Thermal Paste Comparison, Part Two: 39 Products Get Tested
It's time for the numbers. In addition to testing liquid metal compounds and thermally conductive adhesives, each paste is discussed on its own merits before we chart out the results of four usage cases. After all, these products behave differently.

Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
39 Thermal Compounds Get Benchmarked And Tested
If you missed part one of this series, take a quick second and check out Thermal Paste Comparison, Part One: Applying Grease And More.
We Are Curious About Two Special Compound Categories
After discussing the theory of conventional thermal pastes in part one, I want to go into a little more detail about liquid metal compounds, and also shed some light on thermal adhesives, both in paste and pad form. Thermal pads are used to mount small heat sinks on RAM chips or MOSFETs.
But let’s start with those liquid metal pastes. While their theoretical thermal conductivity sounds impressive, that one attribute is no guarantee of success. During the course of our testing, we'll be experimenting with a long burn-in phase and comparing the liquid metal compound to Gelid's Extreme paste.
Article continues belowSeveral years ago, Coollaboratory broke new ground in thermal management by introducing the Liquid Pro liquid metal compound. But while the look (and subsequent application) of Liquid Pro reminded us of a mercury thermometer that didn’t survive a fall, its successor, Liquid Ultra, is better, avoiding some of the first effort's weaknesses. Because Liquid Pro could be so problematic, I'm only presenting Liquid Ultra in the tutorial section. Both compounds show up in our performance charts, though.
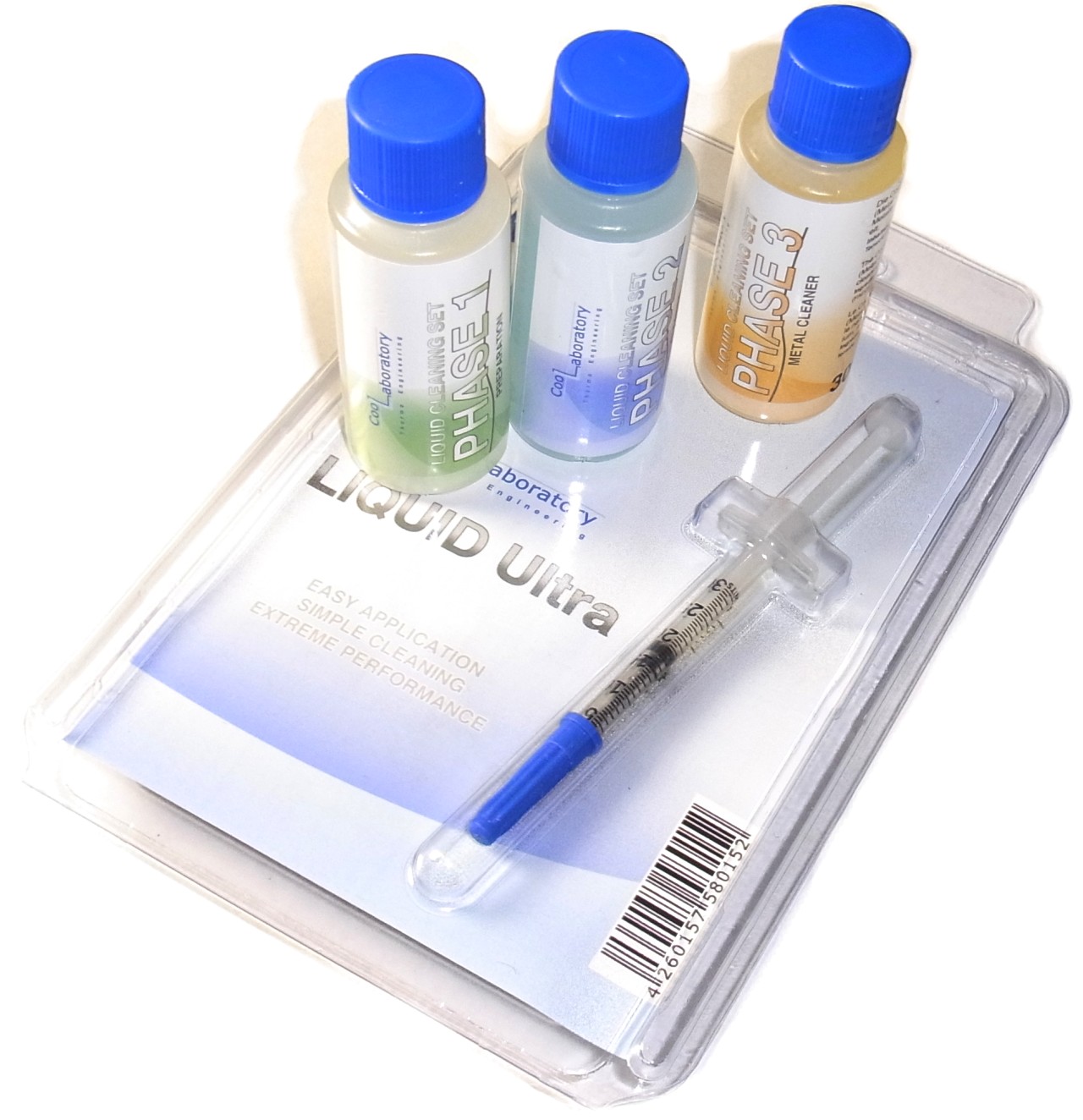
Box Contents
In the Liquid Ultra box you get the paste itself, a cleaning swab, two brushes, a sponge, and an instruction manual. That's an impressive-sounding list, but it's really just the bare minimum to use the product, sufficient for a single application. If you want to apply Liquid Ultra a second time, you'll find yourself without the alcohol swab. At least a second brush is included. While we appreciate the inclusion of the coarse sponge, it's barely adequate for removing the compound. Of course, there's a separate cleaning kit available for a hefty price.
