AMD Ryzen 5 2400G Review: Zen, Meet Vega
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Rendering
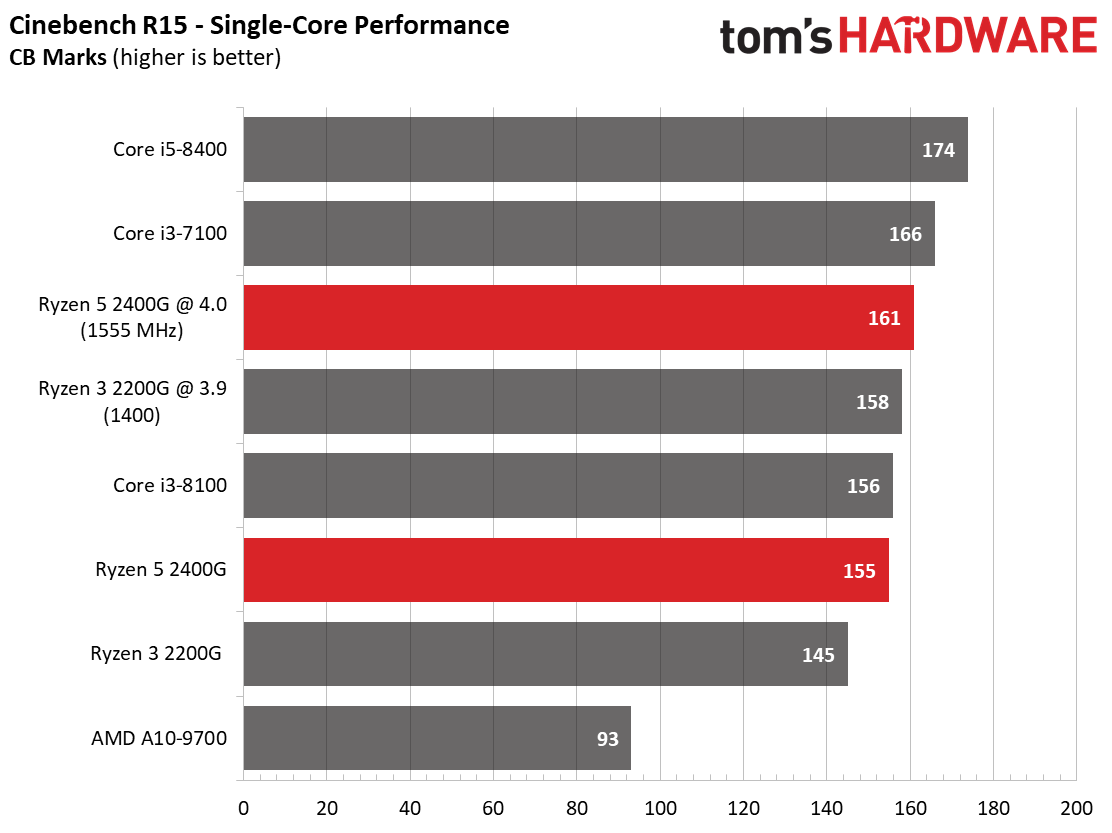
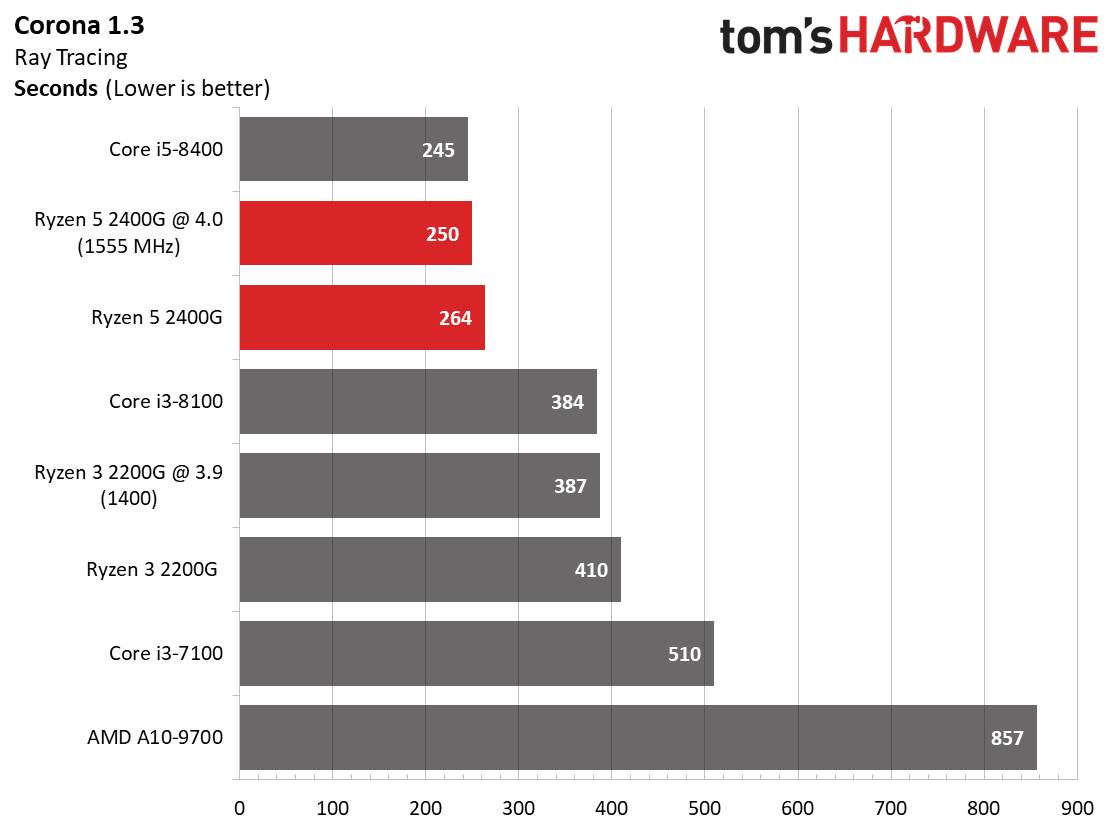
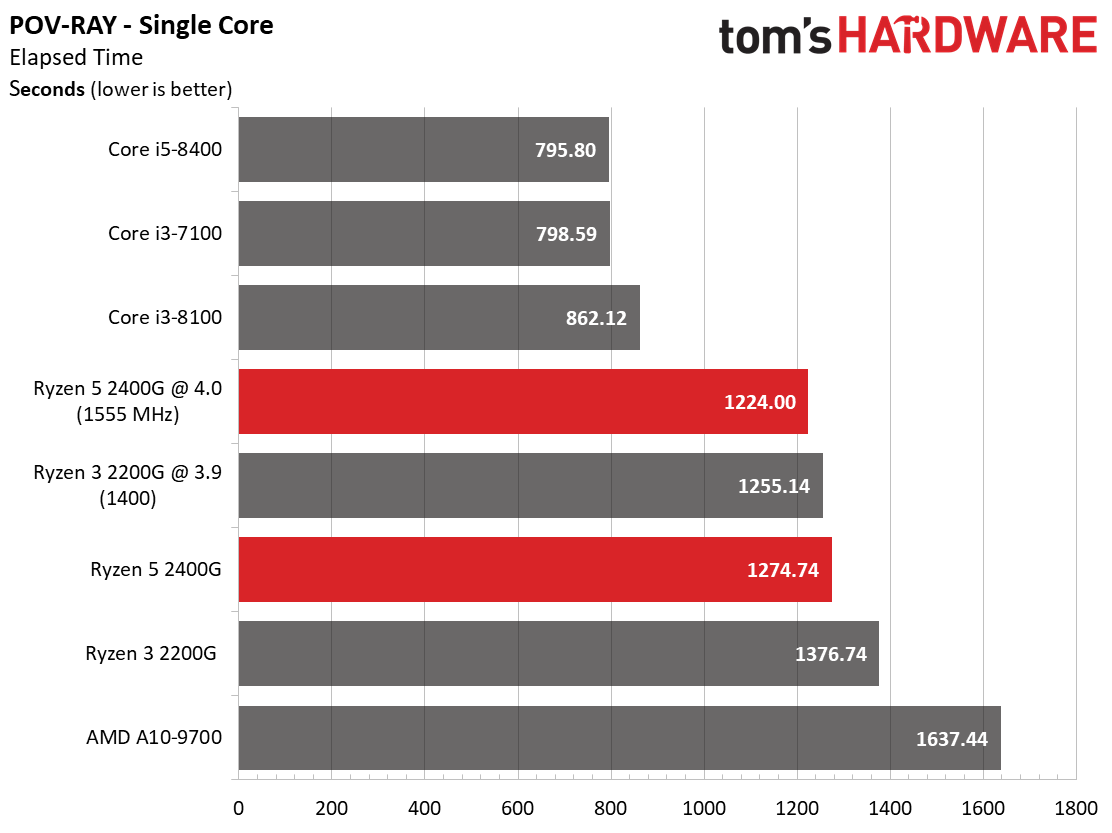
