Partner Cards: Two Radeon R9 290s And Five 290Xs, Updated
Technical Specifications
All of these cards are based on the same Hawaii GPU manufactured at 28 nm with either 2560 (in the case of the Radeon R9 290) or 2816 (for the Radeon R9 290X) shaders and a 512-bit memory bus. The differences between these cards, aside from their coolers, are limited to the core and memory clock frequencies.
| Radeon R9 290 | GPU Clock MHz(Boost) | Memory ClockMHz | Memory BandwidthGB/s | Pixel FillrateGPixel/s | Texture FillrateGTexel/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sapphire Tri-X OC R9 290 | 1000 | 1300 | 332.8 | 64.0 | 160.0 |
| Gigabyte GV-R929OC-4GD R9 290 Windforce OC | 1040 | 1250 | 320.0 | 66.6 | 166.4 |
| Radeon R9 290 Reference + Arctic Accelero Extreme III | 1100 | 1250 | 320.0 | 70.4 | 176.0 |
| Radeon R9 290 Reference + NZXT Kraken G10 + X40 | 1100 | 1250 | 320.0 | 70.4 | 176.0 |
| Radeon R9 290X | GPU Clock MHz(Boost) | Memory ClockMHz | Memory BandwidthGB/s | Pixel FillrateGPixel/s | Texture FillrateGTexel/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asus R9290X-DC2OC-4GD5 R9 290X DirectCU II OC | 1050 | 1350 | 345.6 | 67.2 | 184.8 |
| Sapphire Tri-X OC R9 290X | 1040 | 1300 | 332.8 | 66.6 | 183.0 |
| Gigabyte GV-R929XOC-4GD R9 290X Windforce OC | 1040 | 1250 | 320.0 | 66.6 | 183.0 |
| HIS R9 290X IceQ X² Turbo | 1060 | 1350 | 345.6 | 67.8 | 186.6 |
| MSI R9 290X Gaming 4G | 1040 | 1250 | 320 | 66.6 | 183 |
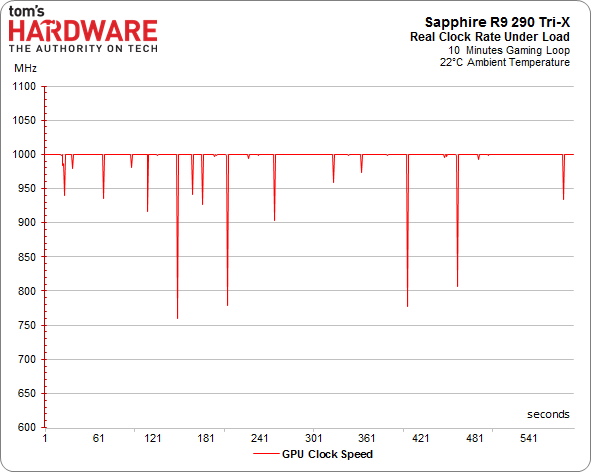
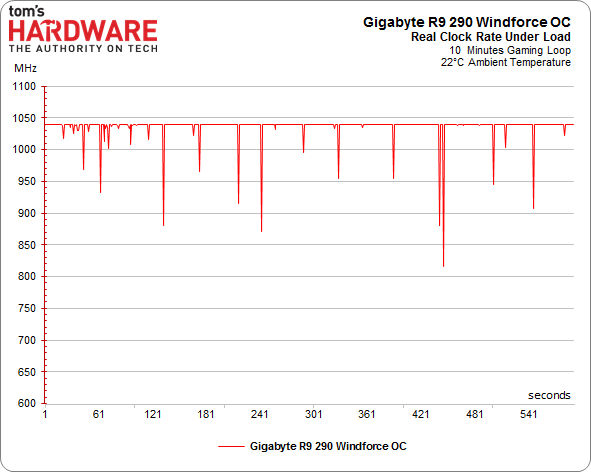
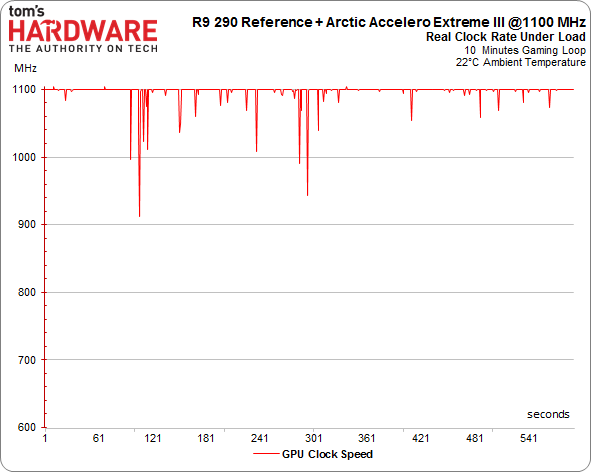
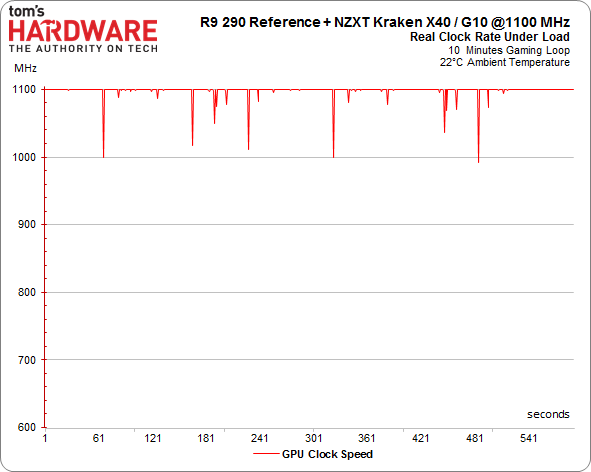
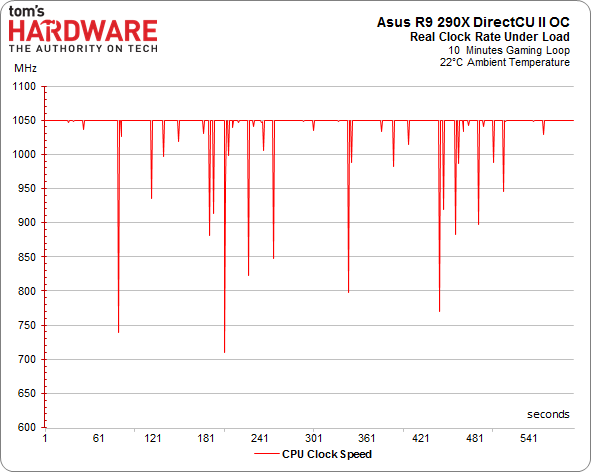
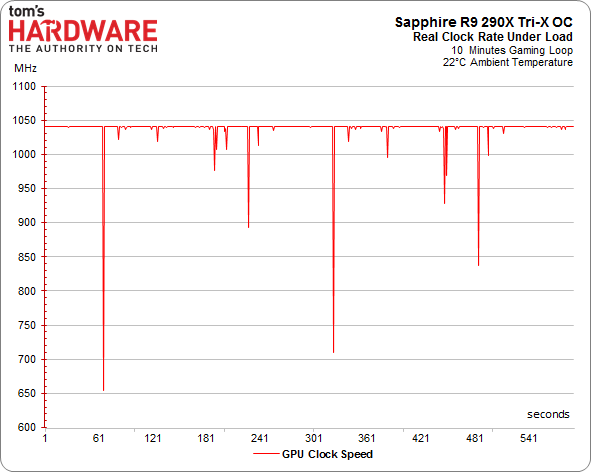
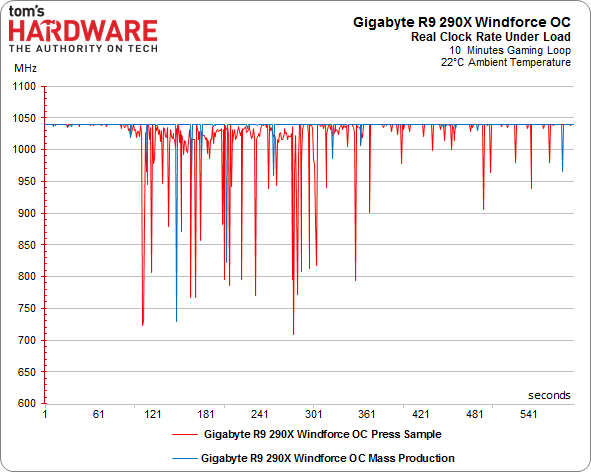
