Samsung 950 Pro 256GB RAID Report
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Mixed Workloads And Steady State
Comparison Products
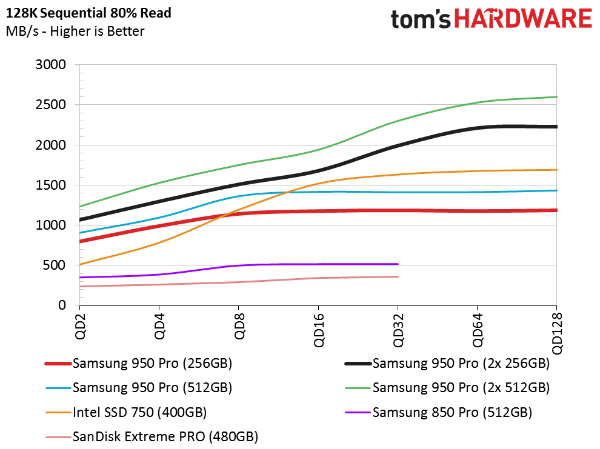
Sequential Mixed Workload Performance
Benchmarking mixed workloads gives us a better look at more real-world applications of storage. If you feel you need what NVMe has to offer, then there's a good chance you multitask. RAID gives you a higher ceiling under these conditions...providing you have a workload able to exploit it.
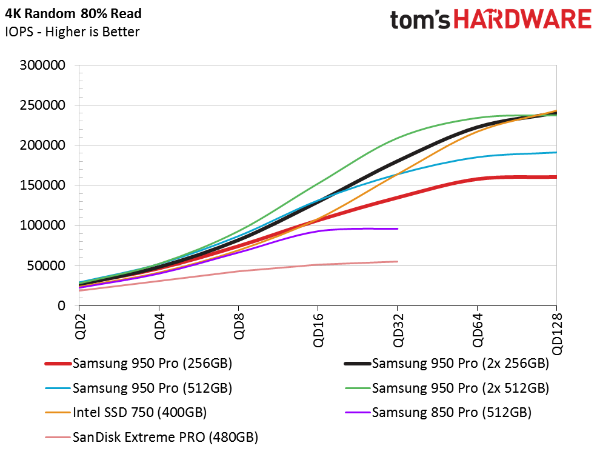
Random Mixed Workload Performance
Again, we see that RAID 0 doesn't give us much of an advantage at low queue depths. The NVMe-based drives even have a hard time pulling away from today's best SATA-based SSDs.
That leaves us with better performance only in sequential workloads.
Sequential Steady State Performance
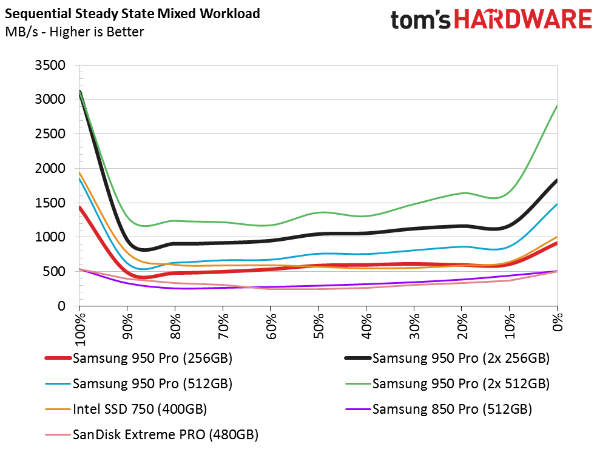
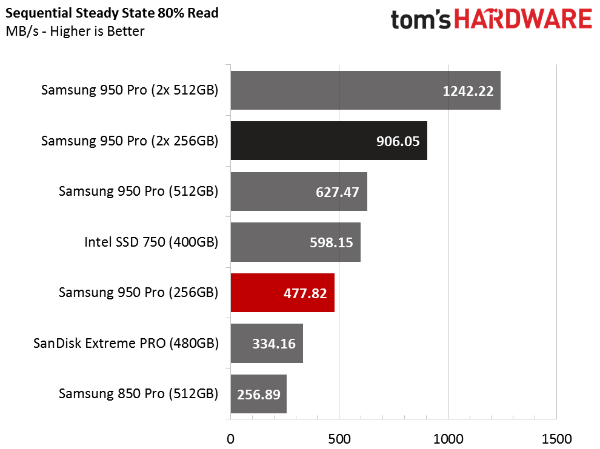
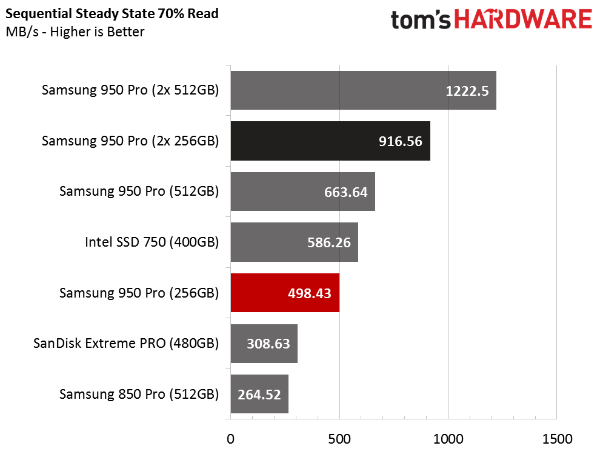
The speed-up in sequential transfers carries over to SSDs in steady state. Given these results, it's safe to say you'll see gains in any read/write mix, so long as the operations are sequential in nature. If your primary application is audio and video editing, RAID is a good way to trim your render times (provided storage is your bottleneck).
