Thecus W5000 WSS NAS Review
Low-cost Windows Storage Servers (WSS) give small businesses access to enterprise-class features at a desktop price.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
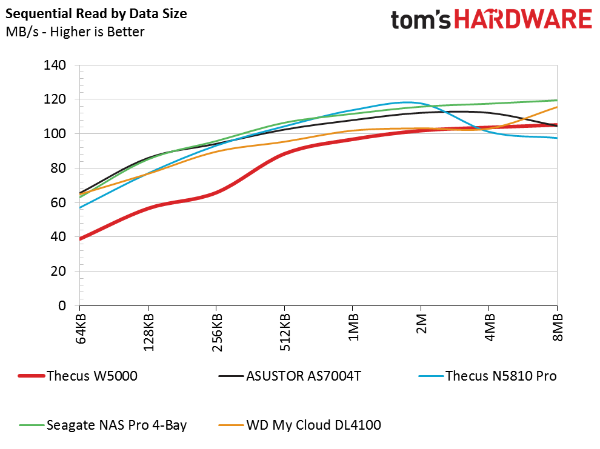
Sequential Data Transfer By Size
Thecus' W5000 delivers acceptable sequential read performance at larger block sizes. However, the system trails its competition, including Seagate's NAS Pro and Western Digital's My Cloud DL4100, both of which also employ low-power Atom processors.
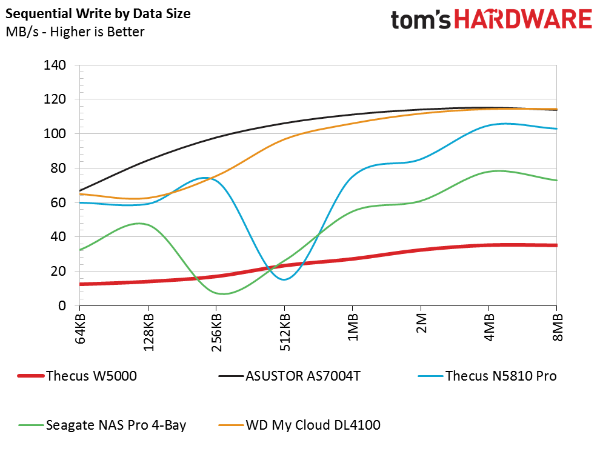
Windows Storage Spaces won't give you the same level of performance as hardware RAID, FreeBSD or Linux-based operating systems. As an example, I recently built a large dual-Xeon server with 32 mixed SSDs and hard drives. In Windows, its write speed hovers around 700 MB/s. And once it's outside of buffers and cache, performance drops to less than 100 MB/s. In Linux, the same hardware delivers over 2000 MB/s. WSS suffers a real performance deficit when writing data.
In today's test, we see that same low sequential write performance outside of the buffers. Our benchmark takes place after the system has exhausted its cache, so we see real disk performance in RAID 5 built using Storage Spaces.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Sequential Data Transfer By Size
Prev Page Software Interface Next Page Random Data Transfer By Size
Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
Deuce65 "Low-cost Windows Storage Servers (WSS) give small businesses access to enterprise-class features at a desktop price."Reply
Um, is this a hardware review or a press release? -
Travis Hershberger While many people may actually use RAID 5 with this device, this is what we call professional malpractice among IT pros.Reply
Ref: http://www.smbitjournal.com/2012/11/one-big-raid-10-a-new-standard-in-server-storage
http://www.smbitjournal.com/2012/11/choosing-raid-for-hard-drives-in-2013
http://www.smbitjournal.com/2012/11/choosing-a-raid-level-by-drive-count
http://www.smbitjournal.com/2013/06/dreaded-array-confusion
http://www.zdnet.com/blog/storage/why-raid-6-stops-working-in-2019/805
http://www.zdnet.com/blog/storage/why-raid-5-stops-working-in-2009/162 -
CRamseyer You need to understand a couple of things about all of those articles. The articles are not talking about your home or small business NAS with four or five drives to start with. The ZDNET author has a history of writing articles and article titles to bring people in. Many disagree with Robin's findings. I wouldn't say that is the case with the only article that relates to this review though, Why RAID 5 Stops Working in 2009. In that article he references a 7-drive RAID 5 array. With 6 or more drives we use RAID 6 (RAID 10 in some cases) for the very reason he cites. With five drives and in a home or small business environment RAID 5 is sufficient as long as you are proactive. Keep the system on a battery backup, keep air vents fee of dust and if a drive fails replace it right away.Reply
Some users may want to take redundancy to the next level and run RAID 6 on a 5 drive array. That is fine and I know people that do. I don't recommend it on a sub-1000 Dollar system that already has performance issues with RAID 5 though. -
Marco Ullasci "We rarely hear of failures in the field"Reply
Here I am.
"In our own experience, NAS failures come from easy-to-replace fans and power supplies, rather than the main components that make up the heart of the system."
Changed power supply and changed fan but still no fun.
I had to dump my DS411Slim after putting some € on it in an attempt to fix.
The brown thing happens.


