Sponsored by Que Publishing
Upgrading And Repairing PCs 21st Edition: Processor Features
Processor Socket And Slot Types
Intel and AMD have created a set of socket and slots for their processors. Each socket or slot is designed to support a different range of original and upgrade processors. The table below shows the designations for the various standard processor sockets/slots and lists the chips that drop into them.
Chip Class | Socket | Pins | Layout | Supported Processors | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Intel P4/Core | 423 | 423 | 39x39 SPGA | Pentium 4 FC-PGA | Nov. 2000 |
478 | 478 | 26x26 mPGA | Pentium 4/Celeron FC-PGA2, Celeron D | Oct. 2001 | |
T (LGA 775) | 775 | 30x33 LGA | Pentium 4/Extreme Edition, Pentium D, Celeron D, Pentium dual-core, Core2 | June 2004 | |
LGA 1156 (Socket H) | 1156 | 40x40 LGA | Pentium, Core i3/i5/i7, Xeon | Sept. 2009 | |
LGA 1136 (Socket B) | 1366 | 41x43 LGA | Core i7, Xeon | Nov. 2008 | |
LGA 1155 (Socket H2) | 1155 | 40x40 LGA | Core i7, i5, i3 | Jan. 2011 | |
LGA 2011 | 2011 | 58x43 hexLGA | Core i7 | Nov. 2011 | |
AMD K8 | 754 | 754 | 29x29 mPGA | Athlon 64 | Sept. 2003 |
939 | 939 | 31x31 mPGA | Athlon 64 v.2 | June 2004 | |
940 | 940 | 31x31 mPGA | Athlon 64 FX, Opteron | Apr. 2003 | |
AM2 | 940 | 31x31 mPGA | Athlon 64/64FX/64 X2, Sempron, Opteron, Phenom | May 2006 | |
AM2+ | 940 | 31x31 mPGA | Athlon 64/64 X2, Opteron, Phenom X2/X3/X4, II X4 | Nov. 2007 | |
AM3 | 9412 | 31x31 mPGA | Athlon II, Phenom II, Sempron | Feb. 2009 | |
AM3+ | 9412 | 31x31 mPGA | "Bulldozer" Processors | Mid-2011 | |
F (1207 FX) | 1207 | 35x35 LGA | Athlon 64 FX, Opteron | Aug. 2006 | |
AMD A | FM1 | 905 | 31x31 LGA | A4, A6, A8, Athlon II, E2, Sempron | Jul. 2011 |
FM2 | 904 | 31x31 LGA | A4, A6, A8, A10 | Sept. 2012 |
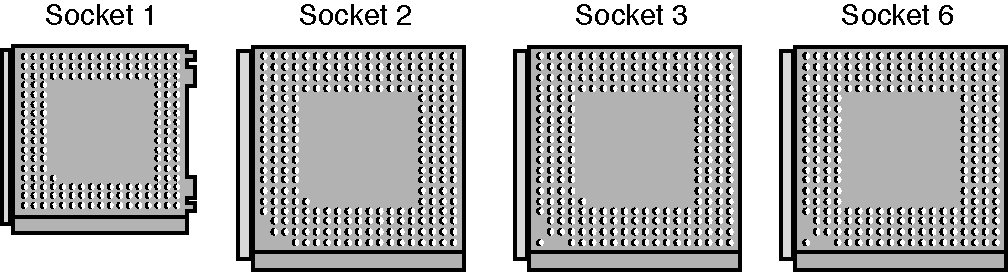
Sockets 1, 2, 3, and 6 are 486 processor sockets and are shown together in the figure below so you can see the overall size comparisons and pin arrangements between these sockets.
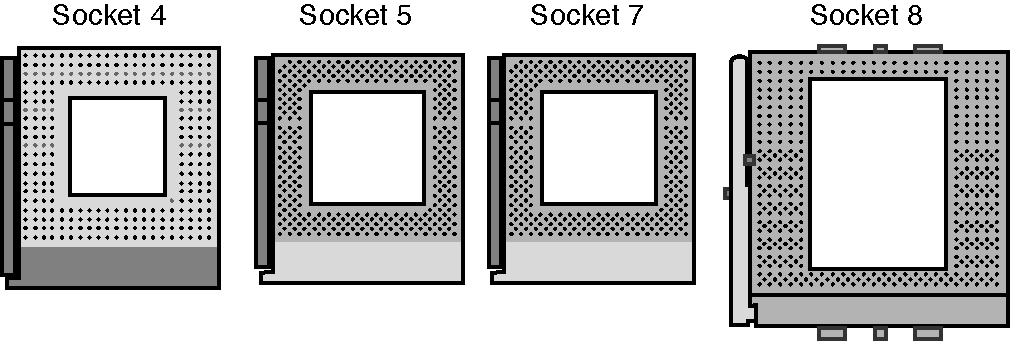
Sockets 4, 5, 7, and 8 are Pentium and Pentium Pro processor sockets and are shown together in the figure below so you can see the overall size comparisons and pin arrangements between these sockets.
When the Socket 1 specification was created, manufacturers realized that if users were going to upgrade processors, they had to make the process easier. The socket manufacturers found that 100 lbs. of insertion force is required to install a chip in a standard 169-pin Socket 1 motherboard. With this much force involved, you easily could damage either the chip or the socket during removal or reinstallation. Because of this, some motherboard manufacturers began using low insertion force (LIF) sockets, which required a smaller 60 lbs. of insertion force for a 169-pin chip. Pressing down on the motherboard with 60–100 lbs. of force can crack the board if it is not supported properly. A special tool is also required to remove a chip from one of these sockets. As you can imagine, even the LIF was relative, and a better solution was needed if the average person was ever going to replace his CPU.
