DWPD | 16.8 PB / 1 DWPD | 33.6 PB / 1 DWPD | 18.6 PB / 3 DWPD | 37.3 PB / 3 DWPD | 74.7 PB / 3 DWPD |
| Part Number | MTFDHAL3T8TDP-1AT1ZAB | MTFDHAL7T6TDP-1AT1ZAB | MTFDHAL15T3TDP-1AT1ZAB | MTFDHAL3T2TDR-1AT1ZAB | MTFDHAL6T4TDR-1AT1ZAB | MTFDHAL12T8TDR-1AT1ZAB |
| Warranty | 5-Years | 5-Years | 5-Years | 5-Years | 5-Years | 5-Years |
While Micron’s 9300 series puts out sequential performance of up to 3.5 GBps read/write, its no slouch in random workloads. These SSDs are rated to deliver up to 850,000/310,000 random 4K read/write IOPS and have average read/write latency ratings of 86/11us.
The 9300 MAX and PRO comes with a 5-year warranty, and endurance figures are variable based on the model and capacity. Designed for read-intensive tasks (one drive write per day), the 9300 PRO’s endurance ranges from 8.4 to 33.6 petabytes (PB) written. While these figures by themselves are quite impressive, the MAX, with its greater over-provisioning, withstands anywhere from 18.6PB of writes at the smallest capacity, and up to a staggering 74.7PB at the highest. The MAX is only rated for three drive writes per day, but its huge capacity helps it to scale endurance to ultra-high levels.