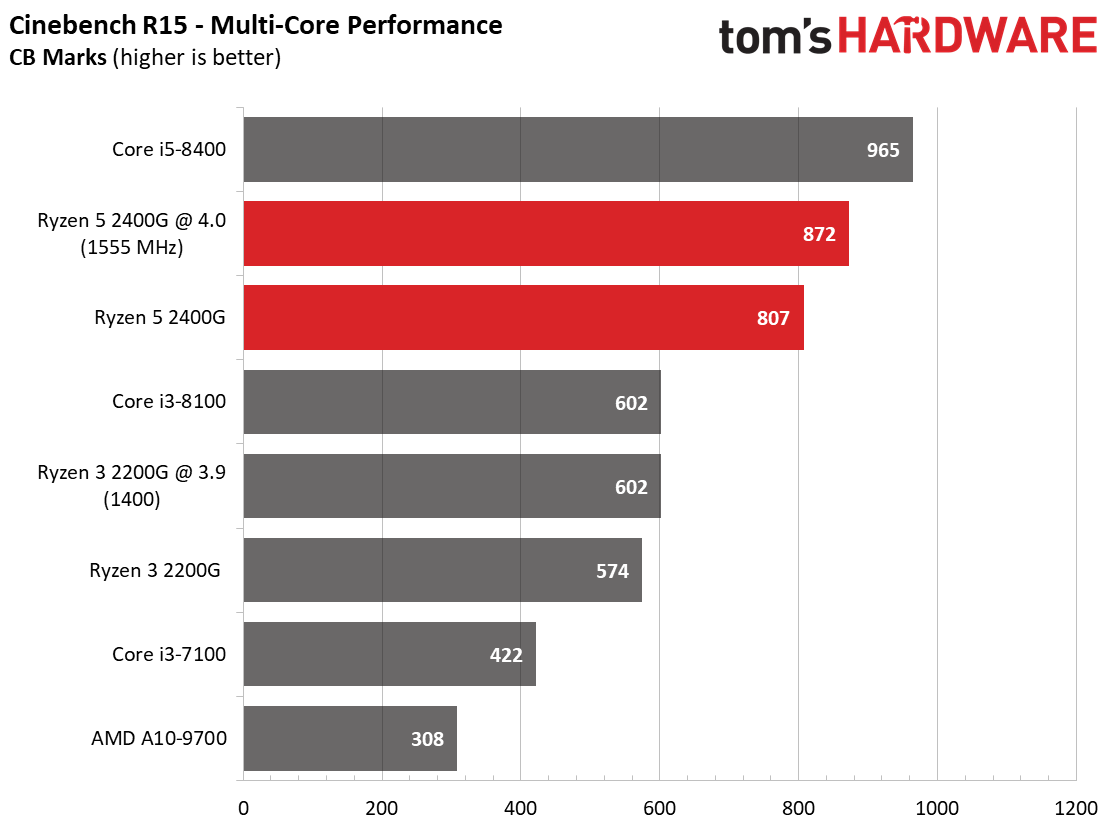
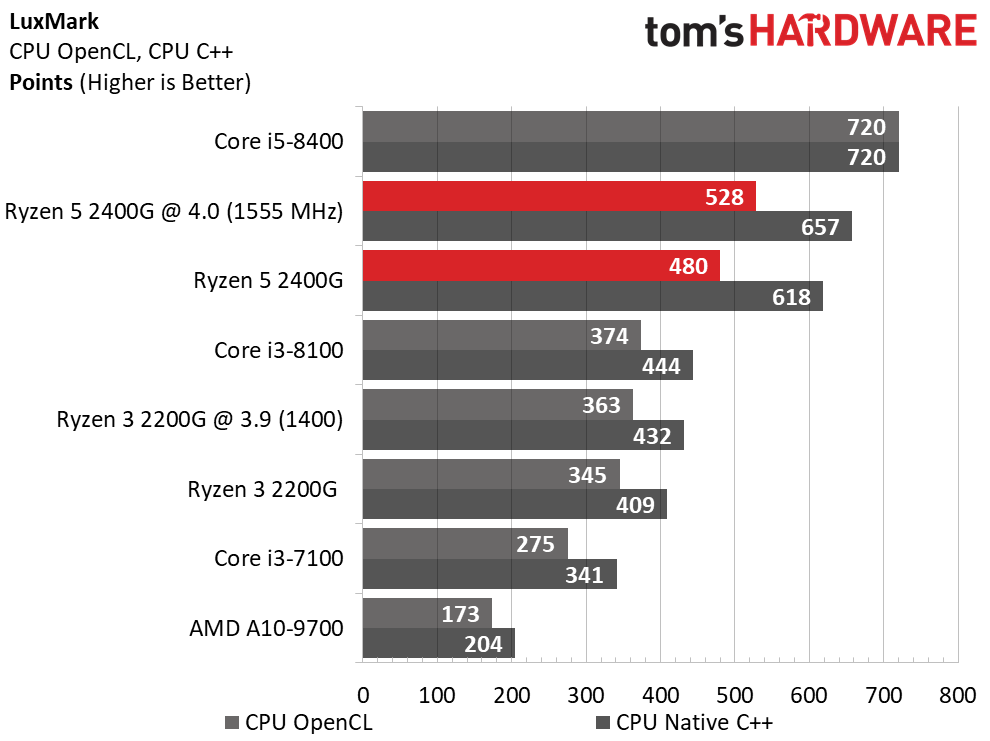
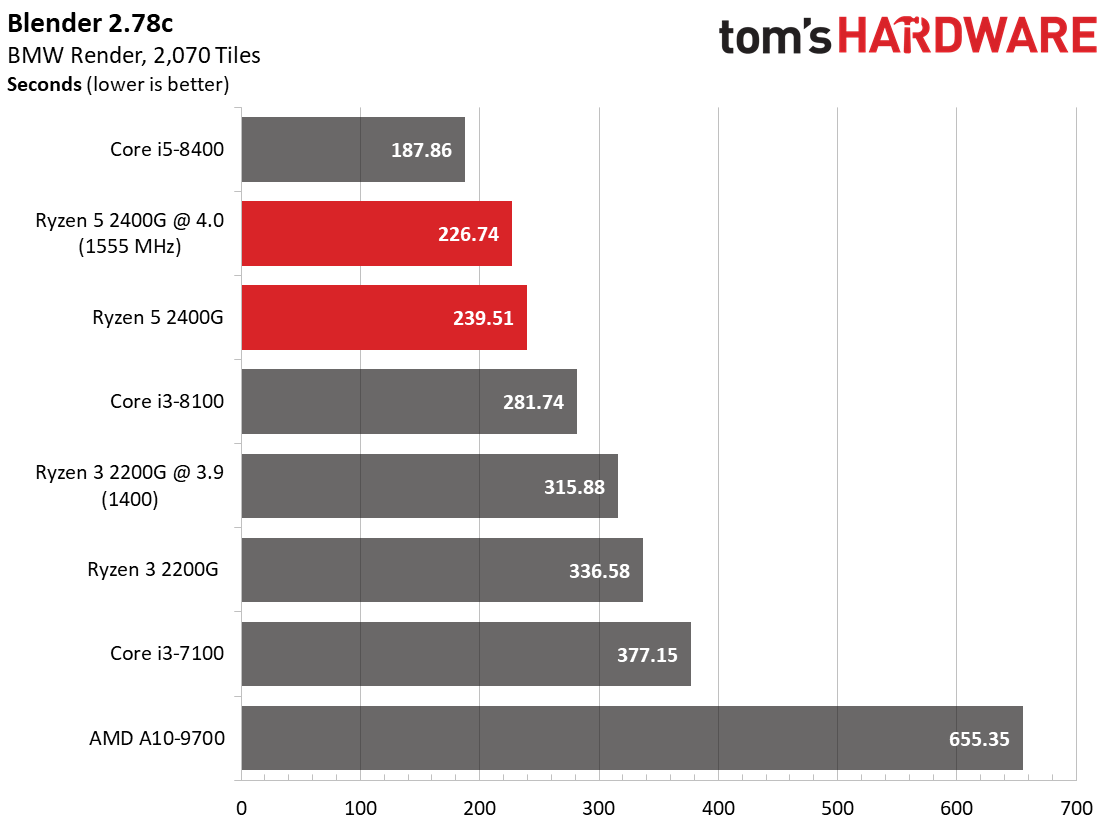
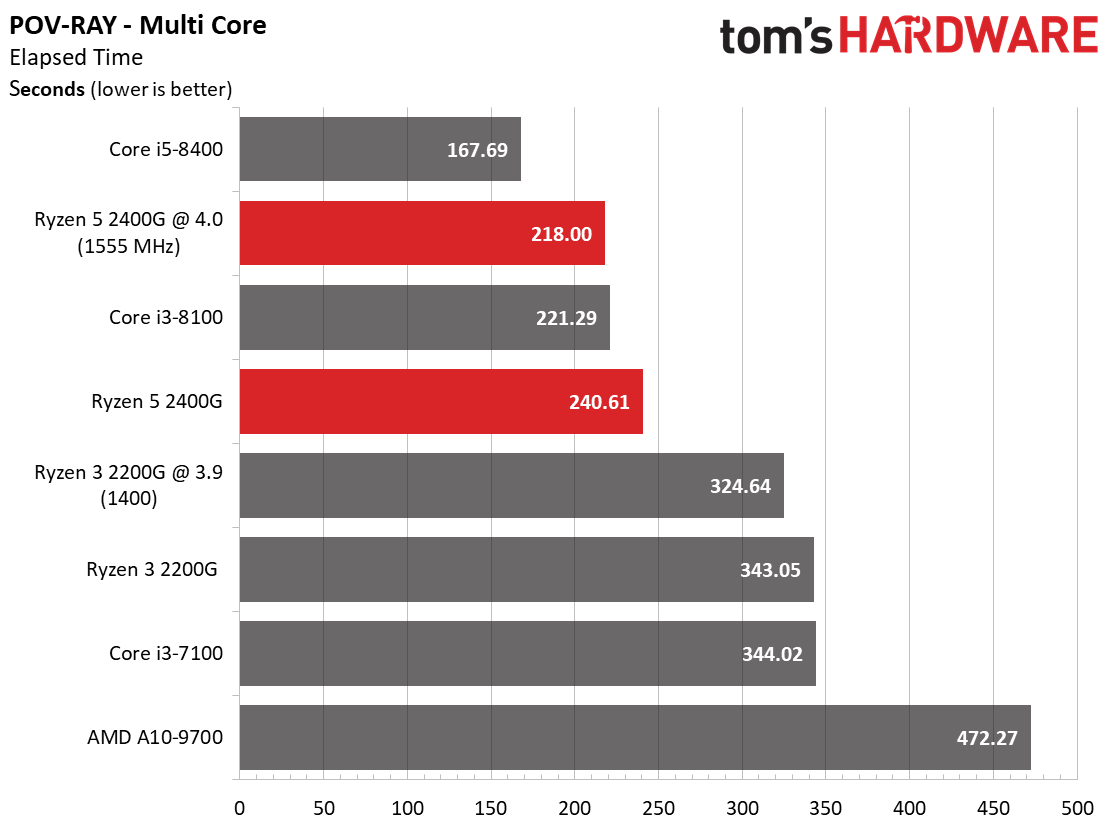
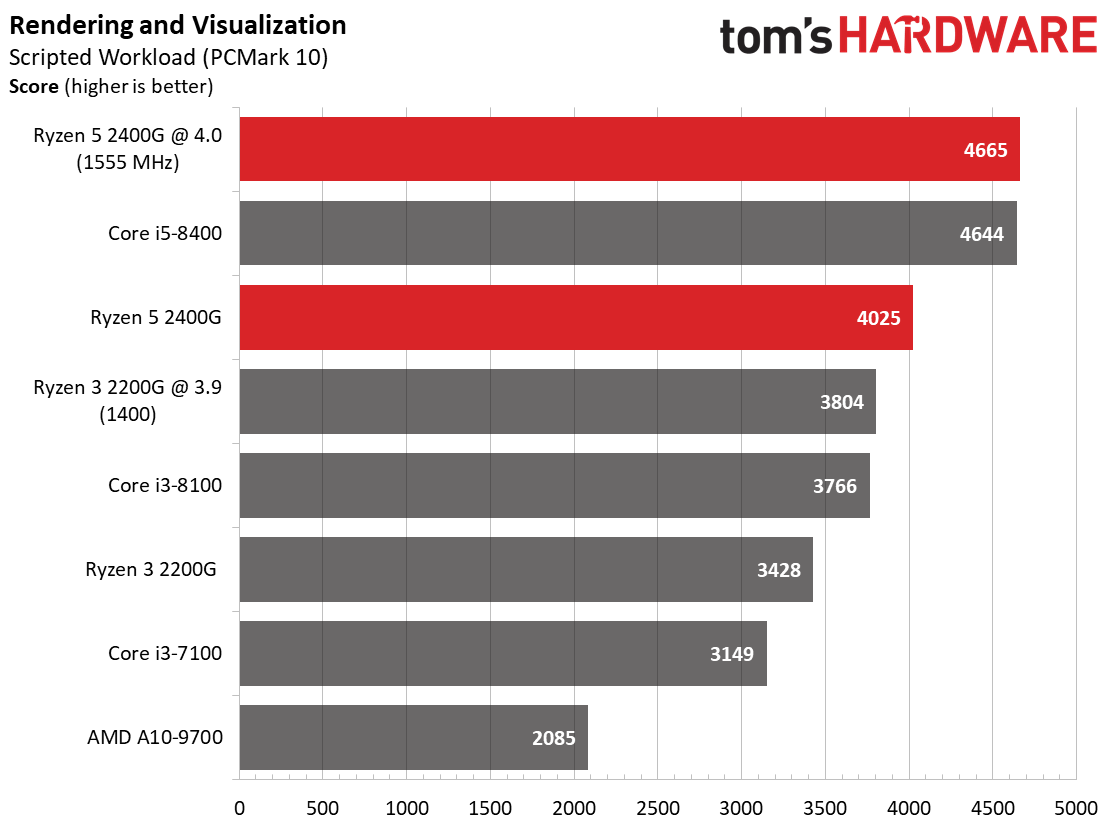
