Video Quality Tested: GeForce Vs. Radeon In HQV 2.0
AMD Video Quality Driver Settings
With the Catalyst 10.12 driver, AMD has revamped the look of its driver settings interface, eliminating the last vestiges of ATI branding. It’s more or less functionally identical when you dig down into the actual options, though.
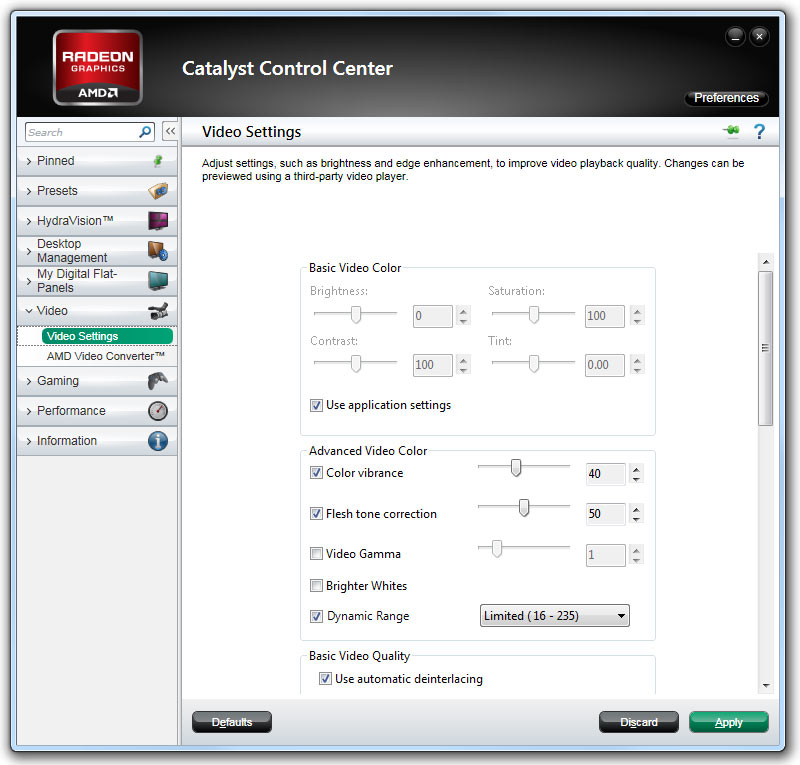
To avoid wasting time in sub-menu navigation levels, the first thing to do is select Preferences and switch to the Advanced view. After this, selecting Video and then Video Settings from the left-side menu delivers all of the relevant selections in one single window. The first section is Basic Video Color. This doesn’t have much to do with video quality, as it’s more geared toward setting the color and saturation to taste. We’ll leave the “Use application settings” checkbox enabled here.
Next is the Advanced Video Color section. Some of these settings, such as “Color vibrance” and “Video gamma,” can be set to taste and aren’t relevant to the benchmark. Flesh-tone correction is benchmarked though, and since this option removes excess reds from flesh tones, we’ll leave it enabled at the default value. The “Brighter whites” option increases the blue value of video for brighter shades of white, but we’ll disable this option because we find it can cause overexposure problems when combined with the dynamic contrast feature.
[EDIT: We’ve set “Dynamic range” to “Limited” to keep things on an even keel with the GeForce cards that default to this value when other enhancements are enabled. Dynamic range doesn’t appear to have an impact on HQV scoring, but the Full setting does provide a wider range of brightness between white and black if it's appropriate for your display. Most televisions expect a 16-235 signal range, while monitors expect a 0-255 range. Choosing an inappropriate range can cause a loss of contrast, but we didn't experience any contrast issues that would affect scoring during our tests.]