Furthermore, the drive comes with crypto erase support, power loss protection for data in-flight and data-at-rest, and enterprise data path protection (user & metadata). The Uncorrectable Bit Error Rate (UBER) is less than 1 sector per 10^17 bits read, and the Mean Time to Failure rating comes in at 2 million device hours.
Software and Management
Micron supports the 9300 series with its Storage Executive Software. It is compatible with both Windows and Linux. With it, you can monitor and manage the SSD. Micron’s 9300 series can also be updated from a single secure signed firmware file without the need to reset the system, helping prevent downtime.
A Closer Look
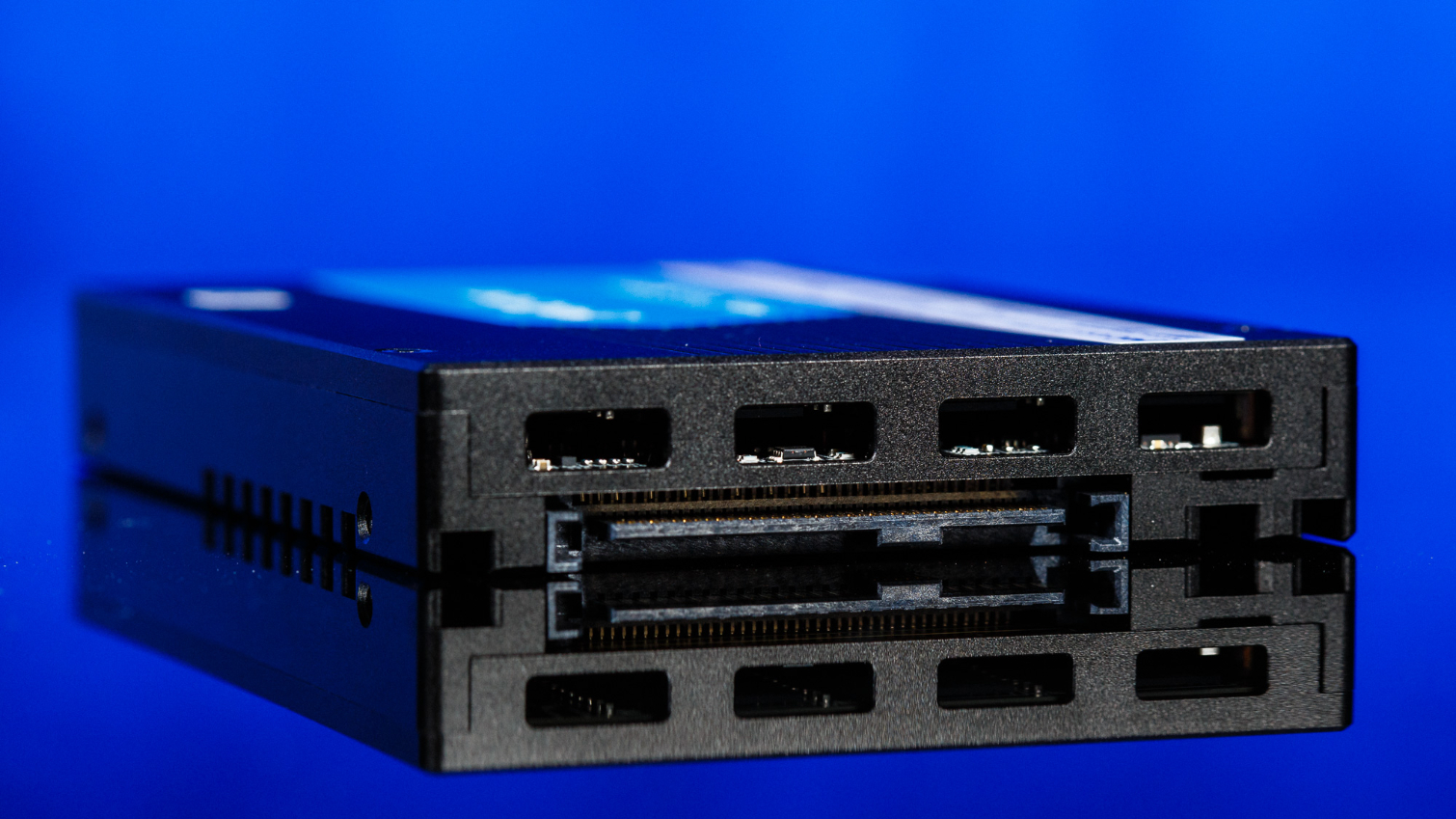



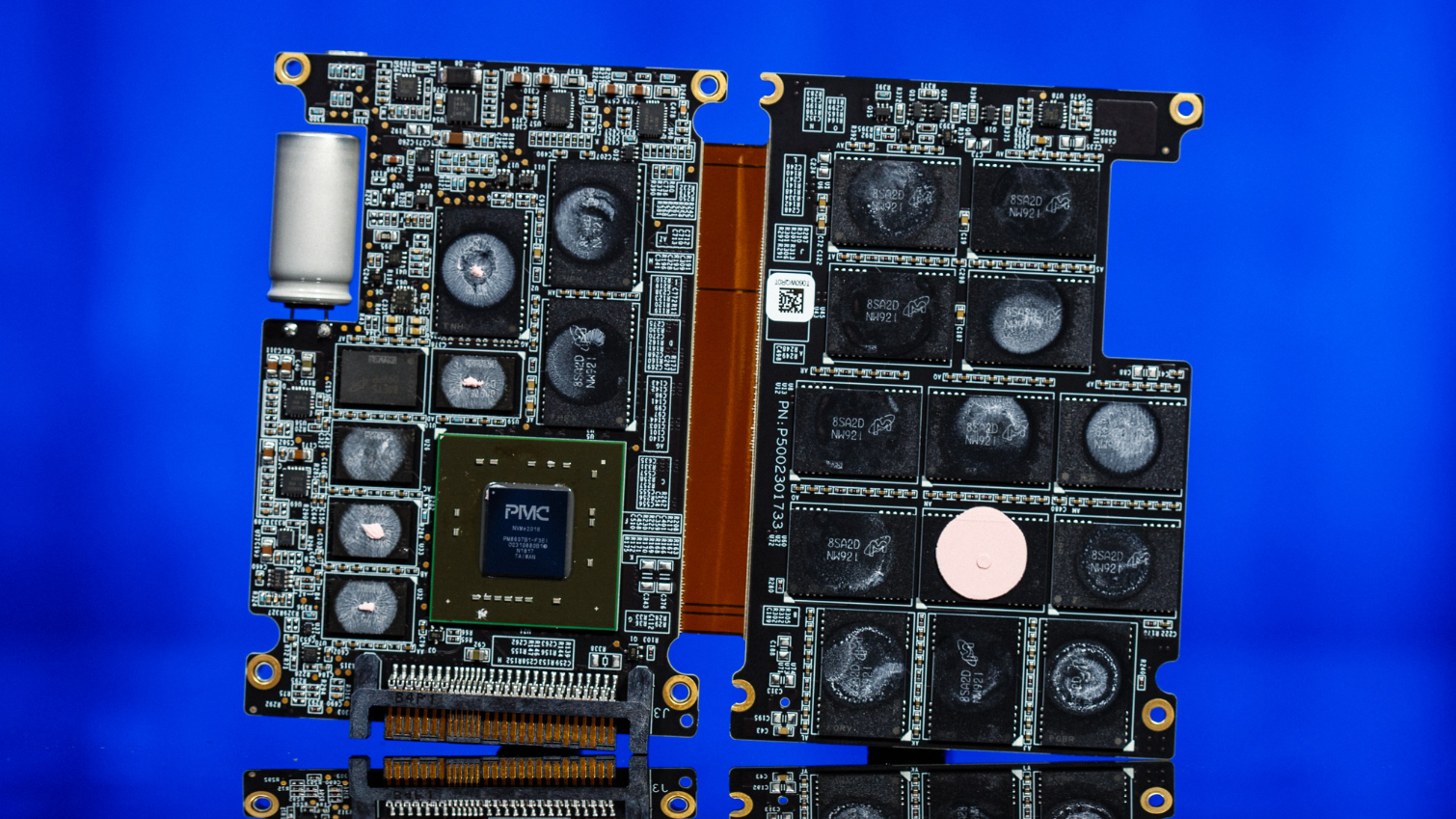
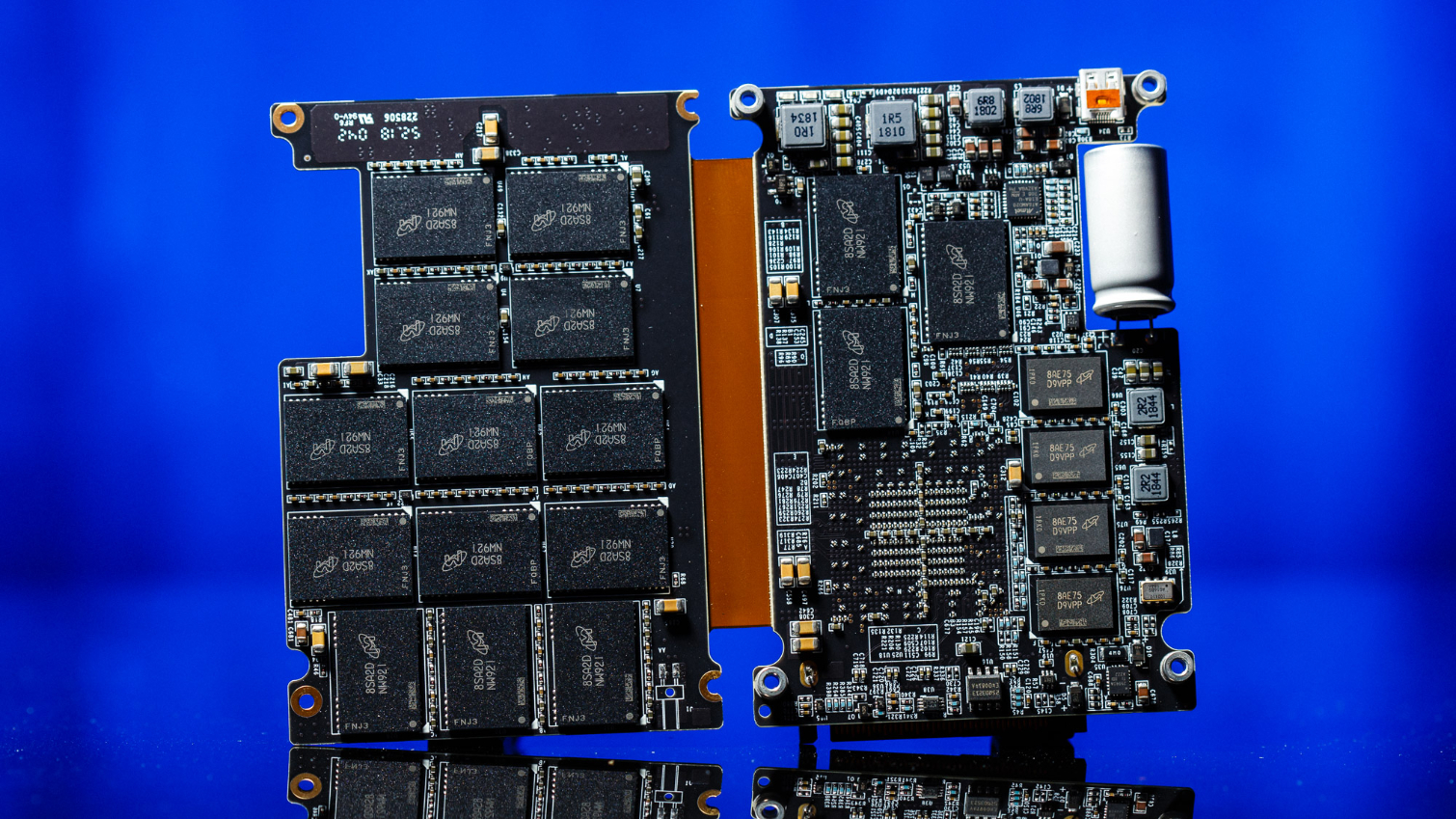
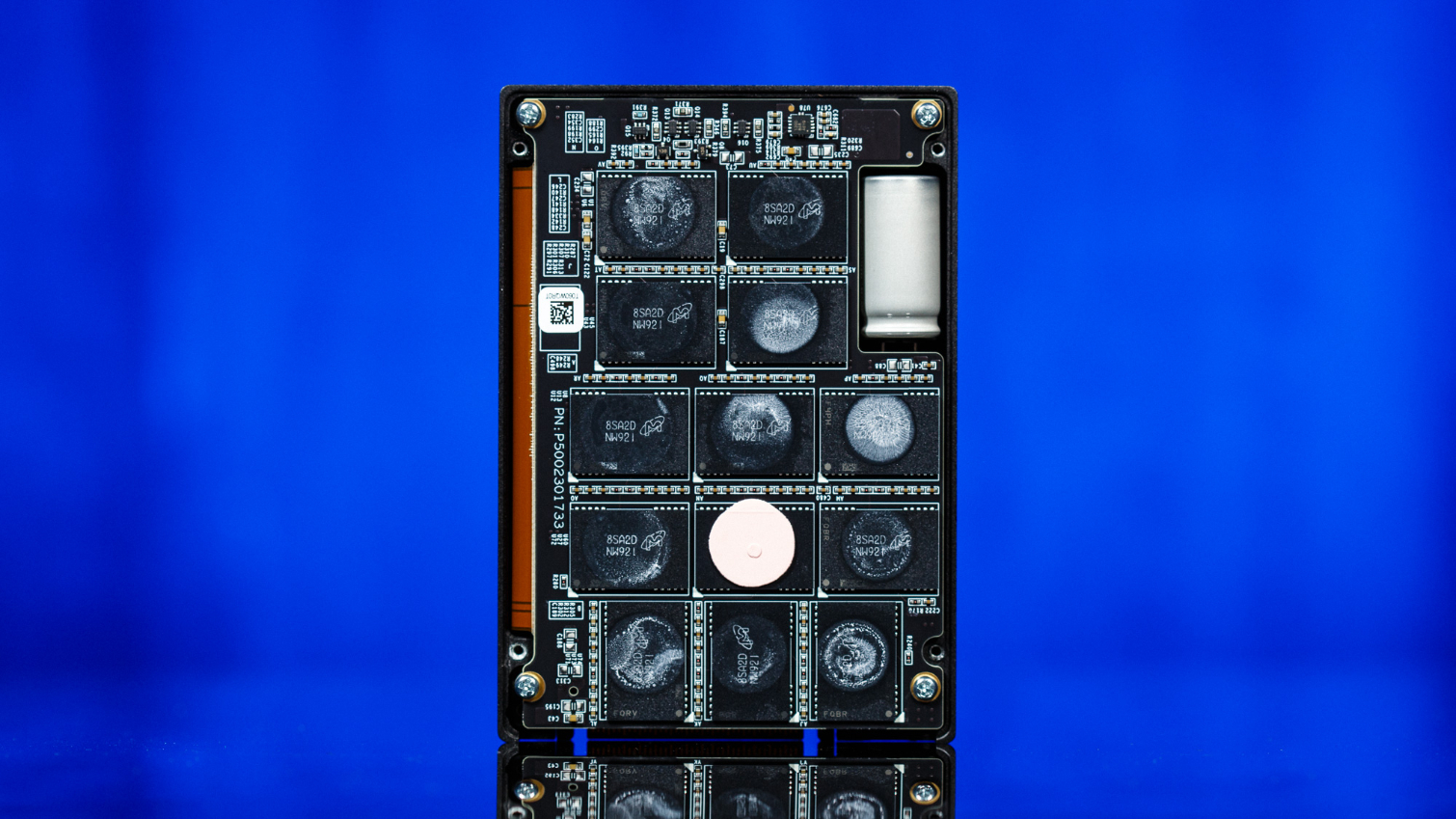


As mentioned earlier, the 9300 series SSDs come in a U.2 15mm form factor, unlike the 9200 series that has models in the HH-HL AIC form factor, too. Stuffing this compact enclosure with so much NAND and such a big controller can heat it up under load when consuming upwards of 21W at the highest capacity. That is why Micron opted to etch fins and cooling vents into the case to aid cooling.
