ATi Radeon 9700 PRO - Pretender To The Throne
The Radeon 9700 PRO, Continued
A large fan cools the 0.15 micron chip with over 100 million transistors.
Thanks to its 256 bit-wide DDR interface, the R300's memory bandwidth is almost twice as high at any given clock speed. In addition, the chip is already DDR-II capable, meaning we may see a new revision of R300-based cards using this faster memory.
ATi has also tweaked and refined the Radeon product line's rendering optimizations with Hyper-Z III. You can find more information about what this technology actually does in the previous technology article . The advantage of an 8x AGP bus seems to be of a more theoretical nature at this point. There just aren't any games at present that would come anywhere near needing this kind of bandwidth, much less saturating it.
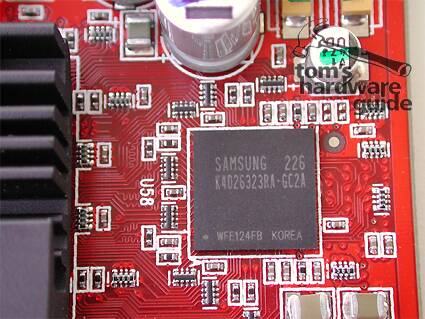
The 256 bit DDR memory with a BGA design runs at 310 MHz (620 MHz DDR).
Finally, ATi has also finally addressed the previous Radeons' greatest weakness: the extremely low performance when using the function for smoothing edges (FSAA). Instead of the slow supersampling method, the 9700 now employs the much faster multisampling technique, which is similar to NVIDIA's implementation. Additionally, the R300's take on multisampling is supposed to include further performance optimizations. Later on in this article, we will take a look at how fast this new method really makes the 9700.
Due to its high power consumption, the Radeon 9700 requires an external power supply, which is provided by the 3.5" cable. The AGP slot would have been overloaded with this task.
2D Features
The R300 has the GeForce4 Ti at a slight disadvantage where 2D features are concerned. The ATi chip carries two 400 MHz RAMDACs that use 10Bit precision internally. This makes the chip fully multi-monitor enabled, just like the NV25. The 165 MHz TMDS transmitter also allows DVI resolutions of up to 2048x1536 (QXGA), while TV-Out works at resolutions up to 1024x768.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
In order to operate two monitors in DualView mode, the Radeon 9700 offers two interfaces: VGA and DVI-I. An adapter plug (included) makes it possible to connect a second CRT monitor to the DVI-I interface. TV-out is located in the middle.
Instead of the conventional hard-coded video optimizations, the pixel shaders now take on the task of filtering video streams. ATi has dubbed this technique "FullStream." Again, we'll talk more about this a bit later on.
Current page: The Radeon 9700 PRO, Continued
Prev Page The Radeon 9700 PRO, Continued Next Page Drivers