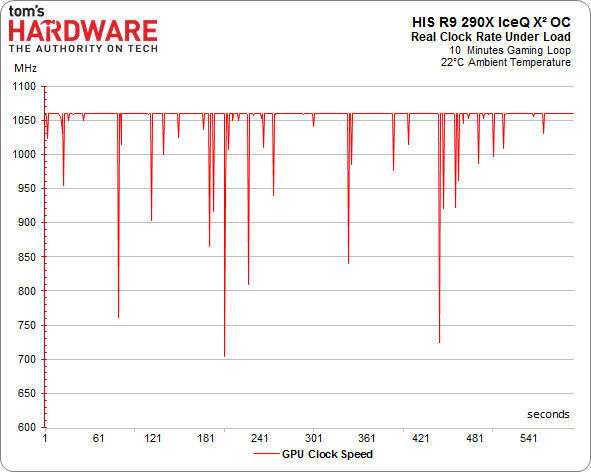
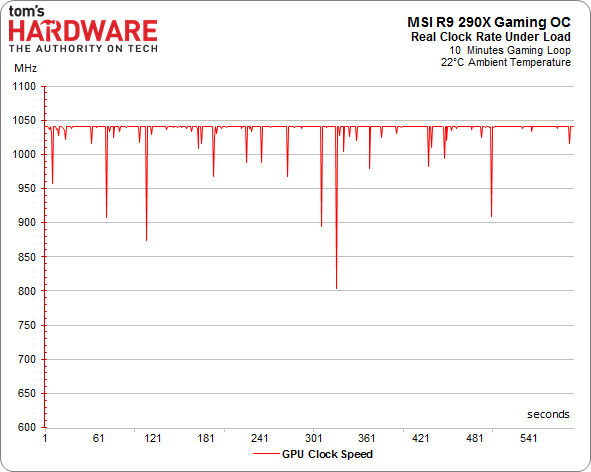
Of course, there’s more to the overall performance story than just the maximum GPU clock rate. As we've already seen, calling your GPU a 1000 MHz part is pointless if it cannot maintain that frequency. This is precisely the problem AMD's reference design suffers from. Once its target temperature is hit, the clock rate starts scaling back and performance follows suit.
We warmed up our various contenders and ran them in a loop while we recorded their frequencies.
R9 290 GPU Clock Frequency
R9 290X GPU Clock Frequency
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Technical Specifications
Prev Page Cooling The Radeon R9 290 And 290X Next Page Dimensions And Weight
Igor Wallossek wrote a wide variety of hardware articles for Tom's Hardware, with a strong focus on technical analysis and in-depth reviews. His contributions have spanned a broad spectrum of PC components, including GPUs, CPUs, workstations, and PC builds. His insightful articles provide readers with detailed knowledge to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape
-
yannigr You can write as many articles as you want about 290/290X coolers. You can write as many excuses as you want. You can continue reminding us that there was/is a problem with Hawaii every 15 days for the whole 2014. That "victory dance" that "excitement" that you found(?) AMD cheating(?) back then, all that rage against AMD, can not be unwritten.Reply -
FormatC Replyall that rage against AMD
I would like to know this more precisely please... I can't found any rage in my articles, only a chip with a very high temperature density and a lot of unusable coolers because the engineers were not able to build a matching cooler for this cards. This high density will be a global problem for all next-gen chips too. Without a vapor chamber this won't work. -
