Intel Core i5-8400 Review: Six Cores On A Budget
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
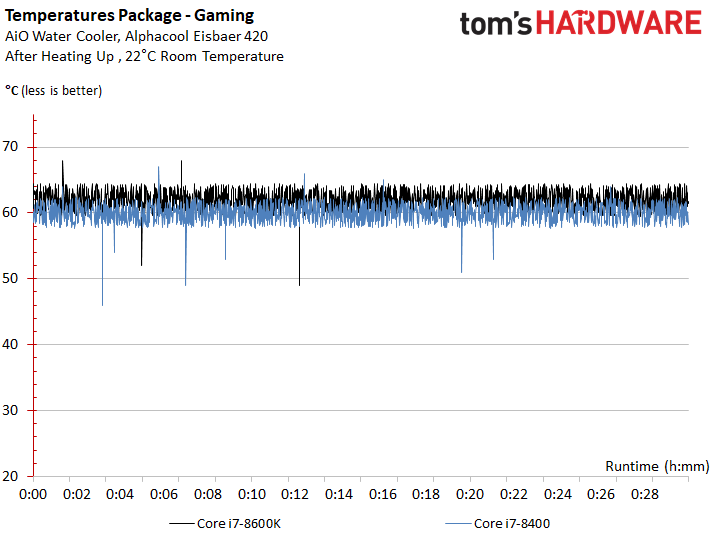
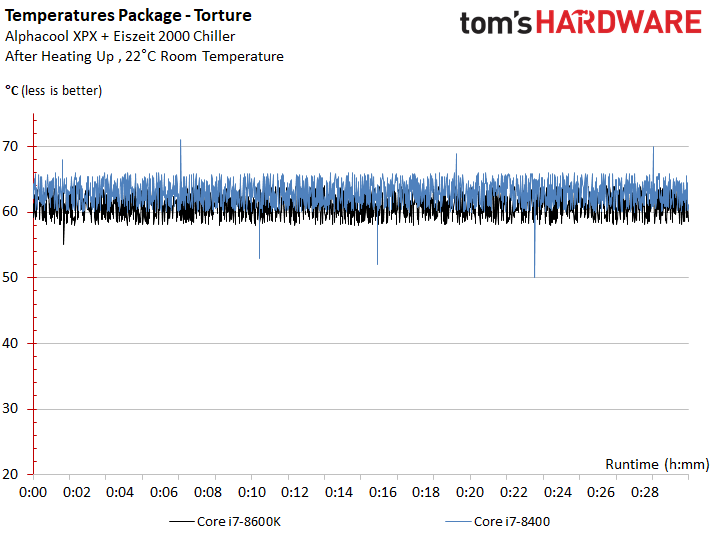
Cooling & Temperature
Power Consumption In Detail
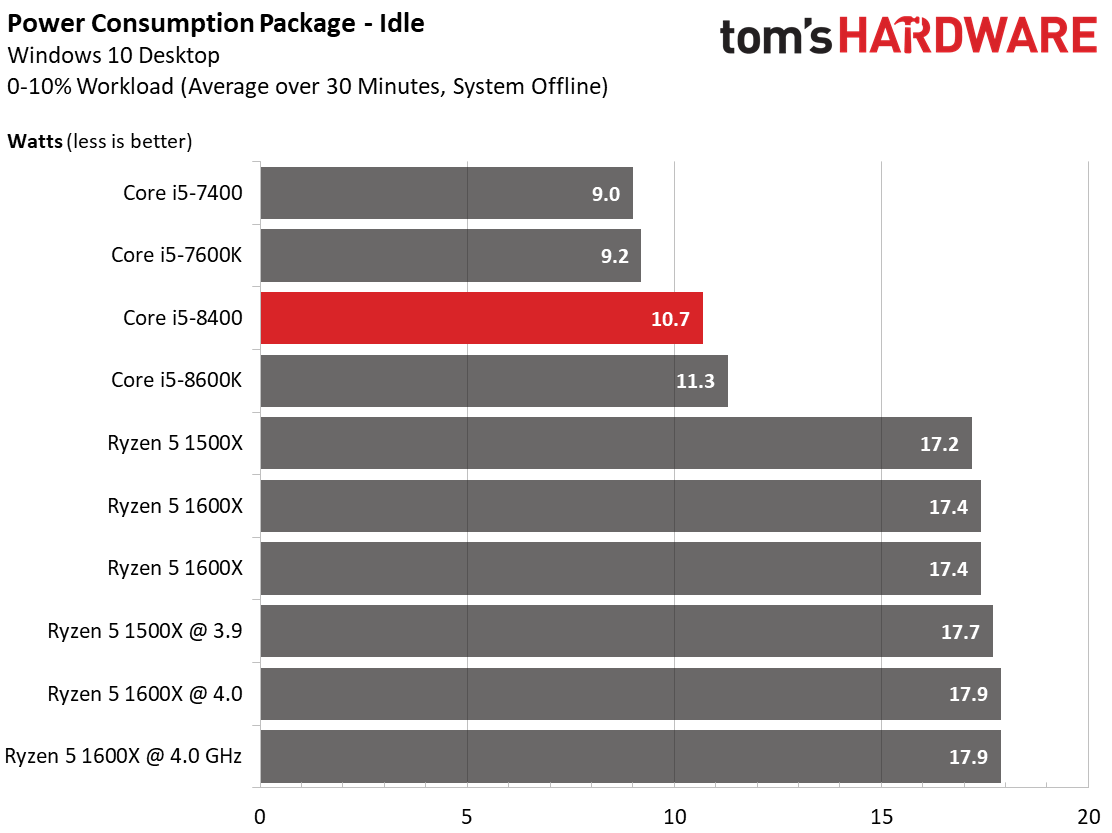
At idle, the differences in power consumption between Intel's CPUs are