High-End Chipset Battle
Intel X48
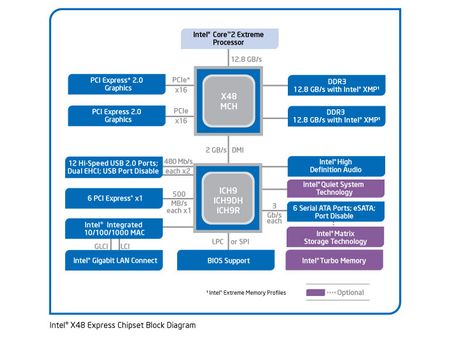
The X48 is a classic chipset that consists of two building blocks: the northbridge 82X48 MCH (Memory Controller Hub) and the southbridge ICH9 (I/O Controller Hub). Intel’s MCH includes the Front Side Bus interface to the processor, the dual channel DDR3 memory controller and two x16 PCI Express 2.0 interfaces. The memory controller supports Intel’s XMP technology, which stands for Extreme Memory Profiles. This is very similar to Nvidia’s SLI-ready memory, as it allows the motherboard to configure the memory according to its maximum capabilities. This means that memory clock speed and timings will automatically be set to ideal performance values. Other auto-configuration mechanisms rely on memory’s Serial Presence Detect (SPD) ROM data, setting workable timings that won’t deliver maximum performance. Intel’s and Nvidia’s approaches are similar, yet you have to get either XMP or SLI-ready memory if you want to use this feature. This chipset not only supports DDR3-1066 and DDR3-1333, but for the first time DDR3-1600 is supported as well.
The ICH9 southbridge is available in three different flavors: ICH9, ICH9DO (Digital Office) and ICH9R (RAID). The last of these is used for enthusiast-class motherboards, as it offers six AHCI SATA/300 ports with Native Command Queuing (NCQ) support, together with flexible RAID configuration options (RAID 0, 1, 0+1, 5). A High Definition audio sound system is mandatory today, and Intel also included a Gigabit Ethernet port (10/100/1000 Mbit/s). Although Intel’s block diagram doesn’t mention 32-bit parallel PCI anymore, it is still part of the ICH9 southbridge. However, Intel wants the industry to focus on PCI Express: the ICH9 offers six lanes, which can be turned into one x4 PCIe slot and two x1 slots, or into a larger number of x1 PCI Express slots. Finally, the ICH9 comes with 12 USB 2.0 ports; SATA and USB ports can be disabled for security.
Technically, the X48 chipset can support all Socket 775 processors, as the socket has only undergone small modifications. However, BIOS support from manufacturers will be limited for Pentium 4 or Pentium D class processors. You can be sure that all X48 motherboards will support the entire Core 2 processor lineup, though.
If you don’t want to go for an expensive X48 motherboard, you can certainly select a P35 or one of the upcoming P45 motherboards. These offer almost the same feature set, with the exception of dual x16 PCI Express dual graphics. Native FSB1600 support requires P45, but most upper-mainstream P35 motherboards will run reliably when overclocked from FSB1333 to FSB1600, if you planned on overclocking your system anyway.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.