The AMD Ryzen 3 2200G Review: Vega Barrels Into Budget Gaming
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Rendering
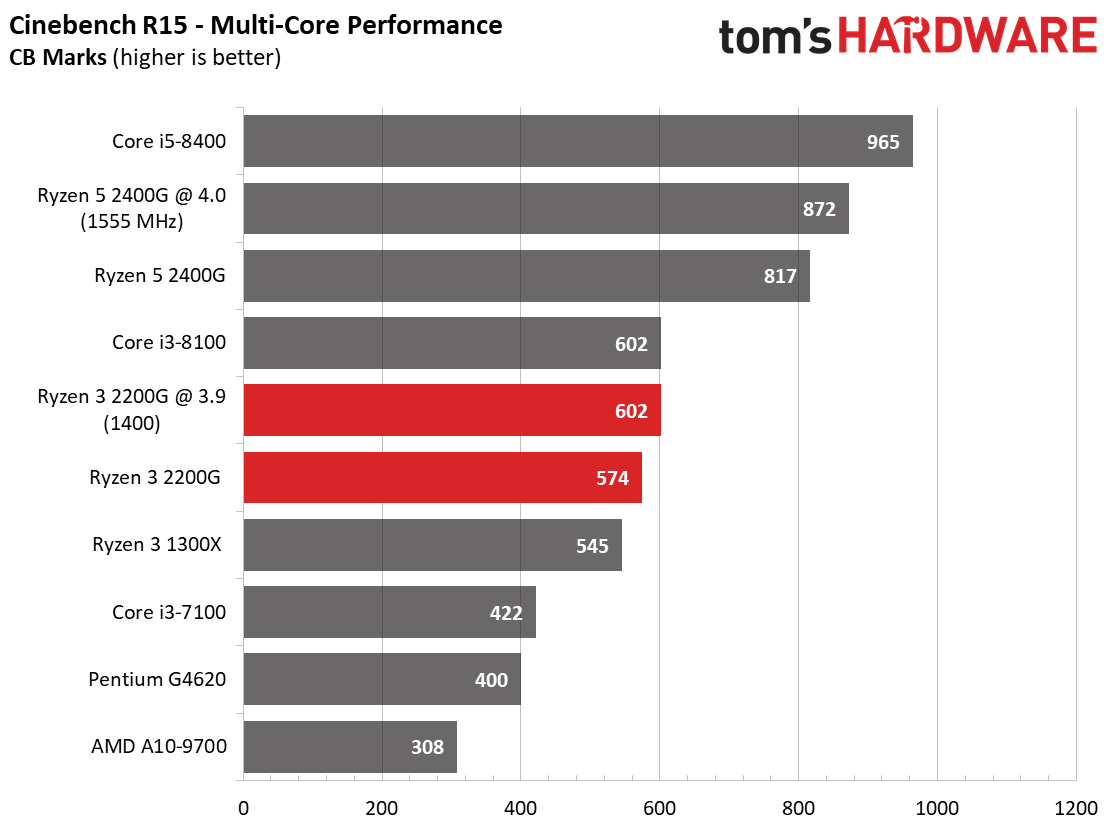
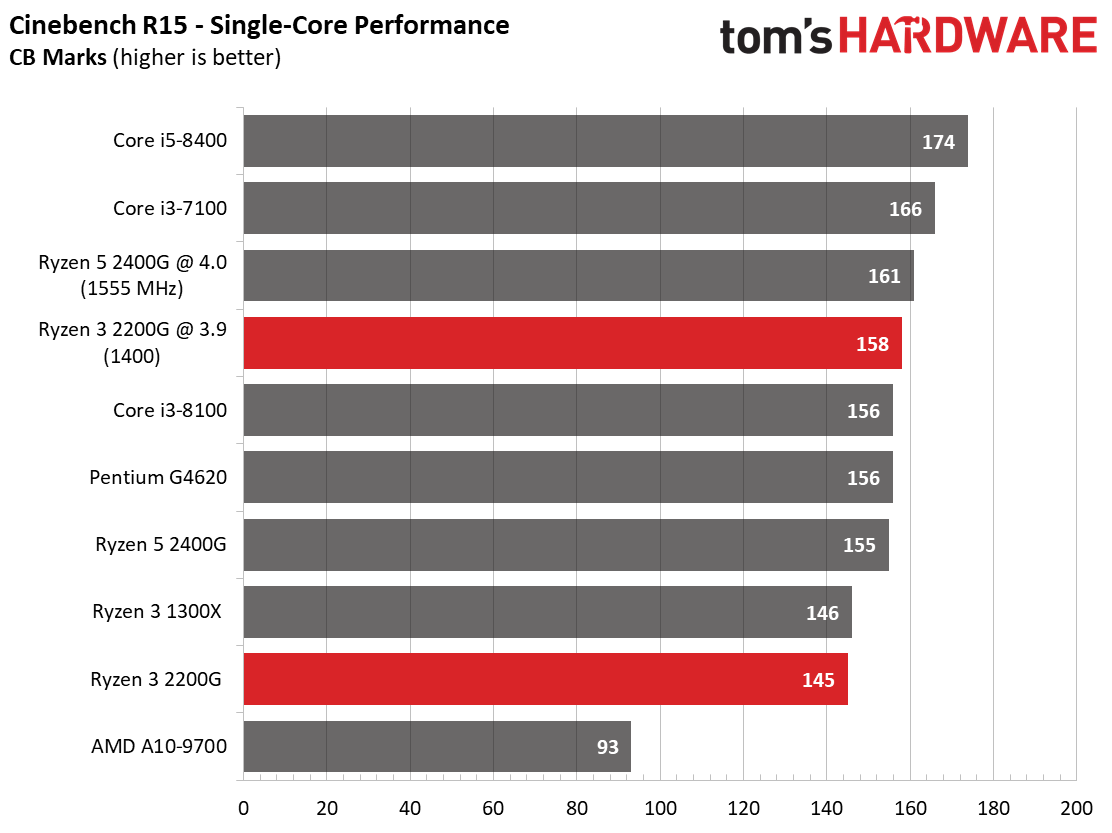
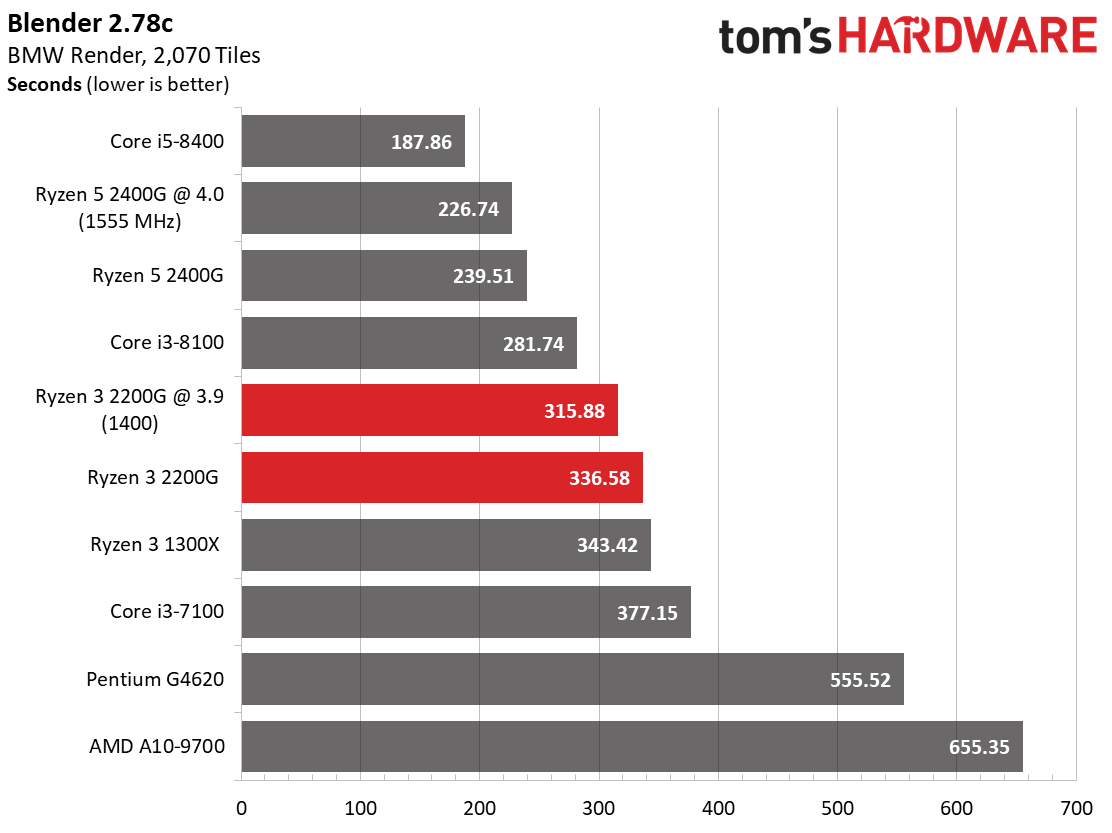
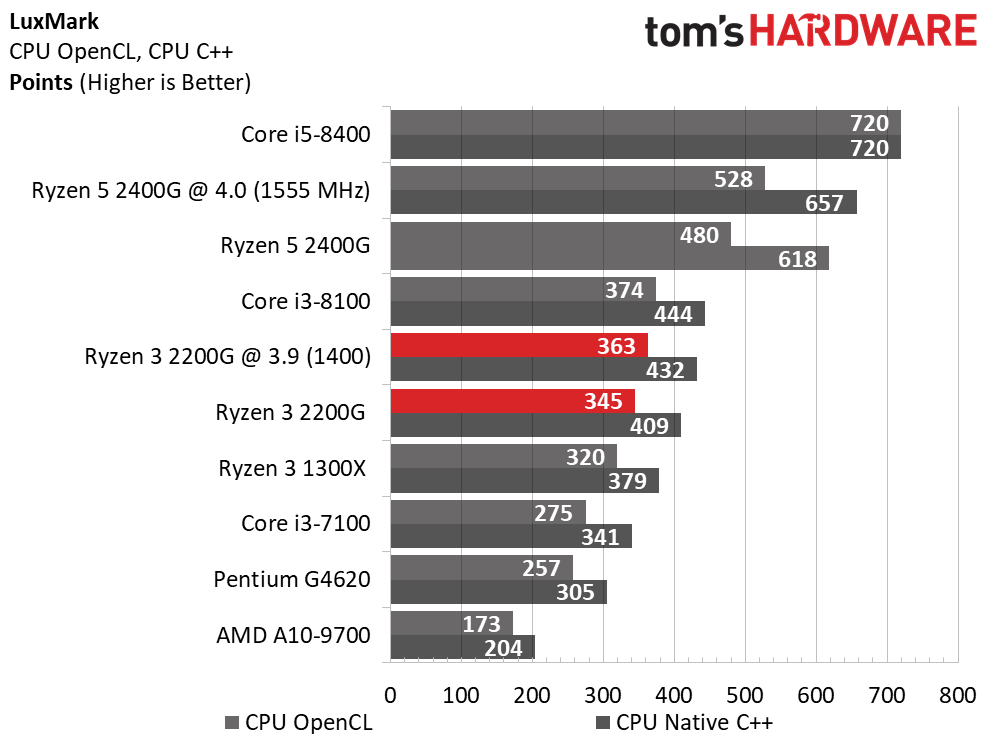
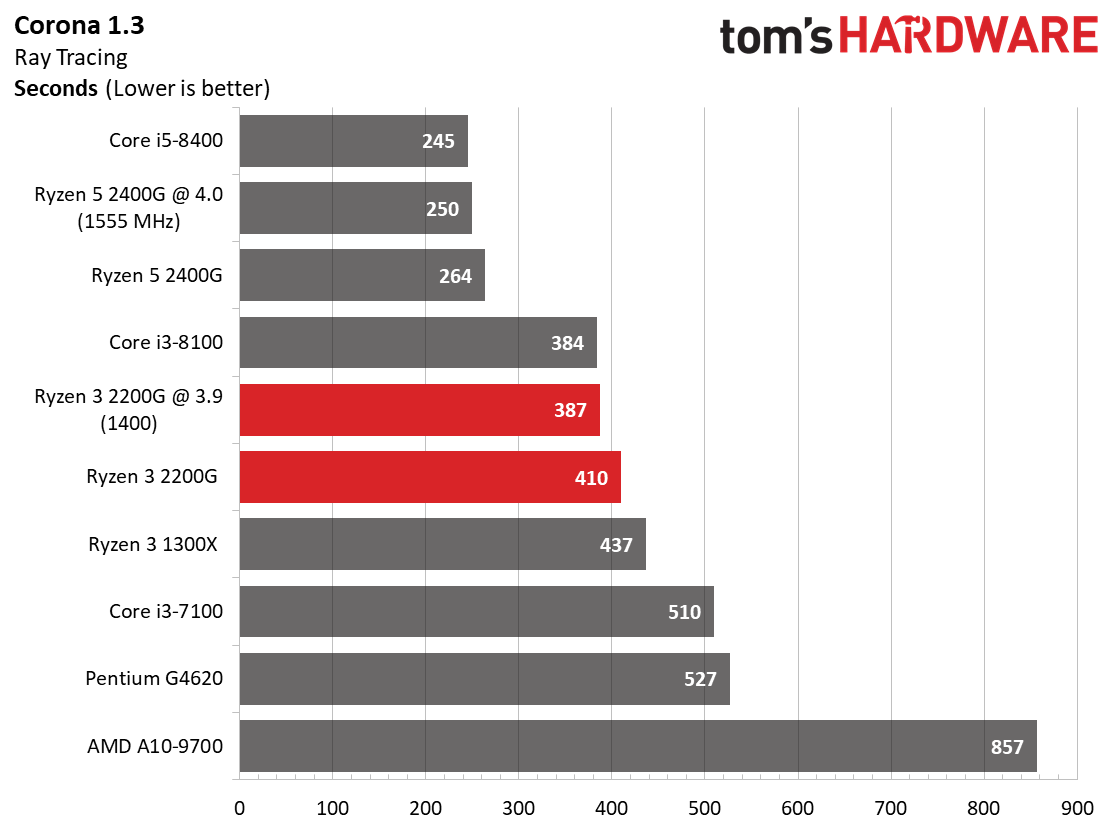