fairly marginal. All of them end up just about where we'd expect.
AMD's Ryzen processors draw significantly more power because their idle clock rates are higher.
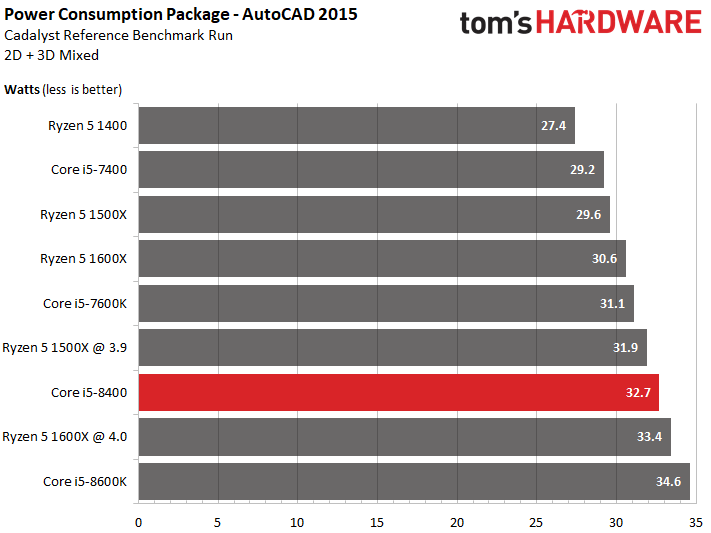
Core i5-8400's average power consumption in applications that combine 2D and 3D loads (like AutoCAD) is in line with the performance we observed.