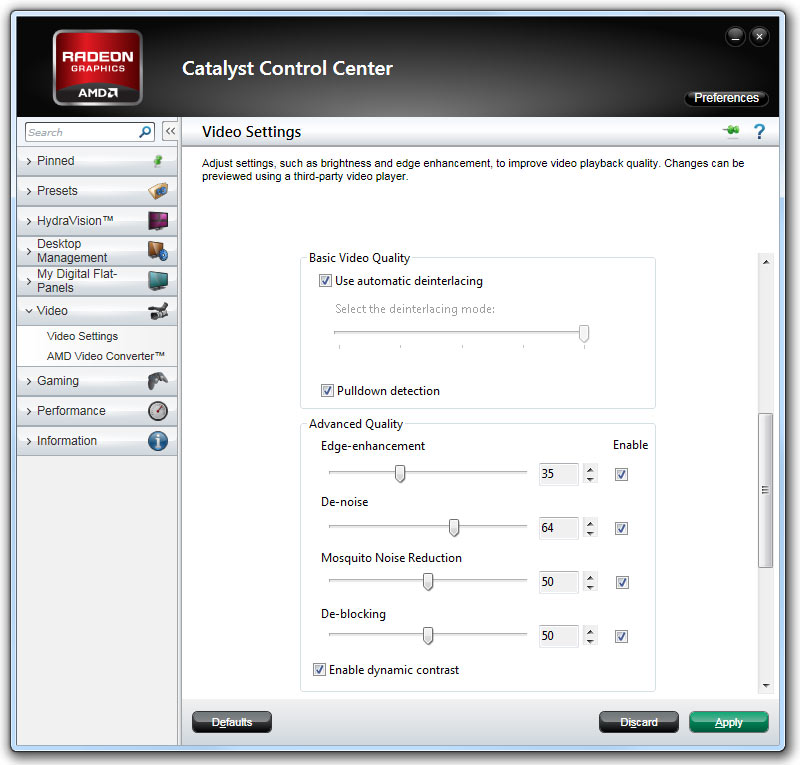
The Basic Video Quality section is just below. We want to make sure that “Use automatic deinterlacing” and “Pulldown detection” are both enabled. Automatic deinterlacing should smooth out the jaggies we’d otherwise see between fields of video playback, and pulldown detection converts videos of various frame rates into 30 frames per second (FPS) video for smooth playback.
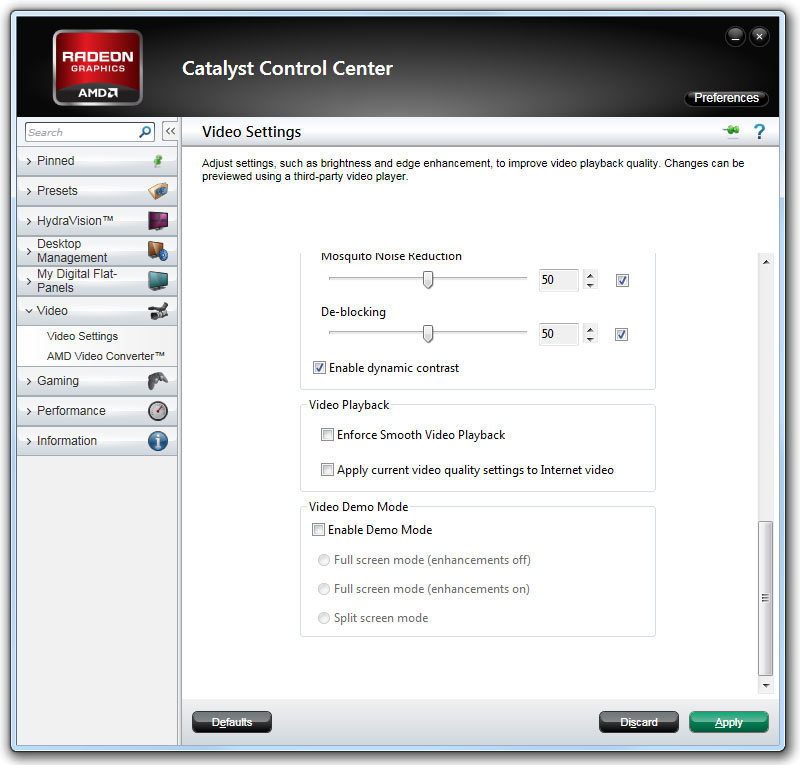
The Advanced Quality section contains a lot of the more powerful toys. “Edge enhancement” can actually take blurry or lower-resolution video and sharpen the detail. “De-noise” is the next setting, which removes random noise from images and can make lower-quality recordings appear clearer by taking out some of the gritty imperfections. “Mosquito Noise Reduction” and “De-blocking” are optimizations designed to remove imperfections in highly compressed video. The former reduces the look of blotchy edges, and the latter smoothes images and decreases unwanted edges. Finally, the “Enable dynamic contrast” option automatically adjusts gamma and contrast to enhance clarity and color vibrance in scenes that are overly bright or dim.