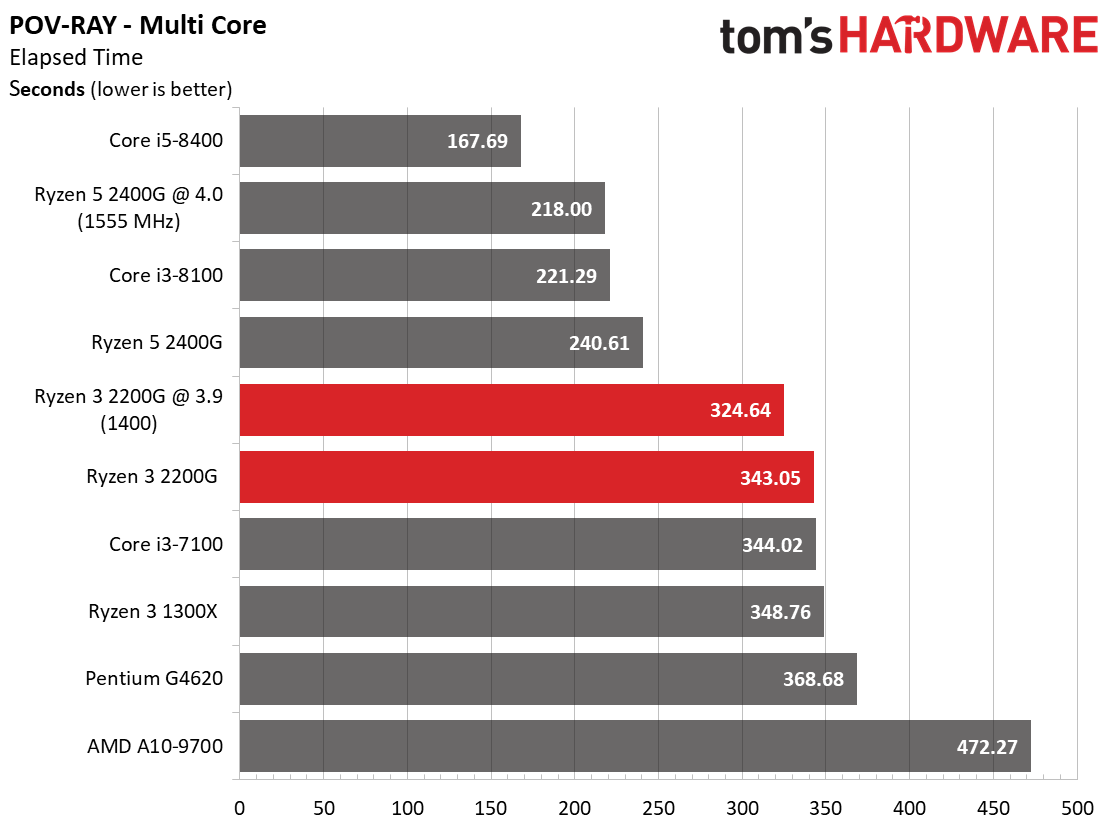
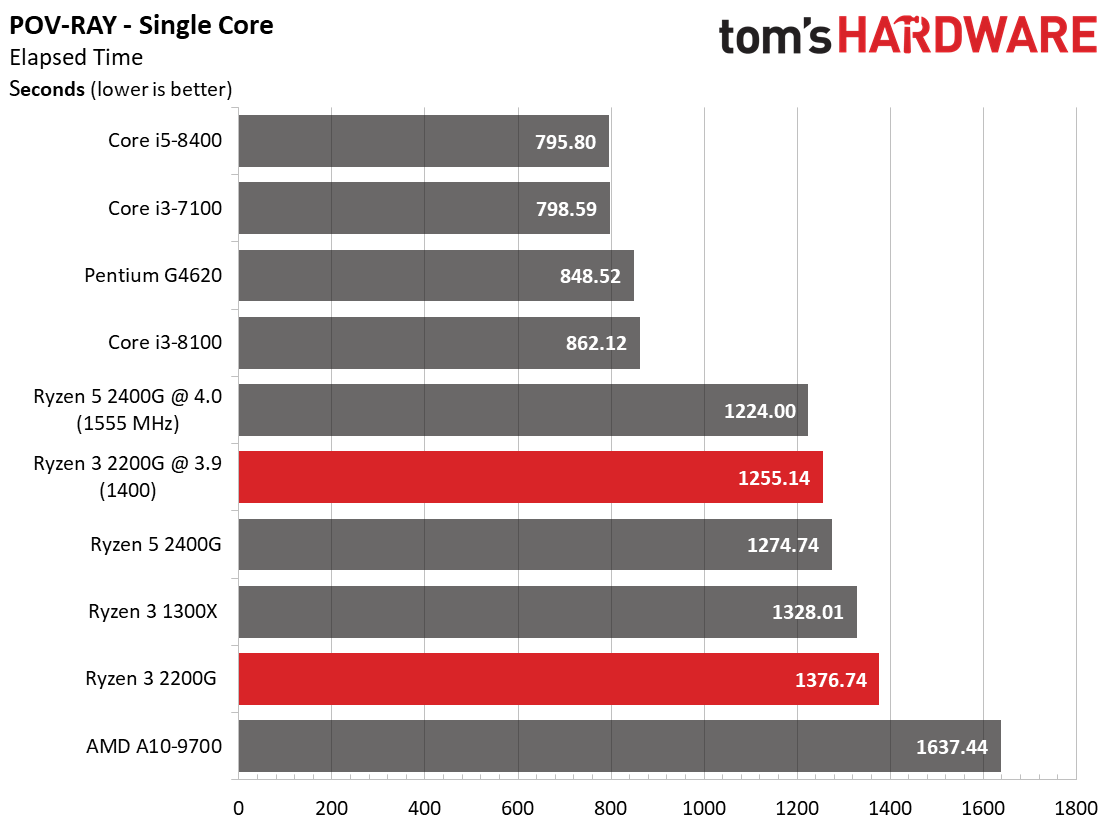
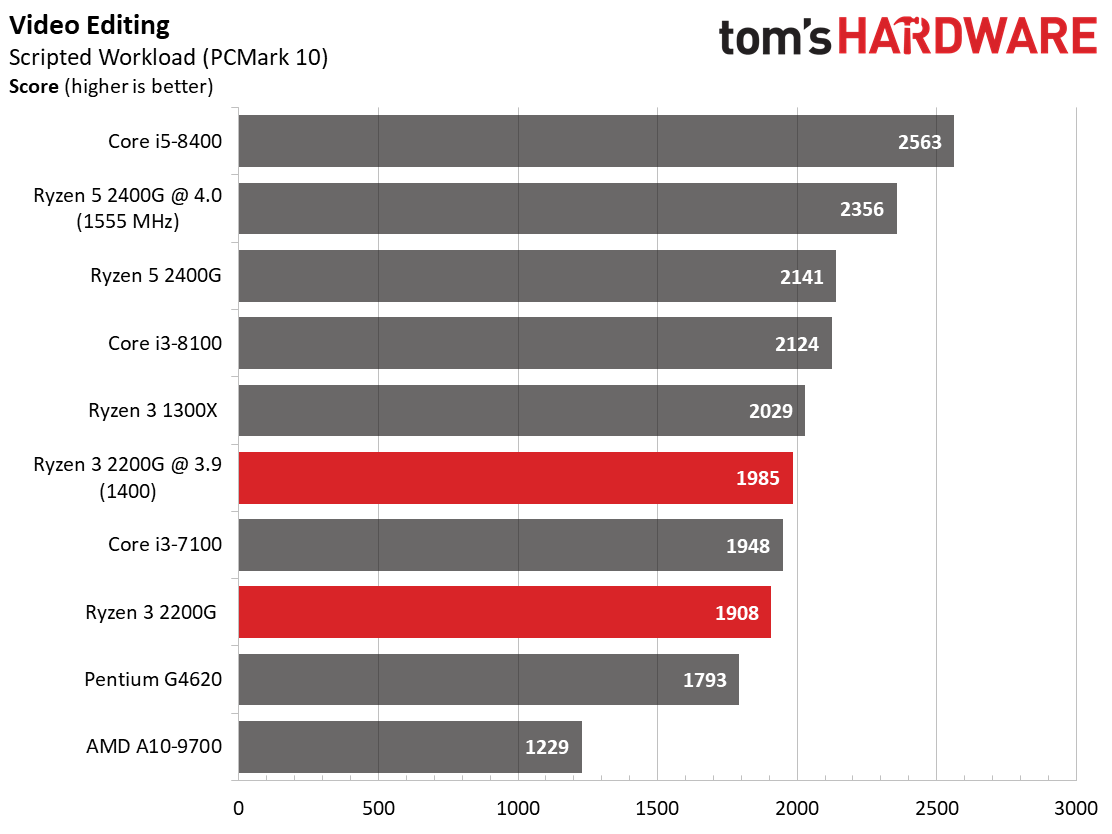
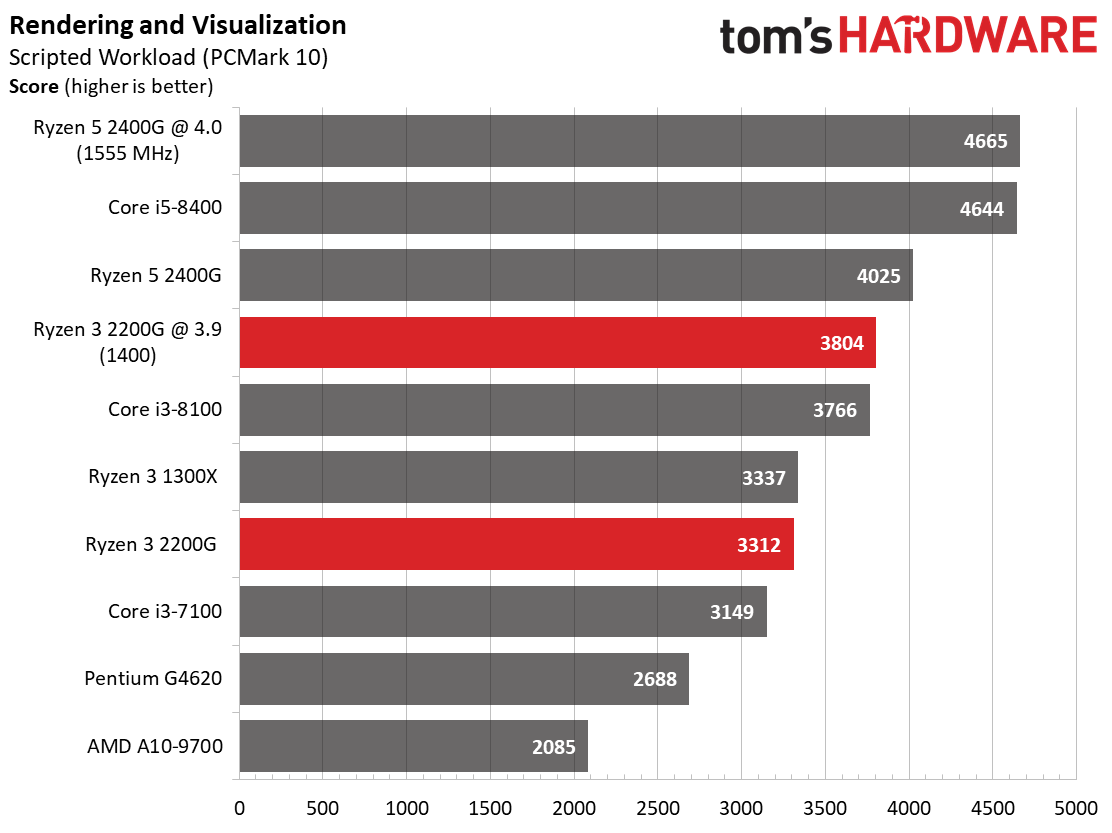
Ryzen 3 2200G effectively ties the Ryzen 3 1300X in Cinebench's single-core test, and then carves out a slight lead in the multi-core metric.
Meanwhile, Intel's Pentium G4620 trails in the parallelized workload. But strong per-core performance gives the little Pentium an advantage in lightly-threaded tasks; it even beats a stock Ryzen 5 2400G in the single-core benchmark. These same observations carry over to the other benchmarks, too.
Ryzen 5 2400G's SMT technology allows it to dominate the Ryzen 3 2200G in threaded workloads, while the 2200G maintains a lead over Ryzen 3 1300X in most of those same tests. These benchmarks are driven by host processing, so the 2200G's available power is dedicated to the Zen cores, facilitating the newer chip's win.
