Picking The Right Power Supply: What You Should Know
How does a power supply work? Why is it important to choose a sufficiently powerful and efficient model? We guide you through discussions of efficiency and tips for getting the best deal before we go on to explain why less can be more in the PSU market.
How To Spot An Efficient PSU?
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Guidelines, Rules And Regulations
One of the most important indicators of a PSU’s efficiency is whether it complies with the Energy Star 5.0 guidelines, and also if it meets the requirements of an 80 PLUS efficiency level. The latter applies primarily to computer power supplies and is recognized worldwide. Additionally, if you’re located in a European country, CE conformity and compliance with ErP guidelines are noteworthy.
80 PLUS PSUs Are More Efficient
The specifications, norms and guidelines we just mentioned all call for high efficiency, as well as improved power quality. Power supplies that conform to these demanding rules by passing a defined set of tests may then be marked with the 80 PLUS badge appropriate to their efficiency level. While the load/stress tests may not correspond to those defined by the ATX specification, that’s acceptable in this case. Here’s some good news for our European readers: since the tests are conducted using the lower U.S. voltages, these power supplies achieve even higher efficiency levels in the 230V grid.
80 PLUS: Titanium, Platinum, Gold, Silver, Bronze
The original concept of the 80 PLUS certification has been revised, adding new, more strictly-defined efficiency levels. The Bronze, Silver, Gold and Platinum certifications each come with their own requirements. Thus, a PSU certified “80 PLUS Gold” or “80 PLUS Platinum” is more efficient than one that's not. On the other hand, more complex circuitry needed to hit those levels generally results in a higher price tag, too.
Below you’ll find a table that shows what efficiency levels a PSU has to achieve at a given load to make the grade for a specific certification level.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Efficiency at 10% Load | Efficiency at 20% Load | Efficiency at 50% Load | Efficiency at 100% Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 PLUS | - | 80% | 80% | 80% (PF>0.9) |
| 80 PLUS Bronze | - | 82% | 85% (PF>0.9) | 82% |
| 80 PLUS Silver | - | 85% | 88%(PF>0.9) | 85% |
| 80 PLUS Gold | - | 87% | 90%(PF>0.9) | 87% |
| 80 PLUS Platinum | - | 90% | 92%(PF>0.95) | 89% |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | 90% | 92% (PF>0.95) | 94% | 90% |
At first the 80 PLUS organization only certified PSUs with 115V input, however recently it added 230V certifications as well, with increased requirements since energy losses are significantly lower at higher loads with this voltage input. In the table below you will find the 80 PLUS 230V EU Internal certifications.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Efficiency at 10% Load | Efficiency at 20% Load | Efficiency at 50% Load | Efficiency at 100% Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 PLUS | - | 82% | 85% (PF>0.9) | 82% |
| 80 PLUS Bronze | - | 85% | 88% (PF>0.9) | 85% |
| 80 PLUS Silver | - | 87% | 90%(PF>0.9) | 87% |
| 80 PLUS Gold | - | 90% | 92%(PF>0.9) | 89% |
| 80 PLUS Platinum | - | 92% | 94%(PF>0.90) | 90% |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | 90% | 94% (PF>0.95) | 96% | 94% |
When Off Isn't Really Off: A Few Words On Standby Power Consumption
When you shut down your computer, the PSU doesn’t really switch off completely. This is necessary for features such as Wake-on-LAN to work. The point is that the power supply keeps drawing some power (called vampire or phantom power), even when the computer is off. Newer PSUs, especially ones sold in Europe and certified to be ErP/EuP-compliant, draw less than 0.5W in this standby mode. If you’re serious about conserving power, go for a newer model with ErP Lot6 2013 support.
Which Power Rails Are Important?
That brings us to one of the most crucial points of modern power supplies: namely, the power they are able to supply at various voltages. Nowadays, PCs draw the majority of their power from the +12 V rail. By comparison, the other two voltages, 3.3 and 5 V, play a far less important role. That’s why you can use the following as a rule of thumb: if a PSU’s 12V rail can supply all of the required power with room to spare, then the lower voltages are sufficient as well.
