Micron P400m SSD Review: High Endurance MLC Is Here To Stay
Endurance. Reliability. Data protection. They're all important factors when it comes time to evaluate high-end storage technology. Micron's P400m, the company's latest enterprise-class SSD, is positioned to not only address those needs, but exceed them.
Results: Enterprise Workload Performance
Our next set of tests simulate different enterprise-oriented workloads, including database, file server, Web server, and workstation configurations.
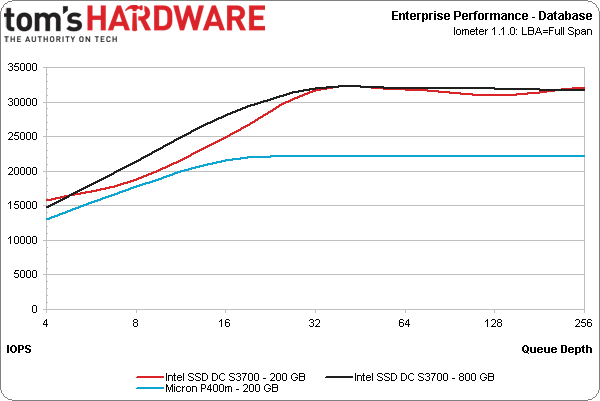
The database workload (also categorized as transaction processing) involves purely random I/O. Its profile consists of 67% reads and 33% writes using 8 KB transfers.
Considering our 4 KB results on the previous page, it should come as no surprise that the SSD DC S3700 outpaces Micron's P400m at all queue depths.
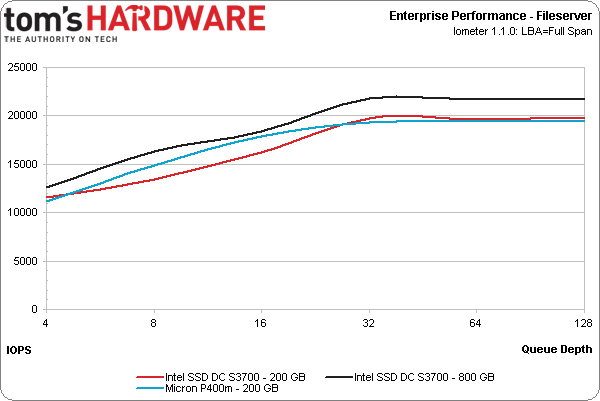
The file server workload, which consists of 80% random reads of varying transfer sizes, does offer more of a surprise. The P400m not only holds its own at higher queue depths, but it actually performs better than Intel's drive at lower queue depths.
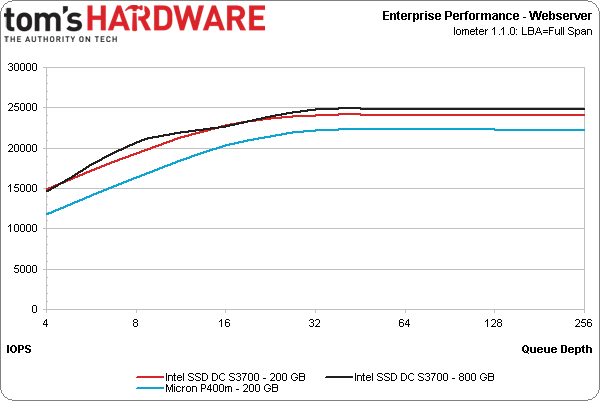
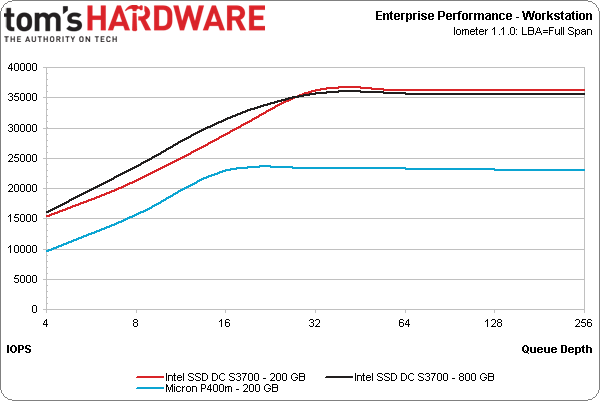
The Web server (100% read, varying transfer size) and workstation (80% reads, 80% random) workloads put Intel's SSD DC S3700 back in the lead. While the P400m comes within 2,000 IOPS on the Web server workload, it trails by a more notable margin when we subject it to the workstation test.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Results: Enterprise Workload Performance
Prev Page Results: 4 KB Random Performance And Latency Next Page Results: Sequential Performance-
Nintendo Maniac 64 に?Reply
Seriously though, I wonder why Tom's doesn't run one of their basic "real-world" tests used on consumer SSDs (such as Tom's 7zip test) on one of these professional SSDs just so that we can get an idea how they compare to the consumer-level stuff.