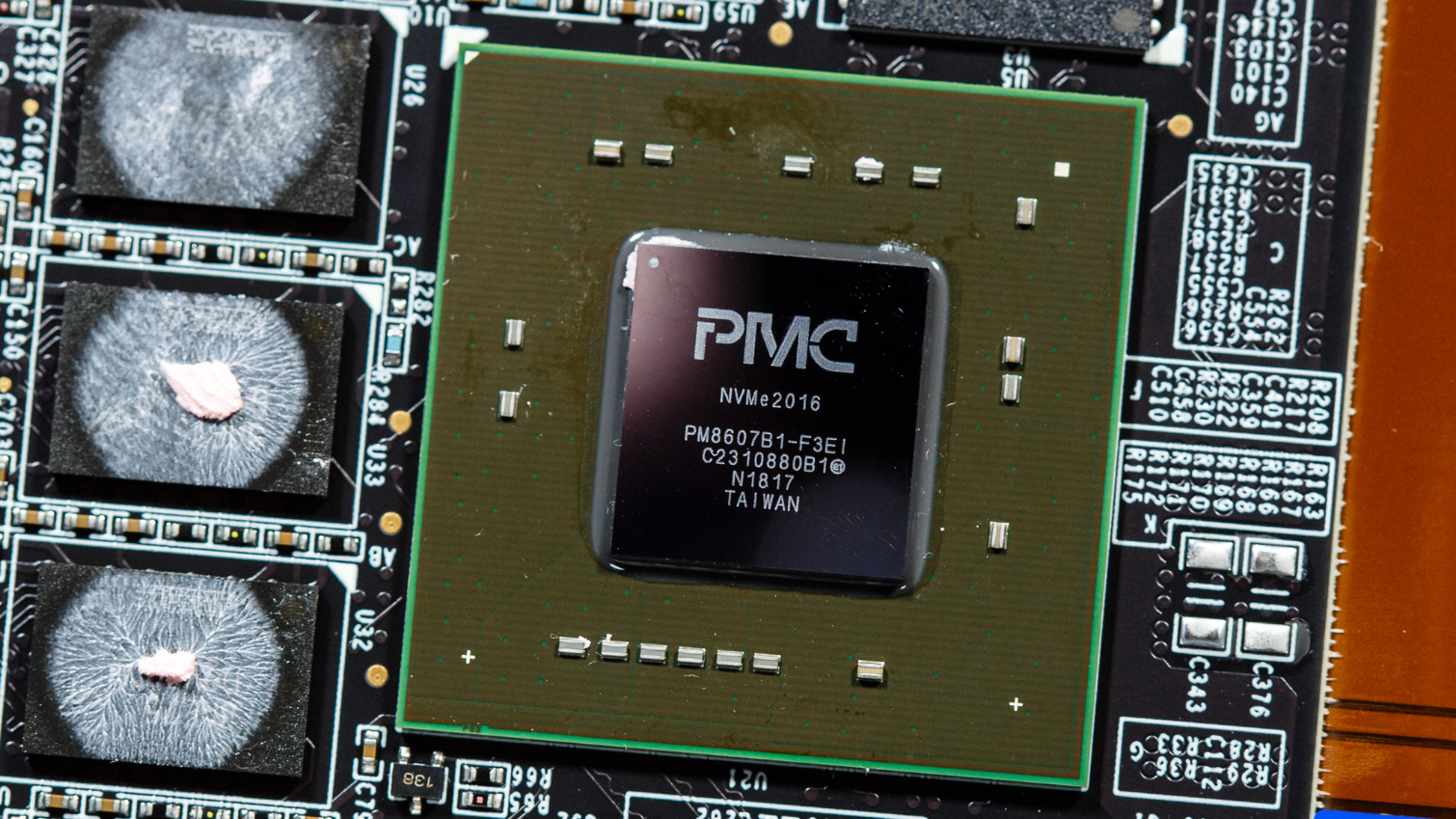
Once cracked open, we see that the PCB in all its glory. The 9300 series is powered by Microsemi's Flashtec 2nd generation NVMe controller, the PM8607 NVMe2016. It features 32 independent flash channels, each supporting up to 8 chip enables for high performance and capacity, but Micron may not be taking advantage of all of them. In Micron’s literature on the drive, it states that it only has 16 channels. Regardless of specifics, it is still quite impressive to open up our 7.68TB sample and see 32 of Micron’s 64L 3D TLC NAND packages jammed in there.
Additionally, the controller supports the nine 1GB DDR4 2666MHz CL19 DRAM chips configured in an ECC arrangement for FTL caching and is backed by a large supercapacitor to improve reliability.
MORE: Best SSDs
MORE: How We Test HDDs And SSDs
MORE: Best External Hard Drives and SSDs
Current page: Micron’s New Heavy Hitter
Next Page Micron 9300 Sequential Performance Results
Sean is a Contributing Editor at Tom’s Hardware US, covering storage hardware.