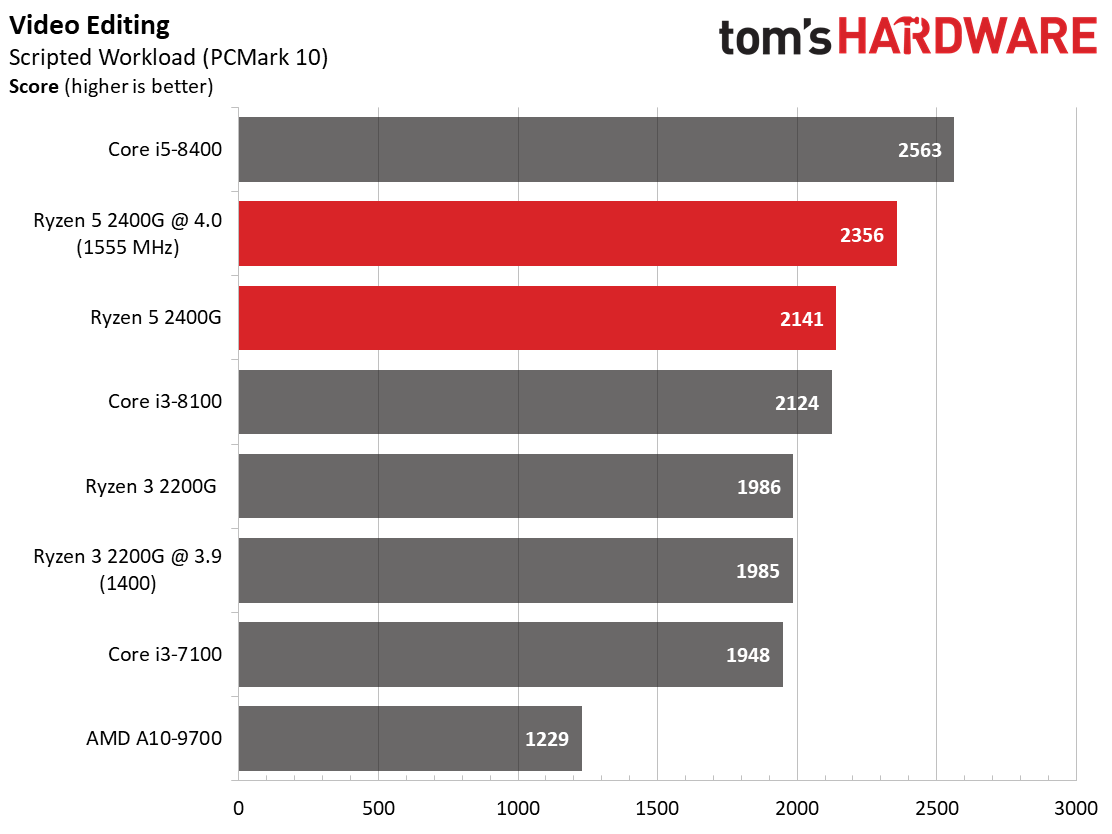
We expect Ryzen 5 2400G's eight threads to compete readily with the more expensive Core i5-8400's six physical cores in well-parallelized tasks. Although AMD never leads at stock settings, it at least holds its own after some casual overclocking.
The Core i5-8400 wins in every benchmark except one. However, the Ryzen 5 2400G is solid in tasks that fully utilize its SMT-enabled cores, such as Cinebench, Corona, and LuxMark.