However, the opposite is not necessarily the case. Let’s compare the spec stickers of two PSU models:
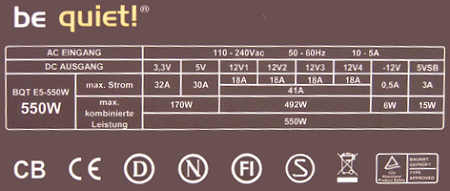
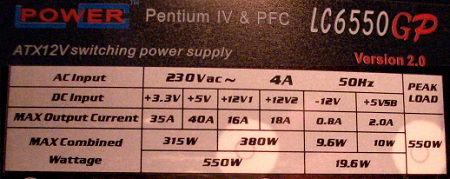
The difference is quite obvious. Although the second model is billed as a 550W unit, its +12 V rails only add up to 380W, and even that only holds true if the other rails aren’t being stressed simultaneously! Nobody needs 315W on the 3.3 and 5 V rails. In practice, this power supply would probably reach its limit at a load of 350W on the 12V rail.
Ironically, even a good 425W PSU could push more power than this model at 12V. Don’t fall for this sort of trickery.
Initial Cost Vs. Energy Savings
Quality products cost more initially, but that doesn’t necessarily always translate into lower cost in the long run. That’s why we’ll take a look at a few specific components and their prices in a moment to determine the type of PSU makes the most sense in a given environment, and what kind of savings you can achieve, if any. Some of the results may surprise you!
It’s not enough to focus solely on the financial aspect, though, because we also have to consider durability, reliability and safety. We go into more detail on these points on the next page.
Current page: How To Spot An Efficient PSU?
Prev Page Of Power Factors, Apparent Power And Effective Power Next Page Don't Get Burned: Safety Before StinginessGet Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
abryant Archived comments are found here: http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/2916-56-picking-power-supply-knowReply -
pjmelect A few more words about active power factor correction. APFC won't save you money on your electric bill although the electric companies will love you for it as it minimizes loss over the power lines saving them money, it does however enable you to use a much lower rated battery backup system. A hypothetical example a computer that uses say 200W without APFC would require a backup system of 700W or much more to cope with the large peaks in current where as a power supply with APFC would require a backup system of 250W or so.Reply
Therefore APFC is only worthwhile if you were to use it with a battery backup system. -
turkey3_scratch Very well written article! Just one thing. You say:Reply
Regardless of whether the PC is idling or under full load, voltages may not deviate from their spec by more than five percent according to the ATX spec.
But the ATX specification seems to disagree. According to the spec, full load or "peak loading" allows 10% deviation from the nominal voltage for the 12V rail.
http://www.formfactors.org/developer/specs/Power_Supply_Design_Guide_Desktop_Platform_Rev_1_2.pdf
Also, Q about the power factor correction. It's probably the most difficult topic to understand. In this case, you say the load would be anything that used power. Are you talking about hardware like a GPU or the internals of the PSU like capacitors and such? Also, say the computer is putting load on the PSU. How is there idle current then? -
jossrik There have been quite a few instances in the past where you could get an XFX PSU 550w or so for 40$ or less with rebates. I know compared to more modern PSUs they may not stack up, but they used to be pretty decent. Ya, more often than not, the cheaper the PSU the worse the quality, but you really do need to do your homework.Reply
Budget PSU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ezk9OA7aKOE -
Aris_Mp The newest ATX spec defines 5% at peak load as well. The 10% is only for the -12V rail which is now optional. The newest ATX spec is confidential (dont know why)Reply -
cats_Paw While I can understand that having a beefy power supply on idle state wont be too efficient, its on loads where you want it as efficient as possible.Reply
Somehow, having a low efficiency under a 65W load is less expensive than low efficiency at 500W load, go figure :D.
-
cats_Paw In all fairness, a PC is not a self-maintenance Robot.Reply
If you want a PC to last a good 10-15 years you need to take care of it:
Clean dust, replace fans when they fail, replace thermalpaste, check your temperatures from time to time, not turn it on-off-on too fast, keep your Hard drives with some spare space and defraged if they are HDDs....
There is quite some work for a PC to keep their form, but its not like a human can lay down in bed eating cheese and drinking cola looking like a model either.
PSUs however have this strange aura of magic around them since some people vastly overestimate what power supply they need (I got a 700W TT one for a load of 320, go figure) and others buy things that are simply bad products, no matter how high the W are.
I did once burn a PC due to a bad PSU (and I even OCed the damn PC, went down in smoke.. I gotta say it was quite fun, but expensive), so I stay on the safe side (I just simply add an extra 20% for 12v rail amps as long as the price of a quality supply is not doubling).