In the video playback section there are only two options. The first is “Enforce Smooth Video Playback.” Enabling it prevents dropped frames by disabling some of the processor-intensive options we’ve just pointed out above. For today’s tests, we’ll disable this feature, as we want to make sure the graphics cards can handle the options we’ve set. But for actual movie playback, it might be a good idea to leave this option enabled if you have lower-end hardware. The next option is “Apply current settings to Internet video,” something you may very well want to enable if you want your YouTube clips to benefit from the quality enhancements we’re discussing.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The final section is called Video Demo Mode, and its only purpose is to allow the user to see the difference that these video enhancements can provide. While you can certainly play with the feature to see what the video hardware can do, it’s not something you need to enable during regular playback.
Now let's move on to the settings we used with each Radeon graphics card we tested. As mentioned previously, low-end cards may have all of the options available, but they can’t handle smooth playback with the complete suite enabled. We’ve tested the cards at the settings we list below to ensure that they can manage 1080p playback with the best quality possible.
| Radeon HD 5450: Video Quality Settings As Tested | |
|---|---|
| Color vibrance: | 40 |
| Flesh tone correction: | 50 |
| Video Gamma: | Disabled |
| Brighter whites: | Disabled |
| Dynamic range: | Limited |
| Use automatic deinterlacing: | Enabled |
| Pulldown detection: | Enabled |
| Edge enhancement: | Disabled |
| De-noise: | 80 |
| Mosquito noise reduction: | N/A |
| De-blocking: | N/A |
| Dynamic contrast: | Disabled |
| Enforce smooth playback: | Disabled |
While the Radeon HD 5450 has the “Edge enhancement” and “Enable dynamic contrast” options available, we find that it isn’t able to provide smooth playback with these turned on. Fortunately, the card is able to handle a de-noise value of 80, which helps smoothing out regular noise, in addition to compression artifacts, despite its lack of “Mosquito Noise Reduction” and “de-blocking” settings.
| Radeon HD 5550: Video Quality Settings As Tested | |
|---|---|
| Color vibrance: | 40 |
| Flesh tone correction: | 50 |
| Video Gamma: | Disabled |
| Brighter whites: | Disabled |
| Dynamic range: | Limited |
| Use automatic deinterlacing: | Enabled |
| Pulldown detection: | Enabled |
| Edge enhancement: | 35 |
| De-noise: | 80 |
| Mosquito noise reduction: | Disabled |
| De-blocking: | Disabled |
| Dynamic contrast: | Disabled |
| Enforce smooth playback: | Disabled |
The Radeon HD 5550 uses the same options as the 5450, but can also handle “Edge enhancement,” an option we think works best when set to 35. Note that the 5550 exposes “Mosquito Noise Reduction” and “De-blocking” enhancements in the driver, but our testing suggests the card is not fast enough to enable them during testing without performance compromises.
| Radeon HD 5670: Video Quality Settings As Tested | |
|---|---|
| Color vibrance: | 40 |
| Flesh tone correction: | 50 |
| Video Gamma: | Disabled |
| Brighter whites: | Disabled |
| Dynamic range: | Limited |
| Use automatic deinterlacing: | Enabled |
| Pulldown detection: | Enabled |
| Edge enhancement: | 35 |
| De-noise: | 80 |
| Mosquito noise reduction: | Disabled |
| De-blocking: | 50 |
| Dynamic contrast: | Enabled |
| Enforce smooth playback: | Disabled |
The Radeon 5670 is powerful enough for us to enable “De-blocking” and “Dynamic contrast,” but “Mosquito Noise Reduction” proves too much for the card to handle. The de-blocking setting doesn’t seem to make a noticeable difference in lowering compression artifacts, but dynamic contrast will help the 5670 gain points in the benchmark.
| Radeon HD 5750 and 6850: Video Quality Settings As Tested | |
|---|---|
| Color vibrance: | 40 |
| Flesh tone correction: | 50 |
| Video Gamma: | Disabled |
| Brighter whites: | Disabled |
| Dynamic range: | Limited |
| Use automatic deinterlacing: | Enabled |
| Pulldown detection: | Enabled |
| Edge enhancement: | 35 |
| De-noise: | 64 |
| Mosquito noise reduction: | 50 |
| De-blocking: | 50 |
| Dynamic contrast: | Enabled |
| Enforce smooth playback: | Disabled |
The Radeon HD 5750 is the lowest-priced Radeon that can handle all of the driver’s video enhancements without choking up playback. With “Mosquito Noise Reduction” enabled, we can reduce the basic “De-noise” value to 64 and still get the highest benchmark score possible for Radeon cards. Note that the Radeon HD 6850 uses the equivalent settings and delivers the same HQV benchmark score.
