Do It Like Tom's: Calibrating Your Monitor With CalMAN RGB
A while back, we introduced you to display calibration with Datacolor's Sypder4Elite. Today we look at CalMAN RGB, which is the other major calibration solution. With extensive meter and pattern source support, it’s positioned as a professional’s tool.
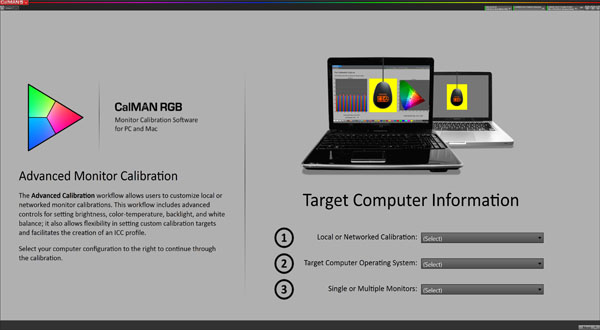
CalMAN RGB How-To: Advanced Calibration, Part 1
The Standard Calibration is great for the occasional touch-up or quick adjustment, but to unlock CalMAN RGB’s full potential, you want to select Advanced Calibration from the first screen.
If it’s your first time calibrating a particular monitor, you should run through the full Advanced Calibration routine in order to hit every imaging parameter. Standard only adjusts the grayscale. In the Advanced workflow, you can calibrate everything: brightness, contrast, grayscale, gamma, and color gamut. Even if your monitor’s OSD doesn’t support all of those adjustments, CalMAN will create a look-up table to make up that shortfall. If your display can be controlled via DDC (a majority can), CalMAN accesses those controls directly during the calibration. You never have to open the OSD yourself. And using windows we’ll show you later, you can access the adjustments manually if you wish.
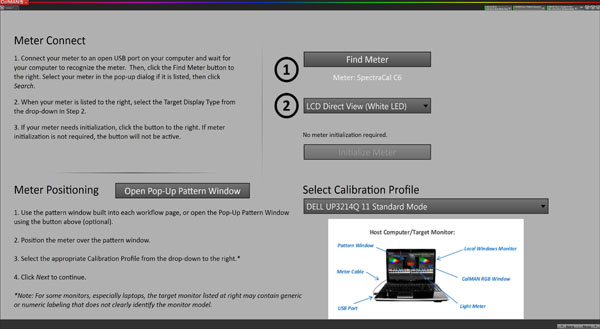
If a meter name appears under the Find Meter button, that step is done. Select Calibration Profile gives you three options for picture modes. Those are set up by CalMAN, so you can easily create multiple profiles and switch between them using the PC Client icon in the system tray.
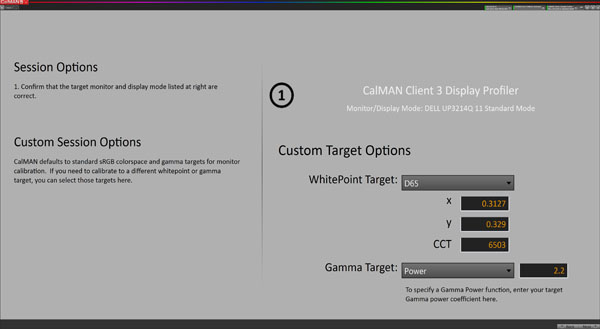
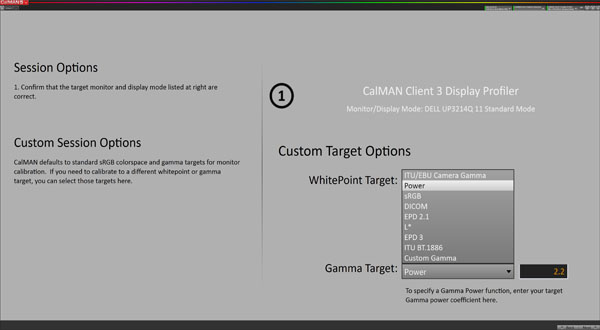
In the next window, you set your white point and gamma targets. While it appears as though there’s no option for a gamut target, there actually is. Open the settings panel from the upper-right.