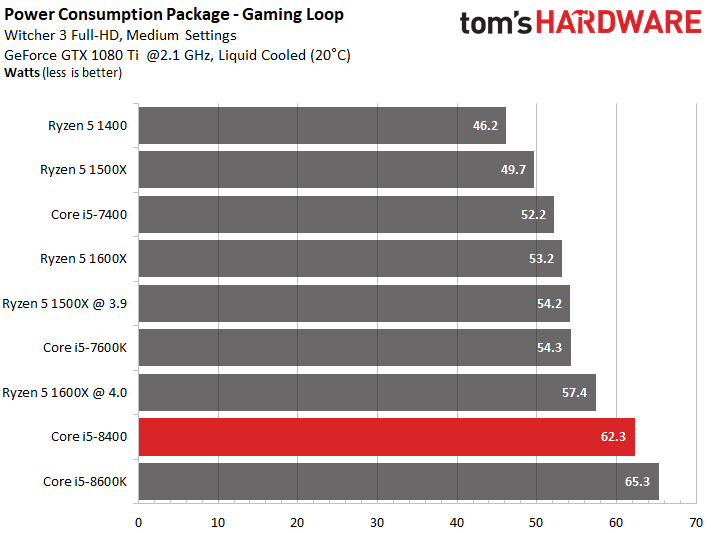
Gaming paints a more balanced, but very similar picture.
Intel's Core i5-8400 falls squarely within its TDP class.
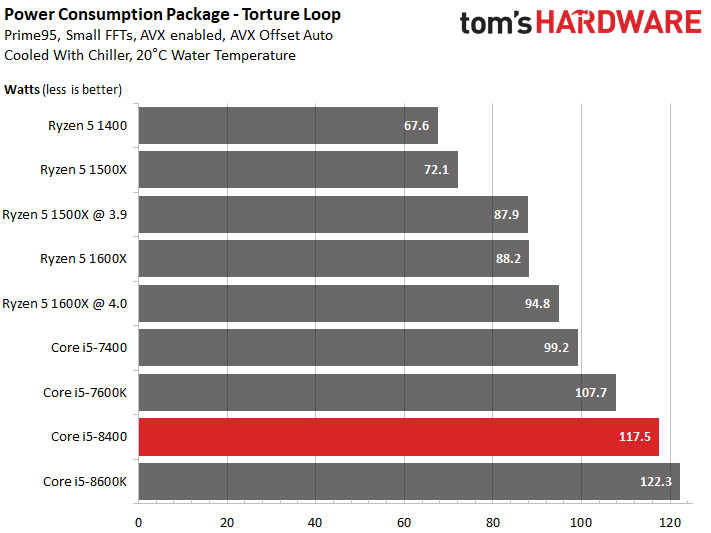
The finishing order changes dramatically once we fire up an AVX-heavy stress test with all cores running at their top Turbo Boost bins.
This benchmark breaks Intel's rated TDP if the motherboard doesn't quickly rein in power consumption. Otherwise, Core i5-8400 hits values well above its thermal design power, as illustrated in our chart.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Temperatures
Core i5-8400 can easily be cooled by a heat sink/fan or compact closed-loop liquid cooler, despite Intel's continued use of thermal paste between the die and heat spreader.
Pricier thermal solutions offer little advantage in cooling Core i5-8400. This is illustrated by the high delta between Intel's die and IHS, which results from that thermal paste the company uses.
The Core i5-8400 is relatively easy to cool, even with a standard heat sink and fan.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Cooling & Temperature
Prev Page CPU Computing & Rendering Performance Next Page Final Analysis
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
velocityg4 I'd be interested in knowing. Under what circumstances can you get it to hit 3.8Ghz reliably under a 6-core load? That is quite a spread.Reply
If one was to delid the CPU and use a decent CPU cooler. Would it reliably maintain the max turbo boost when the CPU usage demands it? Is the stock heatsink and decent case cooling plenty?
On another note. It is time for the return of the Turbo button. That would be pretty sweet to click the button and manually have the CPU jump between 1, 2, 4 and 6 cores at their respective boost frequencies or down to standard. I know it isn't necessary as it is all automated and that wasn't the purpose of the Turbo button. Some people just like manual control. Plus old time computer geeks would get a kick out of it. -
AgentLozen This is a very neat chip at it's price point. Very little has changed between Kaby Lake and Coffee Lake except for the core count. Luckily for Intel, those added cores make all the difference.Reply
This CPU would sit nicely on a budget system. It's a shame that there are no inexpensive motherboards that it could fit into like the conclusion of this article states.
