In Search of True DDR2 Bleeding Edge Memory
BIOS Settings To Boost Performance
There are four primary ways to speed memory access and to thus to improve performance:
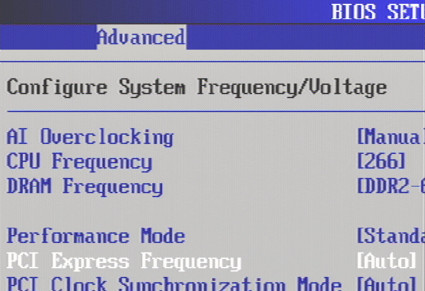
The BIOS offers a range of memory speed settings from which users may choose.
Memory speed settings are independent in most BIOS', and may be set directly or by setting values for underlying speed factors (FSB x multiplier = memory speed).
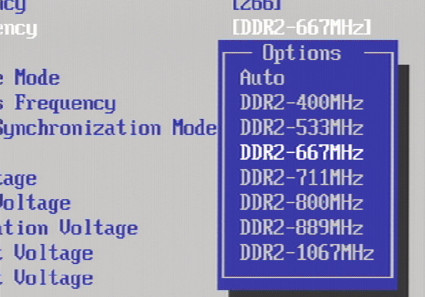
An overview of BIOS memory speed settings:
| Possible Memory Configurations | ||
|---|---|---|
| FSB1066 (266 MHz) | Multiplier | FSB800 (200 MHz) |
| DDR2-400 | 1.50 | n/a |
| DDR2-533 | 2.00 | DDR2-400 |
| DDR2-667 | 2.50 | n/a |
| DDR2-711 | 2.66 | DDR2-533 |
| DDR2-800 | 3.00 | DDR2-600 |
| DDR2-888 | 3.33 | DDR2-667 |
| DDR2-1066 | 4.00 | DDR2-800 |
It's also possible to adjust front side bus speed.
It is no secret that a higher FSB clock rate is the most important setting when overclocking RAM on Intel-based systems, so that data gets delivered more quickly to the CPU.
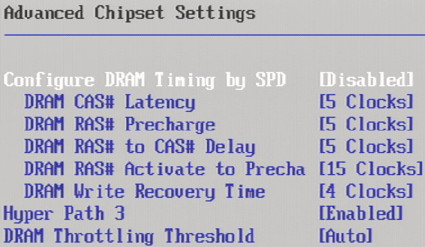
Tightening memory timings also has a positive impact on memory speed, but can quickly lead to system instability. Such changes are best made in small, experimental steps.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The most important timing setting is the CAS latency value because all other values are based on this setting, and have noticeably less influence on performance.
Current page: BIOS Settings To Boost Performance
Prev Page Two DRAM Sides Are Better Than One Next Page CL4 Or CL3: Boosts Performance By Up To 5%Tom's Hardware is the leading destination for hardcore computer enthusiasts. We cover everything from processors to 3D printers, single-board computers, SSDs and high-end gaming rigs, empowering readers to make the most of the tech they love, keep up on the latest developments and buy the right gear. Our staff has more than 100 years of combined experience covering news, solving tech problems and reviewing components and systems.