Manufacturers began using ZIF sockets in Socket 1 designs, and all processor sockets from Socket 2 and higher have been of the ZIF design. ZIF is required for all the higher-density sockets because the insertion force would simply be too great otherwise. ZIF sockets almost eliminate the risk involved in installing or removing a processor because no insertion force is necessary to install the chip and no tool is needed to extract one. Most ZIF sockets are handle-actuated: You lift the handle, drop the chip into the socket, and then close the handle. This design makes installing or removing a processor easy.
The following sections take a closer look at those socket designs you are likely to encounter in active PCs.
Current page: Processor Socket And Slot Types
Prev Page Hardware-Assisted Virtualization Support Next Page Intel Sockets: LGA 775, LGA 1156, LGA 1366, And LGA 1155Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Tom's Hardware is the leading destination for hardcore computer enthusiasts. We cover everything from processors to 3D printers, single-board computers, SSDs and high-end gaming rigs, empowering readers to make the most of the tech they love, keep up on the latest developments and buy the right gear. Our staff has more than 100 years of combined experience covering news, solving tech problems and reviewing components and systems.
-
ta152h Ugggh, got to page two before being disgusted this time. This author is back to writing fiction.Reply
The Pentium (5th generation, in case the author didn't know, thus the "Pent"), DID execute x86 instructions. It was the Pentium Pro that didn't. That was the sixth generation.
CISC and RISC are not arbitary terms, and RISC is better when you have a lot of memory, that's why Intel and AMD use it for x86. They can't execute x86 instructions effectively, so they break it down to RISC type operations, and then execute it. They pay the penalty of adding additional stages in the pipeline which slows down the processor (greater branch mispredict penalty), adds size, and uses power. If they are equal, why would anyone take this penalty?
Being superscalar has nothing to do with being RISC or CISC. Admittedly, the terms aren't carved in stone, and the term can be misleading, as it's not necessarily the number of instructions that defines RISC. Even so, there are clear differences. RISC has fixed length instructions. CISC generally does not. RISC has much simpler memory addressing modes. The main difference is, RISC does not have microcoding to execute instructions - everything is done in hardware. Obviously, this strongly implies much simpler, easier to execute instructions, which make it superior today. However, code density is less for RISC, and that was very important in the 70s and early 80s when memory was not so large. Even now, better density means better performance, since you'll hit the faster caches more often.
This article is also wrong about 3D Now! It was not introduced as an alternative to SSE, SSE was introduced as an alternative to 3D Now!, which predated SSE. In reality, 3D Now! was released because the largest difference between the K6 and Intel processors was floating point. Games, or other software that could use 3D Now!, rather than relying entirely on x87 instructions, could show marked performance improvement for the K6-2. It was relatively small to implement, and in the correct workloads could show dramatic improvements. But, of course, almost no one used it.
The remarks about the dual bus are inaccurate. The reason was that motherboard bus speeds were not able to keep up with microprocessors speeds (starting with the 486DX2). Intel suffered the much slower bus speed to the L2 cache on the Pentium and Pentium MMX, but moved the L2 cache on the same processor package (but not on the same die) with the Pentium Pro. The purpose of having the separate buses was that one could access the L2 cache at a much higher speed; it wasn't limited to the 66 MHz bus speed of the motherboard. The Pentium Pro was never intended to be mainstream, and was too expensive, so Intel moved the L2 cache onto the Slot 1 cartridge, and ran it at half bus speed, which in any case was still much faster than the memory bus.
That was the main reason they went to the two buses.
That was as far as I bothered to read this. It's a pity people can't actually do fact checking when they write books, and make up weird stories that only have a passing resemblance to reality.
And then act like someone winning this misinformation is lucky. Good grief, what a perverse world ...
-
spookyman Yes you are correct on the bus issue. VESA local bus was designed to overcome the limitations of the ISA bus.Reply
As for the reason Intel went with a slot design for the Pentium 2 was to prevent AMD from using it. You can patent and trademark a slot design.
As for the Pentium Pro, it had issues from handling 16bit x86 instruction sets. The solution was to program around it. The was an inherent computational flaw with the Pentium Pro too. -
Kraszmyl I don't think there is a single page that isn't piled with inaccurate or incomplete information.......this is perhaps the worst thing I've ever read on tomshardware and I don't see how you let it get published.Reply -
therogerwilco Kinda nice for generic info, was hoping for more explanation of some of the finer points of cpu architectureReply -
Reynod Perhaps the most important thing to note from this is just how clever some of our users are ... so get into the forums and help out the n00bs with their problems guys !!Reply
:) -
Sprongy Not to be anal but aren't all Core i3 processors, dual cores (2). Some have Hyper-Threading to make it like 4 cores. The last chart above should read Core i3 - 2 cores. Just saying...Reply -
ingtar33 Reply11830610 said:Not to be anal but aren't all Core i3 processors, dual cores (2). Some have Hyper-Threading to make it like 4 cores. The last chart above should read Core i3 - 2 cores. Just saying...
not on mobile. some mobile i3s are single core, same with the mobile i5s... those are all dual core... with hyperthreading.
there are even dual core i5s in haswell on the desktop. (they are the ones with a (t) after the number)