Enthusiasts may be torn about this product, and yes, there may even be those who are more courageous than I and use it on graphics cards. However, my personal opinion is that a majority of the people who read this tutorial are new to thermal compounds, and I wouldn’t want to encourage them to mess around with this stuff due to the skill it requires. I also want to point out that you'll probably void your CPU's warranty if you do use Liquid Ultra. After removing the last remnants of it, we discovered that all of the markings etched into the head spreader were gone. If you still want to try this product after reading our tutorial, you can probably expect very good cooling performance, assuming nothing goes wrong.
Surface Cleaning and Roughing
The most important prerequisites for using a liquid metal compound are clean heat sink and spreader surfaces. You can buy the aforementioned kit with the three cleaning liquids, or simply snag some isopropyl alcohol at the drug store. However, stay away from acetone and cleaning naphtha. Even denatured alcohol may contain additives that are detrimental to achieving a clean, degreased surface. Finally, make sure you wait until any remnants of the liquid have evaporated!
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
If the surface is too smooth, the older Liquid Pro and newer Liquid Ultra may only form loose droplets on your CPU. Thus, in contrast to what you would do for regular thermal pastes, you may consider roughing the heat sink and spreader a little bit. Just remember that you only get enough liquid metal for two tries.
Don't overdo this. If you scrub too hard, the innocent-looking sponge can cause deep grooves. Move in small, graceful circles.
Current page: 39 Thermal Compounds Get Benchmarked And Tested
Next Page Coollaboratory Liquid Ultra: Application
Igor Wallossek wrote a wide variety of hardware articles for Tom's Hardware, with a strong focus on technical analysis and in-depth reviews. His contributions have spanned a broad spectrum of PC components, including GPUs, CPUs, workstations, and PC builds. His insightful articles provide readers with detailed knowledge to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape
-
dragonfang18 I loved the toothpaste part. What about Vicks Vaporub? I wonder how that thing would do.Reply -
TehDudeMan Great article guys! As a reader for over 10 years pretty much daily, this reminds me of the old Tom's Hardware. These type of in depth articles on enthusiast products are what I love.Reply -
Matt Edwards A great article, agree the application of the compound, not the compound itself is most important.Reply
Like ledpellet I too am curious about these diamond compounds. Wonder if it offers similar results to the Coollaboratory products with an easier application, or if the results simply don't justify the price. E.g in Australia, Innovation Cooling IC7 Diamond 7 Carat Thermal Compound Paste - 1.5G can be found for as much as $25. The cheapest I have managed to find it for is $15. For that price it would want to be good considering the leading GELID GC Extreme, can be found for around $8. -
danwat1234 Coollaboratory Liquid Ultra isn't all that good after a year of hard use. In fact, it completely hardens / dries. On my X9100 after 9 months of nearly 24/7 100% load, I started seeing high temps and after 1 year auto shut downs while crunching. Turns out it was shutting off because it hit the 105 C thermal protection.Reply
Opened it up; thermal compound was as hard as a rock. has to pocket knife blade and sand it down.
So for longevity it sucks. That is something to consider, not just initial performance, but performance months and years down the road. Especially for laptops that aren't designed to be opened up frequently for repasting.
After trying Liquid Ultra many times and having it fail on me, I've put on Arctic MX-2 that has a supposed 8 year durability rating. Initial performance is great, we'll see how it lasts (been 3 weeks so far). -
slomo4sho CLU and Arctic MX-4 are both great products. MX-2 and MX-4 can often be found free after rebate so they are an exceptional value.Reply