Four 2.5" Hard Drives From 500 GB To 1 TB, Benchmarked
Thanks to advances in manufacturing and 4 KB sectors, we finally have 2.5" hard drives with 500 GB per platter and a notebook-friendly 9.5 mm Z-height. Thanks to their high data density, even power-friendly 5400 RPM drives offer impressive transfer rates.
Three 5400 RPM Drives Serve Up Solid Results
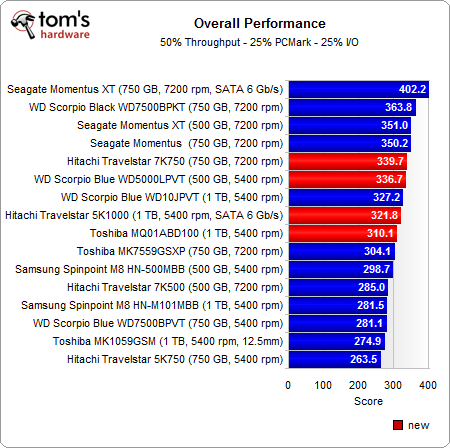
As expected, the performance-oriented Hitachi Travelstar 7K750 leads the pack of our four new test candidates. It's a fast laptop-oriented disk to be sure, achieving the highest average sequential read and write rates we've ever measured from a 2.5" hard drive. However, it can‘t establish a significant lead in PCMark 7 or our I/O-based metrics. In some tests, it actually trails competing models, even though the other three samples are 5400 RPM drives. Comparing the Travelstar 7K750 to all previously-tested disks, it emerges as a solid performer and winds up in the upper third of our charts. Not bad.
The fact that we come away thinking Hitachi's 7K750 is only a so-so performer is colored by solid showings from its "green" competition. Even though the Hitachi Travelstar 5K1000, Toshiba MQ01ABD100, and Western Digital Scorpio Blue WD5000LPVT aren't optimized for performance, they still nip at the 7200 RPM drive's heels. As an added bonus, all three 5400 RPM disks offer low power consumption. The Hitachi Travelstar 5K1000 and Western Digital Scorpio Blue WD5000LPVT even beat the 7200 RPM drive in our performance-per-watt index.
Overall, the Western Digital Scorpio Blue WD5000LPVT gets quite close to the Hitachi Travelstar 7K75, while the Hitachi Travelstar 5K1000 and Toshiba MQ01ABD100 fall behind. But this doesn’t mean they are slow; even the slowest disk in this test achieves almost 90 MB/s in our sequential read and write benchmarks.
As we wrap up, we want to again shine a spotlight on Advanced Format, which facilitates higher data density and helps finesse 1 TB of capacity into a 9.5 mm Z-height, necessary for broad notebook compatibility. Although higher data density helps as well, this has an undesirable side effect. Mainly, seek times continue going up. This is because it's becoming more and more difficult to position and stabilize microscopic read/write heads over the correct track. This might not be a big deal for slow-turning repositories for user data, but it could sabotage attempts to build high-performance disks in the future.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Three 5400 RPM Drives Serve Up Solid Results
Prev Page Power And Performance Per Watt-
this gives me some confidence in my WD scorpio blue, thill thinking about going with an ssd thoughReply
-
freggo "9.5 mm Z-height."Reply
Isn't that like saying 9.5 mm "vertical height".
There is no X-height or Y-height :-)
-
techcurious theconsolegamerWestern Digital and Seagate deceiving Hitachi and Samsung consumers since The Hitachi and Samsung drives are still manufactured in the same factories they were before.. just cause ownership changes doesn't mean performance or features and characteristics of the drives are going to change right away.. that will take time to happen, and who is to say if they will change for the better or worse..Reply -
freggo bennayedepends on your initial orientation of your axesReply
Z-axis is height in any system I am aware of.