Encoding & Compression
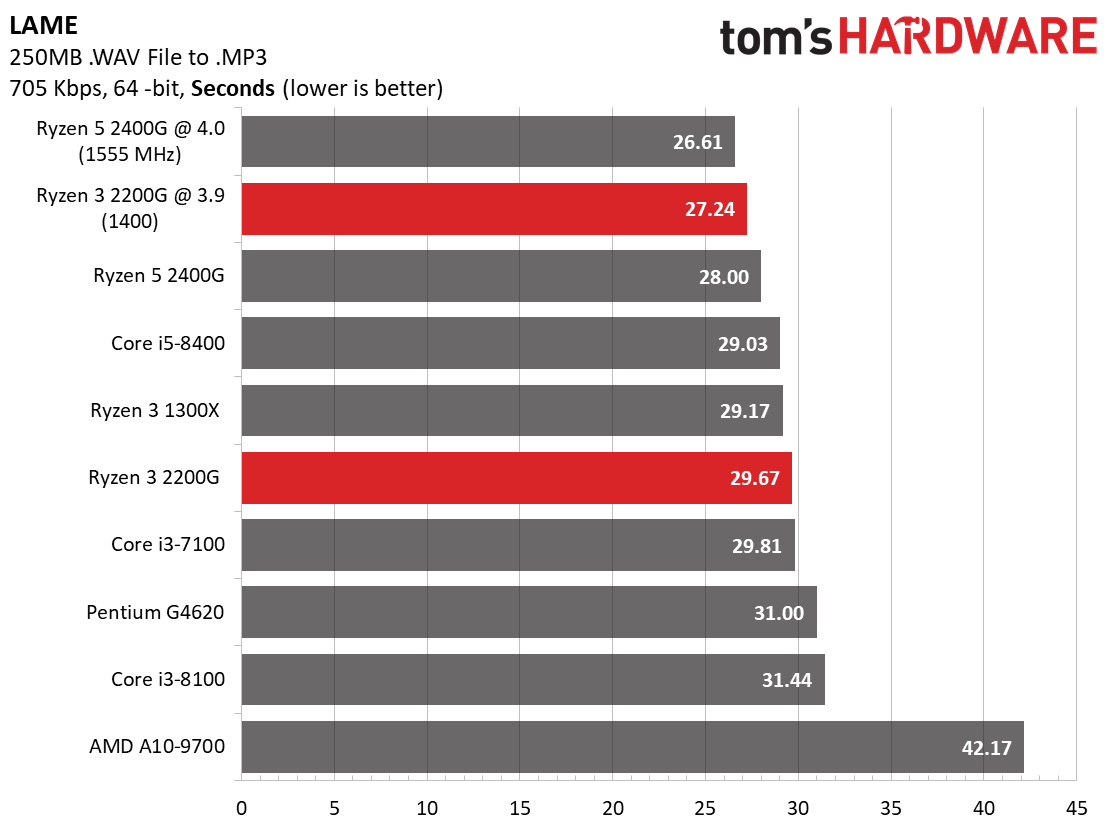
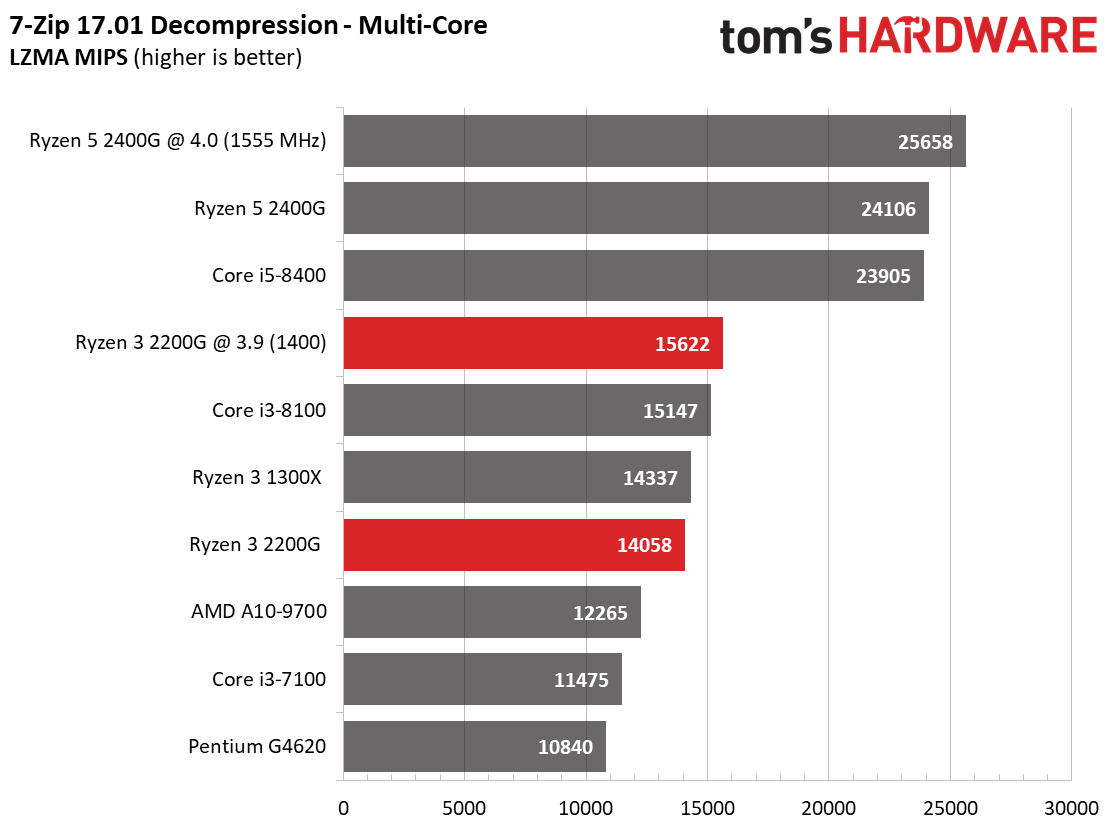
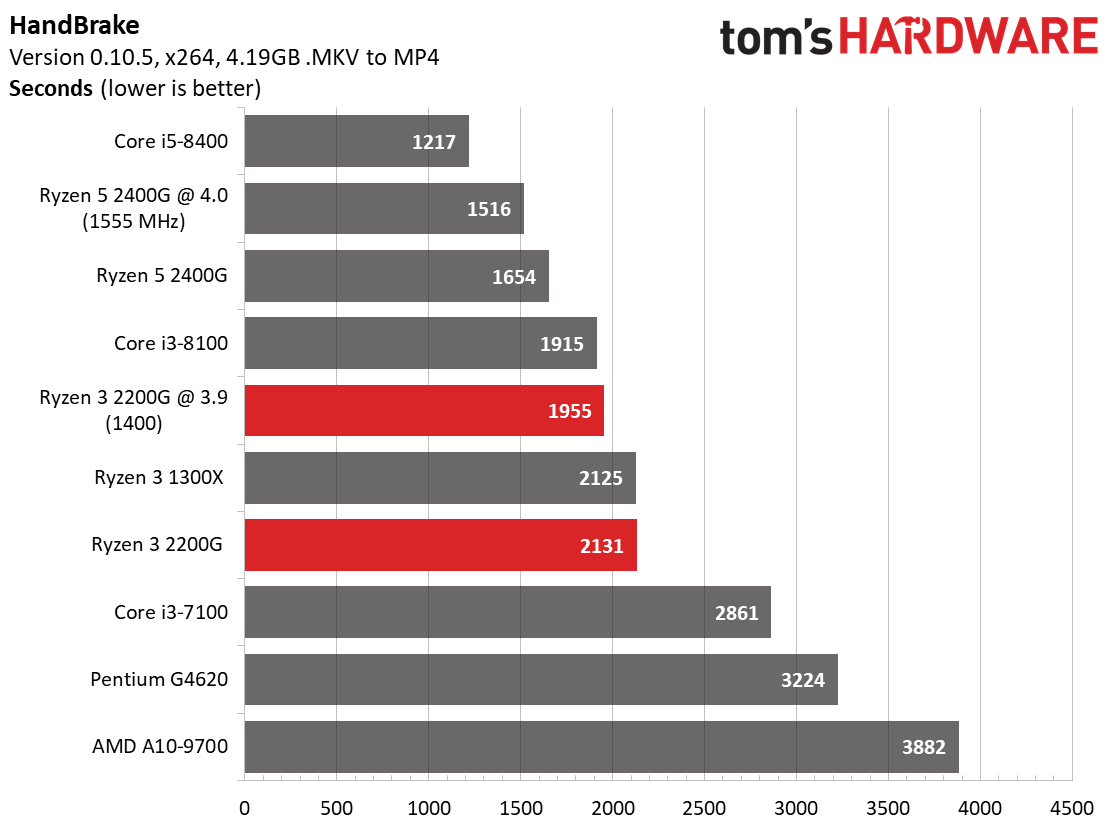
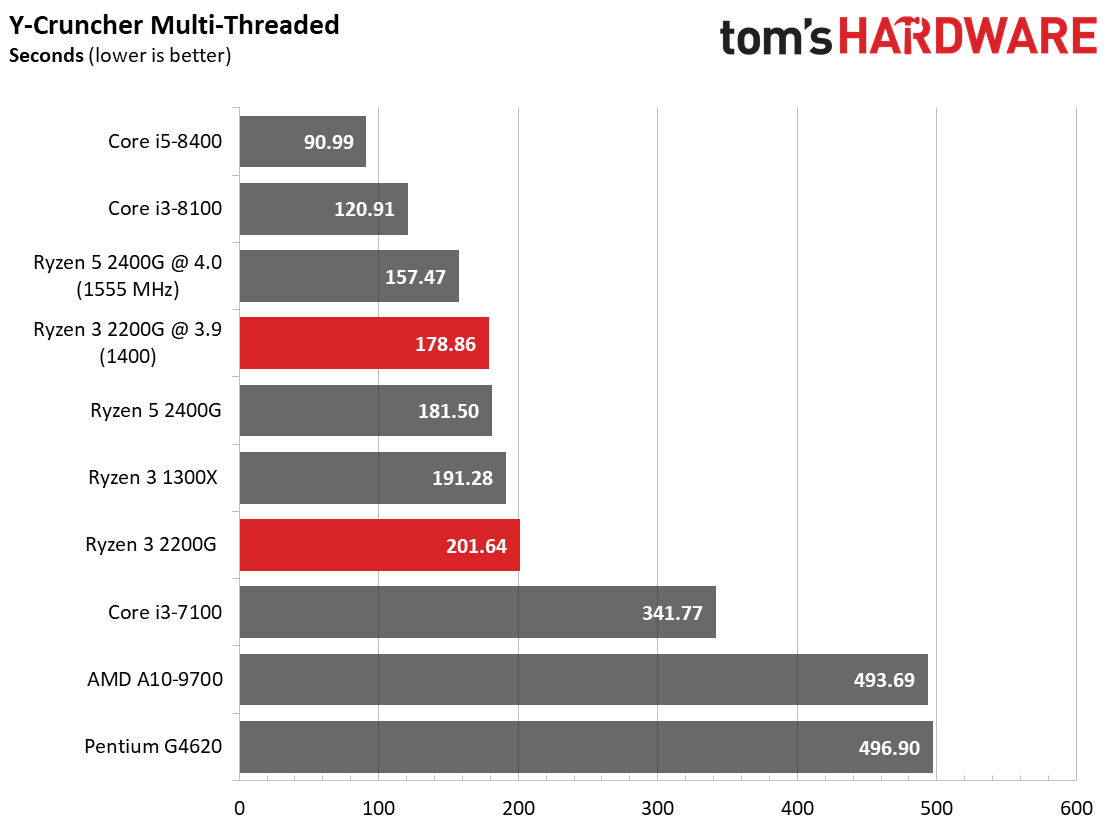
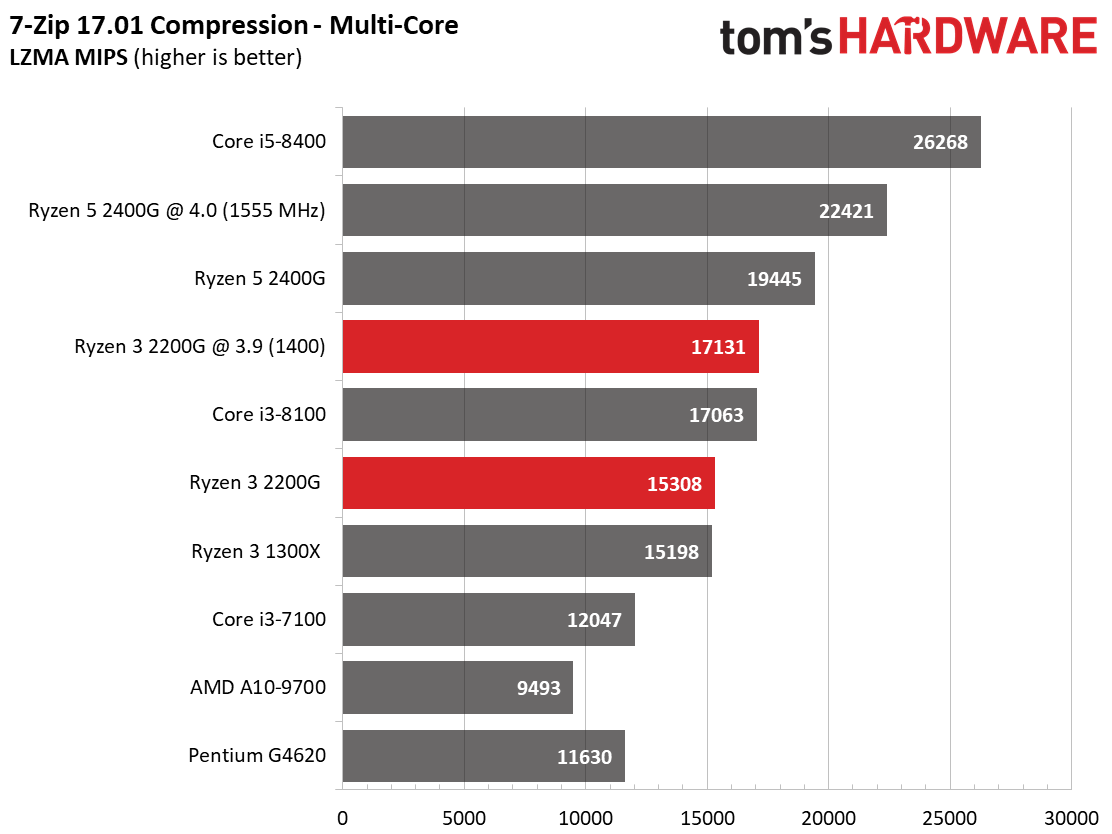
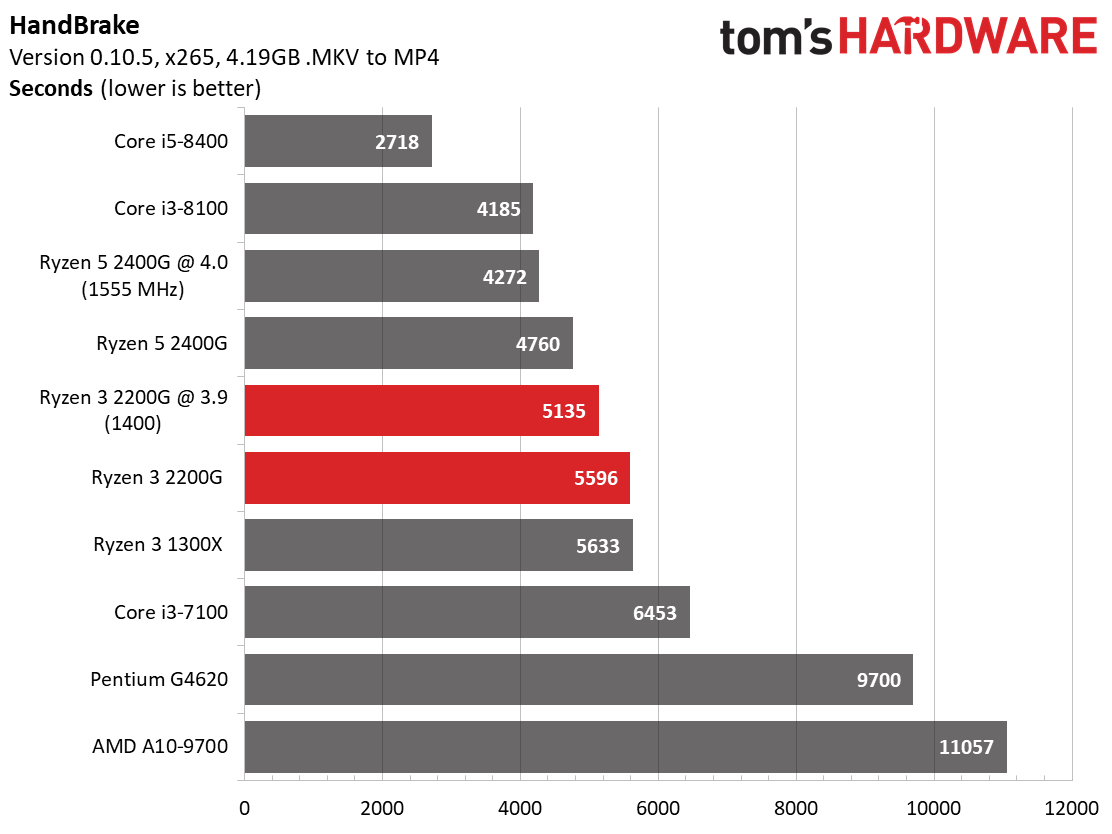
AMD's Ryzen 3 2200G matches the Ryzen 3 1300X in compression