Six SSD DC S3500 Drives And Intel's RST: Performance In RAID, Tested
Intel lent us six SSD DC S3500 drives with its home-brewed 6 Gb/s SATA controller inside. We match them up to the Z87/C226 chipset's six corresponding ports, a handful of software-based RAID modes, and two operating systems to test their performance.
Our Haswell-Based Storage Platform: ASRock C226 WS and Xeon E3-1285 v3
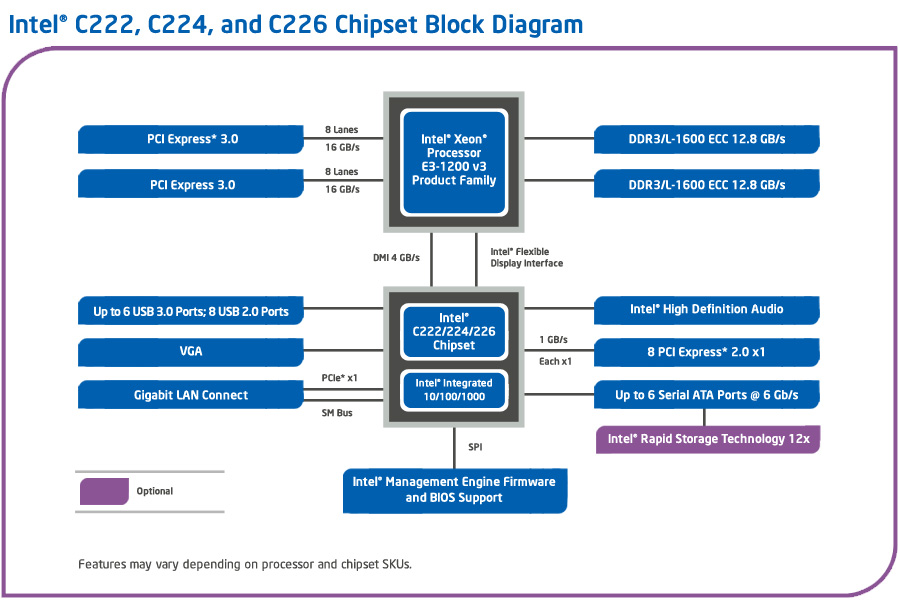
Intel's Lynx Point PCH showed up on the desktop as the 8-series and in server/workstation spaces as the C220-series. It's a lot like the core logic that preceded it, except for its more modern storage controller and additional USB 3.0 connectivity.
The CPU interfaces with the PCH through four second-gen PCIe lanes referred to as the DMI, enabling 4 GB/s of bi-directional bandwidth. That's where Lynx Point's sextet of 6 Gb/s ports live and breathe. At least on paper, six capable SSDs will probably be constrained by that vital link.
And so as we explore performance, we'll keep the platform's artificial ceiling in mind, too.
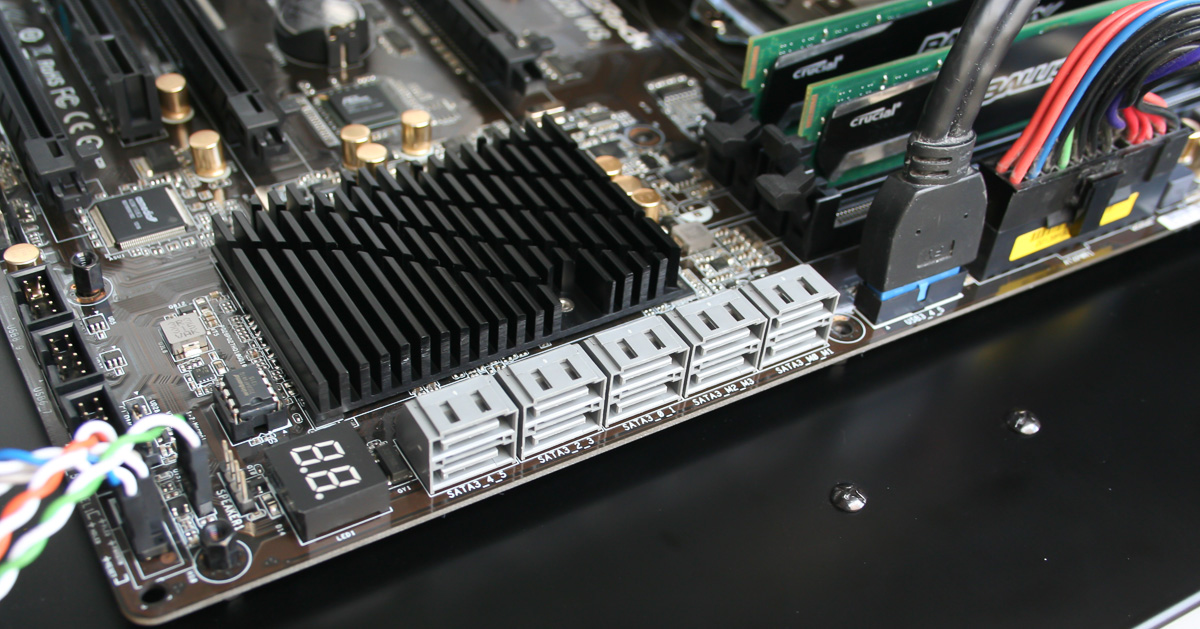
Not just any LGA 1150-equipped motherboard will work for what we want to do. Not every one features all six 6 Gb/s links, to begin. It'd also be helpful to have a third-party storage controller on-board for boot and optical drives, saving Intel's native connectivity for testing.
