AMD A8-3850 Review: Llano Rocks Entry-Level Desktops
Earlier this month we previewed AMD's Llano architecture in a notebook environment. Now we have the desktop version with a 100 W TDP. How much additional performance can the company procure with a loftier thermal ceiling and higher clocks?
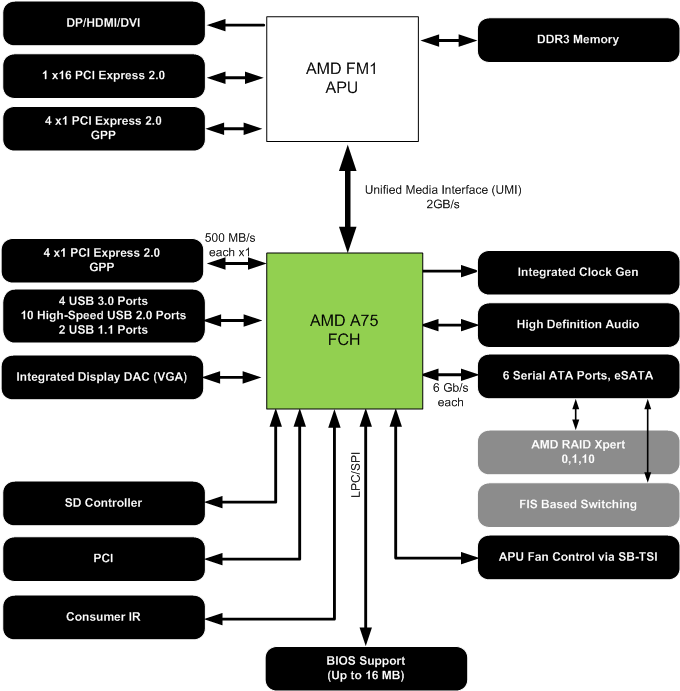
Chipsets
The Llano-based APU family is accompanied by two AMD-branded chipsets: A75 and A55. One is distinctly current-generation, and the other is awkwardly behind the times.
Both boast Socket FM1 (905-pin) interfaces for the desktop Lynx platform. They similarly include six SATA ports, software RAID 0, 1, and 10 support, HD Audio, four second-gen PCI Express lanes, a PCI bus, and mSATA compatibility.
However, A55 is limited to 3 Gb/s storage connectivity, it doesn’t enable FIS-based switching, and it doesn’t include USB 3.0 support. We have to imagine that A55 will be limited to the all-in-one market, where performance takes a back seat to cost and form factor considerations, though USB 3.0 would still seem to be an important feature there.
| Feature | AMD A75 | AMD A55 |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Socket FM1 (Lynx desktop) | Socket FM1 (Lynx desktop) |
| SATA Connectivity | 6 x SATA 6Gb/s | 6 x SATA 3Gb/s |
| Software RAID | 0, 1, 10 | 0, 1, 10 |
| FIS-Based Switching | Yes | No |
| HD Audio | Yes | Yes |
| General-Purpose PCIe | 4 x PCI Express 2.0 lanes | 4 x PCI Express 2.0 lanes |
| UMI (Connection To APU) | Four-lane PCIe + DisplayPort | Four-lane PCIe + DisplayPort |
| USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 | 4/10/2 | 0/14/2 |
| SD Controller | Yes | Yes |
| 33 MHz Legacy PCI | Up To Three Slots | Up To Three Slots |
| mSATA Support | Yes | Yes |
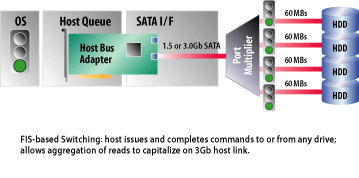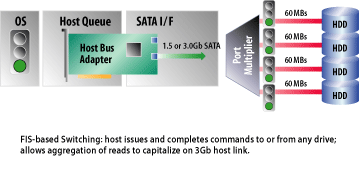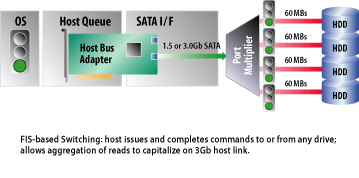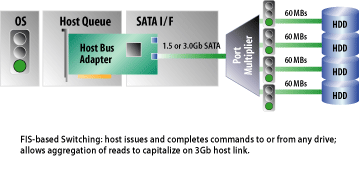
A75 is the better-endowed solution. All six of its SATA ports offer 6 Gb/s signaling. And while A55 simply exposes 14 USB 2.0 ports and two 1.1 ports, A75 splits four of those second-gen connectors off as USB 3.0 ports, leaving 10 potential USB 2.0 ports if motherboard vendors choose to implement them. A75 also support FIS-based switching.
That’s an important feature if you’re building a machine with multiple drives in it. FIS-based switching facilitates communication between the storage controller and more than one disk simultaneously, which lets Native Command Queuing work the way it’s supposed to. A controller that doesn’t support FIS-based switching employs command-based switching, which only lets the host issue command to one drive at a time. Obviously, that can impact storage performance.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Chipsets
Prev Page Dual Graphics: Not Always Your Best Bet Next Page Storage Performance-
SteelCity1981 So then what's the point of getting the Turbo Core versions when they are going to be Turbo Clocked slower then the none Turbo Clocked versions...Reply -
cangelini SteelCity1981So then what's the point of getting the Turbo Core versions when they are going to be Turbo Clocked slower then the none Turbo Clocked versions...Reply
They don't want you to see better performance from a cheaper APU in single-threaded apps by pushing Turbo Core further ;-) -
Known2Bone i really wanted see some amazing gains in the content creation department what with all that gpu power on chip... oh well games are fun too!Reply -
ivan_chess I think this would be good for a young kid's PC. It would be enough to run educational software and a web browser. When he grows up to be a gamer it would be time to replace the whole machine anyway.Reply -
DjEaZy ... it's may be not the greatest APU for desktop... but it will be a powerful thingy in a laptop... the review was nice... but in the gaming department... would be nice to see a standard 15,x'' laptop resolution tests @ 1366x768... or something like that...Reply -
Mathos Actually if you want good DDR3 1600 with aggressive timings, the Ripjaws X series memory that I have does DDR3 1600 at 7-8-7-24 at 1.5v, not all that expensive when it comes down to it either.Reply -
Stardude82 This makes little sense. An Athlon II X3 445 ($75) and a HD 5570 ($60, on a good day you can get a 5670 for the same price) would provide better performance for the same price ($135) and not have to worry about the RAM you use.Reply
So is AM3+ going to be retired in favor of FM1 in the near future? Why are there chipset at all? Why isn't everything SOC by now?
Otherwise this is a very good CPU. If AMD has used 1 MB level 2 caches in their quads when they came out with the Deneb Propus die, they would be much more competitive. -
crisan_tiberiu stardude82This makes little sense. An Athlon II X3 445 ($75) and a HD 5570 ($60, on a good day you can get a 5670 for the same price) would provide better performance for the same price ($135) and not have to worry about the RAM you use. what about power consumption?Reply