UPDATE: Core i7: Blazing Fast, O/C Changes
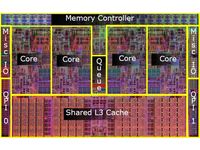
Size Comparison--Bigger Die, Fewer Transistors
The Core i7 Processor
Like the Core 2 before it, the Core i7 processor (code name "Bloomfield") will be produced on a 45 nm process using high-K dielectric and metal gate technologies. The Core i7 also sports four cores. In a departure from Intel’s previous quad-core designs that were comprised of two dual-core processors sharing a processor package, Nehalem’s four cores all reside on one die. A look at the die shots reveals that Intel has designed its CPU to give the company an option of producing it as a dual-core part as well. Thus, it is feasible that we will see dual-core versions of Nehalem at some point.
| Model | Process | Size | Transistors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core i7 | 45 nm | 263 mm² | 731 M |
| Core 2 | 45 nm | 2x 107 mm² | 2x 410 M |
| Core 2 | 65 nm | 2x 143 mm² | 2x 291 M |
Putting all four cores on a single die doesn’t really save a lot of space on the processor package since the die size has increased from 214 mm² (2 x 107 mm²) for the Core 2, to 263 mm² for Core i7. Since we know that 32 nm versions of the chips are already in development—thanks to Intel’s tick-tock cycle—we can assume that the Core i7’s larger heat spreader will be able to house six or even eight cores when the die shrink happens. Perhaps that is even the reason for the larger processor package in the first place.
In the new design, the number of transistors has dropped from 810 million to 731 million. The Core i7 CPU also has some contact pins on the top of the die, but it is obvious that Intel only uses these during manufacturing.
Core i7 Models
Intel is initially introducing three different Core i7 models: the Core i7 920 running at 2.66 GHz, the Core i7 940 at 2.93 GHz, and the Core i7 965 Extreme, which is clocked at 3.20 GHz.
| Model | Clock Speed | QPI | OPR | L3 Cache |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i7 965 Extreme | 3.20 GHz | 6.4 GT/s | yes | 8 MB |
| Core i7 940 | 2.93 GHz | 4.8 GT/s | no | 8 MB |
| Core i7 920 | 2.66 GHz | 4.8 GT/s | no | 8 MB |
OPR = Overspeed Protection Removed
Quick Path Interconnect
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
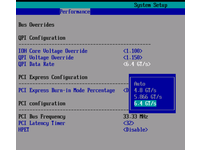
With the Nehalem architecture, Intel is finally saying farewell to the classic front side bus interface we have known for so many years. Instead, Core i7 processors will utilize the new QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) to communicate with the northbridge.
On the lower-end Core i7 models—i.e., the 920 and 940—this interface offers a bandwidth of 4.8 GT/s, which equals a bidirectional bandwidth of 9 GB/s. The Core i7 965 Extreme, on the other hand, comes with a faster QPI connection of 6.4 GT/s, or 12.8 GB/s. That’s the exact same bandwidth that the classic FSB of the Core 2 offered at 400 MHz. AMD’s HyperTransport protocol can transmit up to 25.6 GB/s at 3.20 GHz. However, since the bandwidth-consuming memory interface is no longer part of the northbridge—having instead been integrated directly into the CPU—the advantage of switching to QPI will not have too much of an impact in the desktop segment. Here, the QuickPath Interconnect will only have to handle the data from the PCI Express connections and the southbridge, which is connected to the northbridge via PCI Express as well.
In contrast to the classic FSB, QuickPath Interconnect enables direct communication with another processor. The result is improved performance, since using the FSB design, such communication was previously only possible via a detour through the comparatively slow northbridge.
QPI brings a fascinating possibility to the table: in order to create a dual-CPU motherboard, a company simply has to solder a second processor socket onto its PCB. Since the processors can communicate with each other directly, this option is independent of the chipset, making it very simple, not to mention inexpensive. A good portion of today’s software shows marked performance gains thanks to the four additional virtual processors provided through Hyper-Threading. When adding another CPU with real cores, the performance improvement should be even more pronounced.
