AM2: AMD Reinvents Itself
Evaluating The Benchmark Scores
Athlon 64 FX: No Overclocking Facility
The Athlon 64 FX-62 is the new king of benchmarks. With its two cores both clocked at 2.8 GHz, the DDR2 memory interface develops its full potential, and with this CPU can deliver performance far better than its predecessor (the FX-60 with DDR1 memory).
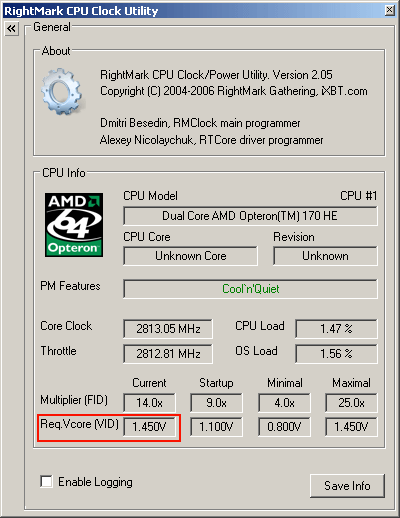
As we're used to from the FX series, the multiplier can be set at the top and bottom of the scale, although the CPU in our test only let us overclock it by 200 MHz to 3 GHz - this is where the limits of the 90 nm production process are revealed. Another indication that the production process currently in use can no longer really deliver the goods is the fact that AMD had to raise the power supply to the core to achieve the figure of 2.8 GHz. This is what has caused the dramatic leap in dissipation from 110 to 125 W.
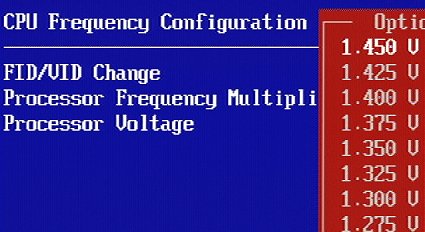
The motherboard recognizes the processor voltage automatically.
Our specimen of the Athlon 64 FX-62 has a supply voltage of 1.45 V.
Comparing the supply voltages specified by AMD between all dual-core processors, it becomes clear that the Athlon 64 FX-62 operates at a 3.7% higher voltage. With current of 90.4 amperes, a 5 watt difference results.
Athlon X2 series: 1.30 V - 1.35 V
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Athlon FX series: 1.35 V - 1.4 V
Note that the second digit after the decimal point in the 1.4 V figure is not specified by AMD in its datasheets.
At a street price of around $1200, the FX-62 is the most expensive desktop CPU currently available. It is around $200 more costly than Intel's top model, the Pentium Extreme Edition 965, and the latter is definitely worth the money for its high performance.
The FX-62 is the CPU to go for if you want the fastest CPU available on the market and don't want to overclock.
Current page: Evaluating The Benchmark Scores
Prev Page Synthetic Benchmarks, Continued Next Page Athlon 64 X2: Now Somewhat SlowerTom's Hardware is the leading destination for hardcore computer enthusiasts. We cover everything from processors to 3D printers, single-board computers, SSDs and high-end gaming rigs, empowering readers to make the most of the tech they love, keep up on the latest developments and buy the right gear. Our staff has more than 100 years of combined experience covering news, solving tech problems and reviewing components and systems.