If you didn't plan to overclock, this is the best CPU on the market for gaming and general productivity. -
The_King We have AMD to thank for all these budget cpu's from Intel, and you all know why! So thank you AMD.Reply -
rwinches No, you can't have charts based on FPS or seconds or related to MSRP. Drivers update, Prices change, Memory Speeds Increase and price lowers, MB prices are wide range.Reply
It is known that Some games work better for AMD when AMD GPUs are used. Game FPS can be dramatically improved by changing just one parameter. Test results that are milliseconds or a few seconds or frames faster are irrelevant and subject to variations in real world use on systems that are not clean installs and have other SW installed and running. -
10tacle Reply20307991 said:No, you can't have charts based on FPS or seconds or related to MSRP. Drivers update, Prices change, Memory Speeds Increase and price lowers, MB prices are wide range.
I don't understand your point. This is a review of the 8400 and comparing it to other CPUs only. Memory, motherboards, and all the other variables are you talking about in a full PC build are irrelevant to this chart comparison. They have to establish a constant standard across the spectrum, and they did so.
20307991 said:It is known that Some games work better for AMD when AMD GPUs are used. Game FPS can be dramatically improved by changing just one parameter. Test results that are milliseconds or a few seconds or frames faster are irrelevant and subject to variations in real world use on systems that are not clean installs and have other SW installed and running.
Again, they are using a single standard across the spectrum comparison. Of course there are infinite combinations of hardware that can game change a little. The bottom line here is that among every major tech review website, all of Intel's chips are better for gaming than Ryzen. The only exception is when dealing with beyond 1080p gaming like QHD or UHD where it's mostly on the GPU. People who buy this chip are the perfect candidate for a 144Hz 1080p G-sync or Freesync monitor.
-
elbert Compared to the Ryzen 1600 with a B350 its $50 higher. That is a higher video card level. IE get the 8400 with a 1050ti the Ryzen budget would get a 1060 3GB. Intel needs their B360 motherboards for the 8100 and 8400 to ever be a budget winner.Reply -
hardwarefox1234 Has the author even bothered to look at the street prices for the CPUs??Reply
Core i5 8400:
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?Item=9SIA7HN6HF3442&cm_re=i5_8400-_-9SIA7HN6HF3442-_-Product
http://www.microcenter.com/product/486090/core_i5-8400_coffee_lake_28_ghz_lga_1151_boxed_processor
http://www.ncixus.com/products/?sku=142465&vpn=BX80684I58400&manufacture=Intel
The lowest price is $249.99!
The Ryzen 5 1600 is much cheaper:
https://www.newegg.com/Product/Product.aspx?Item=N82E16819113435&cm_re=ryzen_5_1600-_-19-113-435-_-Product
http://www.microcenter.com/product/478826/Ryzen_5_1600_32GHz_6_Core_AM4_Boxed_Processor_with_Wraith_Spire_Cooler
http://www.ncixus.com/products/?sku=139481&vpn=YD1600BBAEBOX&manufacture=AMD
https://www.amazon.com/AMD-Processor-Wraith-Cooler-YD1600BBAEBOX/dp/B06XNRQHG4/ref=sr_1_3?s=pc&ie=UTF8&qid=1508952175&sr=1-3&keywords=ryzen+5+1600
Price is $199.99~$219.99!
Then if you add the price of the B350 motherboards,they start at a lower level than the Z370 ones. -
hixbot Why did you label section 10, overclocking, cooling and temperature? There's no overlocking on this chip? I would have like to see at least an attempt at Bclk overlcock with a mobo that has a clock generator.Reply -
TJ Hooker I really wish more reviewers would look at what sort of boost clocks the i5 8400 can sustain under load, with the stock cooler as well as aftermarket. From what I know you could typically assume past Intel CPUs would operate at or near max turbo almost indefinitely, but with a 50% increase in core count and such an unusually wide gap between base and boost clocks (not unlike their mobile CPUs), I'm curious how Coffee Lake will behave in that regard.Reply