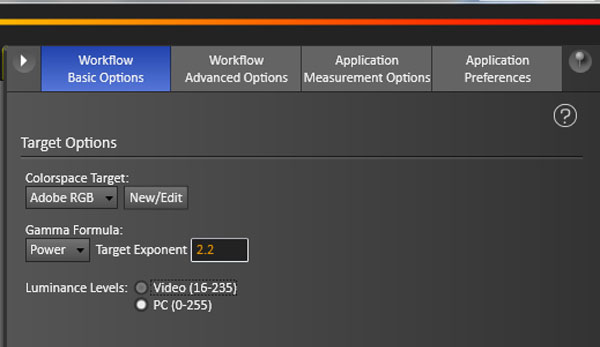
Under the first tab, Workflow Basic Options, you can specify the color target. Since we’re working with Dell's UP3214Q, we'll choose Adobe RGB.
Each gamma option is slightly different in appearance, and you’ll have to choose the one that matches your intended source material. In almost all cases, sRGB or Power is the correct choice. If you choose Power, you can specify any value you wish. PC is 2.2 and Mac is 2.0.
Now that you’ve set your parameters for color, grayscale, and gamma, the calibration itself begins.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: CalMAN RGB How-To: Advanced Calibration, Part 1
Prev Page CalMAN RGB How-To: Getting Started Next Page CalMAN RGB How-To: Advanced Calibration, Part 2
Christian Eberle is a Contributing Editor for Tom's Hardware US. He's a veteran reviewer of A/V equipment, specializing in monitors. Christian began his obsession with tech when he built his first PC in 1991, a 286 running DOS 3.0 at a blazing 12MHz. In 2006, he undertook training from the Imaging Science Foundation in video calibration and testing and thus started a passion for precise imaging that persists to this day. He is also a professional musician with a degree from the New England Conservatory as a classical bassoonist which he used to good effect as a performer with the West Point Army Band from 1987 to 2013. He enjoys watching movies and listening to high-end audio in his custom-built home theater and can be seen riding trails near his home on a race-ready ICE VTX recumbent trike. Christian enjoys the endless summer in Florida where he lives with his wife and Chihuahua and plays with orchestras around the state.
-
merikafyeah I know it's exaggerated for the purpose of demonstrating differences in calibrated views, but you have got to pick a better "before and after" pic than the one you've been using up to now. They don't even compare the same subject. Half of the image is one thing and the other half is something else entirely. It's impossible to compare something if you're not even certain what exactly it is that you're comparing. I'd argue they don't even depict the kind of differences you'd see in calibrated vs uncalibrated displays, just different preferences in regards to artistic color-grading.Reply -
daglesj Are the Datacolor Spyders now properly calibrated out of the factory? Apparently quality control and specs were not very well handled with the Mk3 and befores. Basically every Spyder 3 would give different results.Reply -
sveinan I would recommend a review on ColorHUG (about $110), open source display colorimeter. It's fast, and worth it's money (http://www.hughski.com/index.html).Reply -
MANOFKRYPTONAK CNET reviews TVs and they post their calibration settings that they use for the best results. Each calibration is set up with professional tools, you can look up each tv by model number. I don't know if it is as good as this but.. its free! And it made a difference for me. But others like colorHUG, displaycalGUI, etc... are good just some different options if anyone is looking.Reply -
cangelini ReplyHate to say it, but this one reads like an infomercial....
This is simply the follow-up to an earlier story we did on Datacolor's solution that was well-received: http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/spyder4-monitor-calibration-image-quality,3581.html. Both tools are in-use in our labs--I think it's useful to show our readers what we use to review monitors and how they might achieve similar results. At least, that was the intent. -
Evolution2001 I'd really like to calibrate my projector using more than just my eyes for perception. Using either the Spyder or CalMAN solutions, which ones offers me the least expensive path to that goal? Is it better to buy one of their all-inclusive packages, or find a colorimeter and software independently?Reply