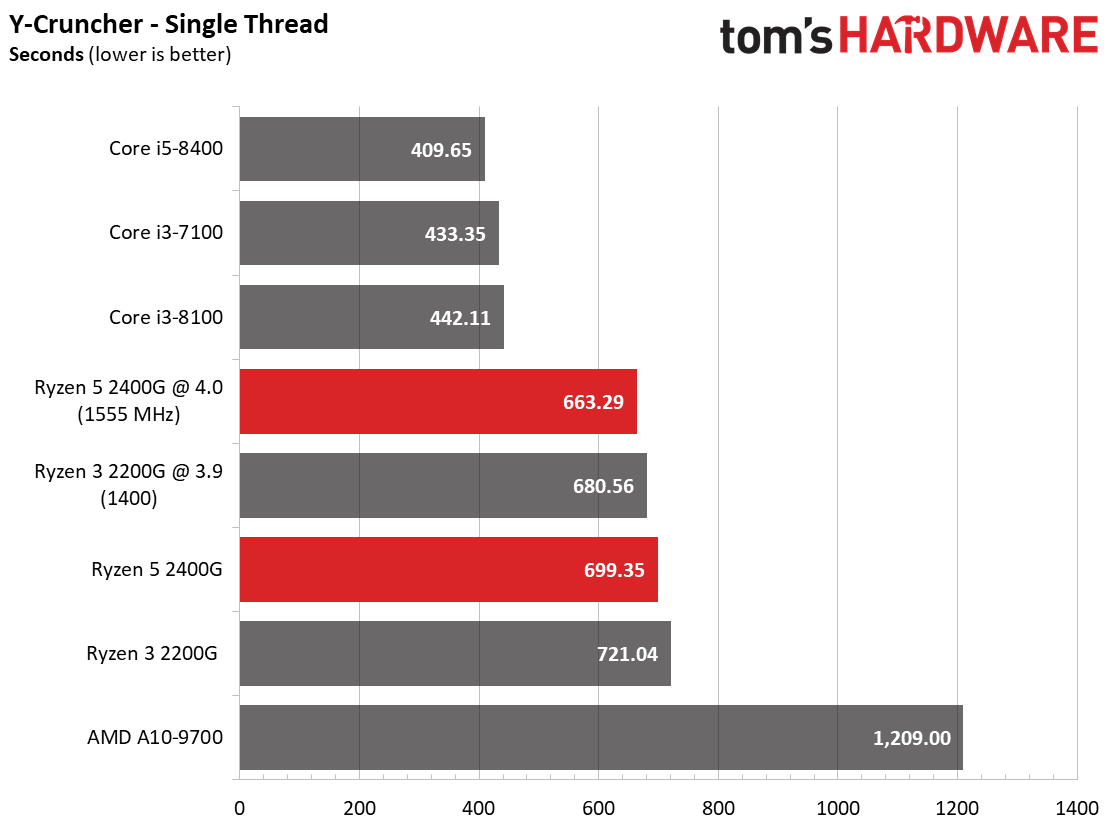
As expected, the single-threaded benchmarks go Intel's way. Tuning does help Ryzen close the gap, though.
Encoding & Compression
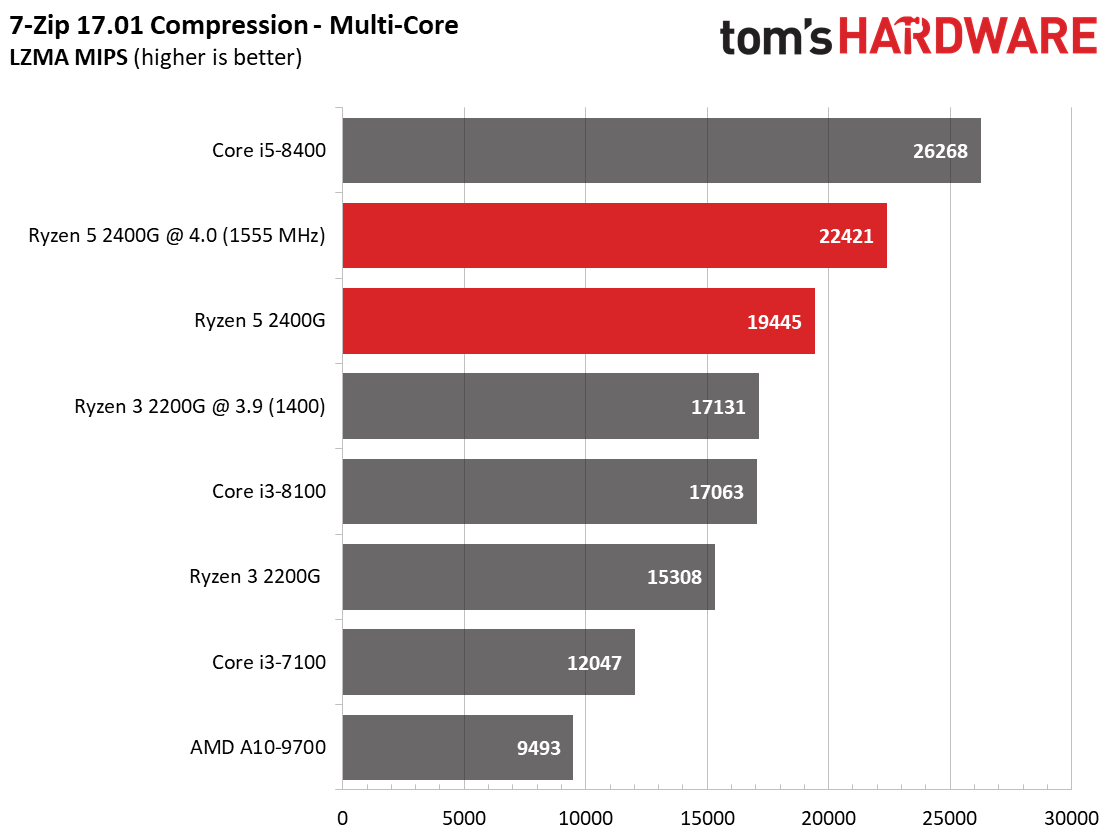
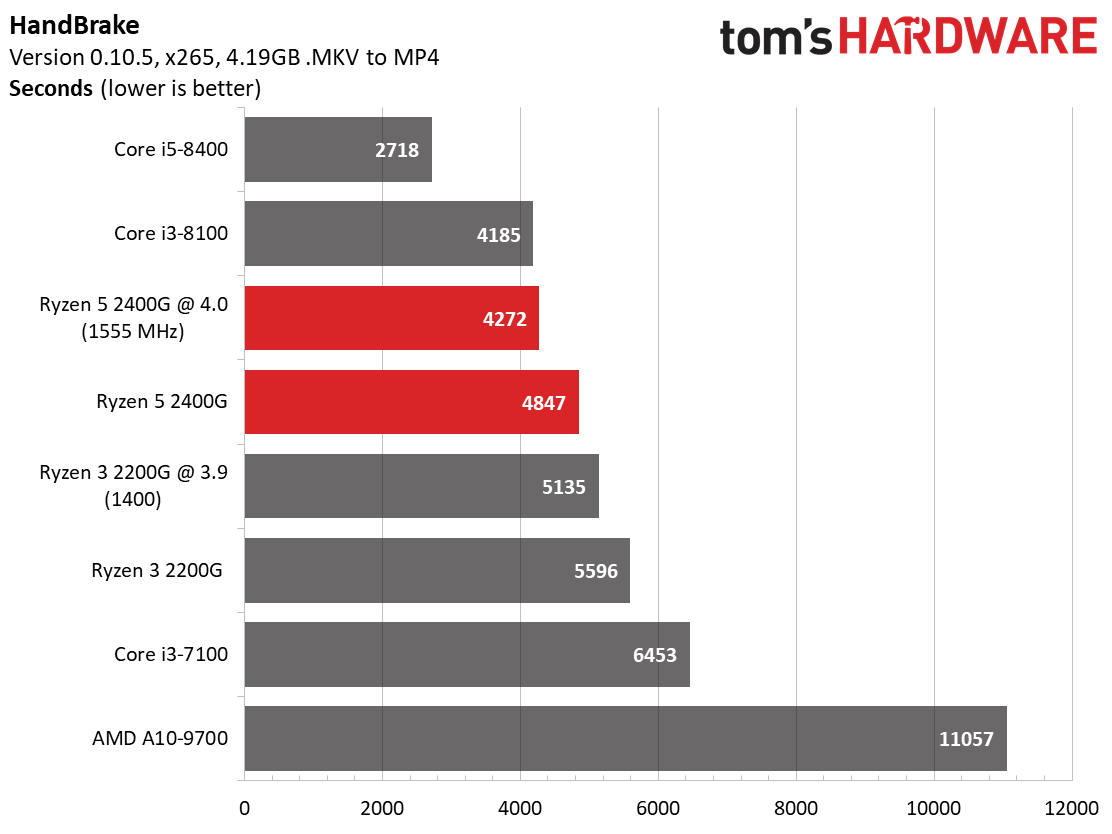
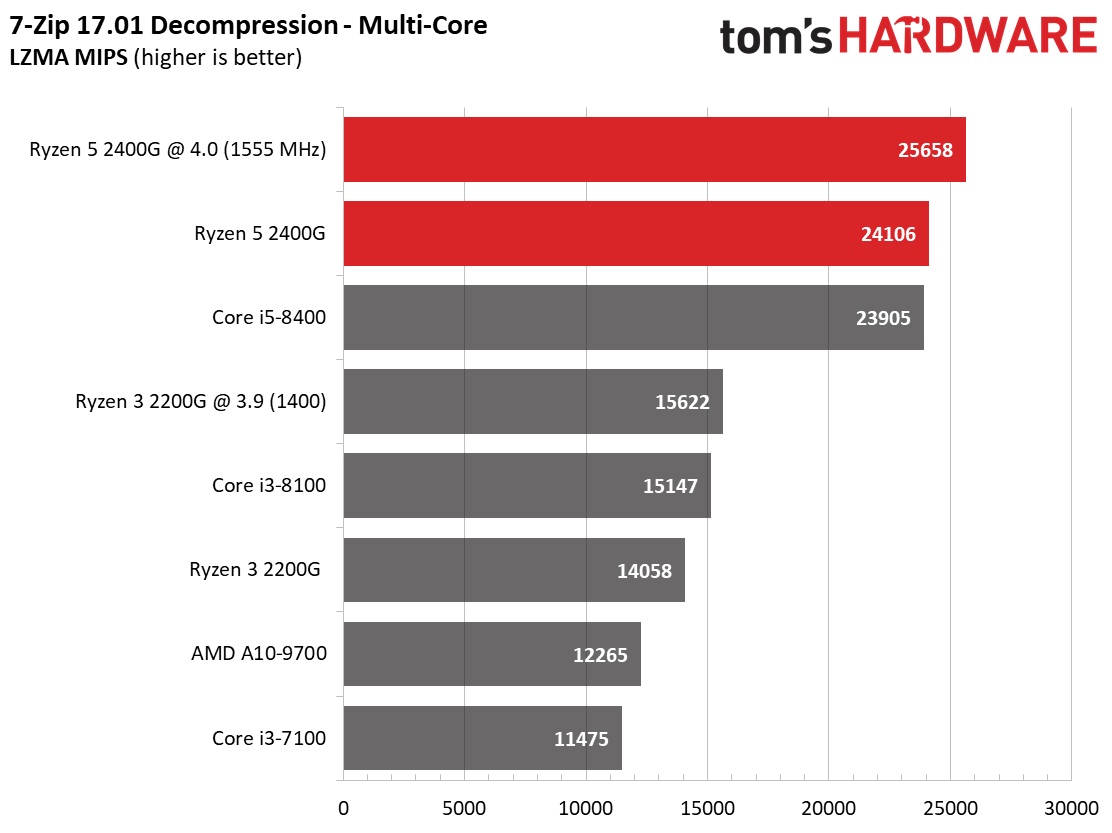
The Ryzen architecture has always excelled in decompression workloads. This continues with Raven Ridge. AMD's Ryzen 5 2400G shows well in