Parallel Processing, Part 2: RAM and HDD
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
HDD Parallelism: Single, Dual Or Quad Hard Drives
Hard drive parallelism sounds awkward, but it has been possible to combine the performance of multiple hard drives for years. The key to it is Redundant Array of Independent Drives (RAID) technology, which allows a RAID controller to distribute data across multiple hard drive, combining the throughput of the individual drives. While add-on RAID controllers have been popular on enthusiast motherboards since the times of the Athlon XP or Pentium 4 on Socket 478, chipset makers soon added basic RAID capabilities to their core logic products.
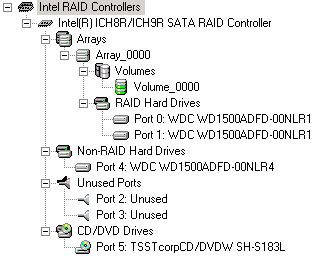
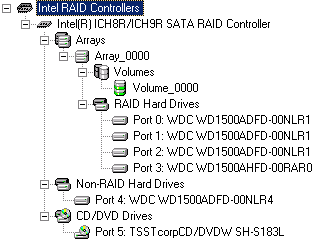
The option to combine two hard drives in a RAID 0 stripeset or mirrored in a RAID 1 array has been around for years. Current chipsets with four or six Serial ATA ports are capable of spanning arrays across all ports. We decided to put up a conventional setup with a single hard drive against two RAID 0 configurations: one with two hard drives and the other with four drives. We selected four WD1500 Raptor hard drives for these tests.
Most enthusiast motherboards offer at least six Serial ATA ports.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: HDD Parallelism: Single, Dual Or Quad Hard Drives
Prev Page Dual Channel To The Rescue Next Page Test Setup
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.
-
(Firt of all: Excuse my poor English... )Reply
mmm yours memory tests don't convince me. You should run, for example, Winrar AND Lame IN PARALLEL/SIMULTANEOUS (i.e multitasking), otherwise, caches don't are flushed (and it's when dual channel really is important). Note that it's not a superflous situation; under normal use a system commonly have several huge memory applications run concurrently (word, browser whith a lot of tabs open, anti-virus, etc. )
el_bot -
hellwig I doubt anyone from Tom's will see this comment on such an old article, but it would have been interesting to see Single-vs.-Dual channel memory using an AMD processor. Since Tom's like Intel, the new Core i7's would also be beneficial. The point is, the article acknowledges the Core 2's have a tremendous amount of L2 cache to combat FSB (and consequently Memory) latencies. How is the comparison with an AMD or nwe Core i7 where there is NO FSB and the L2 Cache is significantly reduce? I would imagine this is where dual/tripple-channel shows is mustard. I hope we see a single vs. dual vs. triple channel comparison soon.Reply -
junghm69 My Windows Experience Index 3D gaming graphics score goes up from 3.8 to 5.1 when I switch from dual channel to single channel. This makes absolutely no sense. I thought dual channel was supposed to be better than single channel. Can anyone explain this?Reply
I seriously doubt that this score is accurate. I am using the built in graphics controller on the motherboard which is an AMD 760G chipset (ATI HD 3000 or 3200 I think). I've used Radeon HD 5450 video cards on similar systems and they give me a score of 5.4. How can a built in graphics controller give me a 5.1?
AMD Athlon II X3 435 Rana (2.9 ghz)
Asus M4A78LT-M motherboard
4 GB G.Skill DDR3-1333 (2x2GB) F3-10600CL9D-4GBNT CL9-9-9-24 1.5V
Windows 7 Ultimate 64-bit -
junghm69Reply
because if you used 2 different memory chips both will run at the speed of the lowest memory chip when you activate dual channel in your motherboard -
Caramac That earlier article on Processors doesn't work, so I'll add this:Reply
Intel HyperThreading - leading to the "H T" on the 'Intel Inside' sticker of computers with that 875p chipset and a single core Pentium 4 processor.
It equals simulated dual core tech.
Some Core processors also have HT.
http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/340555-28-intel-hyperthreading-helpful