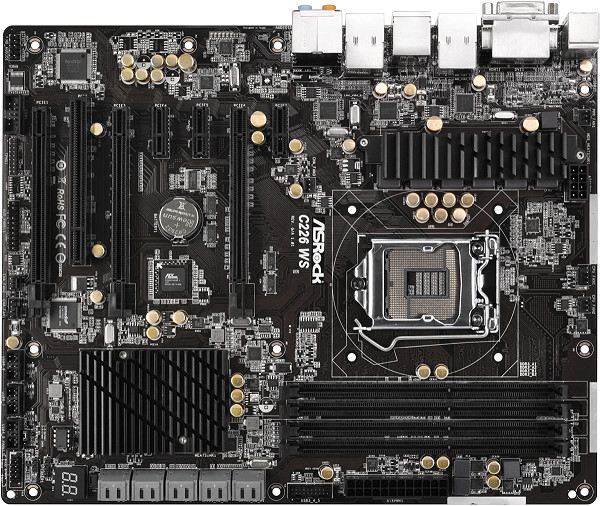
ASRock sent along its C226 WS, which does exactly what we need it to. In fact, we get a massive 10 SATA 6Gb/s-capable ports, six from Intel's PCH and four from a pair of Marvell 9172 controllers.
The board also employs a text-based UEFI, full support for Intel's virtualization features, and a good mix of PCI Express slots. It's also a natural fit for Haswell-based Xeon E3-1200 v3-series CPUs. From there, we need the right model. Dual-core processors don't have the muscle for wailing on SSD arrays, so you're left with the quad-core chips.
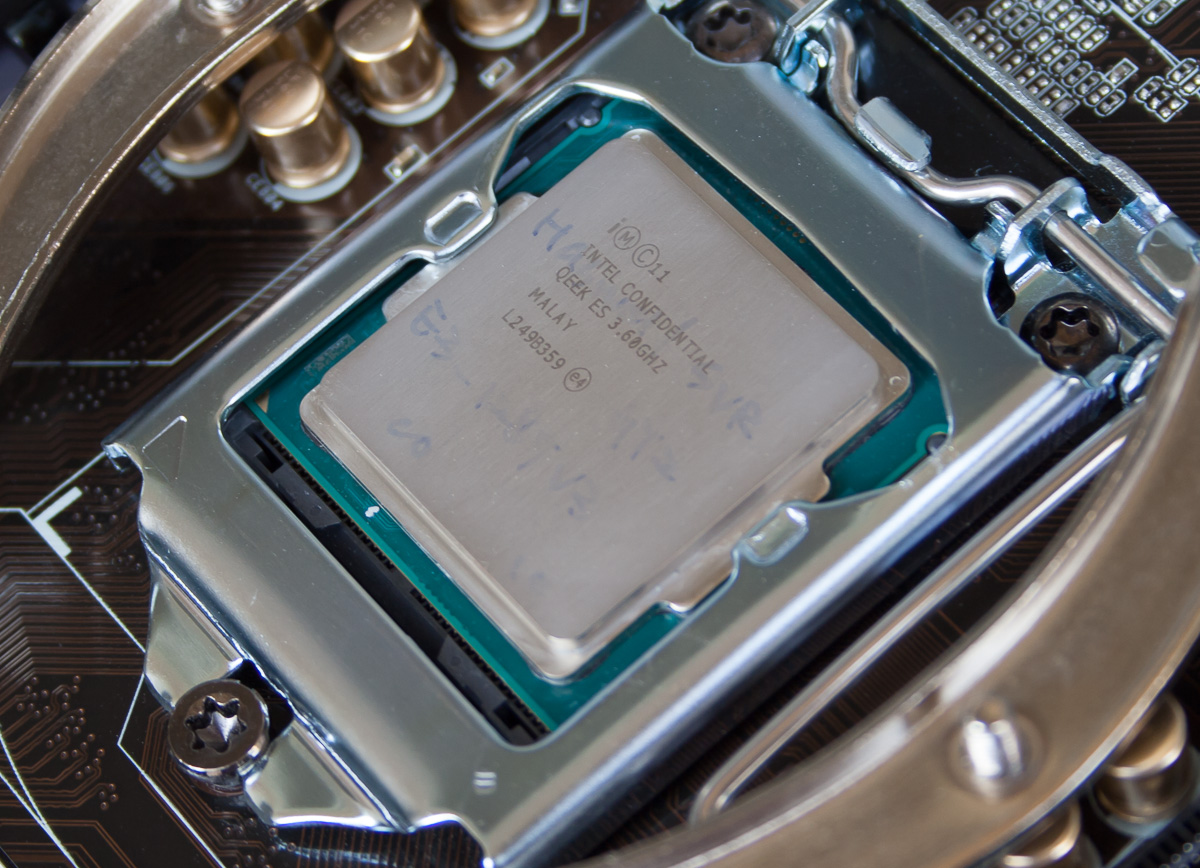
We're using the Xeon E3-1285 v3, with four cores and Hyper-Threading support. A base clock rate of 3.6 GHz jumps up to 4 GHz via Turbo Boost when the thermal headroom allows. Going the Xeon route means giving up overclocking. However, ECC-capable memory support and HD Graphics P4700 are more workstation-oriented features anyway. The top-end Xeon boasts 8 MB of shared L3 cache and an 84 W TDP.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
What About The Operating System?