Random Steady State Performance
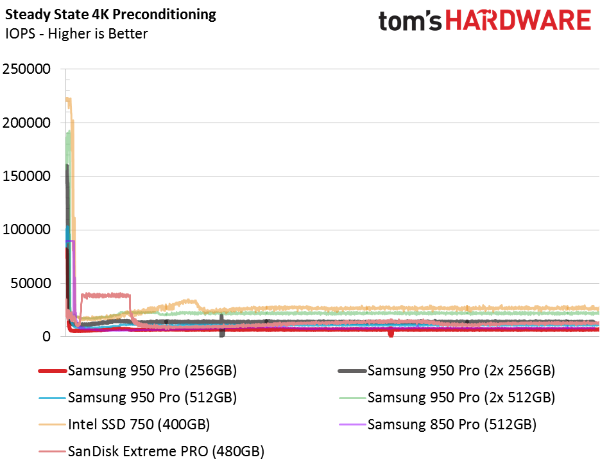
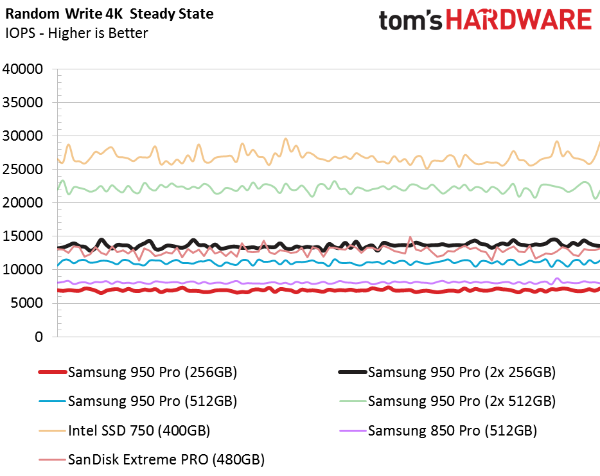
We rarely get a chance to show how random 4KB writes in steady state carry over to RAID 0 arrays. With each doubling of drive count, any performance inconsistencies also double. That's why, in this test, we look for drives without large peaks or valleys to call out as potential champions in multi-drive configurations.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Mixed Workloads And Steady State
Prev Page What Is RAID And Initial Performance Testing Next Page Real World Software Performance Testing
Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
USAFRet Reply17700323 said:Why do you expect gains in video games when everything relevant is loaded in RAM?
A lot of people do.
Assuming that the performance gains we saw with spinning disks in RAID 0 automagically does the same with SSD's. It does not. -
Tibeardius Did it have any sort of thermal throttling occur? These pcie m.2 drives can get pretty hot.Reply -
Integr8d "Once upon a time, you could sling a couple of Western Digital Raptors together, fire up a level in Battlefield 2 before anyone else, get the plane and dominate the map."Reply
Someone just explained 24 months of my life:) -
HT ReplyWhy do you expect gains in video games when everything relevant is loaded in RAM?
that's the point of faster drives, loading it all in ram. do you think it magically appears there by itself ? -
HT good article Chris, i'm intrigued by your statement of the samsung driver vs the M$ one, i would've liked to see some numbers comparing the two.Reply -
Virtual_Singularity Interesting article. Also: am a lil' dumbfounded at how much the price of the 850 pro series has dropped since the holidays, a mere 3+ months ago...Reply