and decompression workloads, again indicating that its execution cores (and single CCX configuration) are far more potent when the graphics engine is idle.
The Pentium G4620 struggles mightily through this round of testing due to its dual-core design.
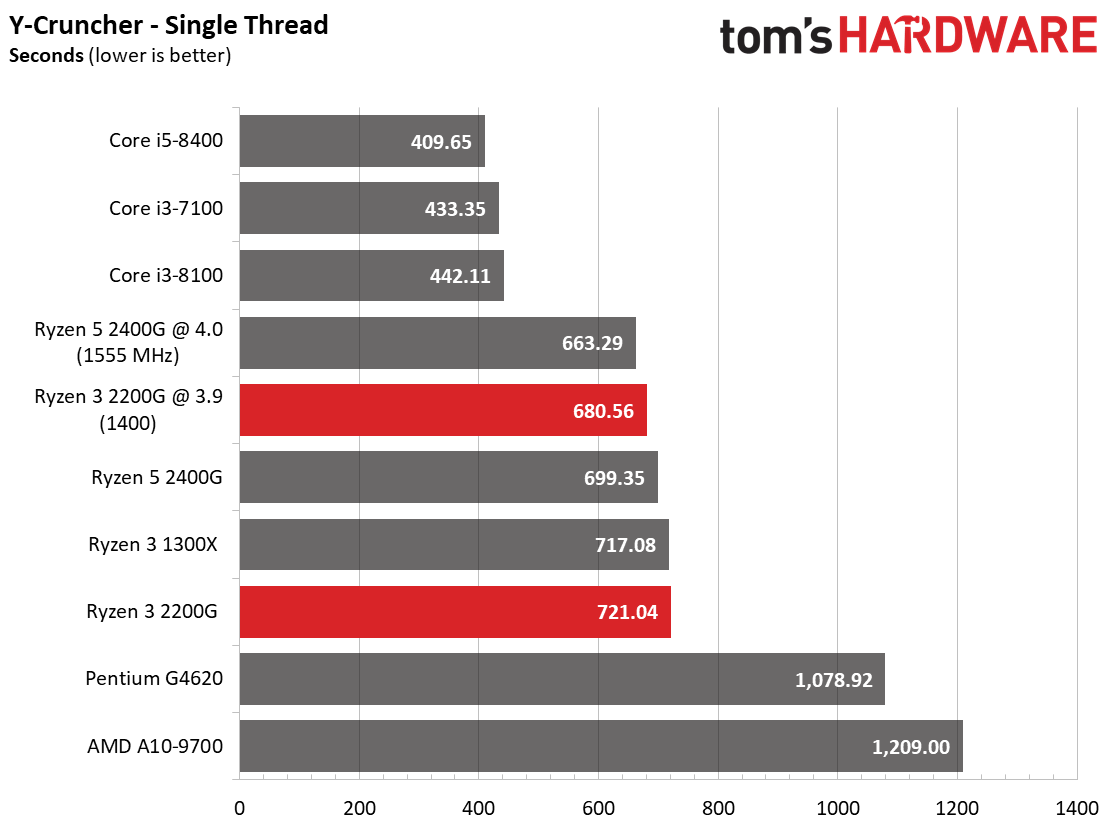
We also provide results from y-cruncher, a single- and multi-threaded program that computes Pi using AVX instructions. We tested with version 0.7.3.9474, which includes Ryzen optimizations. Coffee Lake-based processors lead the single-threaded tests convincingly, while AMD's Raven Ridge processors are naturally more competitive in the threaded workload.