In particular, Tom's always says that comparing one SSD to another is nearly moot point when you consider the magnitude of improvement an SSD has over a traditional HDD; it would be nice to know if these pro-level SSDs are of a similar magnitude of improvement over consumer SSDs or whether the difference is actually less. -
blazorthon Nintendo Maniac 64に?Seriously though, I wonder why Tom's doesn't run one of their basic "real-world" tests used on consumer SSDs (such as Tom's 7zip test) on one of these professional SSDs just so that we can get an idea how they compare to the consumer-level stuff.In particular, Tom's always says that comparing one SSD to another is nearly moot point when you consider the magnitude of improvement an SSD has over a traditional HDD; it would be nice to know if these pro-level SSDs are of a similar magnitude of improvement over consumer SSDs or whether the difference is actually less.Reply
The difference is much, much less in terms of performance difference. Tom's has told us this time and time again. -
mayankleoboy1 Nintendo Maniac 64に?Seriously though, I wonder why Tom's doesn't run one of their basic "real-world" tests used on consumer SSDs (such as Tom's 7zip test) on one of these professional SSDs just so that we can get an idea how they compare to the consumer-level stuff.In particular, Tom's always says that comparing one SSD to another is nearly moot point when you consider the magnitude of improvement an SSD has over a traditional HDD; it would be nice to know if these pro-level SSDs are of a similar magnitude of improvement over consumer SSDs or whether the difference is actually less.Reply
In desktop loads, very very less difference.
In server loads, huge difference. Plus, these server SSD's wil maintain high speeds even after large amounts of data is continuously being written. -
mayankleoboy1 theoretical question : how much life would 100% provisioning give ? So you ship a 512GB MLC drive, but the usable is only 256GB. The rest 256GB is for getting better wrtite endurance.Reply
How would this compare to a true SLC SSD ? -
blazorthon mayankleoboy1theoretical question : how much life would 100% provisioning give ? So you ship a 512GB MLC drive, but the usable is only 256GB. The rest 256GB is for getting better wrtite endurance. How would this compare to a true SLC SSD ?Reply
It'd probably still be inferior overall and not even be cheaper at that point. Over-provisioning is only good for mitigating MLC's disadvantages over SLC AFAIK, not replacing SLC. -
blazorthon mayankleoboy1In desktop loads, very very less difference.In server loads, huge difference. Plus, these server SSD's wil maintain high speeds even after large amounts of data is continuously being written.Reply
Even in server workloads, there are many desktop drives where the performance difference is still not great. For example, Vector is right up there at the tops of the charts with Samsung 840 Pro in performance and many cheaper alternatives are often not far behind in performance. Endurance is another matter, but that wasn't the question. If you want a seriously significant performance difference like with HDDs versus cheap consumer SSDs, you have to consider SSD RAID and/or extreme PCIe storage.
Also, many consumer drives have no trouble keeping performance over time with lots of data written. That's also not an enterprise-only feature. -
drewriley mayankleoboy1theoretical question : how much life would 100% provisioning give ? So you ship a 512GB MLC drive, but the usable is only 256GB. The rest 256GB is for getting better wrtite endurance. How would this compare to a true SLC SSD ?Reply
Some back of the napkin calculations - If you have a consumer 512GB MLC SSD with no over-provisioning, and the MLC was high grade consumer, you could expect 5K P/E cycles. In order to mimic the P400m, which is 35K P/E cycles, the usable space would be ~75GB. By dong that, you would be paying roughly $7/GB for usable storage(assuming you paid $512 for your consumer drive). For SLC, you are looking at 17GB of usable space and $30/GB.
No matter how you look at it, consumer grade MLC will never get close to eMLC and SLC in terms of write endurance, unless the price goes down by orders of magnitude compared to eMLC and SLC. -
drewriley blazorthonEven in server workloads, there are many desktop drives where the performance difference is still not great. For example, Vector is right up there at the tops of the charts with Samsung 840 Pro in performance and many cheaper alternatives are often not far behind in performance. Endurance is another matter, but that wasn't the question. If you want a seriously significant performance difference like with HDDs versus cheap consumer SSDs, you have to consider SSD RAID and/or extreme PCIe storage.Also, many consumer drives have no trouble keeping performance over time with lots of data written. That's also not an enterprise-only feature.Reply
You are correct. Many drives, such as the 840 PRO, would perform great on the enterprise performance tests. There are also a lot of consumer drives that would have problems over time if they aren't allowed to TRIM every so often. We limit the scope of our testing because the main use cases for these drives are enterprise. Will some companies use them in workstations, absolutely. The same can be said for high-end RAID cards too. Nearly every consumer drive would perform very poorly when you take into account write endurance and other enterprise features. -
themdg This technology is moving so fast...hard to keep up. I feel like these articles could use that line from Tommy Boy and get the same point across (to me, at least).Reply
"These hard drives are really cool...you're not even gonna believe it..."