the multi-core compression workload as well. Meanwhile, the Core i3-7100 and AMD A10-9700 demonstrate just how under-powered they are in demanding tests.
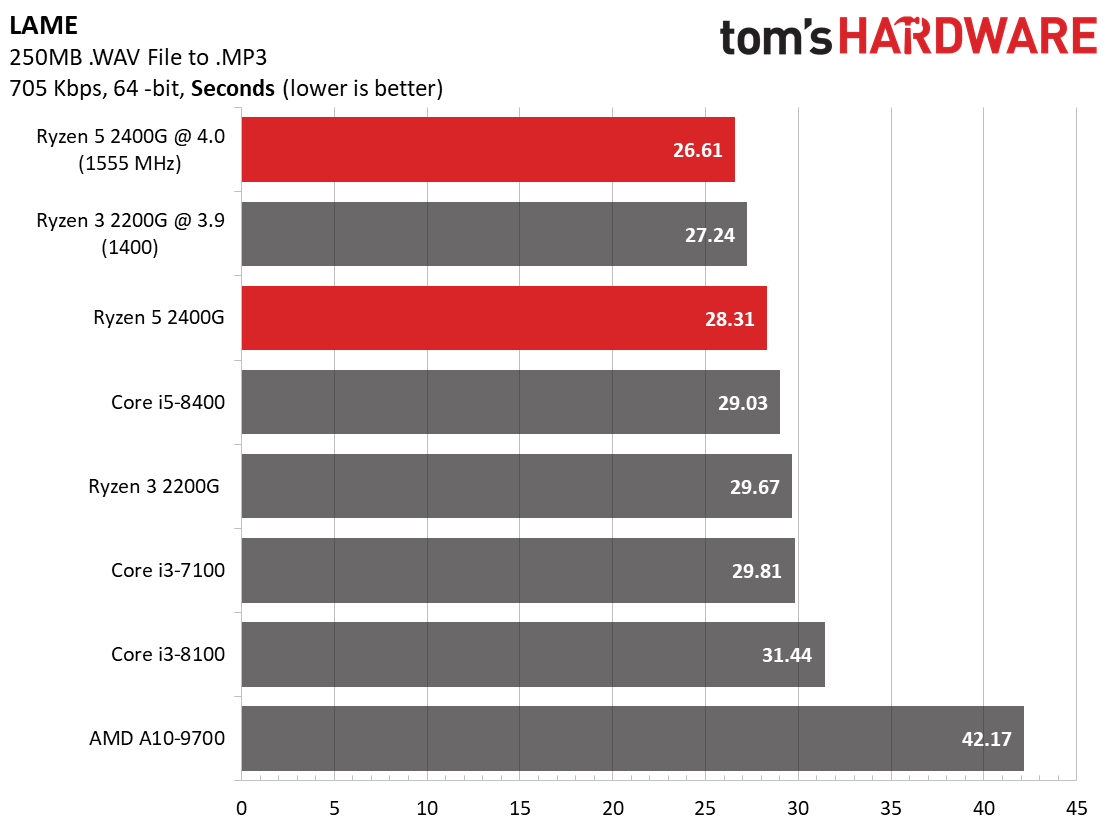
The Ryzen 5 2400G performs exceedingly well in LAME, which is primarily single-threaded. This result leads us to believe that the benchmark benefits from low cache latency, as Intel processors maintain their per-core performance advantage.