Current page: AMD Video Quality Driver Settings
Prev Page How Do We Scrutinize High-Definition Video Quality? Next Page Nvidia Video Quality Driver SettingsDon Woligroski was a former senior hardware editor for Tom's Hardware. He has covered a wide range of PC hardware topics, including CPUs, GPUs, system building, and emerging technologies.
-
jimmysmitty I second the test using SB HD graphics. It might be just an IGP but I would like to see the quality in case I want to make a HTPC and since SB has amazing encoding/decoding results compared to anything else out there (even $500+ GPUs) it would be nice to see if it can give decent picture quality.Reply
But as for the results, I am not that suprised. Even when their GPUs might not perform the same as nVidia, ATI has always had great image quality enhancements, even before CCC. Thats an area of focus that nVidia might not see as important when it is. I want my Blu-Ray and DVDs to look great, not just ok. -
compton Great article. I had wondered what the testing criteria was about, and Lo! Tom's to the rescue. I have 4 primary devices that I use to watch Netflix's streaming service. Each is radically different in terms of hardware. They all look pretty good. But they all work differently. Using my 47" LG LED TV I did an informal comparison of each.Reply
My desktop, which uses a 460 really suffers from the lack of noise reduction options.
My Samsung BD player looks less spectacular that the others.
My Xbox looks a little better than the BD player.
My PS3 actually looks the best to me, no matter what display I use.
I'm not sure why, but it's the only one I could pick out just based on it's image quality. Netflix streaming is basically all I use my PS3 for. Compared to it, my desktop looks good and has several options to tweak but doesn't come close. I don't know how the PS3 stacks up, but I'm thinking about giving the test suite a spin.
Thanks for the awesome article. -
cleeve Reply9508697 said:Could you give the same evaluation to Sandy Bridge's Intel HD Graphics?.
That's Definitely on our to-do list!
Trying to organize that one now.
-
lucuis Too bad this stuff usually makes things look worse. I tried out the full array of settings on my GTX 470 in multiple BD Rips of varying quality, most very good.Reply
Noise reduction did next to nothing. And in many cases causes blockiness.
Dynamic Contrast in many cases does make things look better, but in some it revealed tons of noise in the greyscale which the noise reduction doesn't remove...not even a little.
Color correction seemed to make anything blueish bluer, even purples.
Edge correction seems to sharpen some details, but introduces noise after about 20%.
All in all, bunch of worthless settings. -
killerclick jimmysmittyEven when their GPUs might not perform the same as nVidia, ATI has always had great image quality enhancementsReply
ATI/AMD is demolishing nVidia in all price segments on performance and power efficiency... and image quality.
-
alidan killerclickATI/AMD is demolishing nVidia in all price segments on performance and power efficiency... and image quality.Reply
i thought they were loosing, not by enough to call it a loss, but not as good and the latest nvidia refreshes. but i got a 5770 due to its power consumption, i didn't have to swap out my psu to put it in and that was the deciding factor for me. -
haplo602 this made me lol ...Reply
1. cadence tests ... why do you marginalise the 2:2 cadence ? these cards are not US exclusive. The rest of the world has the same requirements for picture quality.
2. skin tone correction: I see this as an error on the part of the card to even include this. why are you correcting something that the video creator wanted to be as it is ? I mean the movie is checked by video profesionals for anything they don't want there. not completely correct skin tones are part of the product by design. this test should not even exist.
3. dynamic contrast: cannot help it, but the example scene with the cats had blown higlights on my laptopt LCD in the "correct" part. how can you judge that if the constraint is the display device and not the GPU itself ? after all you can output on a 6-bit LCD or on a 10-bit LCD. the card does not have to know that ... -
mitch074 "obscure" cadence detection? Oh, of course... Nevermind that a few countries do use PAL and its 50Hz cadence on movies, and that it's frustrating to those few people who watch movies outside of the Pacific zone... As in, Europe, Africa, and parts of Asia up to and including mainland China.Reply
It's only worth more than half the world population, after all. -
cleeve mitch074"obscure" cadence detection? Oh, of course... Nevermind that a few countries do use PAL and its 50Hz cadence on movies...Reply
You misunderstand the text, I think.
To clear it up: I wasn't talking about 2:2 when I said that, I was talking about the Multi-Cadence Tests: 8 FPS animation, etc.