Windows isn't always the best environment for benchmarking storage with the potential for high I/O performance. Linux is really preferable, and not just because it offers so much flexibility. You also have more efficient I/O schedulers (and more options for configuring them). That doesn't mean you'll always see different results from Linux; you just might not need as much processing horsepower to get there. Small-block random workloads can fully load a modern quad-core CPU, so efficiency is always a boon.
With that said, our many days of testing RAID using Intel's Rapid Storage Technology software all happened in Windows (not just Windows 7, but also the 8.1 Preview and a pair of Server releases). At the end of our experimentation, we settled on Windows 7 though. As of right now, I/O performance doesn't look as good in the latest builds of Windows.
There is one situation where we're publishing results from CentOS 6.4 instead. This is an enterprise-grade Linux distro that simplifies some of the variables that are harder to manage in Windows. Largely to make life easier, the last page of testing is all Linux-based.
| Test Hardware | |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel E3-1285v3 Xeon (Haswell), 22 nm, 3.6 GHz, LGA 1150, 8 MB Shared L3, Turbo Boost Enabled |
| Motherboard | ASRock C226 WS, ATX Worstation, BIOS Rev: 1.00 |
| Memory | Crucial Ballistix Sport 16 GB (2 x 8 GB) DDR3-1600 1.5 V |
| System Drive | Crucial M500 120 GB SATA 6Gb/s, Firmware: MU02 |
| Benchmarked Drives | 6 x Intel SSD DC S3500 SATA 6Gb/s, Firmware: 0306 |
| Graphics | Intel HD Graphics P4700 |
| Power Supply | Seasonic X-650, 650 W 80 PLUS Gold |
| Chassis | Lian Li Pitstop |
| RAID | LSI 9266-8i PCIe Gen2 x8, FastPath and CacheCade AFK, Firmware: 3.270.65-2578 |
| HBA | LSI 9207-8i PCIe Gen3 x8 HBA |
| System Software and Drivers | |
| OperatingSystem | Windows 7 x64 Pro SP1 |
| DirectX | DirectX 11 |
| Drivers | Graphics: Intel 9.18.10.365RST: 12.6.1033IMEI: 9.0.0.1287Generic AHCI: MSAHCI.SYSMarvell 6Gb/s: 1.2.0.1032 |
| Benchmarks | |
|---|---|
| Tom's Hardware Storage Bench v1.0 | Trace-Based |
| Iometer 1.1.0 | # Workers = 2, 4 KB Random: LBA=100% Varying QDs, 128 KB Sequential, 4 KB Randoms, Exponential QD Scaling |
| FIO | 2.0.14 |
Current page: Our Haswell-Based Storage Platform: ASRock C226 WS and Xeon E3-1285 v3
Prev Page Six SSD DC S3500 Drives, Three Configurations, All At 6 Gb/s Next Page Intel Rapid Storage Technology Gets More Useful With RAID-
SteelCity1981 "we settled on Windows 7 though. As of right now, I/O performance doesn't look as good in the latest builds of Windows."Reply
Ha. Good ol Windows 7... -
vertexx In your follow-up, it would really be interesting to see Linux Software RAID vs. On-Board vs. RAID controller.Reply -
tripleX Wow, some of those graphs are unintelligible. Did anyone even read this article? Surely more would complain if they did.Reply -
utomo There is Huge market on Tablet. to Use SSD in near future. the SSD must be cheap to catch this huge market.Reply -
tripleX Wow, some of those graphs are unintelligible. Did anyone even read this article? Surely more would complain if they did.Reply -
tripleX Wow, some of those graphs are unintelligible. Did anyone even read this article? Surely more would complain if they did.Reply -
klimax "You also have more efficient I/O schedulers (and more options for configuring them)." Unproven assertion. (BTW: Comparison should have been against Server edition - different configuration for schedulers and some other parameters are different too)Reply
As for 8.1, you should have by now full release. (Or you don't have TechNet or other access?) -
rwinches " The RAID 5 option facilitates data protection as well, but makes more efficient use of capacity by reserving one drive for parity information."Reply
RAID 5 has distributed parity across all member drives. Doh!