Prescott Reworked: The P4 600 Series and Extreme Edition 3.73 GHz
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
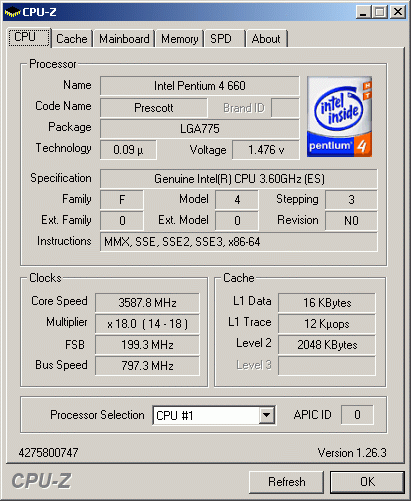
Pentium 4 Processor 660 And EE 3.73 GHz
All the P4 processors look alike.
The new Pentium 4 Prescott core is fairly well-known. We will give a quick overview on the new features here; you can read all the basic information in the following articles:
The new Prescott's power management consists of three components that are all based on the same transistors and mechanisms. A primary goal of the design is modulating core voltage and clock speed on the fly to reduce power consumption and thermal loss.
- Enhanced Halt State C1E
Halt State is a feature that is already supported by most processors. In simple terms, the operating system is able to send the HALT command in order to force the CPU to make a full stop. This is usually done only when there is not much to do, but you might be surprised how often this is the case with fast computers. Enhanced Halt State not only allows the OS to stop the processor clock, but applies the same mechanisms that run the two other features. - Thermal Monitoring 2
TM2 is overheat protection, controlled by the processor's PROCHOT signal (processor hot). This signal is activated if the CPU's thermal diode detects critical temperature levels. TM2 will dynamically reduce core voltage and clock speed in order to cool down the CPU. - Enhanced SpeedStep
SpeedStep does exactly the same as TM2, with the difference that it is initiated by the operating system. Whenever the system load is low, Windows XP SP2 will cause the CPU to lower the clock speed in 200 MHz increments by using ACPI mechanisms. Again, this is performed dynamically, which means that executing a demanding application will cause the system to speed up again.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Pentium 4 Processor 660 And EE 3.73 GHz
Prev Page One Upon A Time There Was Prescott Next Page 64 Bits: Windows XP X64 Edition
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.