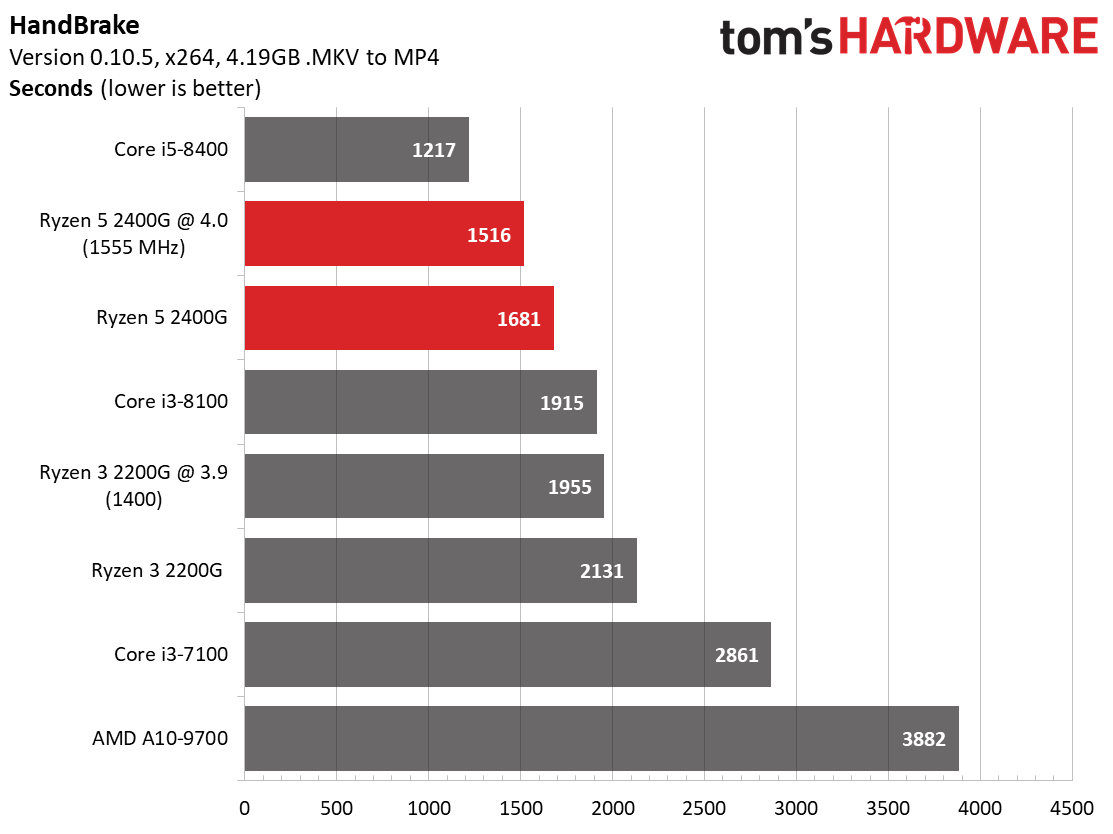
There's normally a larger delta between Intel and AMD processors during our HandBrake x265 test compared to the x264 benchmark due to the former's heavy use of AVX instructions. But we don't really see that this time around. The Ryzen 5 2400G is much more competitive in AVX-heavy workloads than we expected.
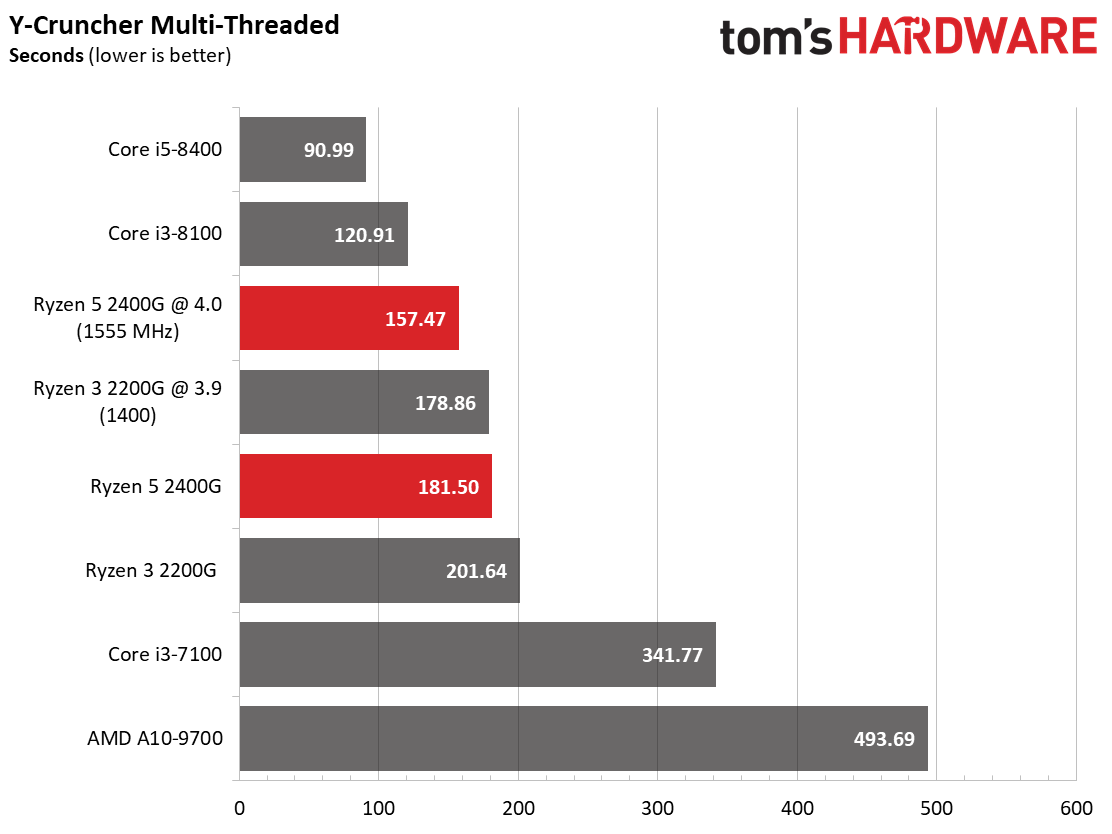
Speaking of AVX, we also provide results from y-cruncher, a single- and multi-threaded program that computes Pi using AVX instructions. We tested with version 0.7.3.9474, which includes Ryzen optimizations. The Intel processors take a big lead in our single-threaded run. Again, though, the delta between Intel and AMD contenders is smaller than expected when we divide this task across available physical and logical cores. We theorize that a lower cache latency helps feed the cores in these data-hungry AVX workloads, thus speeding performance.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Rendering, Encoding & Compression
Prev Page Office & Productivity Next Page Final Thoughts
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
InvalidError Looking at Zeppelin and Raven dies side by side, proportionally, Raven seems to be spending a whole lot more die area on glue logic than Zeppelin did. Since the IGP takes the place of the second CCX, I seriously doubt its presence has anything to do with the removal of 8x PCIe lanes. Since PCIe x8 vs x16 still makes very little difference on modern GPUs where you're CPU-bound long before PCIe bandwidth becomes a significant concern, AMD likely figured that nearly nobody is going to pair a sufficiently powerful GPU with a 2200G/2400G for PCIe x8 to matter.Reply -
Olle P 1. Why did you use 32GB RAM for the Coffee Lake CPUs instead of the very same RAM used for the other CPUs?Reply
2. In the memory access tests I feel to see the relevance of comparing to higher teer Ryzen/ThreadRipper. Would rather see comparison to the four core Ryzens.