outlw6669 Good job on the review Tom's German team and great work from AMD's partners!Reply
Coupled with other recent reviews, Sapphire's Tri-X OC series looks to be great cards, especially when you make a custom fan curve to further reduce idle and load noise.
I can not wait to see the 20nm updates, especially if AMD gets around to pulling a Titan with their reference coolers! -
FormatC I will add in the next days more cards like Gigabyte's R9 290 (without X), the MSI R9 290X and something other (secret) :)Reply -
rdc85 I think this card is made/means to be WC -ed..... 290 in Kraken looks promising.. (trying imagine how good if in full water block, good radiator)Reply -
roymustang The main problem with the 290 and 290X isn't the cooling, it's the fact that bitcoin and litecoin miners have driven the price of these cards up by $100-150; to the point where they are no longer a good deal at all.I was waiting for the custom cooled 290s to come out to upgrade my GTX 670 but now I may just wait for the next cards and maybe stick with nVidia.Reply -
Phillip Wager i want so badly the 290 to go back to 400 bucks cuz that is like my hard limit on a video card ive been waiting but i don't think i can wait much longer and i guess i'll just get a 770. i'm even willing to put up with the reference coolers bah.Reply -
patrick47018 "You can see this in the image below, where two of the heat pipes don't **tough** Hawaii at all, and two others make partial contact. " Spelling mistake, on topic I like the Sapphire Toxic's design and performance.Reply