MORE: Best Cheap CPUs
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Rendering, Encoding & Compression
Prev Page Office & Productivity Next Page Final Analysis
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
wh3resmycar add mid/high 30 fps target for FC and witcher 3 and see if it can hold its own against a ps4. that would make more sense instead of playing it at 60 fps - low.Reply -
salgado18 "In the end, there's no way we'd recommend a Pentium's two physical cores over Ryzen 3 2200G's four. And the dead-end Z270 chipset does little to help Intel's case. Coffee Lake-based Pentium processors can't get here fast enough. Even then, though, it's a safe bet they won't arrive with on-die graphics capable of battling AMD's Radeon Vega."Reply
There, so you guys stop saying the G4560 is better. -
drinkingcola86 Did you run these processors with the standard bios or did you change the limit of the video side of it to 2 gig from the 512meg that it is defaulted to?Reply -
Shumok I would like to see the APU's tested with 1080ti's to see how they hold up when the user upgrades to discrete eventually.Reply -
nate1492 Reply20713408 said:"In the end, there's no way we'd recommend a Pentium's two physical cores over Ryzen 3 2200G's four. And the dead-end Z270 chipset does little to help Intel's case. Coffee Lake-based Pentium processors can't get here fast enough. Even then, though, it's a safe bet they won't arrive with on-die graphics capable of battling AMD's Radeon Vega."
There, so you guys stop saying the G4560 is better.
Would you really suggest the Ryzen 3 2200g or the Ryzen 5 2400g to someone over a G4560 and a 1050 (200 quid!)? Heck, take the AMD 1200 and the 1050, doesn't matter, I couldn't suggest gaming at low 720p to anyone, we are talking 90 quid, 140 quid, or 200 quid here. If you can't pony up 200 quid, just wait longer.
And at this price point, who is even considering upgrading CPUs in short order? -
logainofhades Reply20713566 said:Would you really suggest the Ryzen 3 2200g or the Ryzen 5 2400g to someone over a G4560 and a 1050 (200 quid!)? Heck, take the AMD 1200 and the 1050, doesn't matter, I couldn't suggest gaming at low 720p to anyone, we are talking 90 quid, 140 quid, or 200 quid here. If you can't pony up 200 quid, just wait longer.
And at this price point, who is even considering upgrading CPUs in short order?
US pricing is far different apparently. The cheapest 1050, on pcpartpicker, is $154.98.
The G4560 is a great chip, but is on a dead platform, and hyperthreading can only do so much.
@$99, the 2200g gets you in the door, for low budget gaming, and has enough horsepower to handle a midrange graphics card, once GPU prices get back to normal. Ram price difference isn't much different between the slower and higher clocked models, 3200 and lower. Also you have ability to go up to a higher cored Ryzen 5 or 7, if the need arises. Also current AM4 boards are supposed to be compatible with Ryzen II, with a bios update. With the Pentium G, you are stuck with a 7700k at best, and most likely will have a board that cannot even overclock it. A decently priced B350, on the other hand, can overclock.
AMD has the low end locked in, for now. Once coffee lake Pentiums and we get non Z chipset boards, the tables will probably turn, to some degree. That is the beauty of competition though, and that is a good thing. -
BulkZerker "Then again, we don't expect anyone to run a multi-GPU config on an entry-level platform."Reply
Cryptomining enthusiasts non-withstanding -
ghettogamer not an xbox one killer , but you can build a mini itx & get into pc gaming with this cpu for almost the same price albeit at 720p custom medium-low settings. This cpu is probably the power plant of the future ps5/xbox2, great for console fans!Reply -
AlistairAB Reply20713566 said:20713408 said:"In the end, there's no way we'd recommend a Pentium's two physical cores over Ryzen 3 2200G's four. And the dead-end Z270 chipset does little to help Intel's case. Coffee Lake-based Pentium processors can't get here fast enough. Even then, though, it's a safe bet they won't arrive with on-die graphics capable of battling AMD's Radeon Vega."
There, so you guys stop saying the G4560 is better.
Would you really suggest the Ryzen 3 2200g or the Ryzen 5 2400g to someone over a G4560 and a 1050 (200 quid!)? Heck, take the AMD 1200 and the 1050, doesn't matter, I couldn't suggest gaming at low 720p to anyone, we are talking 90 quid, 140 quid, or 200 quid here. If you can't pony up 200 quid, just wait longer.
And at this price point, who is even considering upgrading CPUs in short order?
-
AlistairAB Reply20713566 said:20713408 said:"In the end, there's no way we'd recommend a Pentium's two physical cores over Ryzen 3 2200G's four. And the dead-end Z270 chipset does little to help Intel's case. Coffee Lake-based Pentium processors can't get here fast enough. Even then, though, it's a safe bet they won't arrive with on-die graphics capable of battling AMD's Radeon Vega."
There, so you guys stop saying the G4560 is better.
Would you really suggest the Ryzen 3 2200g or the Ryzen 5 2400g to someone over a G4560 and a 1050 (200 quid!)? Heck, take the AMD 1200 and the 1050, doesn't matter, I couldn't suggest gaming at low 720p to anyone, we are talking 90 quid, 140 quid, or 200 quid here. If you can't pony up 200 quid, just wait longer.
And at this price point, who is even considering upgrading CPUs in short order?
The 2400G is 10 (single core) to 120 (multicore) percent faster as a CPU after a mild OC. It costs $275 for a G4560 and a GTX 1050 in Canada, much more than $210 for the Ryzen 2400G, which almost has GTX 1050 level graphics as it easily outperforms the gt 1030.
As for the 2200G, an extra $30 gets you a modern motherboard platform, a better cooler, more multi core performance, and easy upgrade-ability. Kind of funny criticizing it's lack of 1080p chops, when everything works perfectly at 900p. (Can't even play Overwatch at 360p properly with Intel integrated graphics).