-
Two hitachi drives have failed for me in the past year, i've got one Samsung drive that's been running for over two years(no issues) and a scorpio black that's much better. I don't know if it's just me but I don't really trust Hitachi HDD's anymoreReply
-
ovymoont Some of these drives are sold not only as low power but also as low noise options so I think a noise benchmark would have also been useful.Reply
I actually have a Western Digital Scorpio Blue WD10JVPT as the data storage drive in my desktop PC (I use a 64GB SSD as my boot drive) and the reason I went for it is exactly this, i.e. low noise, and I can say that it does deliver on that. It is clearly slower than my old 1TB 3.5" Samsung HDD at 7200RPM with 32MB of cache but I must say that it is noticeably quieter. And the noise difference comes in two flavors, on the one hand the actual noise generated by the drive motor which is clearly noticeable on a 3.5" 7200RPM drive but much less so on a 2.5" 5400RPM, and on the other hand in terms of the drive vibrations which are then passed onto the case to create a very disturbing humming noise even through the rubber vibration insulators I had installed on my old 3.5". -
f-14 techcuriousThe Hitachi and Samsung drives are still manufactured in the same factories they were before.. just cause ownership changes doesn't mean performance or features and characteristics of the drives are going to change right away.. that will take time to happen, and who is to say if they will change for the better or worse..Reply
you sir have no experience in the real world or in business i see. try being a business analyst. first thing to change is the staff like within 6 weeks and still goes on for 6 months to 2 years, then the thinking which is also why alot of staff who can't cope or disagree are gone. while doing all the contracts for everything are evaluated and everything that can be cut to help pay for the acquisition is gutted as much as is still profitable, that means whole segments can and typically are sold off if the buyer has a cheaper solution already implemented in such types of acquisition deals. supply contracts are bought out or cancelled if they don't meet profitability requirements ASAP.
so what you said isn't true because what happens in reality is not only does the staff change almost immediately if they are not superior in EVERY WAY (cost most importantly) parts and materials are changed very quickly if they are not superior in EVERY WAY (cost most importantly) any segment that can be cut to improve profitability is cut.
typically 30-66% of a bought out company gets cut as it is duplicate of what the buying company already has and can supply and or make already. i have seen as much as 90% get cut and as little as 10% cut.
when dealing with american companies, labor force seems to be the most change made due to costs. i have seen labor forces that were 300-500% more cost effective for the work they get done cut due to labor costs as it meant less billable hours and profitability in squeezing a client for. those are some of the saddest things i have seen happen after an evaluation. i have also seen the same thing happen to products that were superior gutted down just so some one else can say they made the best on the market with out ever having to improve their product, change their ways or spend more money countless times.
the aim of buying out another company in the same business in a bad economy is to eliminate competition and or buy them for their IP/patents, not to spend more money in a bad economy, i don't think that can be stressed enough companies are just fighting to stay in business in a bad economy. -
ovymoont I am afraid I do not agree with your view. In the current economy many mergers and acquisitions are made in order to consolidate a business and to increase the market share. If say you have 20% of the market and the company you are buying has 10% of the market you don't close down it's manufacturing capacities just to get rid of competition. If you do that you run the risk of not being able to deliver the capacity that you are supposed to deliver to your clients because you can't possibly increase the production in your own facilities to make up for the 10% you close down. Also, most companies these days are listed on the stock market and the fundamental aspect of such a company is that year on year it has to deliver growth to its shareholders. In a bad economy it is difficult to achieve organic growth and many businesses resort to mergers and acquisitions to deliver that growth although quite often that is more on paper that in actual fact. Also, in the case of companies in the HDD business the bulk of the production facilities are already base in low income economies such as China, Thailand, etc. and as such it is simply not possible to reduce the production costs even further through a reduction in the cost of labor.Reply
The one situation when you would buy off a competitor just to close it down is when there is an excess production capacity on the market which is driving down prices. In that situation you would try to reduce the level of supply so that you can get an increase in prices. However, in the HDD business that's not the case as production levels have only just recovered to the levels they were at before the floods in Thailand which took out a number of large HDD facilities and created major shortages on the market. This means there is hardly an excess in production capacity so it does not make business sense to close down facilities that have just been restarted. Plus, these acquisitions have been made for a cost which is not negligible and it is unlikely that cost can be offset by an increase in prices generated by a shortage in supply.
Anyway, there's a lot more I can explain in terms of business policies and so on but I just don't have the time so in short I agree with techcurious in saying that right now the facilities that have been taken over are still producing drives and will still do for a while. That is not to say that will still be the case in few years time but that is definitely the case at the moment.