3. Why not also test overclocking with the Stealth cooler? (Works okay for Ryzen 3!)
4. Your comments about Coffee Lake on the last page:
"Their locked multipliers ... hurt their value proposition...
... a half-hearted attempt to court power users with an unlocked K-series Core i3, ... it requires a Z-series chipset..."As of right now all Coffee Lake CPUs require a Z-series chipset, so that's not an added cost for overclocking. I'd say a locked multiplier combined with the demand for a costly motherboard is even worse. (This is suppsed to change soon though.) -
AgentLozen Tom's must think highly of this APU to give it the Editor's Choice award. It seems to be your best bet for an extremely limited budget.Reply
I totally understand if you only have a few hundred dollars to build your PC with and you desperately want to get in on some master race action. That's the situation where the 2400G shines brightest. But the benchmarks show that games typically don't run well on this chip. They DO work under the right circumstances, but GTAV isn't as fun to play at low settings.
Buying a pre-built PC from a boutique with a GeForce 1050Ti in it will make your experience noticeably better if you can swing the price. -
akamateau What most writers and critics of integrated graphics processors such as AMD's APU or Intel iGP all seem to forget, is not EVERYONE in the world has a disposable or discretionary income equal to that of the United States, Europe, Japan etc. Not everyone can afford bleeding edge gaming PC's or laptops. Food, housing and clothing must come first for 80% of the population of the world.Reply
An APU can grant anyone who can afford at least a decent basic APU the enjoyment of playing most computer games. The visual quality of these games may not be up to the arrogantly high standards of most western gamers, but then again these same folks who are happy to have an APU also can not barely afford a 750p crt monitor much less a 4k flat screen.
This simple idea is huge not only for the laptop and pc market but especially game developers who can only expect to see an expansion of their Total Addressable Market. And that is good for everybody as broader markets help reduce the cost of development.
This in fact was the whole point behind AMD's release of Mantle and Microsoft and The Kronos Group's release of DX12 and Vulkan respectively.
Today's AMD APU has all of the power of a GPU Add In Board of not more than a several years back. -
Blas "Meanwhile, every AMD CPU is overclockable on every Socket AM4-equipped motherboard" (in the last page)Reply
That is not correct, afaik, not for A320 chipsets. It is for B350 and X370, though. -
salgado18 "with a GeForce 1050Ti in it will make your experience noticeably better if you can swing the price."Reply
"a card is still needed"
You do realize that these CPUs have an integrated graphics chip as strong as a GT 1030, right? And that you are comparing a ~$90 GPU to a ~$220 GPU?
If you can swing the price, grab a GTX 1080ti already, and let us mITX/poor/HTPC builders enjoy Witcher 3 in 1080p for a fraction of the price ;) -
InvalidError Reply
When 1080p displays are available for as little as $80, there isn't much point in talking about 720p displays. I'm not even sure I can still buy one of those even if I wanted to unless I shopped used. (But then I could also shop for used 1080p displays and likely find one for less than $50.)20700012 said:but then again these same folks who are happy to have an APU also can not barely afford a 750p crt monitor much less a 4k flat screen.
The price of 4k TVs is coming down nicely, I periodically see some 40+" models with HDR listed for as little as $300, cheaper than most monitors beyond 1080p.
Depends for who, not everyone is hell-bent on playing everything at 4k Ultra 120fps 0.1% lows. Once the early firmware/driver bugs get sorted out, it'll be good enough for people who aren't interested in shelling out ~$200 for a 1050/1050Ti alone or $300+ for anything beyond that. If your CPU+GPU budget is only $200, that only buys you a $100 CPU and GT1030 which is worse than Vega 11 stock.20700022 said:Graphics still too weak , a card is still needed.
If my current PC had a catastrophic failure and I had to rebuild in a pinch, I'd probably go with the 2400G instead of paying a grossly inflated price for a 1050 or better. -
Istarion People come here expecting to find an overclockeable 4 core with a 1080-like performance for 160$. And a good cooler. I'd love to be so optimistic :DReply
Summarizing: we are saving around 50-100$ for the same low-end performance. That's 25% to 40% cheaper. What are we complaining about?!? I'd be partying right now if that happened in high-end too!!! 300$ for a 1080...
All those comments saying "too weak", or "isn't fun to play at low settings", seriously, travel around the globe or just open your mind, there's poor people in 90% of the world, do you think they'll buy a frakking 1080 and a 8700k?!?
And there's even non-poor people that doesn't care about good graphics! Go figure!
Otherwise, why there are pixel graphics games all over the place? Or unoptimized/breaking early access games??
I have a high-end pc and still lower fps to minimum for competitive play, so I won't see any difference between a 1080Ti vs a 1070 (250 vs 170fps, who's gonna see that, my cat?!? No 'cause my monitor is not fast enough!). -
rush21hit As a cyber cafe owner, I would love to replace my old A5400s to the lower R3.Reply
Except that the DDR4 sticks went crazy expensive over here. FML