Inside the Core i7 processor, the base clock with its multiplier for setting the correct clock speed still lives on. It runs at 133 MHz, meaning the multipliers are higher than those found on the Core 2 models. Enthusiasts with Core i7 920 or 940 processors will achieve overclocking by adjusting this base clock upward, since multipliers on these chips cannot be increased.
Current page: Size Comparison--Bigger Die, Fewer Transistors
Prev Page Introduction Next Page SSE 4.2 And The Technical Nitty-Gritty-
pullmyfoot AMD’s HyperTransport protocol can transmit up to 25.6 GB/s at 3.20 GHz.Reply
You mean Intel don't you? Other than that little mistake, good article
-
wh3resmycar hmm, question. once this nehalems come out. will we ever see a dieshrunk c2q again after the penryns? im expecting the price of this procs along with the mobo and ram to be too far off from my budget. orReply -
skywalker9952 One of the first side effects of Intel's domination of the CPU market is beginning to show. Since they don't have to compete with AMD in any market segment the i7 occupies, they have limited (significant) overclocking to only extreme models.Reply
RIP AMD.
May Abu Dhabi restore you to life soon so we don't have to suffer through more Intel ripoffs. -
sonar610 "The fastest Core i7, the 965 Extreme, is more than 2.6 times as fast as AMD’s current flagship CPU, the Phenom X4 9550 BE."Reply
This seems like an editing mistake maybe it should be 9950BE. -
cryogenic Core i7 is a great CPU, the article is not. I can't believe after all this time you still stack overclocked CPUs with unoverclocked ones. It's great to find out the overclocking potential of Nehalem but, at least include some overclocked Penryns in there too, to see how overclocked Nehalem stacks agains OTHER overclocked CPUs, because it's fairly evident that and overclocked new gen CPU will stack well with older non overclocked ones.Reply
-
joseph85 CryogenicCore i7 is a great CPU, the article is not. I can't believe after all this time you still stack overclocked CPUs with unoverclocked ones. It's great to find out the overclocking potential of Nehalem but, at least include some overclocked Penryns in there too, to see how overclocked Nehalem stacks agains OTHER overclocked CPUs, because it's fairly evident that and overclocked new gen CPU will stack well with older non overclocked ones.If it's evident then who cares?Reply -
fender22 skywalker9952One of the first side effects of Intel's domination of the CPU market is beginning to show. Since they don't have to compete with AMD in any market segment the i7 occupies, they have limited (significant) overclocking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overclocking to only extreme models.RIP AMD. May Abu Dhabi restore you to life soon so we don't have to suffer through more Intel ripoffs.Reply
My thoughts exactly... I wonder if there will be some sort of resistance to this sort of thing... It's like buying a car, you can do whatever you want to it (within the limits of the law) to make it as fast as you want. Sure, you may void your factory warranty, but it's your deal. You don't see car companies making it impossible for you to do what you want to their cars so you have to buy their expensive high end just to get your kicks... (not a perfect comparison, but it works)
I dunno, it's just pretty weak. And they are just taking advantage of the situation... -
cangelini sonar610"The fastest Core i7, the 965 Extreme, is more than 2.6 times as fast as AMD’s current flagship CPU, the Phenom X4 9550 BE." This seems like an editing mistake maybe it should be 9950BE.Reply
Fixed, thanks! -
onearmedscissorb Aside from the all too prevalent and potentially misleading typos, which someone needed to get a handle on as of months ago, I must say that the overall quality of this article is MUCH better than pretty much anything I can remember of the last few months. It's actually informative and thought out, rather than being a mess of assumptions that many people reading already know better than.Reply
Keep it up, and maybe I'll pay attention to this site like I used to.
But just for the record, I don't believe that it's particularly appropriate to use the overall average performance percentages as a basis for comparison between the "speed" of Core 2 vs. Core i7. Obviously, most people are going to be interested in the difference with games, where it's likely to be pretty minimal. But here and there, you have something like the 55% WinRAR difference pretty much skewing what otherwise would have been an accurate depiction of average expectations across the board.